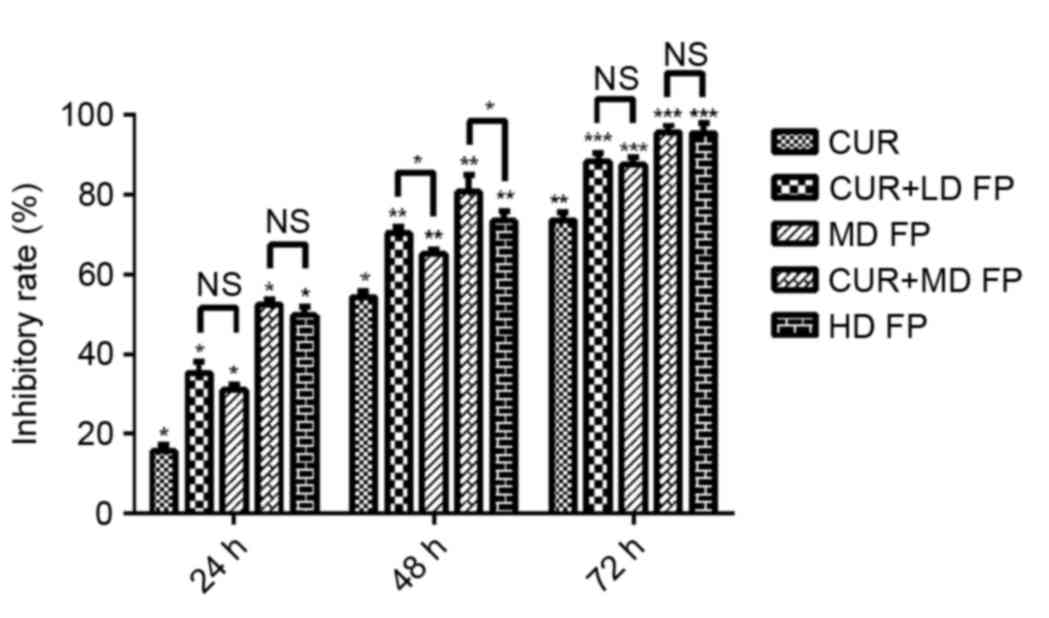
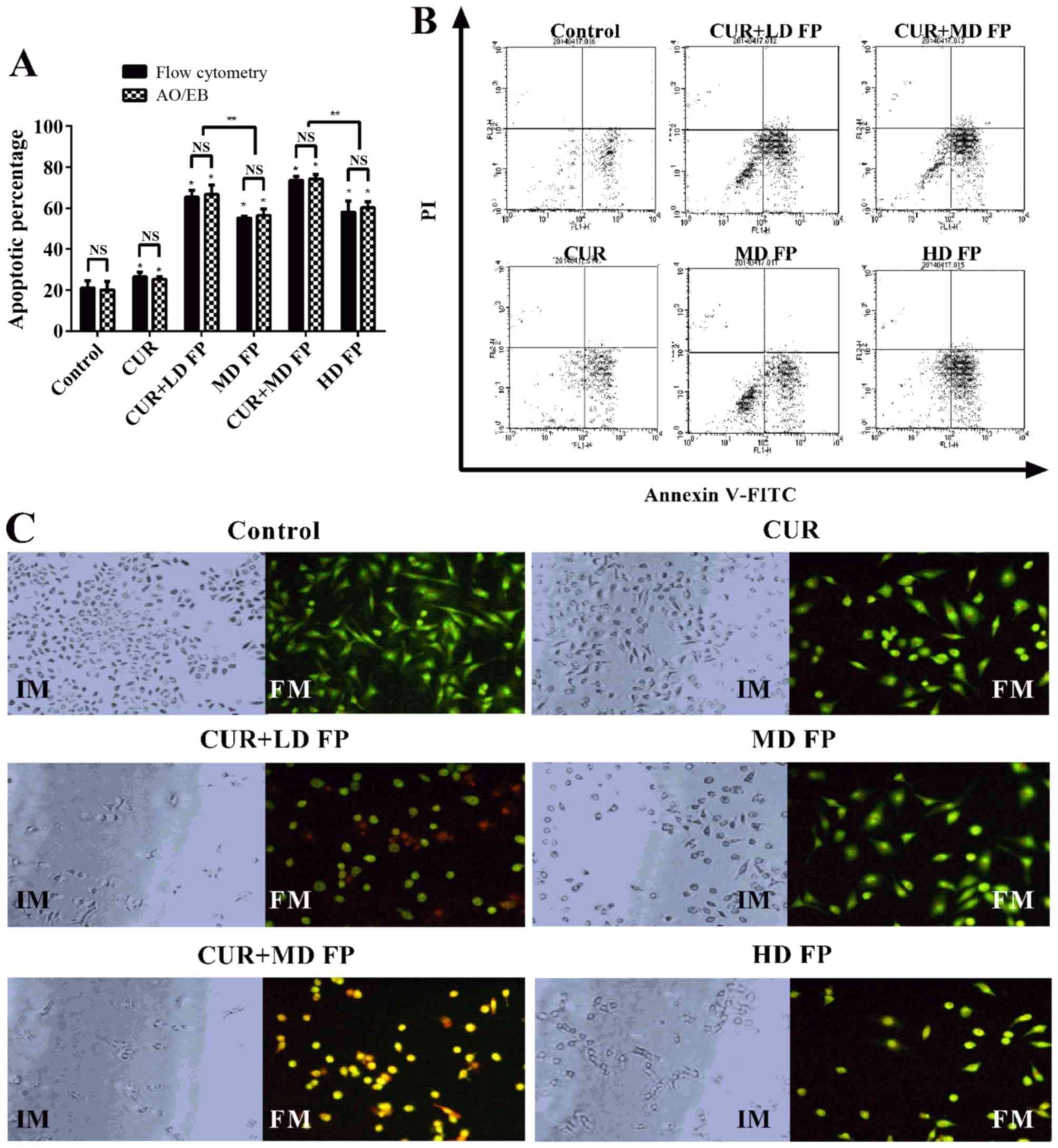
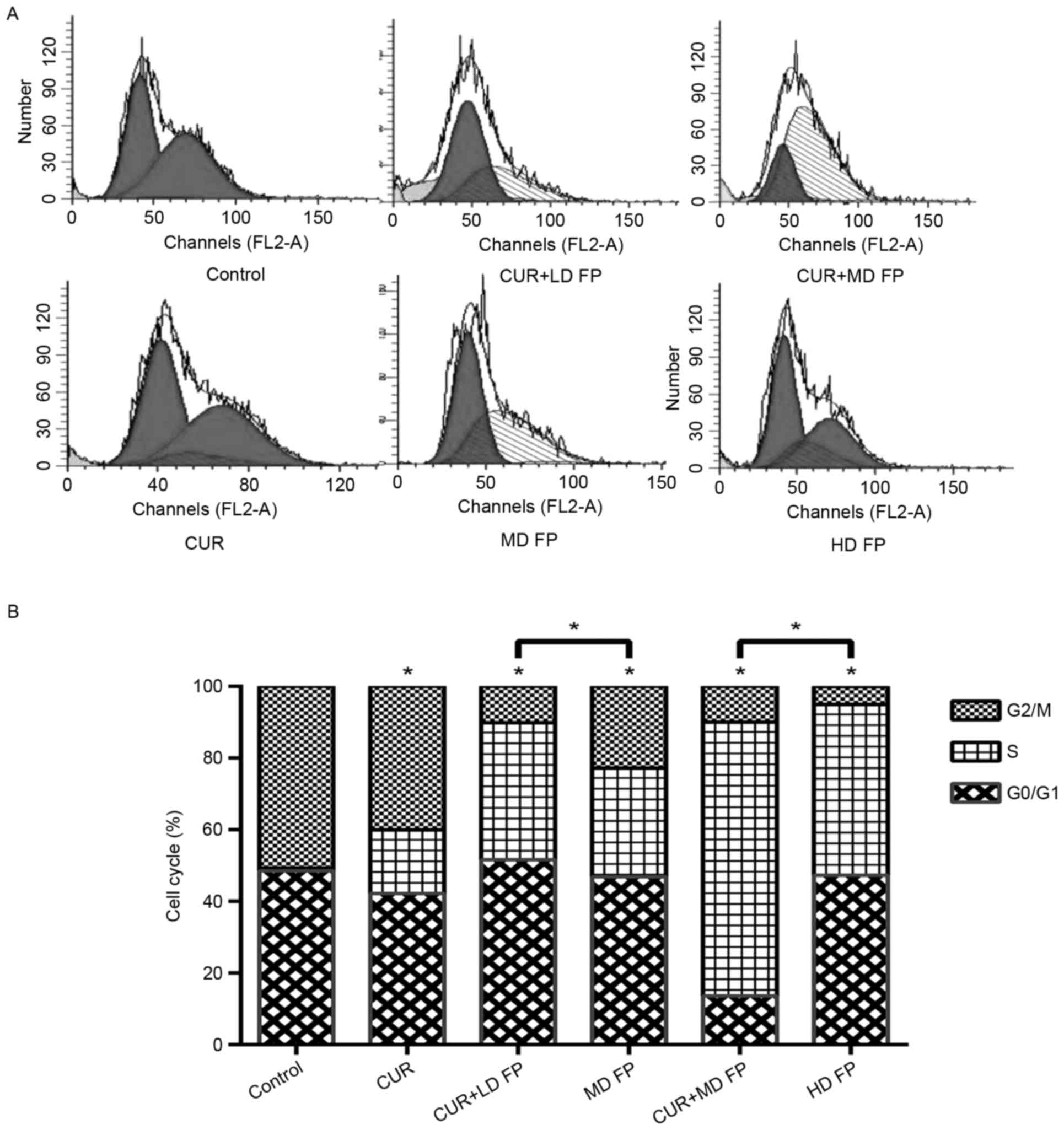
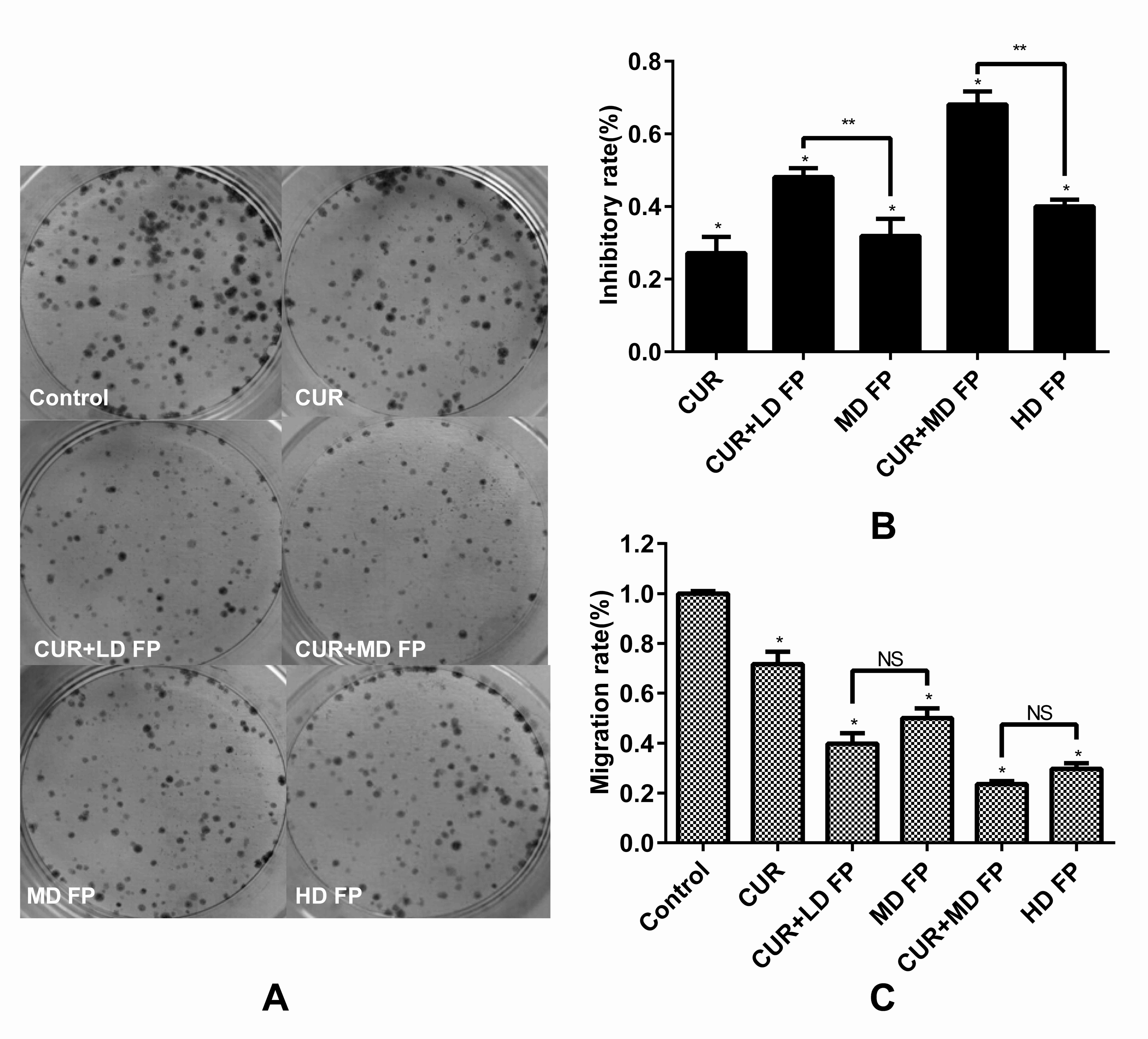
|
1
|
Chen Y, Li Y, Wang H, Lu J, Jin M and
Zhang Z: Maternal gastric carcinoma with metastasis to the
placenta: A case report. Oncol Lett. 8:2509–2510. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Nagini S: Carcinoma of the stomach: A
review of epidemiology, pathogenesis, molecular genetics and
chemoprevention. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 4:156–169. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser
S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D and Bray F: Cancer
incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major
patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 136:E359–E386. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yang D, Hendifar A, Lenz C, Togawa K, Lenz
F, Lurje G, Pohl A, Winder T, Ning Y, Groshen S and Lenz HJ:
Survival of metastatic gastric cancer: Significance of age, sex and
race/ethnicity. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2:77–84. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Pulido-Moran M, Moreno-Fernandez J,
Ramirez-Tortosa C and Ramirez-Tortosa M: Curcumin and health.
Molecules. 21:2642016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Aggarwal BB, Kumar A, Aggarwal MS and
Shishodia S: Curcumin derived from turmeric (Curcuma longa): A
spice for all seasons. Phytopharm Cancer Chemo Prev. 349–387.
2005.
|
|
7
|
Lao CD, Ruffin MT IV, Normolle D, Heath
DD, Murray SI, Bailey JM, Boggs ME, Crowell J, Rock CL and Brenner
DE: Dose escalation of a curcuminoid formulation. BMC Complement
Altern Med. 6:102006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kamat AM, Tharakan ST, Sung B and Aggarwal
BB: Curcumin potentiates the anticancer effects of Bacillus
Calmette-Guerin against bladder cancer through the downregulation
of NF-kappaB and upregulation of TRAIL receptors. Cancer Res.
69:8958–8966. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kunnumakkara AB, Anand P and Aggarwal BB:
Curcumin inhibits proliferation, invasion, angiogenesis and
metastasis of different cancers through interaction with multiple
cell signaling proteins. Cancer Lett. 269:199–225. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mahajanakatti AB, Murthy G, Sharma N and
Skariyachan S: Exploring inhibitory potential of Curcumin against
various cancer targets by in silico virtual screening. Interdiscip
Sci. 6:13–24. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Van Cutsem E: The treatment of advanced
gastric cancer: New findings on the activity of the taxanes.
Oncologist. 9:(Suppl). S9–S15. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
LoRusso P, Pazdur R, Redman BG, Kinzie J
and Vaitkevicius V: Low-dose continuous infusion 5-fluorouracil and
cisplatin: Phase II evaluation in advanced colorectal carcinoma. Am
J Clin Oncol. 12:486–490. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bouché O, Ychou M, Burtin P, Bedenne L,
Ducreux M, Lebreton G, Baulieux J, Nordlinger B, Martin C, Seitz
JF, et al: Adjuvant chemotherapy with 5-fluorouracil and cisplatin
compared with surgery alone for gastric cancer: 7-year results of
the FFCD randomized phase III trial (8801). Ann Oncol.
16:1488–1497. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Nakata B, Sowa M, Tsuji A, Kamano T,
Sasaki K, Fukunaga Y, Takahashi M, Tsujitani S, Mikami Y, Mitachi
Y, et al: Continuous infusion of 5-fluorouracil with versus without
low-dose, consecutive administration of cisplatin in advanced
colorectal cancer. A prospective randomized phase II study. J Exp
Clin Cancer Res. 26:51–60. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kim R, Nishimoto N, Inoue H, Yoshida K and
Toge T: An analysis of the therapeutic efficacy of protracted
infusion of low-dose 5-fluorouracil and cisplatin in advanced
gastric cancer. J Infect Chemother. 6:222–228. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Xingde W, Xingqiu H, Chengxian G, et al:
Long-period virulent test of Curcumin. J Zhejiang College TCM.
24:61–65. 2000.
|
|
17
|
Perkins S, Verschoyle RD, Hill K, Parveen
I, Threadgill MD, Sharma RA, Williams ML, Steward WP and Gescher
AJ: Chemopreventive efficacy and pharmacokinetics of curcumin in
the min/+ mouse, a model of familial adenomatous polyposis. Cancer
Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 11:535–540. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Aggarwal BB, Sundaram C, Malani N and
Ichikawa H: Curcumin: The Indian solid gold. Adv Exp Med Biol.
595:1–75. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Esatbeyoglu T, Huebbe P, Ernst IM, Chin D,
Wagner AE and Rimbach G: Curcumin-from molecule to biological
function. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 51:5308–5332. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Calaf GM, Echiburú-Chau C, Roy D, Chai Y,
Wen G and Balajee AS: Protective role of curcumin in oxidative
stress of breast cells. Oncol Rep. 26:1029–1035. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li PM, Li YL, Liu B, Wang WJ, Wang YZ and
Li Z: Curcumin induces MHCC97H liver cancer cell apoptosis by
activating ROS/TLR-4/caspase signaling pathway. Asian Pac J Cancer
Prev. 15:2329–2334. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wu SH, Hang LW, Yang JS, Chen HY, Lin HY,
Chiang JH, Lu CC, Yang JL, Lai TY, Ko YC and Chung JG: Curcumin
induces apoptosis in human non-small cell lung cancer NCI-H460
cells through ER stress and caspase cascade and
mitochondria-dependent pathways. Anticancer Res. 30:2125–2133.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Goel A and Aggarwal BB: Curcumin, the
golden spice from Indian saffron, is a chemosensitizer and
radiosensitizer for tumors and chemoprotector and radioprotector
for normal organs. Nut Cancer. 62:919–930. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Subramaniam D, Ponnurangam S, Ramamoorthy
P, Standing D, Battafarano RJ, Anant S and Sharma P: Curcumin
induces cell death in esophageal cancer cells through modulating
notch signaling. PLoS One. 7:e305902012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gupta SC, Patchva S and Aggarwal BB:
Therapeutic roles of curcumin: Lessons learned from clinical
trials. AAPS J. 15:195–218. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Su CC, Wang MJ and Chiu TL: The
anti-cancer efficacy of curcumin scrutinized through core signaling
pathways in glioblastoma. Int J Mol Med. 26:217–224.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhu L, Han MB, Gao Y, Wang H, Dai L, Wen Y
and Na LX: Curcumin triggers apoptosis via upregulation of
Bax/Bcl-2 ratio and caspase activation in SW872 human adipocytes.
Mol Med Rep. 12:1151–1156. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sintara K, Thong-Ngam D, Patumraj S and
Klaikeaw N: Curcumin attenuates gastric cancer induced by
N-Methyl-N-nitrosourea and saturated sodium chloride in rats. J
Biomed Biotechnol. 2012:9153802012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wu J, Lu WY and Cui LL: Inhibitory effect
of curcumin on invasion of skin squamous cell carcinoma A431 cells.
Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 16:2813–2818. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Tu SP, Jin H, Shi JD, Zhu LM, Suo Y, Lu G,
Liu A, Wang TC and Yang CS: Curcumin induces the differentiation of
myeloid-derived suppressor cells and inhibits their interaction
with cancer cells and related tumor growth. Cancer Prev Res
(Phila). 5:205–215. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yu LL, Wu JG, Dai N, Yu HG and Si JM:
Curcumin reverses chemoresistance of human gastric cancer cells by
downregulating the NF-κB transcription factor. Oncol Rep.
26:1197–1203. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Cai XZ, Wang J, Li XD, Wang GL, Liu FN,
Cheng MS and Li F: Curcumin suppresses proliferation and invasion
in human gastric cancer cells by downregulation of PAK1 activity
and cyclin D1 expression. Cancer Biol Ther. 8:1360–1368. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chen Q, Gao Q, Chen K, Wang Y, Chen L and
Li XU: Curcumin suppresses migration and invasion of human
endometrial carcinoma cells. Oncol Lett. 10:1297–1302.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Meiyanto E, Putri DD, Susidarti RA,
Murwanti R, Sardjiman Fitriasari A, Husnaa U, Purnomo H and
Kawaichi M: Curcumin and its analogues (PGV-0 and PGV-1) enhance
sensitivity of resistant MCF-7 cells to doxorubicin through
inhibition of HER2 and NF-κB activation Asian Pac. J Cancer Prev.
15:179–184. 2014.
|
|
35
|
Hong JM, Park CS, Nam-Goong IS, Kim YS,
Lee JC, Han MW, Choi JI, Kim YI and Kim ES: Curcumin enhances
docetaxel-induced apoptosis of 8505C anaplastic thyroid carcinoma
cells. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 29:54–61. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Xu JD, Cao XX, Long ZW, Liu XP, Furuya T,
Xu JW, Liu XL, De Xu Z, Sasaki K and Li QQ: BCL2L10 protein
regulates apoptosis/proliferation through differential pathways in
gastric cancer cells. J Pathol. 223:400–409. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Barrezueta LF, Oshima CT, Lima FO, De
Oliveira Costa H, Gomes TS, Neto RA and De Franco MF: The intrinsic
apoptotic signaling pathway in gastric adenocarcinomas of Brazilian
patients: Immunoexpression of the Bcl-2 family (Bcl-2, Bcl-x, Bak,
Bax, Bad) determined by tissue microarray analysis. Mol Med Rep.
3:261–267. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|