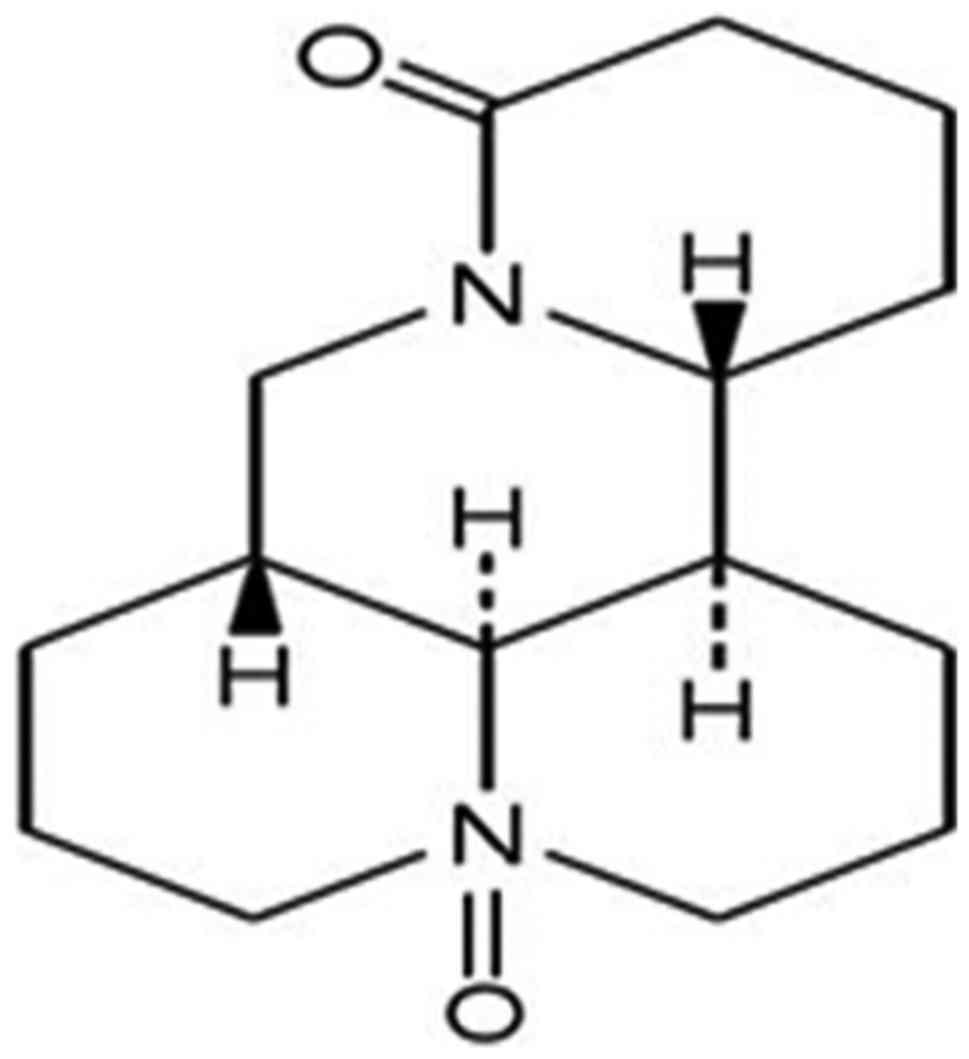
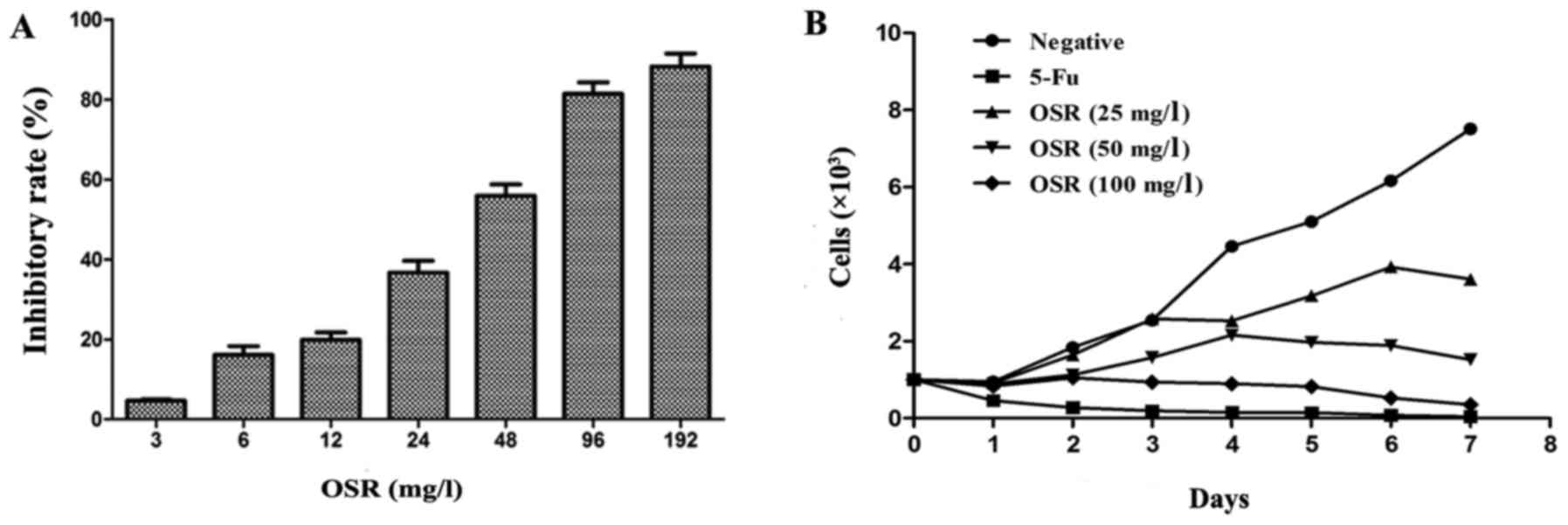
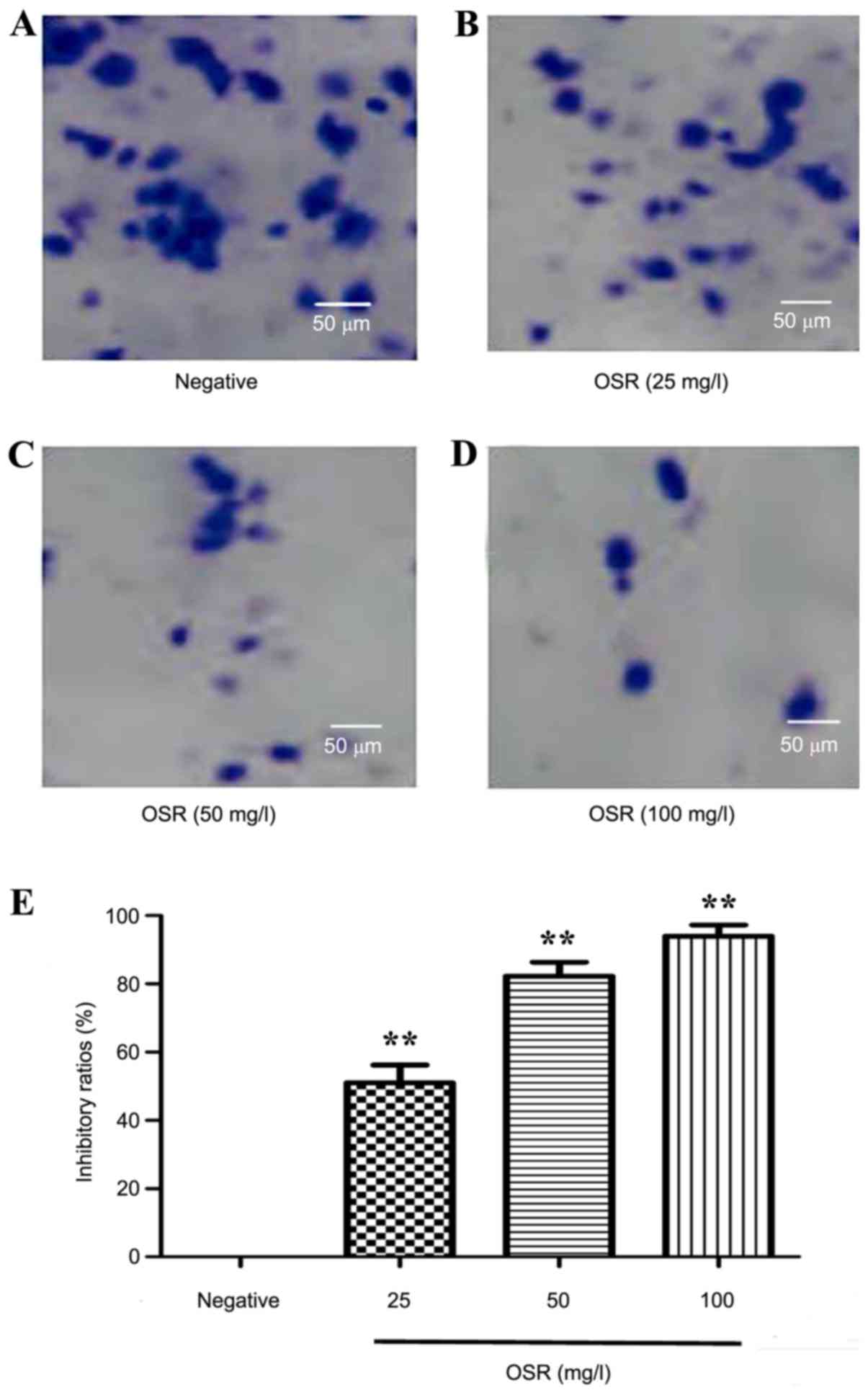
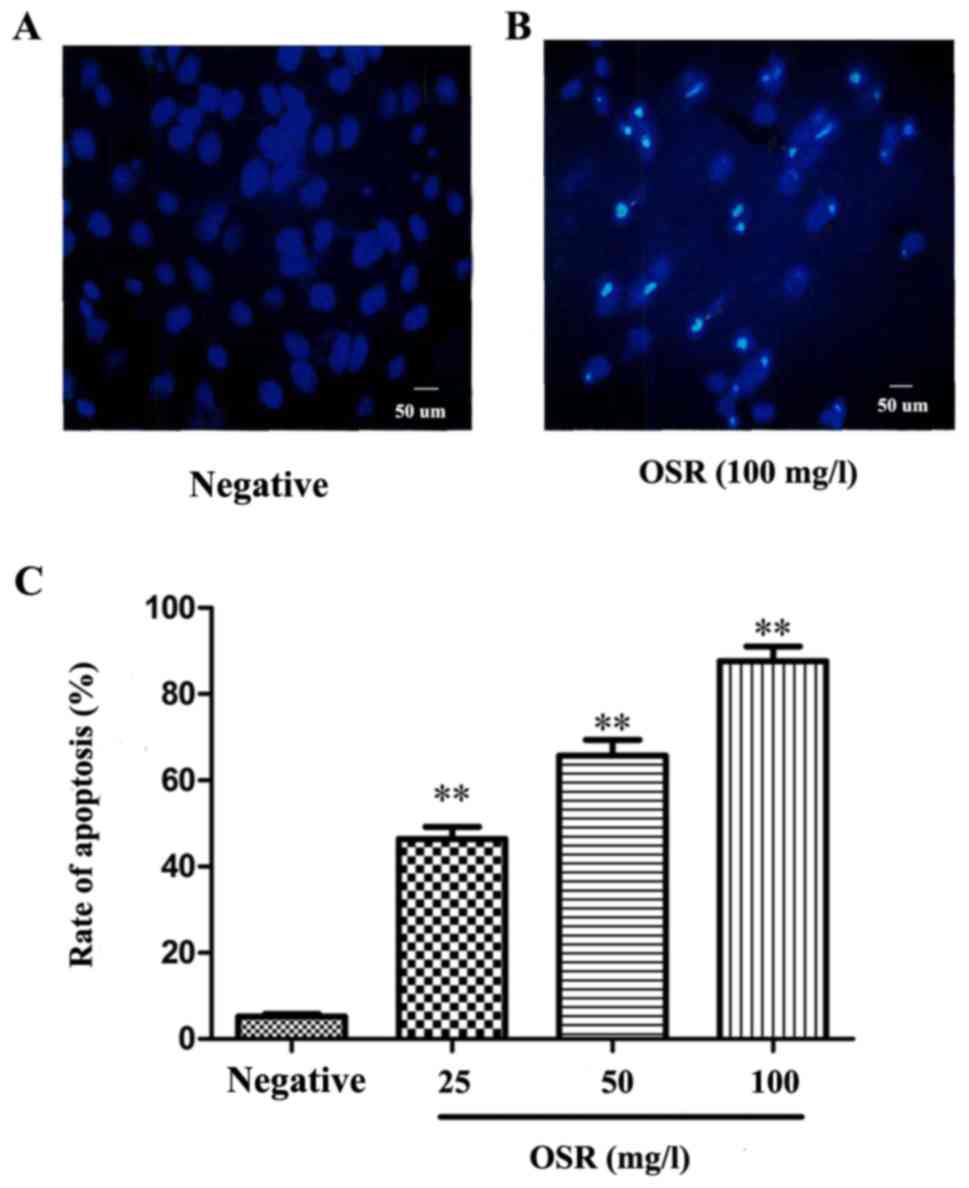
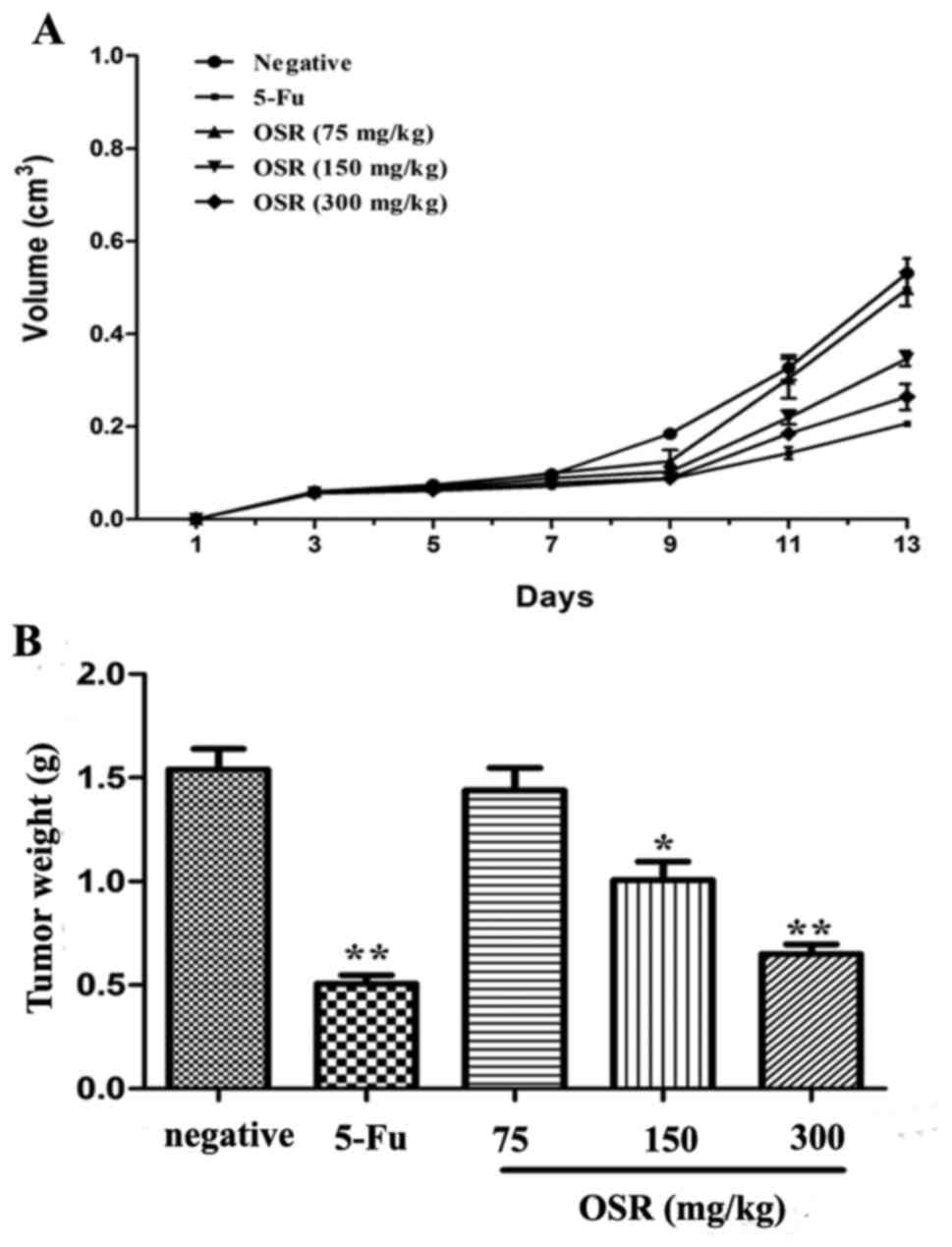
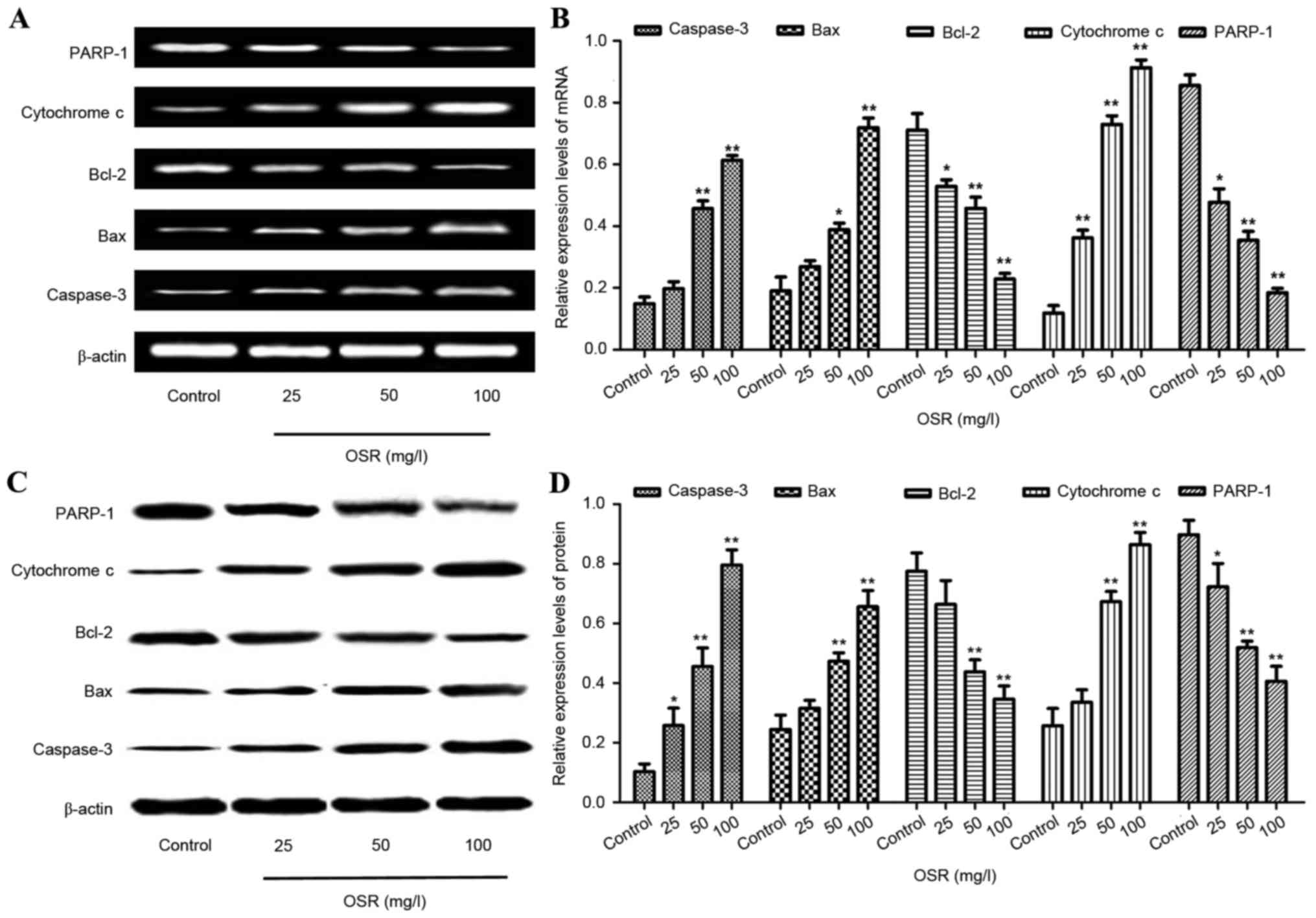
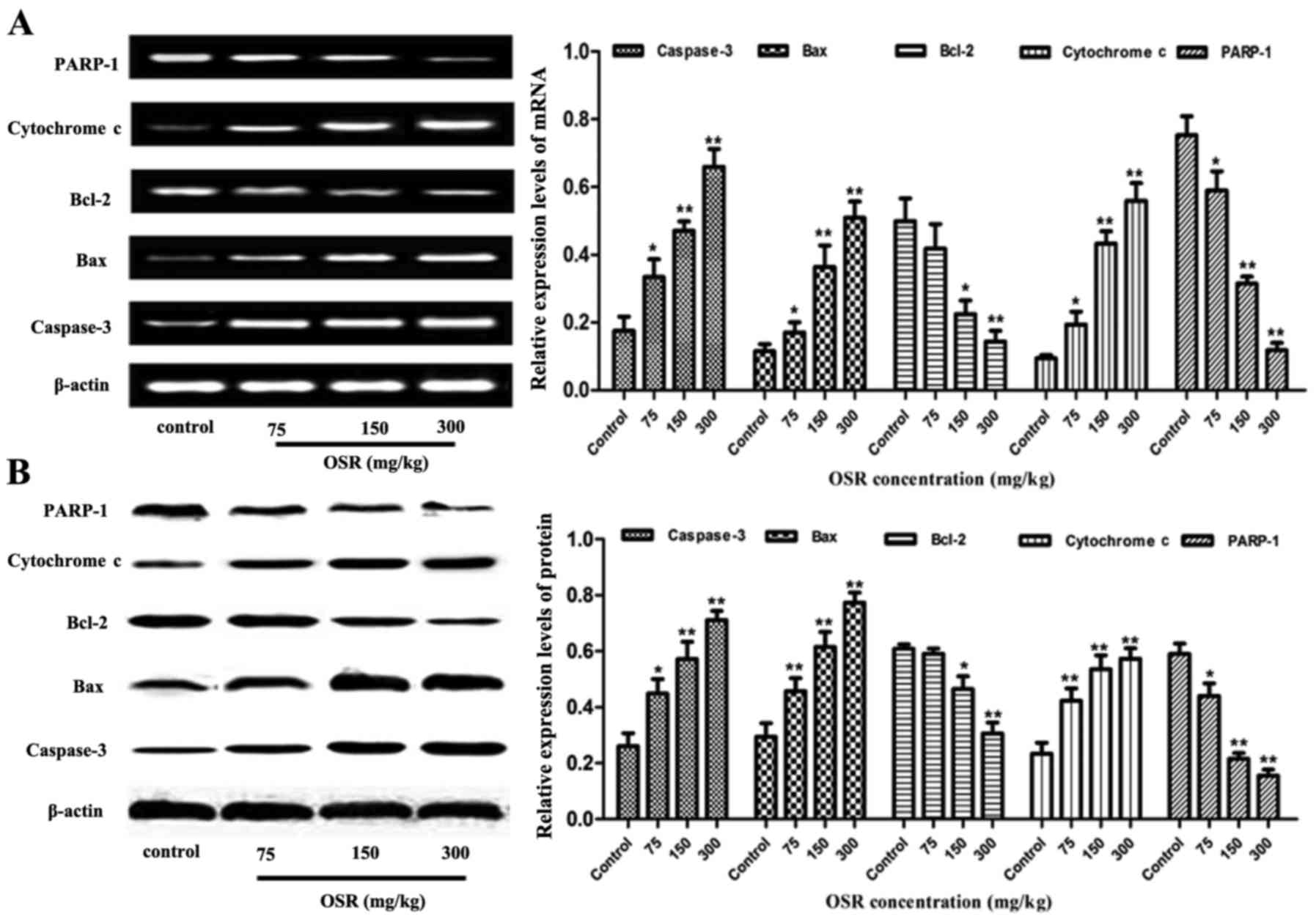
|
1
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser
S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D and Bray F: Cancer
incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major
patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 136:E359–E386. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Young GP, Senore C, Mandel JS, Allison JE,
Atkin WS, Benamouzig R, Bossuyt PM, Silva MD, Guittet L, Halloran
SP, et al: Recommendations for a step-wise comparative approach to
the evaluation of new screening tests for colorectal cancer.
Cancer. 122:826–839. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Aykan NF: Red meat and colorectal cancer.
Oncol Rev. 9:2882015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Martinez-Useros J and Garcia-Foncillas J:
Obesity and colorectal cancer: Molecular features of adipose
tissue. J Transl Med. 14:212016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cetinkaya E, Dogrul AB and Tirnaksiz MB:
Role of self-expandable stents in management of colorectal cancers.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. 8:113–120. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Palma S, Zwenger AO, Croce MV, Abba MC and
Lacunza E: From molecular biology to clinical trials: Toward
personalized colorectal cancer therapy. Clin Colorectal Cancer.
15:104–115. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Buckley H, Wilson C and Ajithkumar T:
High-dose-rate brachytherapy in the management of operable rectal
cancer: A systematic review. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys.
99:111–127. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hammond WA, Swaika A and Mody K:
Pharmacologic resistance in colorectal cancer: A review. Ther Adv
Med Oncol. 8:57–84. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chibaudel B, Tournigand C, Bonnetain F,
Richa H, Benetkiewicz M, André T and de Gramont A: Therapeutic
strategy in unresectable metastatic colorectal cancer: An updated
review. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 7:153–169. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lu X, Li Y, Li X and Aisa HA: Luteolin
induces apoptosis in vitro through suppressing the MAPK and PI3K
signaling pathways in gastric cancer. Oncol Lett. 14:1993–2000.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li B, Chen D, Li W and Xiao D:
20(S)-Protopanaxadiol saponins inhibit SKOV3 cell migration. Oncol
Lett. 11:1693–1698. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chang A, Cai Z, Wang Z and Sun S:
Extraction and isolation of alkaloids of Sophora alopecuroides and
their anti-tumor effects in H22 tumor-bearing mice. Afr J Tradit
Complement Altern Med. 11:245–248. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang CZ, Zhang Z, Anderson S and Yuan CS:
Natural products and chemotherapeutic agents on cancer: Prevention
vs. treatment. Am J Chin Med. 42:1555–1558. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Park GH, Park JH, Song HM, Eo HJ, Kim MK,
Lee JW, Lee MH, Cho KH, Lee JR, Cho HJ and Jeong JB: Anti-cancer
activity of Ginger (Zingiber officinale) leaf through the
expression of activating transcription factor 3 in human colorectal
cancer cells. BMC Complement Altern Med. 14:4082014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Meng C, Liu C, Liu Y and Wu F:
Oxysophoridine attenuates the injury caused by acute myocardial
infarction in rats through anti-oxidative, anti-inflammatory and
anti-apoptotic pathways. Mol Med Rep. 11:527–532. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang YS, Li YX, Zhao P, Wang HB, Zhou R,
Hao YJ, Wang J, Wang SJ, Du J, Ma L, et al: Anti-inflammation
effects of oxysophoridine on cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury
in mice. Inflammation. 38:2259–2268. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yang G, Gao J, Jia Y, Yan L, Yu J and
Jiang Y: Oxysophoridine through intrathecal injection induces
antinociception and increases the expression of the GABAAa1
receptor in the spinal cord of mice. Planta Med. 78:874–880. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yao XQ, Zhang YH, Long W and Liu PX:
Oxysophoridine suppresses the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma in
mice: In vivo and cDNA microarray studies. Chin J Integr Med.
18:209–213. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yu J, Li Y, Zhao C, Gong X, Liu J, Wang F
and Jiang Y: Effect of oxysophoridine on electric activities and
its power spectrum of reticular formation in rats. Zhongguo Zhong
Yao Za Zhi. 35:1170–1172. 2010.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang HM and Li HQ: Anti-arrhythmic
effects of sophoridine and oxysophoridine. Zhongguo Yao Li Xue Bao.
20:517–520. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang JT, Zhou WL, He C, Liu T, Li CY and
Wang L: 5-Fluorouracil induces apoptosis of colorectal cancer
cells. Genet Mol Res. 15:150173262016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Little EC, Kubic JD, Salgia R, Grippo PJ
and Lang D: Canonical and alternative transcript expression of PAX6
and CXCR4 in pancreatic cancer. Oncol Lett. 13:4027–4034.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Aakif M, Balfe P, Elfaedy O, Awan FN,
Pretorius F, Silvio L, Castinera C and Mustafa H: Study on
colorectal cancer presentation, treatment and follow-up. Int J
Colorectal Dis. 31:1361–1363. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bold RJ, Termuhlen PM and McConkey DJ:
Apoptosis, cancer and cancer therapy. Surg Oncol. 6:133–142. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Scatena R: Mitochondria and cancer: A
growing role in apoptosis, cancer cell metabolism and
dedifferentiation. Adv Exp Med Biol. 942:287–308. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Elkholi R, Renault TT, Serasinghe MN and
Chipuk JE: Putting the pieces together: How is the mitochondrial
pathway of apoptosis regulated in cancer and chemotherapy? Cancer
Metab. 2:162014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yang D, Okamura H, Teramachi J and Haneji
T: Histone demethylase Jmjd3 regulates osteoblast apoptosis through
targeting anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2 and pro-apoptotic protein
Bim. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1863:650–659. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Luna-Vargas MP and Chipuk JE: The deadly
landscape of pro-apoptotic BCL-2 proteins in the outer
mitochondrial membrane. FEBS J. 283:2676–2689. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Um HD: Bcl-2 family proteins as regulators
of cancer cell invasion and metastasis: A review focusing on
mitochondrial respiration and reactive oxygen species. Oncotarget.
7:5193–5203. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lalier L, Cartron PF, Juin P, Nedelkina S,
Manon S, Bechinger B and Vallette FM: Bax activation and
mitochondrial insertion during apoptosis. Apoptosis. 12:887–896.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Horwacik I and Rokita H: Targeting of
tumor-associated gangliosides with antibodies affects signaling
pathways and leads to cell death including apoptosis. Apoptosis.
20:679–688. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ishii Y, Nhiayi MK, Tse E, Cheng J,
Massimino M, Durden DL, Vigneri P and Wang JY: Knockout serum
replacement promotes cell survival by preventing BIM from inducing
mitochondrial cytochrome C release. PLoS One. 10:e01405852015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Węsierska-Gądek J, Mauritz M, Mitulovic G
and Cupo M: Differential potential of pharmacological PARP
inhibitors for inhibiting cell proliferation and inducing apoptosis
in human breast cancer cells. J Cell Biochem. 116:2824–2839. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Dias MM, Noratto G, Martino HS, et al:
Pro-apoptotic activities of polyphenolics from açai (Euterpe
oleracea Martius) in human SW-480 colon cancer cells. Nutr Cancer.
66:1394–1405. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zheng JH, Follis Viacava A, Kriwacki RW
and Moldoveanu T: Discoveries and controversies in BCL-2
protein-mediated apoptosis. FEBS J. 283:2690–2700. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Julien O and Wells JA: Caspases and their
substrates. Cell Death Differ. 24:1380–1389. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Yuan J, Najafov A and Py BF: Roles of
caspases in necrotic cell death. Cell. 167:1693–1704. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Fiandalo MV and Kyprianou N: Caspase
control: Protagonists of cancer cell apoptosis. Exp Oncol.
34:165–175. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Caroppi P, Sinibaldi F, Fiorucci L and
Santucci R: Apoptosis and human diseases: Mitochondrion damage and
lethal role of released cytochrome C as proapoptotic protein. Curr
Med Chem. 16:4058–4065. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhao Y, Jing Z, Lv J, Zhang Z, Lin J, Cao
X, Zhao Z, Liu P and Mao W: Berberine activates
caspase-9/cytochrome c-mediated apoptosis to suppress
triple-negative breast cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Biomed
Pharmacother. 95:18–24. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Koh DW, Dawson TM and Dawson VL: Mediation
of cell death by poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1. Pharmacol Res.
52:5–14. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yu SW, Wang H, Poitras MF, Coombs C,
Bowers WJ, Federoff HJ, Poirier GG, Dawson TM and Dawson VL:
Mediation of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1-dependent cell death by
apoptosis-inducing factor. Science. 297:259–263. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Schon EA and Manfredi G: Neuronal
degeneration and mitochondrial dysfunction. J Clin Invest.
111:303–312. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Voutsadakis IA: Apoptosis and the
pathogenesis of lymphoma. Acta Oncol. 39:151–156. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|