|
1
|
Esteller M: Cancer epigenetics for the
21st Century: What's next? Genes Cancer. 2:604–606. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Dahl C, Grønbæk K and Guldberg P: Advances
in DNA methylation: 5-hydroxymethylcytosine revisited. Clin Chim
Acta. 412:831–836. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sun M, Song CX, Huang H, Frankenberger CA,
Sankarasharma D, Gomes S, Chen P, Chen J, Chada KK, He C and Rosner
MR: HMGA2/TET1/HOXA9 signaling pathway regulates breast cancer
growth and metastasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 110:pp. 9920–9925.
2013; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
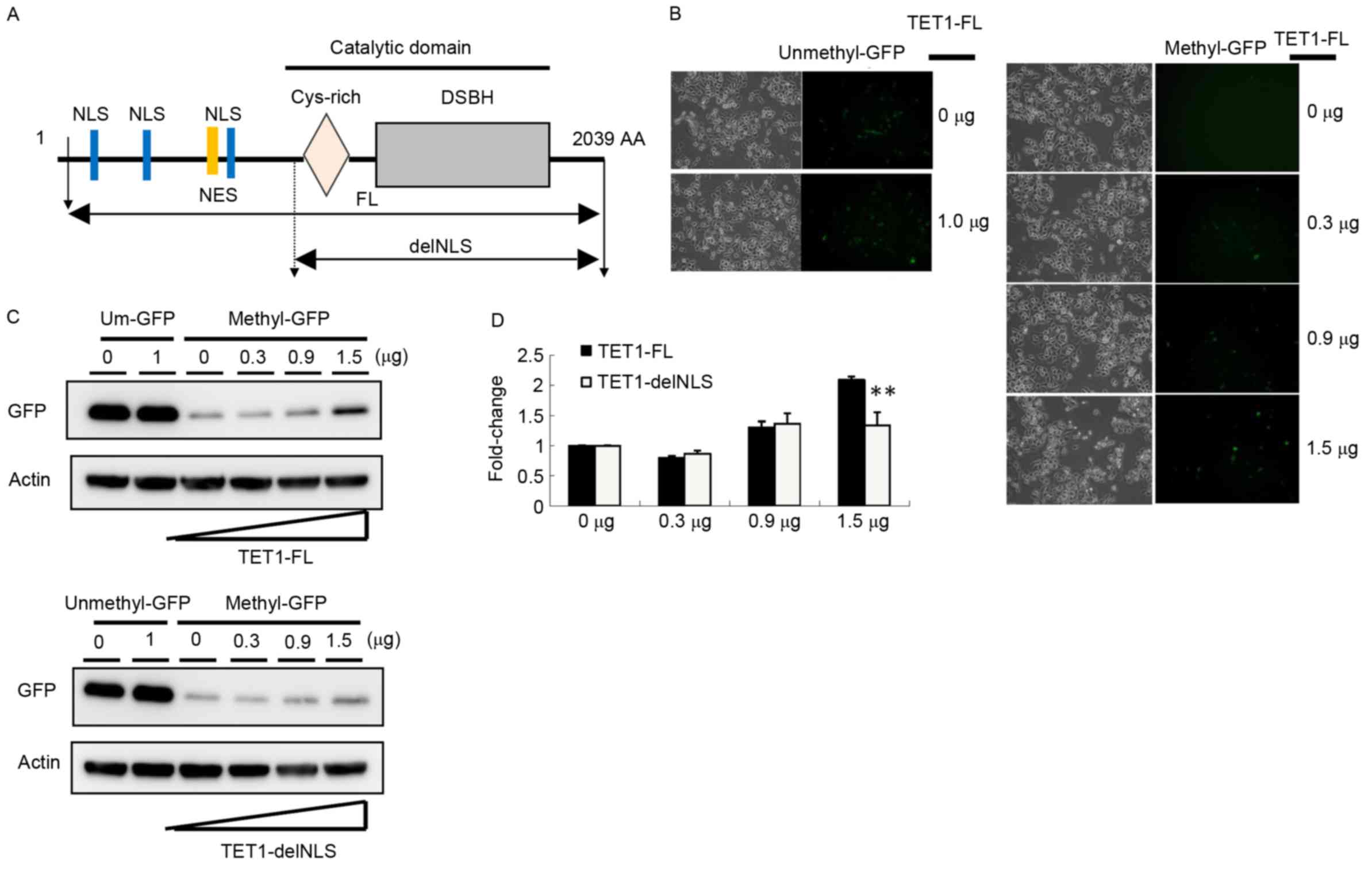
|
4
|
Lim B, Kim JH, Kim M and Kim SY: Genomic
and epigenomic heterogeneity in molecular subtypes of gastric
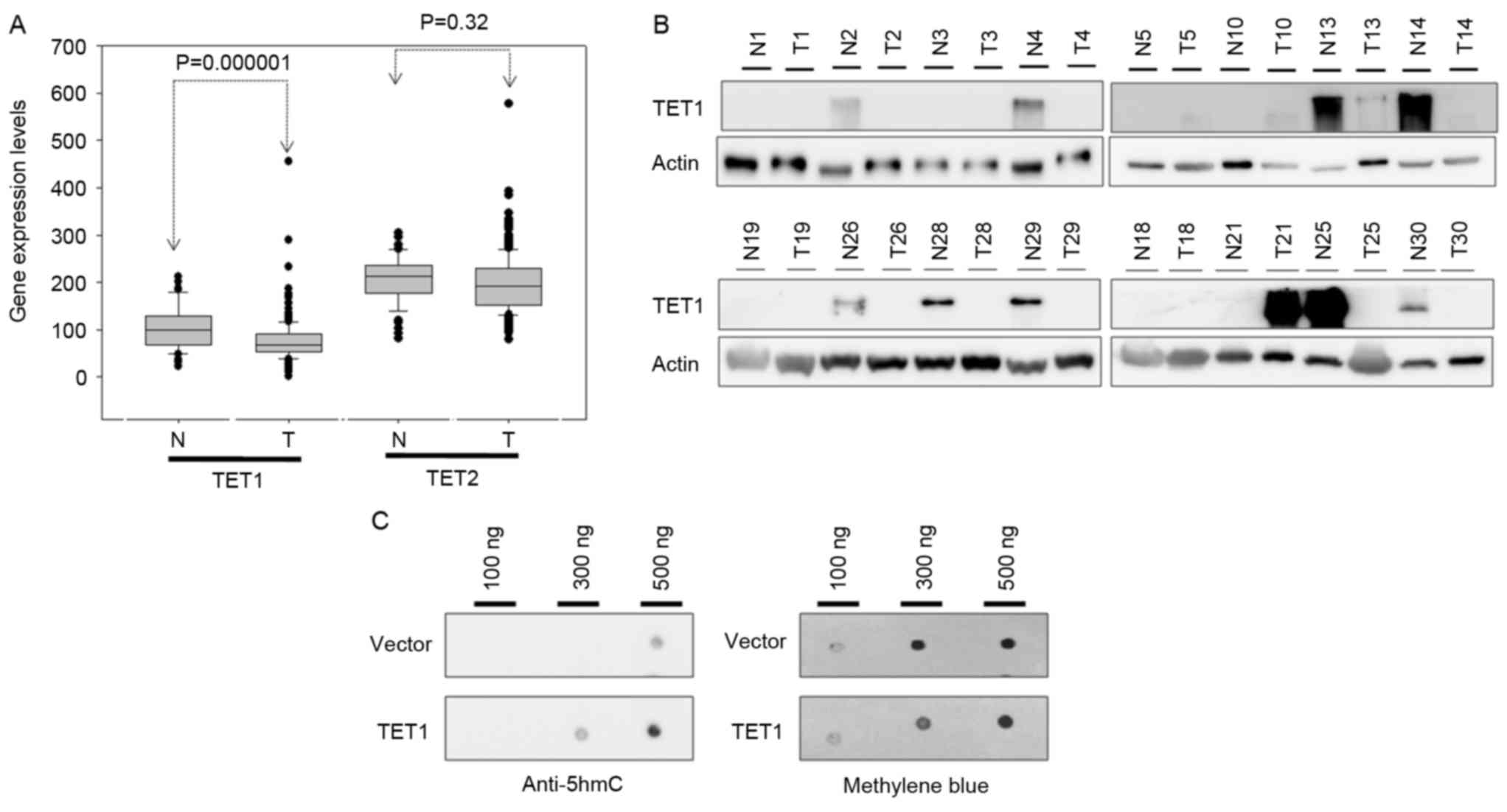
cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 22:1190–1201. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
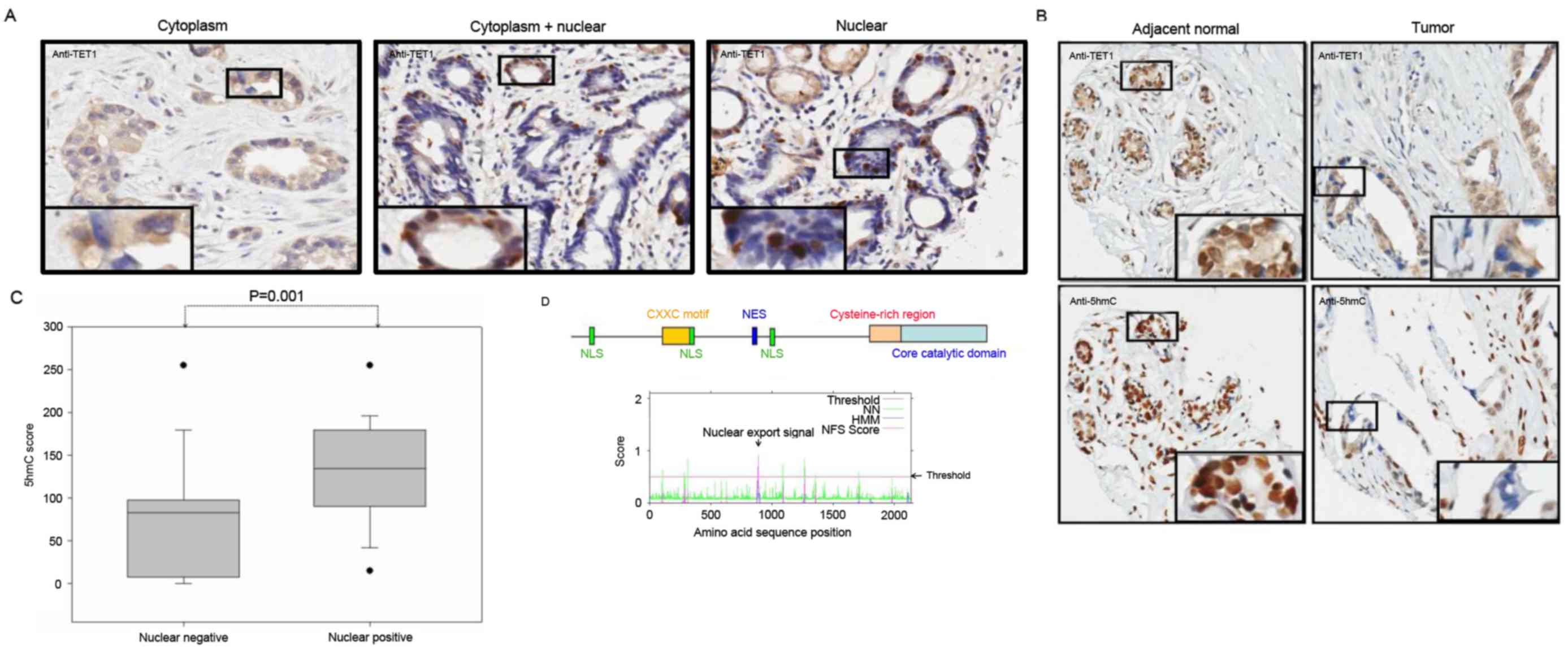
5
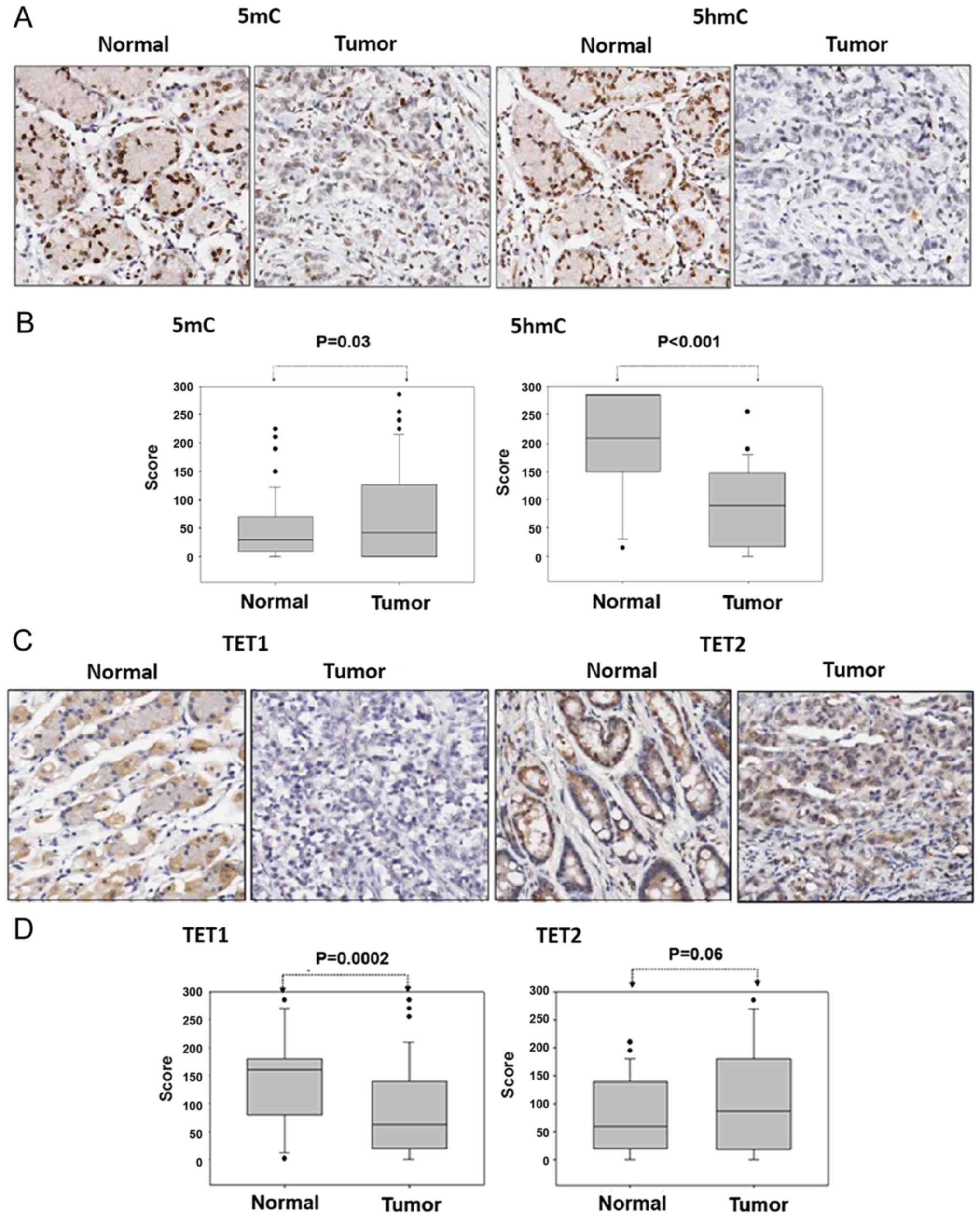
|
Yamamoto H and Imai K: Microsatellite
instability: An update. Arch Toxicol. 89:899–921. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kim KJ, Lee TH, Cho NY, Yang HK, Kim WH
and Kang GH: Differential clinicopathologic features in
microsatellite-unstable gastric cancers with and without MLH1
methylation. Hum Pathol. 44:1055–1064. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ling ZQ, Tanaka A, Li P, Nakayama T,
Fujiyama Y, Hattori T and Sugihara H: Microsatellite instability
with promoter methylation and silencing of hMLH1 can regionally
occur during progression of gastric carcinoma. Cancer Lett.
297:244–251. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tsai KW, Hu LY, Wu CW, Li SC, Lai CH, Kao
HW, Fang WL and Lin WC: Epigenetic regulation of miR-196b
expression in gastric cancer. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 49:969–980.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tsai KW, Liao YL, Wu CW, Hu LY, Li SC,
Chan WC, Ho MR, Lai CH, Kao HW, Fang WL, et al: Aberrant
hypermethylation of miR-9 genes in gastric cancer. Epigenetics.
6:1189–1197. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tsai KW, Wu CW, Hu LY, Li SC, Liao YL, Lai
CH, Kao HW, Fang WL, Huang KH, Chan WC and Lin WC: Epigenetic
regulation of miR-34b and miR-129 expression in gastric cancer. Int
J Cancer. 129:2600–2610. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Qu Y, Dang S and Hou P: Gene methylation
in gastric cancer. Clin Chim Acta. 424:53–65. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ehrlich M, Gama-Sosa MA, Huang LH, Midgett
RM, Kuo KC, McCune RA and Gehrke C: Amount and distribution of
5-methylcytosine in human DNA from different types of tissues of
cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 10:2709–2721. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jin SG, Wu X, Li AX and Pfeifer GP:
Genomic mapping of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in the human brain.
Nucleic Acids Res. 39:5015–5024. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Koh KP, Yabuuchi A, Rao S, Huang Y,
Cunniff K, Nardone J, Laiho A, Tahiliani M, Sommer CA, Mostoslavsky
G, et al: Tet1 and Tet2 regulate 5-hydroxymethylcytosine production
and cell lineage specification in mouse embryonic stem cells. Cell
Stem Cell. 8:200–213. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Pastor WA, Pape UJ, Huang Y, Henderson HR,
Lister R, Ko M, McLoughlin EM, Brudno Y, Mahapatra S, Kapranov P,
et al: Genome-wide mapping of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in embryonic
stem cells. Nature. 473:394–397. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cimmino L, Abdel-Wahab O, Levine RL and
Aifantis I: TET family proteins and their role in stem cell
differentiation and transformation. Cell Stem Cell. 9:193–204.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ficz G, Branco MR, Seisenberger S, Santos
F, Krueger F, Hore TA, Marques CJ, Andrews S and Reik W: Dynamic
regulation of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in mouse ES cells and during
differentiation. Nature. 473:398–402. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gu TP, Guo F, Yang H, Wu HP, Xu GF, Liu W,
Xie ZG, Shi L, He X, Jin SG, et al: The role of Tet3 DNA
dioxygenase in epigenetic reprogramming by oocytes. Nature.
477:606–610. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Guo JU, Su Y, Zhong C, Ming GL and Song H:
Emerging roles of TET proteins and 5-hydroxymethylcytosines in
active DNA demethylation and beyond. Cell Cycle. 10:2662–2668.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
He YF, Li BZ, Li Z, Liu P, Wang Y, Tang Q,
Ding J, Jia Y, Chen Z, Li L, et al: Tet-mediated formation of
5-carboxylcytosine and its excision by TDG in mammalian DNA.
Science. 333:1303–1307. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ito S, D'Alessio AC, Taranova OV, Hong K,
Sowers LC and Zhang Y: Role of Tet proteins in 5mC to 5hmC
conversion, ES-cell self-renewal and inner cell mass specification.
Nature. 466:1129–1133. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ito S, Shen L, Dai Q, Wu SC, Collins LB,
Swenberg JA, He C and Zhang Y: Tet proteins can convert
5-methylcytosine to 5-formylcytosine and 5-carboxylcytosine.
Science. 333:1300–1303. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hsu CH, Peng KL, Kang ML, Chen YR, Yang
YC, Tsai CH, Chu CS, Jeng YM, Chen YT, Lin FM, et al: TET1
suppresses cancer invasion by activating the tissue inhibitors of
metalloproteinases. Cell Rep. 2:568–579. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Williams K, Christensen J, Pedersen MT,
Johansen JV, Cloos PA, Rappsilber J and Helin K: TET1 and
hydroxymethylcytosine in transcription and DNA methylation
fidelity. Nature. 473:343–348. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tsai KW, Li GC, Chen CH, Yeh MH, Huang JS,
Tseng HH, Fu TY, Liou HH, Pan HW, Huang SF, et al: Reduction of
global 5-hydroxymethylcytosine is a poor prognostic factor in
breast cancer patients, especially for an ER/PR-negative subtype.
Breast Cancer Res Treat. 153:219–234. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kinney SR and Pradhan S: Ten eleven
translocation enzymes and 5-hydroxymethylation in mammalian
development and cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol. 754:57–79. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Pérez C, Martínez-Calle N, Martín-Subero
JI, Segura V, Delabesse E, Fernandez-Mercado M, Garate L, Alvarez
S, Rifon J, Varea S, et al: TET2 mutations are associated with
specific 5-methylcytosine and 5-hydroxymethylcytosine profiles in
patients with chronic myelomonocytic leukemia. PLoS One.
7:e316052012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yang H, Liu Y, Bai F, Zhang JY, Ma SH, Liu
J, Xu ZD, Zhu HG, Ling ZQ, Ye D, et al: Tumor development is
associated with decrease of TET gene expression and
5-methylcytosine hydroxylation. Oncogene. 32:663–669. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Shin G, Kang TW, Yang S, Baek SJ, Jeong YS
and Kim SY: GENT: Gene expression database of normal and tumor
tissues. Cancer Inform. 10:149–157. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Duhamel RC, Meezan E and Brendel K: The
addition of SDS to the Bradford dye-binding protein assay, a
modification with increased sensitivity to collagen. J Biochem
Biophys Methods. 5:67–74. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
la Cour T, Kiemer L, Mølgaard A, Gupta R,
Skriver K and Brunak S: Analysis and prediction of leucine-rich
nuclear export signals. Protein Eng Des Sel. 17:527–536. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Park JL, Kim HJ, Seo EH, Kwon OH, Lim B,
Kim M, Kim SY, Song KS, Kang GH, Kim HJ, et al: Decrease of 5hmC in
gastric cancers is associated with TET1 silencing due to with DNA
methylation and bivalent histone marks at TET1 CpG island 3′-shore.
Oncotarget. 6:37647–37662. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yang Q, Wu K, Ji M, Jin W, He N, Shi B and
Hou P: Decreased 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5-hmC) is an independent
poor prognostic factor in gastric cancer patients. J Biomed
Nanotechnol. 9:1607–1616. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kudo Y, Tateishi K, Yamamoto K, Yamamoto
S, Asaoka Y, Ijichi H, Nagae G, Yoshida H, Aburatani H and Koike K:
Loss of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine is accompanied with malignant
cellular transformation. Cancer Sci. 103:670–676. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Frycz BA, Murawa D, Borejsza-Wysocki M,
Marciniak R, Murawa P, Drews M, Kołodziejczak A, Tomela K and
Jagodziński PP: Decreased expression of ten-eleven translocation 1
protein is associated with some clinicopathological features in
gastric cancer. Biomed Pharmacother. 68:209–212. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Müller T, Gessi M, Waha A, Isselstein LJ,
Luxen D, Freihoff D, Freihoff J, Becker A, Simon M, Hammes J, et
al: Nuclear exclusion of TET1 is associated with loss of
5-hydroxymethylcytosine in IDH1 wild-type gliomas. Am J Pathol.
181:675–683. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|