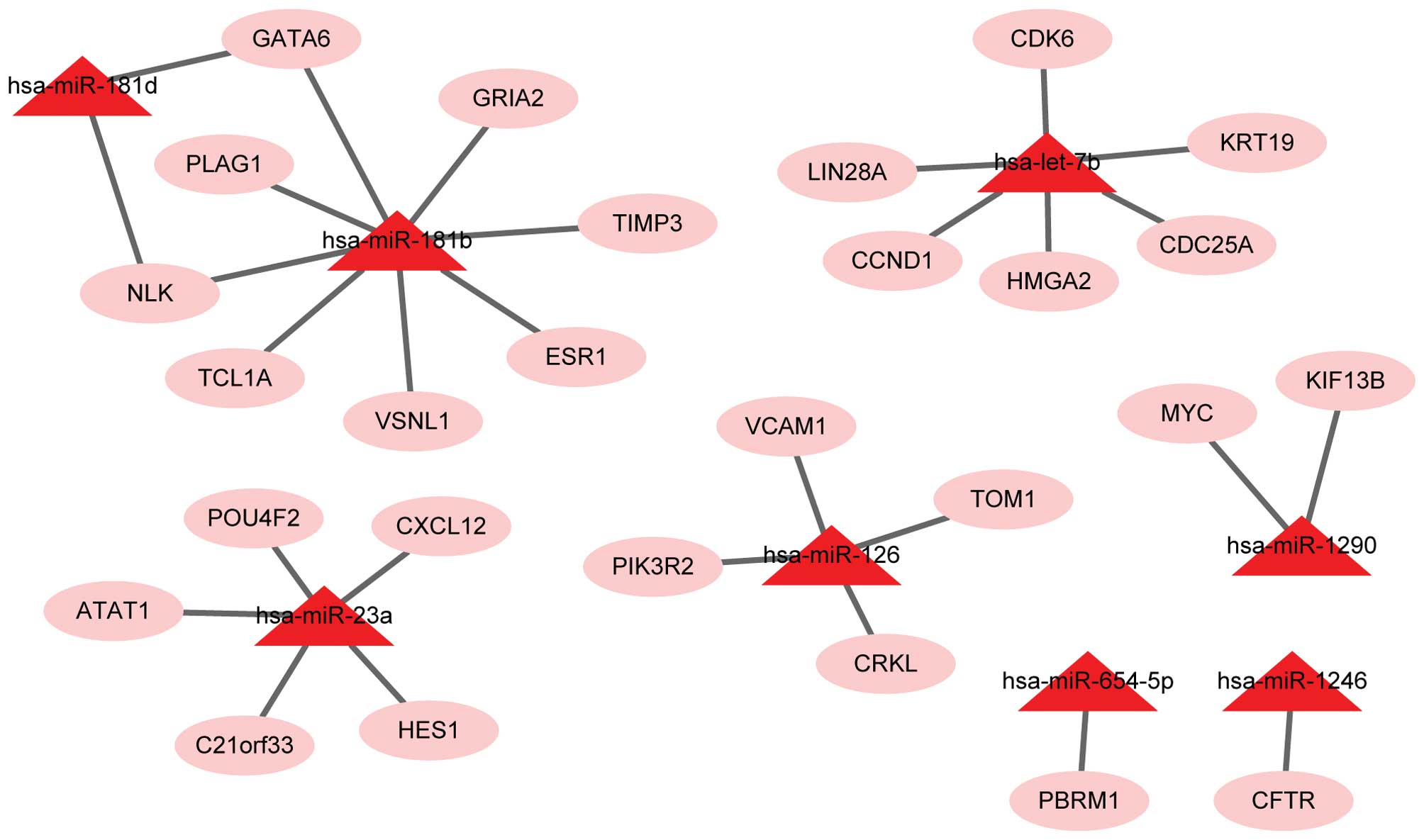
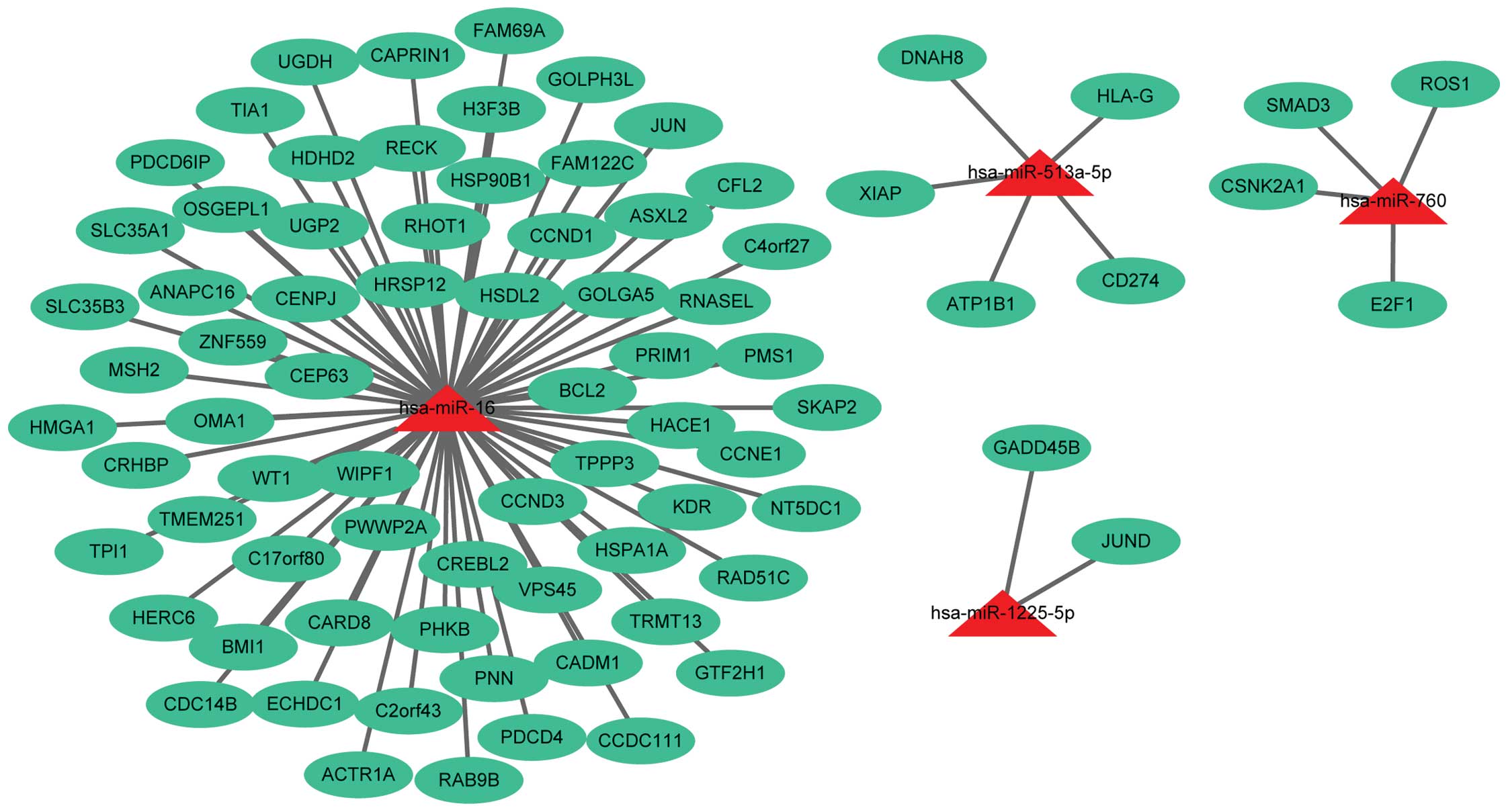
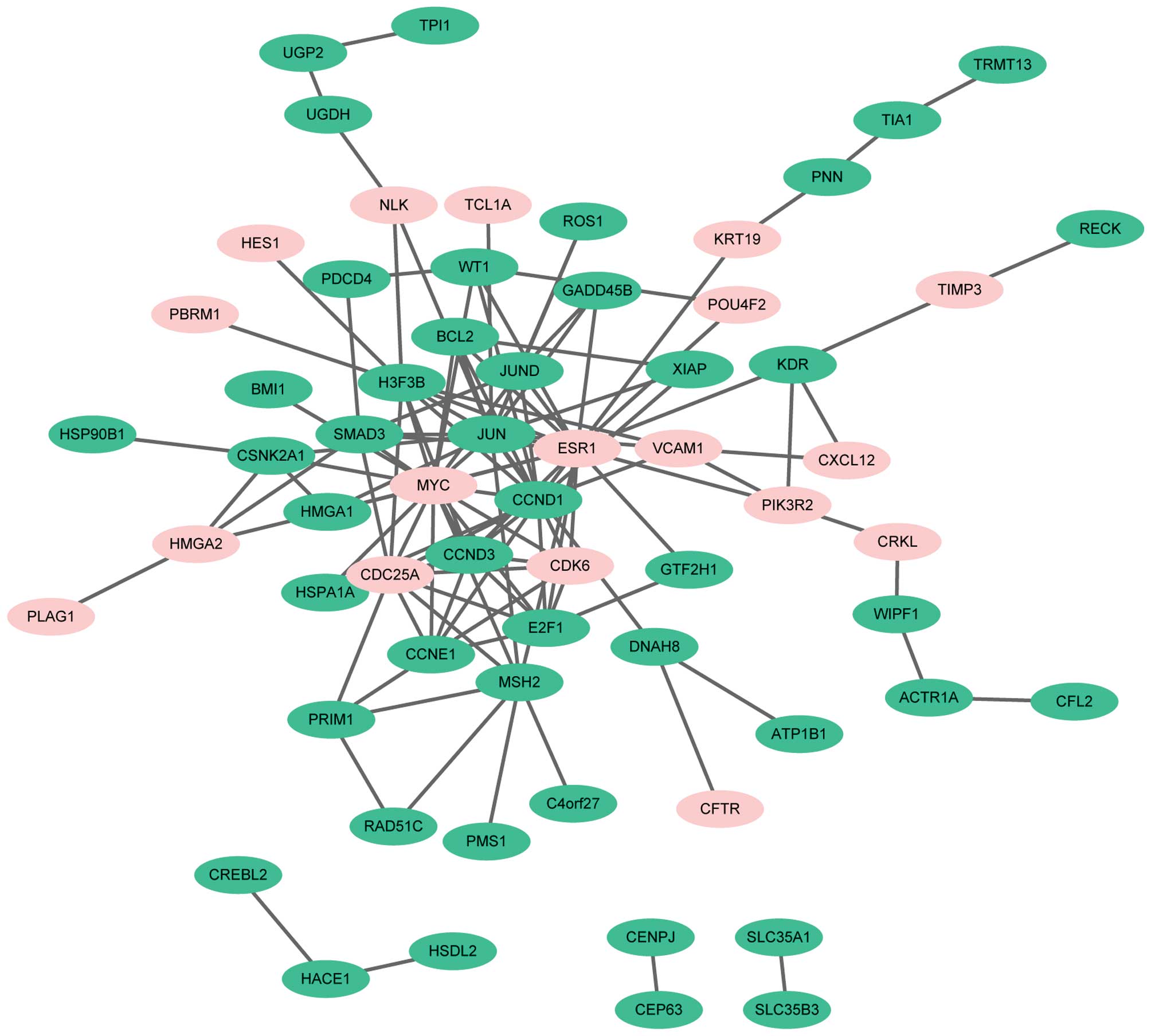
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Løvf M, Nome T, Bruun J, Eknaes M, Bakken
AC, Mpindi JP, Kilpinen S, Rognum TO, Nesbakken A, Kallioniemi O,
et al: A novel transcript, VNN1-AB, as a biomarker for colorectal
cancer. Int J Cancer. 135:2077–2084. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ogata-Kawata H, Izumiya M, Kurioka D,
Honma Y, Yamada Y, Furuta K, Gunji T, Ohta H, Okamoto H, Sonoda H,
et al: Circulating exosomal microRNAs as biomarkers of colon
cancer. Plos One. 9:e929212014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bretthauer M: Evidence for colorectal
cancer screening. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 24:417–425.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Atkin WS, Edwards R, Kralj-Hans I,
Wooldrage K, Hart AR, Northover J, Parkin DM, Wardle J, Duffy SW
and Cuzick J: UK Flexible Sigmoidoscopy Trial Investigators:
Once-only flexible sigmoidoscopy screening in prevention of
colorectal cancer: A multicentre randomised controlled trial.
Lancet. 375:1624–1633. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chen CC, Yang SH, Lin JK, Lin TC, Chen WS,
Jiang JK, Wang HS and Chang SC: Is it reasonable to add
preoperative serum level of CEA and CA19-9 to staging for
colorectal cancer? J Surg Res. 124:169–174. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Garzon R, Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNAs
in cancer. Annu Rev Med. 60:167–179. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Fabian MR, Sonenberg N and Filipowicz W:
Regulation of mRNA translation and stability by microRNAs. Annu Rev
Biochem. 79:351–379. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Esquela-Kerscher A and Slack FJ:
Oncomirs-microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
6:259–269. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mencía A, Modamio-Høybjør S, Redshaw N,
Morín M, Mayo-Merino F, Olavarrieta L, Aguirre LA, del Castillo I,
Steel KP, Dalmay T, et al: Mutations in the seed region of human
miR-96 are responsible for nonsyndromic progressive hearing loss.
Nat Genet. 41:609–613. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Asangani IA, Rasheed SA, Nikolova DA,
Leupold JH, Colburn NH, Post S and Allgayer H: MicroRNA-21 (miR-21)
post-transcriptionally downregulates tumor suppressor Pdcd4 and
stimulates invasion, intravasation and metastasis in colorectal
cancer. Oncogene. 27:2128–2136. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li H, Xie S, Liu M, Chen Z, Liu X, Wang L,
Li D and Zhou Y: The clinical significance of downregulation of
mir-124-3p, mir-146a-5p, mir-155-5p and mir-335-5p in gastric
cancer tumorigenesis. Int J Oncol. 45:197–208. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cao J, Cai J, Huang D, Han Q, Yang Q, Li
T, Ding H and Wang Z: miR-335 represents an invasion suppressor
gene in ovarian cancer by targeting Bcl-w. Oncol Rep. 30:701–706.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sun Z, Zhang Z, Liu Z, Qiu B, Liu K and
Dong G: MicroRNA-335 inhibits invasion and metastasis of colorectal
cancer by targeting ZEB2. Med Oncol. 31:9822014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Farh KK, Grimson A, Jan C, Lewis BP,
Johnston WK, Lim LP, Burge CB and Bartel DP: The widespread impact
of mammalian MicroRNAs on mRNA repression and evolution. Science.
310:1817–1821. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Baskerville S and Bartel DP: Microarray
profiling of microRNAs reveals frequent coexpression with
neighboring miRNAs and host genes. RNA. 11:241–247. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu CG, Ambs S,
Cimmino A, Petrocca F, Visone R, Iorio M, Roldo C, Ferracin M, et
al: A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines
cancer gene targets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:2257–2261. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra
E, Lamb J, Peck D, Sweet-Cordero A, Ebert BL, Mak RH, Ferrando AA,
et al: MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature.
435:834–838. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Montecalvo A, Larregina AT, Shufesky WJ,
Stolz DB, Sullivan ML, Karlsson JM, Baty CJ, Gibson GA, Erdos G,
Wang Z, et al: Mechanism of transfer of functional microRNAs
between mouse dendritic cells via exosomes. Blood. 119:756–766.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ogawa Y, Kanai-Azuma M, Akimoto Y,
Kawakami H and Yanoshita R: Exosome-like vesicles with dipeptidyl
peptidase IV in human saliva. Biol Pharm Bull. 31:1059–1062. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hu G, Drescher KM and Chen XM: Exosomal
miRNAs: Biological properties and therapeutic potential. Front
Genet. 3:562012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Théry C, Ostrowski M and Segura E:
Membrane vesicles as conveyors of immune responses. Nat Rev
Immunol. 9:581–593. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Pegtel DM, Cosmopoulos K, Thorley-Lawson
DA, van Eijndhoven MA, Hopmans ES, Lindenberg JL, de Gruijl TD,
Würdinger T and Middeldorp JM: Functional delivery of viral miRNAs
via exosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:6328–6333. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Skog J, Würdinger T, van Rijn S, Meijer
DH, Gainche L, Sena-Esteves M, Curry WT Jr, Carter BS, Krichevsky
AM and Breakefield XO: Glioblastoma microvesicles transport RNA and
proteins that promote tumour growth and provide diagnostic
biomarkers. Nat Cell Biol. 10:1470–1476. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Igaz I and Igaz P: Tumor surveillance by
circulating microRNAs: A hypothesis. Cell Mol Life Sci.
71:4081–4087. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Smyth GK: Limma: Linear models for
microarray dataBioinformatics and Computational Biology Solutions
using R and Bioconductor. Gentleman R, Carey V, Dudoit S, Irizarry
R and Huber W: Springer; New York, PA: pp. 397–420. 2005,
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Xiao F, Zuo Z, Cai G, Kang S, Gao X and Li
T: miRecords: An integrated resource for microRNA-target
interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 37:(Database Issue). D105–D110.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Dweep H, Sticht C, Pandey P and Gretz N:
miRWalk-database: Prediction of possible miRNA binding sites by
‘walking’ the genes of three genomes. J Biomed Inform. 44:839–847.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Huangda W, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Bioinformatics enrichment tools: Paths toward the comprehensive
functional analysis of large gene lists. Nucleic Acids Res.
37:1–13. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hulsegge I, Kommadath A and Smits MA:
Globaltest and GOEAST: Two different approaches for gene ontology
analysis. BMC Proc. 3(Suppl 4): S102009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kanehisa M: The KEGG database. Novartis
Found Symp. 247:91–101; discussion 101–103, 119–128, 244–252. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Huangda W, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID
bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 4:44–57. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Franceschini A, Szklarczyk D, Frankild S,
Kuhn M, Simonovic M, Roth A, Lin J, Minguez P, Bork P, von Mering C
and Jensen LJ: STRING v9. 1: Protein-protein interaction networks,
with increased coverage and integration. Nucleic Acids Res.
41:(Database Issue). D808–D815. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Patil A and Nakamura H: Filtering
high-throughput protein-protein interaction data using a
combination of genomic features. BMC Bioinformatics. 6:1002005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Takahashi M, Sung B, Shen Y, Hur K, Link
A, Boland CR, Aggarwal BB and Goel A: Boswellic acid exerts
antitumor effects in colorectal cancer cells by modulating
expression of the let-7 and miR-200 microRNA family.
Carcinogenesis. 33:2441–2449. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Chen F, Chen C, Yang S, Gong W, Wang Y,
Cianflone K, Tang J and Wang DW: Let-7b inhibits human cancer
phenotype by targeting cytochrome P450 epoxygenase 2J2. Plos One.
7:e391972012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Yan X, Liang H, Deng T, Zhu K, Zhang S,
Wang N, Jiang X, Wang X, Liu R, Zen K, et al: The identification of
novel targets of miR-16 and characterization of their biological
functions in cancer cells. Mol Cancer. 12:922013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ma Q, Wang X, Li Z, Li B, Ma F, Peng L,
Zhang Y, Xu A and Jiang B: microRNA-16 represses colorectal cancer
cell growth in vitro by regulating the p53/survivin signaling
pathway. Oncol Rep. 29:1652–1658. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yang Y, Wang F, Shi C, Zou Y, Qin H and Ma
Y: Cyclin D1 G870A polymorphism contributes to colorectal cancer
susceptibility: Evidence from a systematic review of 22
case-control studies. Plos One. 7:e368132012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Probst-Hensch NM, Sun CL, Van Den Berg D,
Ceschi M, Koh WP and Yu MC: The effect of the cyclin D1 (CCND1)
A870G polymorphism on colorectal cancer risk is modified by
glutathione-S-transferase polymorphisms and isothiocyanate intake
in the Singapore Chinese Health Study. Carcinogenesis.
27:2475–2482. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Liu Q, Fu H, Sun F, Zhang H, Tie Y, Zhu J,
Xing R, Sun Z and Zheng X: miR-16 family induces cell cycle arrest
by regulating multiple cell cycle genes. Nucleic Acids Res.
36:5391–5404. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Schultz J, Lorenz P, Gross G, Ibrahim S
and Kunz M: MicroRNA let-7b targets important cell cycle molecules
in malignant melanoma cells and interferes with
anchorage-independent growth. Cell Res. 18:549–557. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wu J, Ji X, Zhu L, Jiang Q, Wen Z, Xu S,
Shao W, Cai J, Du Q, Zhu Y and Mao J: Up-regulation of
microRNA-1290 impairs cytokinesis and affects the reprogramming of
colon cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 329:155–163. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Behrens J: The role of the Wnt signalling
pathway in colorectal tumorigenesis. Biochem Soc Trans. 33:672–675.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Karim RZ, Tse GM, Putti TC, Scolyer RA and
Lee CS: The significance of the Wnt pathway in the pathology of
human cancers. Pathology. 36:120–128. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zeller KI, Jegga AG, Aronow BJ, O'Donnell
KA and Dang CV: An integrated database of genes responsive to the
Myc oncogenic transcription factor: Identification of direct
genomic targets. Genome Biol. 4:R692003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Pelengaris S, Khan M and Evan G: c-MYC:
More than just a matter of life and death. Nat Rev Cancer.
2:764–776. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
González V and Hurley LH: The c-MYC NHE
III(1): Function and regulation. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol.
50:111–129. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Hermeking H: The MYC oncogene as a cancer
drug target. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 3:163–175. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Li XM, Wang AM, Zhang J and Yi H:
Down-regulation of miR-126 expression in colorectal cancer and its
clinical significance. Med Oncol. 28:1054–1057. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Zhang Y, Wang X, Xu B, Wang B, Wang Z,
Liang Y, Zhou J, Hu J and Jiang B: Epigenetic silencing of miR-126
contributes to tumor invasion and angiogenesis in colorectal
cancer. Oncol Rep. 30:1976–1984. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Liu P, Cheng H, Roberts TM and Zhao JJ:
Targeting the phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway in cancer. Nat Rev
Drug Discov. 8:627–644. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Zhu N, Zhang D, Xie H, Zhou Z, Chen H, Hu
T, Bai Y, Shen Y, Yuan W, Jing Q and Qin Y: Endothelial-specific
intron-derived miR-126 is down-regulated in human breast cancer and
targets both VEGFA and PIK3R2. Mol Cell Biochem. 351:157–164. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Kang HY, Lin HK, Hu YC, Yeh S, Huang KE
and Chang C: From transforming growth factor-beta signaling to
androgen action: Identification of Smad3 as an androgen receptor
coregulator in prostate cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
98:3018–3023. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Bierie B and Moses HL: TGF-beta and
cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 17:29–40. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Han SU, Kim HT, Seong DH, Kim YS, Park YS,
Bang YJ, Yang HK and Kim SJ: Loss of the Smad3 expression increases
susceptibility to tumorigenicity in human gastric cancer. Oncogene.
23:1333–1341. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Liu G, Fang Y, Zhang H, Li Y, Li X, Yu J
and Wang X: Computational identification and microarray-based
validation of microRNAs in Oryctolagus cuniculus. Mol Biol Rep.
37:3575–3581. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|