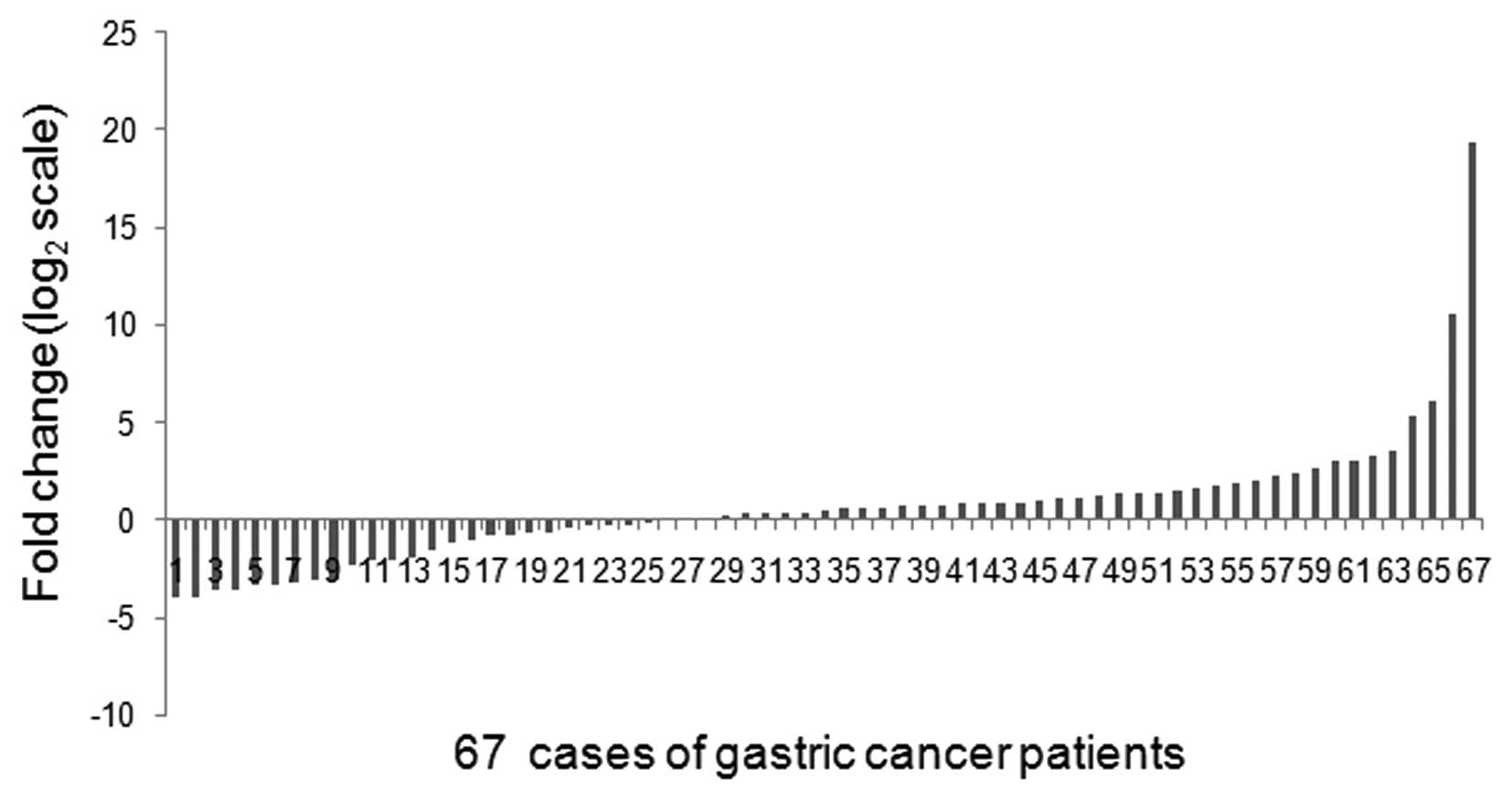
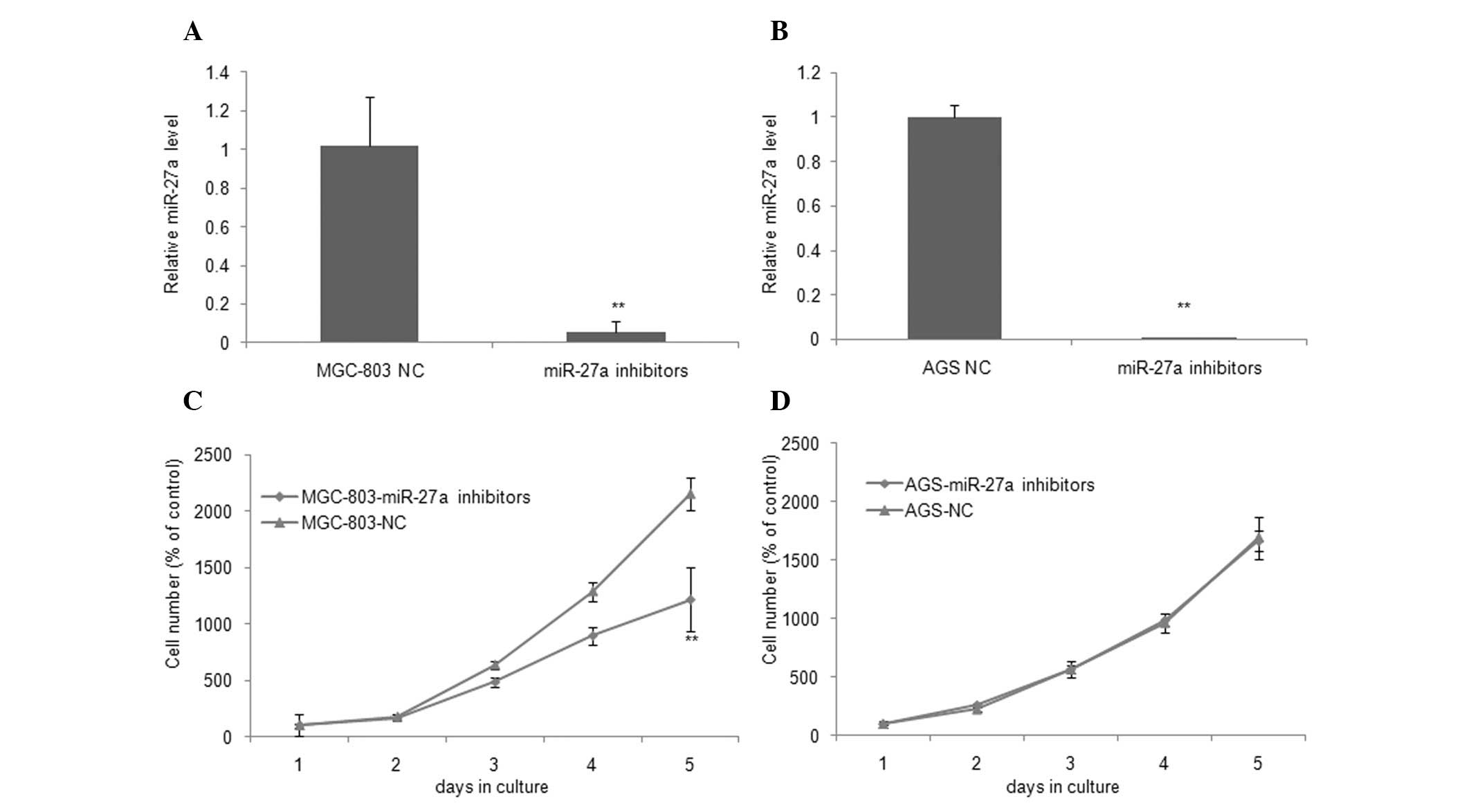
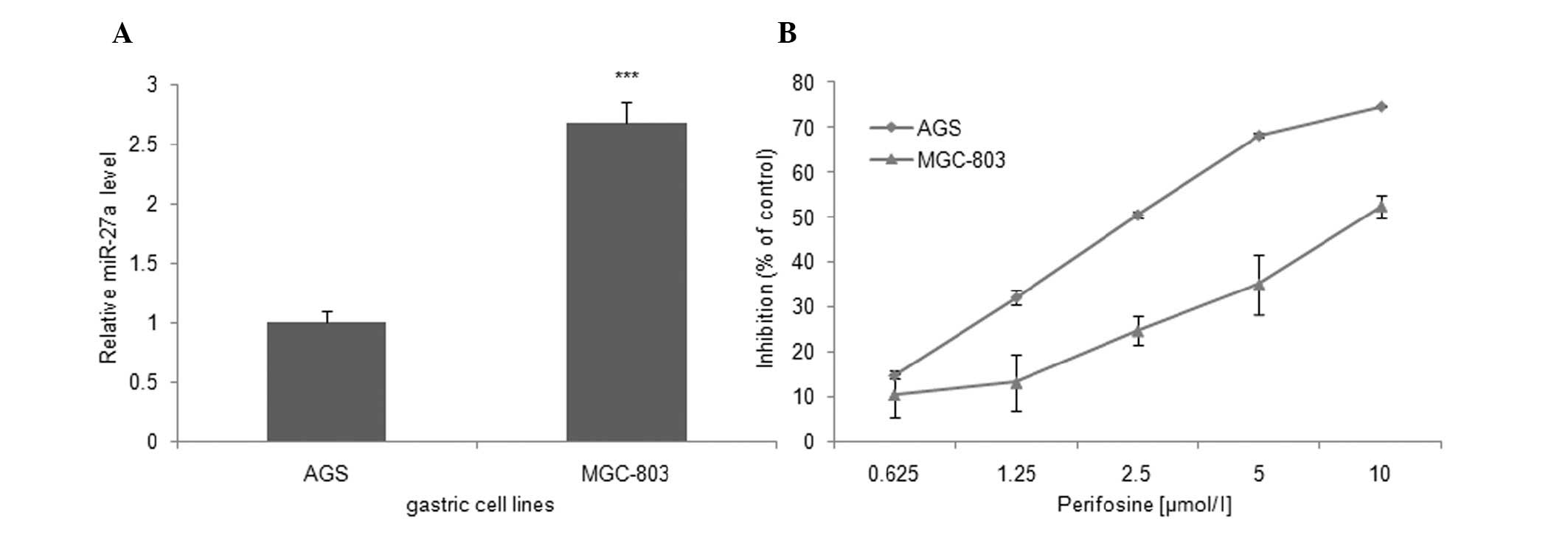
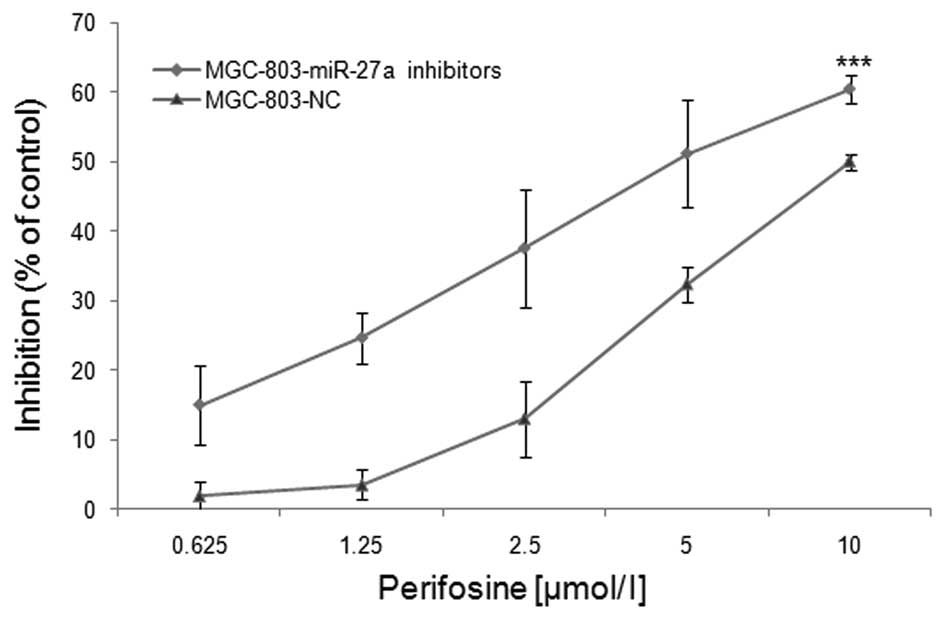
|
1
|
Pisani P, Parkin DM, Bray F and Ferlay J:
Erratum: estimates of the worldwide mortality from 25 cancers in
1990. Int J Cancer. 83:870–873. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Danaei G, Vander Hoorn S, Lopez AD, Murray
CJ and Ezzati M: Causes of cancer in the world: comparative risk
assessment of nine behavioural and environmental risk factors.
Lancet. 366:1784–1793. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Orditura M, De Vita F, Muto P, et al:
Adjuvant chemoradiotherapy in patients with stage III or IV
radically resected gastric cancer: a pilot study. Arch Surg.
145:233–238. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Milne AN, Carneiro F, O’Morain C and
Offerhaus GJ: Nature meets nurture: molecular genetics of gastric
cancer. Hum Genet. 126:615–628. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Dykxhoorn DM: MicroRNAs and metastasis:
little RNAs go a long way. Cancer Res. 70:6401–6406. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Croce CM: Causes and consequences of
microRNA dysregulation in cancer. Nat Rev Genet. 10:704–714. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yang H, Kong W, He L, et al: MicroRNA
expression profiling in human ovarian cancer: miR-214 induces cell
survival and cisplatin resistance by targeting PTEN. Cancer Res.
68:425–433. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sorrentino A, Liu CG, Addario A, Peschle
C, Scambia G and Ferlini C: Role of microRNAs in drug-resistant
ovarian cancer cells. Gynecol Oncol. 111:478–486. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhu H, Wu H, Liu X, et al: Role of
MicroRNA miR-27a and miR-451 in the regulation of
MDR1/P-glycoprotein expression in human cancer cells. Biochem
Pharmacol. 76:582–588. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mertens-Talcott SU, Chintharlapalli S, Li
X and Safe S: The oncogenic microRNA-27a targets genes that
regulate specificity protein transcription factors and the G2-M
checkpoint in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Cancer Res.
67:11001–11011. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Pathi SS, Jutooru I, Chadalapaka G, et al:
GT-094, a NO-NSAID, inhibits colon cancer cell growth by activation
of a reactive oxygen species-microRNA-27a: ZBTB10-specificity
protein pathway. Mol Cancer Res. 9:195–202. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu T, Tang H, Lang Y, Liu M and Li X:
MicroRNA-27a functions as an oncogene in gastric adenocarcinoma by
targeting prohibitin. Cancer Lett. 273:233–242. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sun Q, Cong R, Yan H, et al: Genistein
inhibits growth of human uveal melanoma cells and affects
microRNA-27a and target gene expression. Oncol Rep. 22:563–567.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhao X, Yang L and Hu J: Down-regulation
of miR-27a might inhibit proliferation and drug resistance of
gastric cancer cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 30:552011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang H, Li M, Han Y, et al:
Down-regulation of miR-27a might reverse multidrug resistance of
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Dig Dis Sci. 55:2545–2551.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li Z, Hu S, Wang J, et al: MiR-27a
modulates MDR1/P-glycoprotein expression by targeting HIPK2 in
human ovarian cancer cells. Gynecol Oncol. 119:125–130. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Feng DD, Zhang H, Zhang P, et al:
Down-regulated miR-331–5p and miR-27a are associated with
chemotherapy resistance and relapse in leukemia. J Cell Mol Med.
15:2164–2175. 2011.
|
|
18
|
Vink SR, Schellens JH, van Blitterswijk WJ
and Verheij M: Tumor and normal tissue pharmacokinetics of
perifosine, an oral anti-cancer alkylphospholipid. Invest New
Drugs. 23:279–286. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hilgard P, Klenner T, Stekar J, Nossner G,
Kutscher B and Engel J: D-21266, a new heterocyclic
alkylphospholipid with antitumour activity. Eur J Cancer.
33:442–446. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Nyakern M, Cappellini A, Mantovani I and
Martelli AM: Synergistic induction of apoptosis in human leukemia T
cells by the Akt inhibitor perifosine and etoposide through
activation of intrinsic and Fas-mediated extrinsic cell death
pathways. Mol Cancer Ther. 5:1559–1570. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Dasmahapatra GP, Didolkar P, Alley MC,
Ghosh S, Sausville EA and Roy KK: In vitro combination treatment
with perifosine and UCN-01 demonstrates synergism against prostate
(PC-3) and lung (A549) epithelial adenocarcinoma cell lines. Clin
Cancer Res. 10:5242–5252. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Van Ummersen L, Binger K, Volkman J, et
al: A phase I trial of perifosine (NSC 639966) on a loading
dose/maintenance dose schedule in patients with advanced cancer.
Clin Cancer Res. 10:7450–7456. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Richardson PG, Wolf J, Jakubowiak A, et
al: Perifosine plus bortezomib and dexamethasone in patients with
relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma previously treated with
bortezomib: results of a multicenter phase I/II trial. J Clin
Oncol. 29:4243–4249. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Papazisis KT, Geromichalos GD, Dimitriadis
KA and Kortsaris AH: Optimization of the sulforhodamine B
colorimetric assay. J Immunol Methods. 208:151–158. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ueda T, Volinia S, Okumura H, et al:
Relation between microRNA expression and progression and prognosis
of gastric cancer: a microRNA expression analysis. Lancet Oncol.
11:136–146. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
De Vita F, Giuliani F, Silvestris N,
Catalano G, Ciardiello F and Orditura M: Human epidermal growth
factor receptor 2 (HER2) in gastric cancer: a new therapeutic
target. Cancer Treat Rev. 36(Suppl 3): S11–S15. 2010.
|
|
27
|
Ruan K, Fang X and Ouyang G: MicroRNAs:
novel regulators in the hallmarks of human cancer. Cancer Lett.
285:116–126. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Mirnezami AH, Pickard K, Zhang L, Primrose
JN and Packham G: MicroRNAs: key players in carcinogenesis and
novel therapeutic targets. Eur J Surg Oncol. 35:339–347. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Vink SR, Lagerwerf S, Mesman E, et al:
Radiosensitization of squamous cell carcinoma by the
alkylphospholipid perifosine in cell culture and xenografts. Clin
Cancer Res. 12:1615–1622. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Momota H, Nerio E and Holland EC:
Perifosine inhibits multiple signaling pathways in glial
progenitors and cooperates with temozolomide to arrest cell
proliferation in gliomas in vivo. Cancer Res. 65:7429–7435. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Gills JJ and Dennis PA: Perifosine: update
on a novel Akt inhibitor. Curr Oncol Rep. 11:102–110. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|