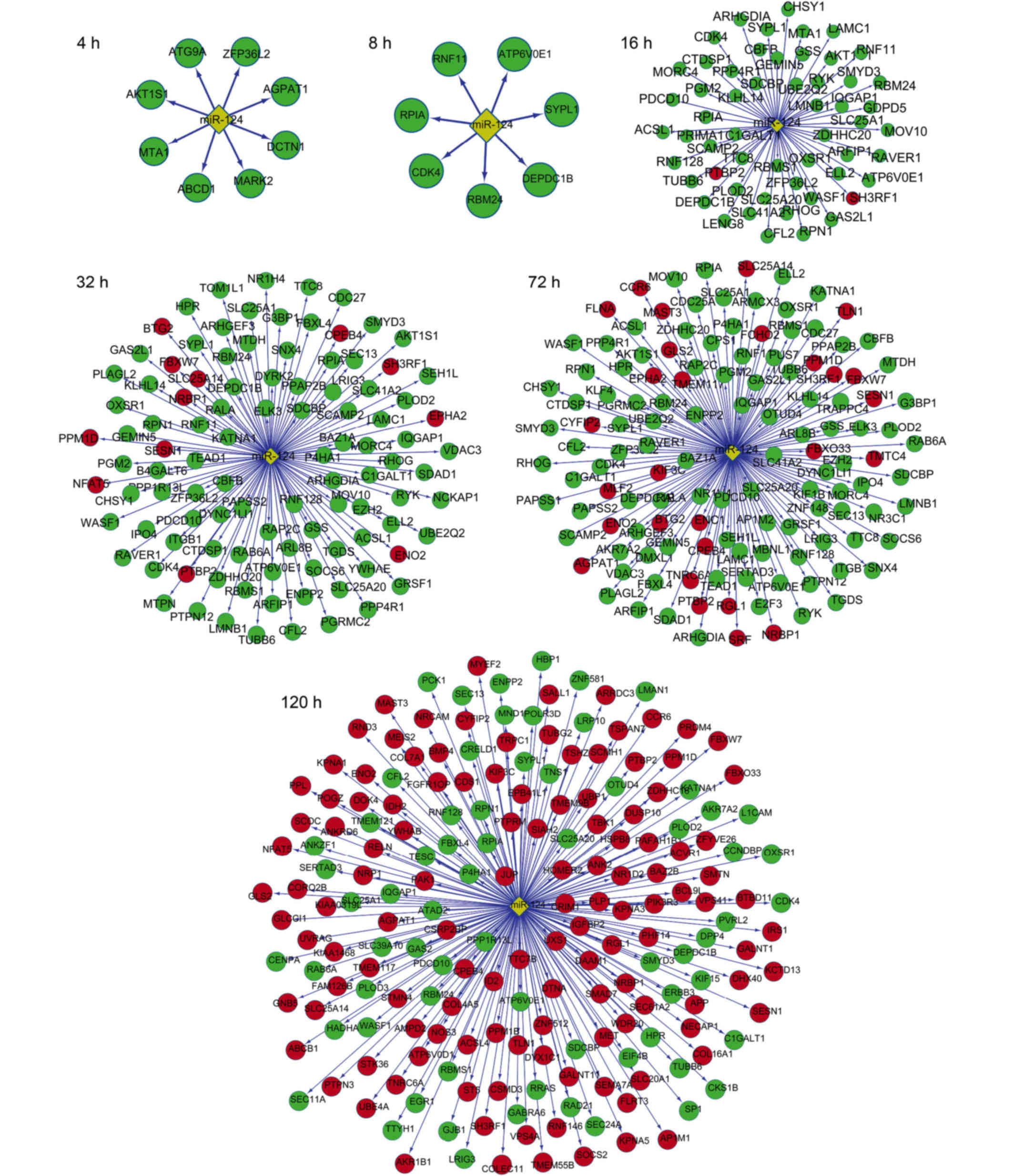
|
1
|
Stewart BW and Wild CP: World cancer
report 2014. World Health Organization. 2014.
|
|
2
|
Ringe B, Pichlmayr R, Wittekind C and
Tusch G: Surgical treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: Experience
with liver resection and transplantation in 198 patients. World J
Surg. 15:270–285. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Maluccio M and Covey A: Recent progress in
understanding, diagnosing, and treating hepatocellular carcinoma.
CA Cancer J Clin. 62:394–399. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bruix J and Sherman M: American
Association for the Study of Liver Diseases: Management of
hepatocellular carcinoma: An update. Hepatology. 53:1020–1022.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Meyers RL, Tiao G, de Ville de Goyet J,
Superina R and Aronson DC: Hepatoblastoma state of the art:
Pre-treatment extent of disease, surgical resection guidelines and
the role of liver transplantation. Curr Opin Pediatr. 26:29–36.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Osada H and Takahashi T: MicroRNAs in
biological processes and carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis. 28:2–12.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Shi XB, Xue L, Ma AH, Tepper CG,
Gandour-Edwards R, Kung HJ and deVere White RW: Tumor suppressive
miR-124 targets androgen receptor and inhibits proliferation of
prostate cancer cells. Oncogene. 32:4130–4138. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zheng H, Song F, Zhang L, Yang D, Ji P,
Wang Y, Almeida M, Calin GA, Hao X, Wei Q, et al: Genetic variants
at the miR-124 binding site on the cytoskeleton-organizing IQGAP1
gene confer differential predisposition to breast cancer. Int J
Oncol. 38:1153–1161. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zheng F, Liao YJ, Cai MY, Liu YH, Liu TH,
Chen SP, Bian XW, Guan XY, Lin MC, Zeng YX, et al: The putative
tumour suppressor microRNA-124 modulates hepatocellular carcinoma
cell aggressiveness by repressing ROCK2 and EZH2. Gut. 61:278–289.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zeng B, Li Z, Chen R, Guo N, Zhou J, Zhou
Q, Lin Q, Cheng D, Liao Q, Zheng L and Gong Y: Epigenetic
regulation of miR-124 by hepatitis C virus core protein promotes
migration and invasion of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma cells by
targeting SMYD3. FEBS Lett. 586:3271–3278. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Krützfeldt J, Rajewsky N, Braich R, Rajeev
KG, Tuschl T, Manoharan M and Stoffel M: Silencing of microRNAs in
vivo with ‘antagomirs’. Nature. 438:685–689. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cheng C and Li LM: Inferring microRNA
activities by combining gene expression with microRNA target
prediction. PLoS One. 3:e19892008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lim LP, Lau NC, Garrett-Engele P, Grimson
A, Schelter JM, Castle J, Bartel DP, Linsley PS and Johnson JM:
Microarray analysis shows that some microRNAs downregulate large
numbers of target mRNAs. Nature. 433:769–773. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang X and Wang X: Systematic
identification of microRNA functions by combining target prediction
and expression profiling. Nucleic Acids Res. 34:1646–1652. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Irizarry RA, Hobbs B, Collin F,
Beazer-Barclay YD, Antonellis KJ, Scherf U and Speed TP:
Exploration, normalization and summaries of high density
oligonucleotide array probe level data. Biostatistics. 4:249–264.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bernhardt V, Hotchkiss MT, Garcia-Reyero
N, Escalon BL, Denslow N and Davenport PW: Tracheal occlusion
conditioning in conscious rats modulates gene expression profile of
medial thalamus. Front Physiol. 2:242011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shannon W, Culverhouse R and Duncan J:
Analyzing microarray data using cluster analysis. Pharmacogenomics.
4:41–52. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Huang da W, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID
bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 4:44–57. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lewis BP, Shih IH, Jones-Rhoades MW,
Bartel DP and Burge CB: Prediction of mammalian microRNA targets.
Cell. 115:787–798. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kertesz M, Iovino N, Unnerstall U, Gaul U
and Segal E: The role of site accessibility in microRNA target
recognition. Nat Genet. 39:1278–1284. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lall S, Grün D, Krek A, Chen K, Wang YL,
Dewey CN, Sood P, Colombo T, Bray N, Macmenamin P, et al: A
genome-wide map of conserved microRNA targets in C. elegans. Curr
Biol. 16:460–471. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang X: miRDB: A microRNA target
prediction and functional annotation database with a wiki
interface. RNA. 14:1012–1017. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Betel D, Wilson M, Gabow A, Marks DS and
Sander C: The microRNA.org resource: targets and expression.
Nucleic Acids Res. 36:D149–D153. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Harris MA, Clark J, Ireland A, Lomax J,
Ashburner M, Foulger R, Eilbeck K, Lewis S, Marshall B, Mungall C,
et al: The gene ontology (GO) database and informatics resource.
Nucleic Acids Res. 32:(Database Issue). D258–D261. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Weis SM and Cheresh DA: Tumor
angiogenesis: Molecular pathways and therapeutic targets. Nat Med.
17:1359–1370. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Pillai RS: MicroRNA function: Multiple
mechanisms for a tiny RNA? RNA. 11:1753–1761. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hobert O: Common logic of transcription
factor and microRNA action. Trends Biochem Sci. 29:462–468. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Etienne-Manneville S and Hall A: Rho
GTPases in cell biology. Nature. 420:629–635. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jaffe AB and Hall A: Rho GTPases:
Biochemistry and biology. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 21:247–269. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yoshimura T, Arimura N, Kawano Y, Kawabata
S, Wang S and Kaibuchi K: Ras regulates neuronal polarity via the
PI3-kinase/Akt/GSK-3beta/CRMP-2 pathway. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 340:62–68. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chang L and Karin M: Mammalian MAP kinase
signalling cascades. Nature. 410:37–40. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wong CM, Yam JW, Ching YP, Yau TO, Leung
TH, Jin DY and Ng IO: Rho GTPase-activating protein deleted in
liver cancer suppresses cell proliferation and invasion in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. 65:8861–8868. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Calvisi DF, Ladu S, Conner EA, Seo D,
Hsieh JT, Factor VM and Thorgeirsson SS: Inactivation of Ras
GTPase-activating proteins promotes unrestrained activity of
wild-type Ras in human liver cancer. J Hepatol. 54:311–319. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Beekman JM and Coffer PJ: The ins and outs
of syntenin, a multifunctional intracellular adaptor protein. J
Cell Sci. 121:1349–1355. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lee H, Kim Y, Choi Y, Choi S, Hong E and
Oh ES: Syndecan-2 cytoplasmic domain regulates colon cancer cell
migration via interaction with syntenin-1. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 409:148–153. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Bustelo XR, Sauzeau V and Berenjeno IM:
GTP-binding proteins of the Rho/Rac family: Regulation, effectors
and functions in vivo. Bioessays. 29:356–370. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Liang L, Li Q, Huang LY, Li DW, Wang YW,
Li XX and Cai SJ: Loss of ARHGDIA expression is associated with
poor prognosis in HCC and promotes invasion and metastasis of HCC
cells. Int J Oncol. 45:659–666. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yamaguchi H and Condeelis J: Regulation of
the actin cytoskeleton in cancer cell migration and invasion.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1773:642–652. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Maciver SK and Hussey PJ: The ADF/cofilin
family: Actin-remodeling proteins. Genome Biol. 3:reviews30072002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Aledo JC: Glutamine breakdown in rapidly
dividing cells: Waste or investment? Bioessays. 26:778–785. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Le Bacquer O, Laboisse C and Darmaun D:
Glutamine preserves protein synthesis and paracellular permeability
in Caco-2 cells submitted to ‘luminal fasting’. Am J Physiol
Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 285:G128–G136. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Spanaki C, Kotzamani D and Plaitakis A:
Widening spectrum of cellular and subcellular expression of human
Glud1 and Glud2 glutamate dehydrogenases suggests novel functions.
Neurochem Res. 42:92–107. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Biankin AV, Waddell N, Kassahn KS, Gingras
MC, Muthuswamy LB, Johns AL, Miller DK, Wilson PJ, Patch AM, Wu J,
et al: Pancreatic cancer genomes reveal aberrations in axon
guidance pathway genes. Nature. 491:399–405. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Gu C, Rodriguez ER, Reimert DV, Shu T,
Fritzsch B, Richards LJ, Kolodkin AL and Ginty DD: Neuropilin-1
conveys semaphorin and VEGF signaling during neural and
cardiovascular development. Dev Cell. 5:45–57. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Xu J and Xia J: NRP-1 silencing suppresses
hepatocellular carcinoma cell growth in vitro and in vivo. Exp Ther
Med. 5:150–154. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Pasterkamp RJ, Peschon JJ, Spriggs MK and
Kolodkin AL: Semaphorin 7A promotes axon outgrowth through
integrins and MAPKs. Nature. 424:398–405. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Monvoisin A, Neaud V, Lédinghen V,
Dubuisson L, Balabaud C, Bioulac-Sage P, Desmoulière A and
Rosenbaum J: Direct evidence that hepatocyte growth factor-induced
invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells is mediated by
urokinase. J Hepatol. 30:511–518. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Scagliotti GV, Novello S and von Pawel J:
The emerging role of MET/HGF inhibitors in oncology. Cancer Treat
Rev. 39:793–801. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|