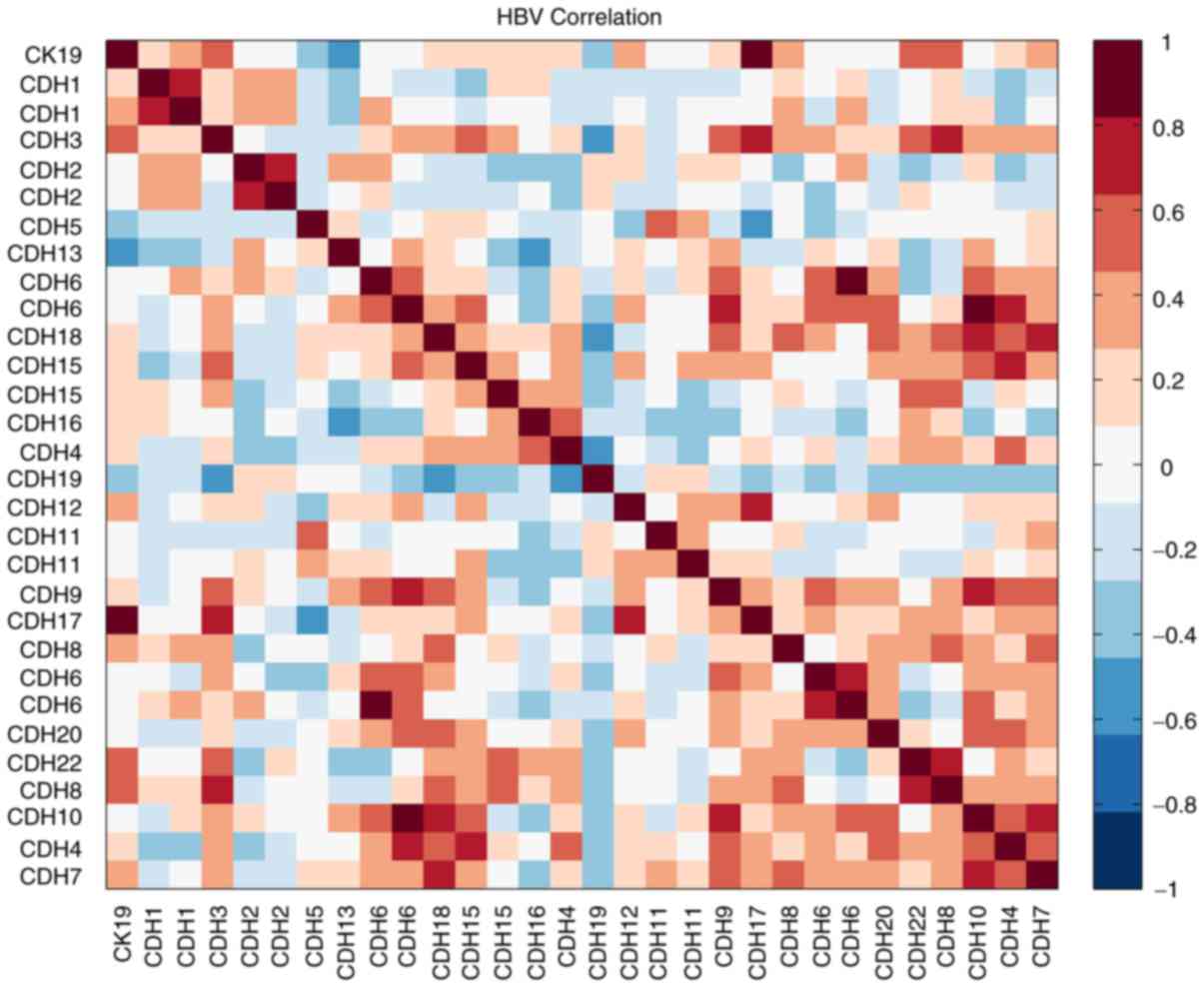
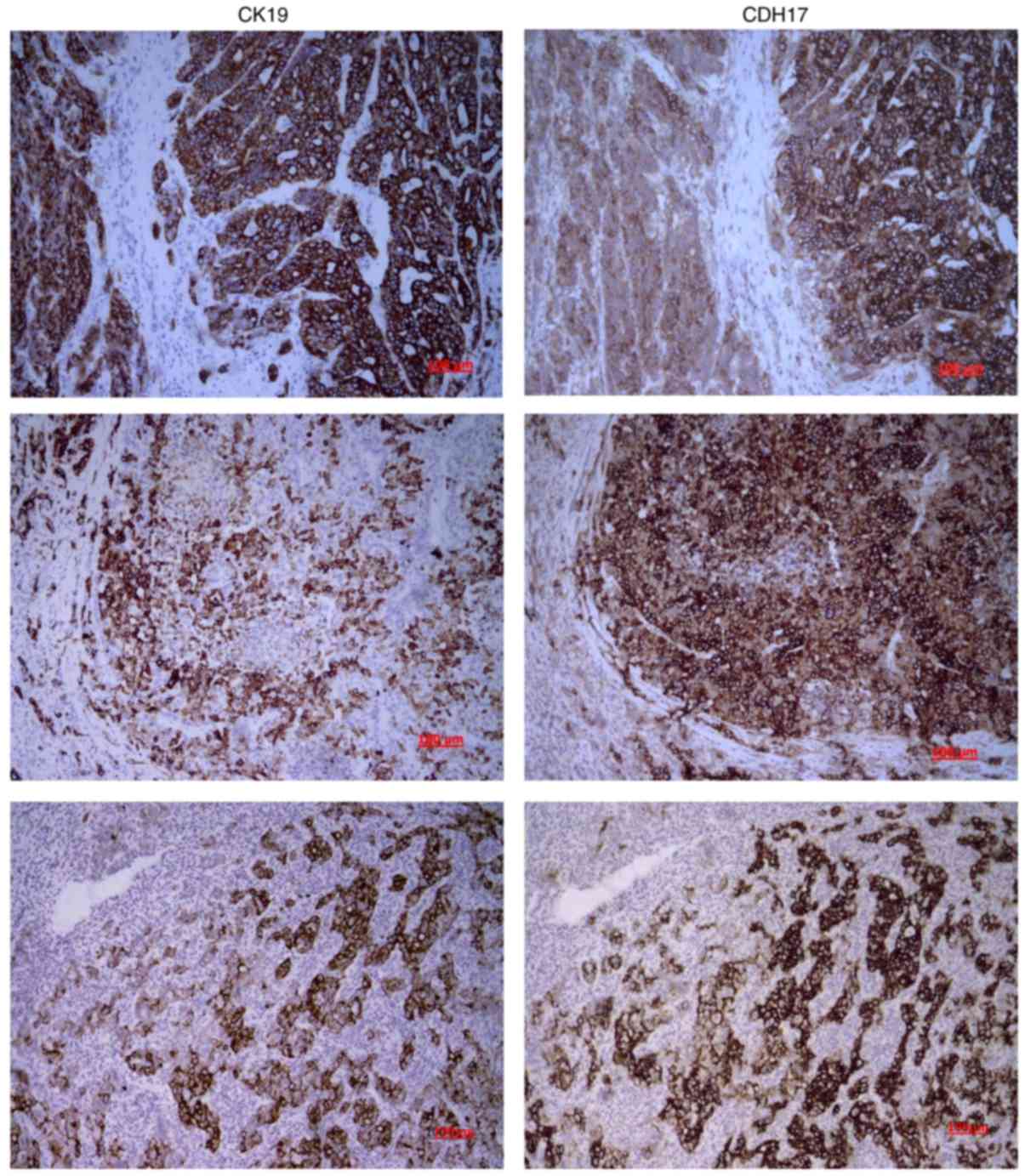
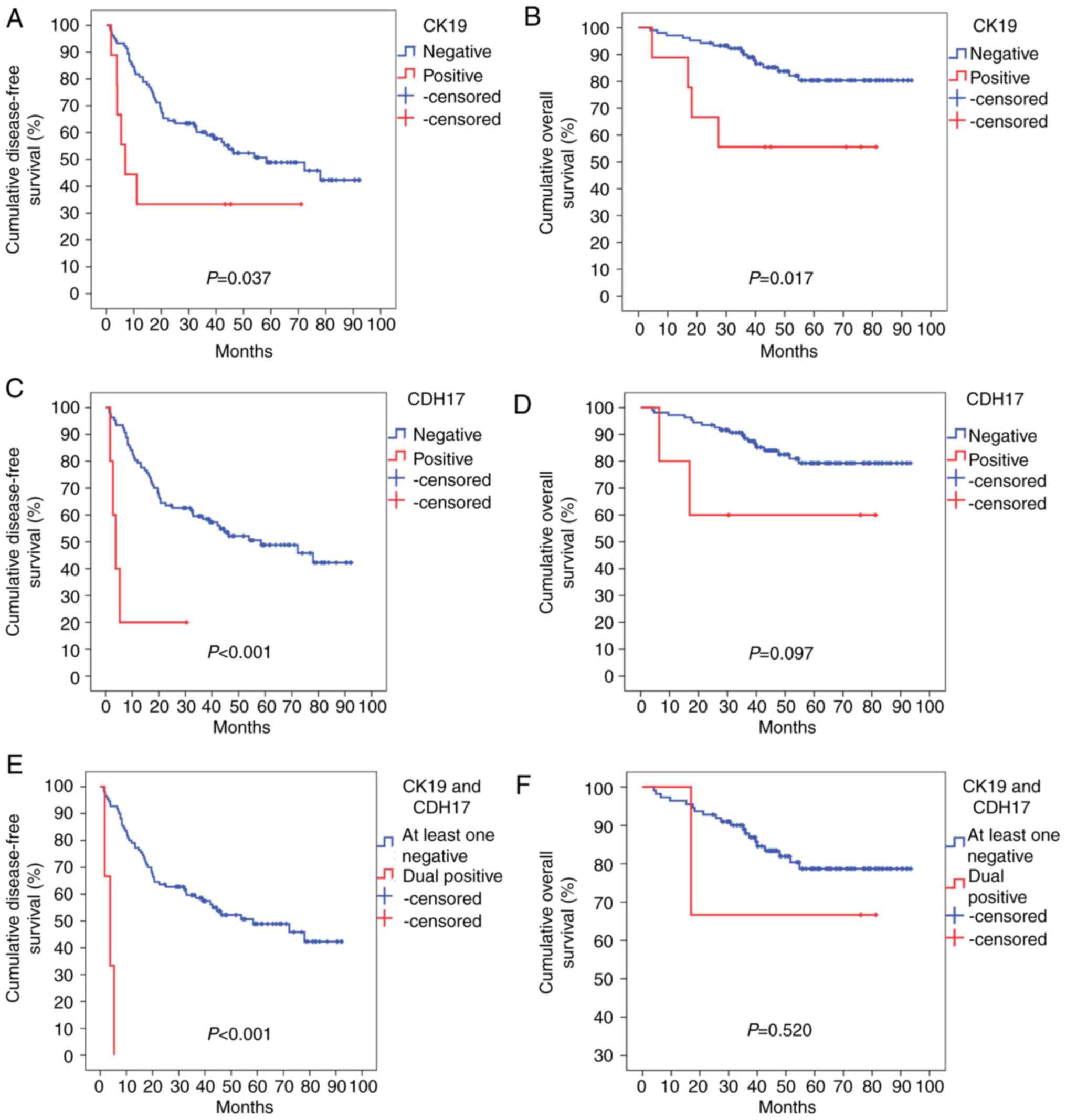
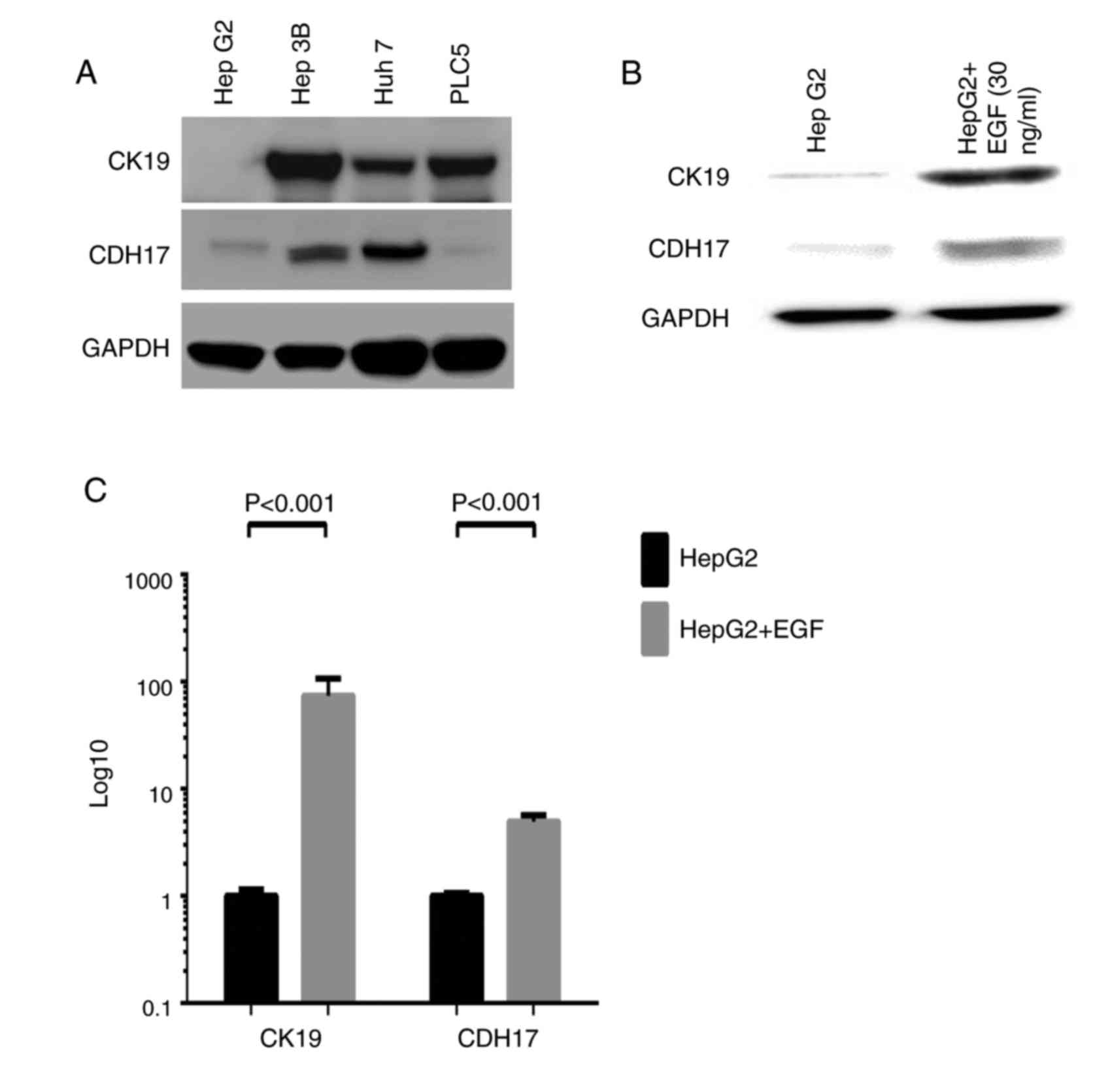
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sartorius K, Sartorius B, Aldous C,
Govender PS and Madiba TE: Global and country underestimation of
hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in 2012 and its implications. Cancer
Epidemiol. 39:284–290. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ministry of Health and Welfare. Executive
Yuan, R.O.C: Report of leading cancer-related death in 2014.
2015.
|
|
4
|
Lee CW, Kuo WL, Yu MC, Chen TC, Tsai CN,
Lee WC and Chen MF: The expression of cytokeratin 19 in lymph nodes
was a poor prognostic factor for hepatocellular carcinoma after
hepatic resection. World J Surg Oncol. 11:1362013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Corcelle V, Stieger B, Gjinovci A,
Wollheim CB and Gauthier BR: Characterization of two distinct liver
progenitor cell subpopulations of hematopoietic and hepatic
origins. Exp Cell Res. 312:2826–2836. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yamamoto T, Uenishi T, Ogawa M, Ichikawa
T, Hai S, Sakabe K, Tanaka S, Kato H, Mikami S, Ikebe T, et al:
Immunohistologic attempt to find carcinogenesis from hepatic
progenitor cell in hepatocellular carcinoma. Dig Surg. 22:364–370.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yoneda N, Sato Y, Kitao A, Ikeda H,
Sawada-Kitamura S, Miyakoshi M, Harada K, Sasaki M, Matsui O and
Nakanuma Y: Epidermal growth factor induces cytokeratin 19
expression accompanied by increased growth abilities in human
hepatocellular carcinoma. Lab Invest. 91:262–272. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hoshida Y, Toffanin S, Lachenmayer A,
Villanueva A, Minguez B and Llovet JM: Molecular classification and
novel targets in hepatocellular carcinoma: Recent advancements.
Semin Liver Dis. 30:35–51. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Uenishi T, Hirohashi K, Shuto T, Kubo S,
Tanaka H, Sakata C, Ikebe T and Kinoshita H: The clinical
significance of lymph node metastases in patients undergoing
surgery for hepatocellular carcinoma. Surg Today. 30:892–895. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chu KM, Lai EC, Al-Hadeedi S, Arcilla CE
Jr, Lo CM, Liu CL, Fan ST and Wong J: Intrahepatic
cholangiocarcinoma. World J Surg. 21:301–305; discussion 305–306.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lee CW, Chan KM, Lee CF, Yu MC, Lee WC, Wu
TJ and Chen MF: Hepatic resection for hepatocellular carcinoma with
lymph node metastasis: Clinicopathological analysis and survival
outcome. Asian J Surg. 34:53–62. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ding ZB, Shi YH, Zhou J, Shi GM, Ke AW,
Qiu SJ, Wang XY, Dai Z, Xu Y and Fan J: Liver-intestine cadherin
predicts microvascular invasion and poor prognosis of hepatitis B
virus-positive hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer. 115:4753–4765.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lee NP, Poon RT, Shek FH, Ng IO and Luk
JM: Role of cadherin-17 in oncogenesis and potential therapeutic
implications in hepatocellular carcinoma. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1806:138–145. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
International Union Against Cancer (UICC),
. TNM Classification of Malignant Tumours. Sobin LH, Gospodarowicz
MK and Wittekind C: 7th. Wiley-Blackwell; Hoboken, NJ: 2009
|
|
15
|
Yu MC, Lee YS, Lin SE, Wu HY, Chen TC, Lee
WC, Chen MF and Tsai CN: Recurrence and poor prognosis following
resection of small hepatitis B-related hepatocellular carcinoma
lesions are associated with aberrant tumor expression profiles of
glypican 3 and osteopontin. Ann Surg Oncol. 3 Suppl 19:S455–S463.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Libbrecht L, Desmet V, Van Damme B and
Roskams T: The immunohistochemical phenotype of dysplastic foci in
human liver: Correlation with putative progenitor cells. J Hepatol.
33:76–84. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Takano M, Shimada K, Fujii T, Morita K,
Takeda M, Nakajima Y, Nonomura A, Konishi N and Obayashi C: Keratin
19 as a key molecule in progression of human hepatocellular
carcinomas through invasion and angiogenesis. BMC Cancer.
16:9032016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Qiu HB, Zhang LY, Ren C, Zeng ZL, Wu WJ,
Luo HY, Zhou ZW and Xu RH: Targeting CDH17 suppresses tumor
progression in gastric cancer by downregulating Wnt/β-catenin
signaling. PLoS One. 8:e569592013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liu LX, Lee NP, Chan VW, Xue W, Zender L,
Zhang C, Mao M, Dai H, Wang XL, Xu MZ, et al: Targeting cadherin-17
inactivates Wnt signaling and inhibits tumor growth in liver
carcinoma. Hepatology. 50:1453–1463. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang Y, Shek FH, Wong KF, Liu LX, Zhang
XQ, Yuan Y, Khin E, Hu MY, Wang JH, Poon RT, et al:
Anti-cadherin-17 antibody modulates beta-catenin signaling and
tumorigenicity of hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS One. 8:e723862013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yamamoto Y, Ikoma H, Morimura R, Konishi
H, Murayama Y, Komatsu S, Shiozaki A, Kuriu Y, Kubota T, Nakanishi
M, et al: Optimal duration of the early and late recurrence of
hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatectomy. World J Gastroenterol.
21:1207–1215. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Seshacharyulu P, Ponnusamy MP, Haridas D,
Jain M, Ganti AK and Batra SK: Targeting the EGFR signaling pathway
in cancer therapy. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 16:15–31. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Blobel CP: ADAMs: Key components in EGFR
signalling and development. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 6:32–43. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|