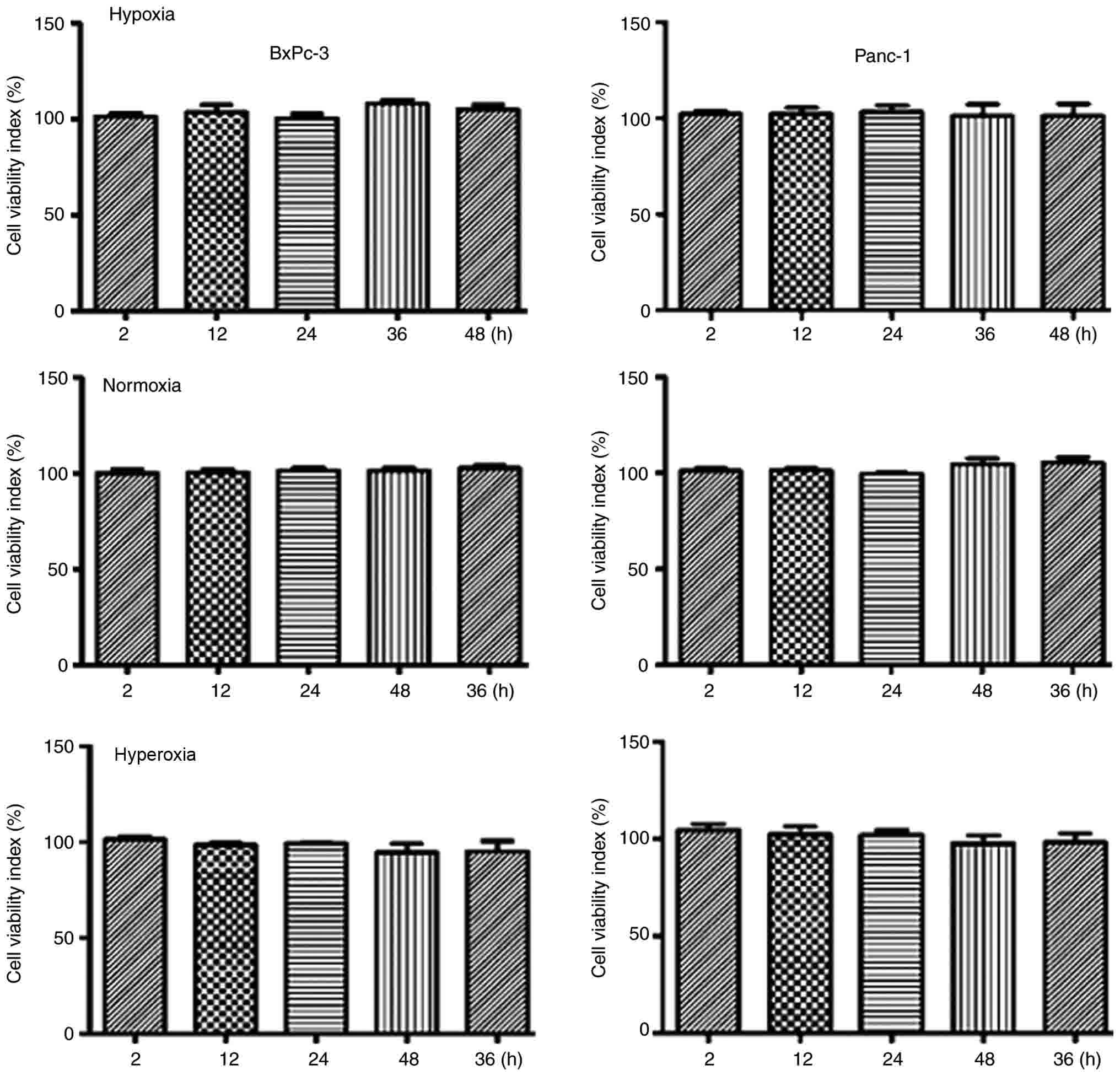
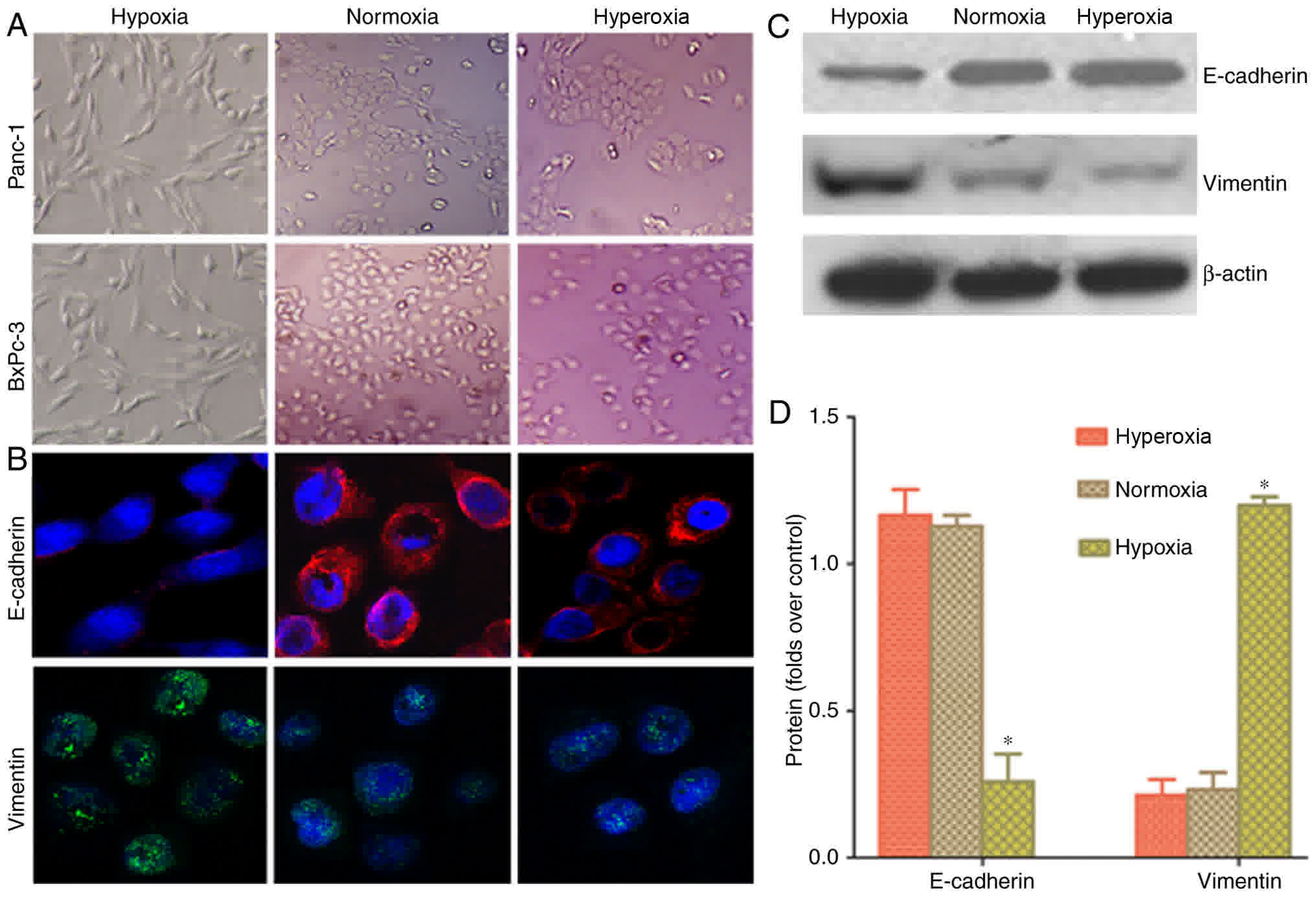
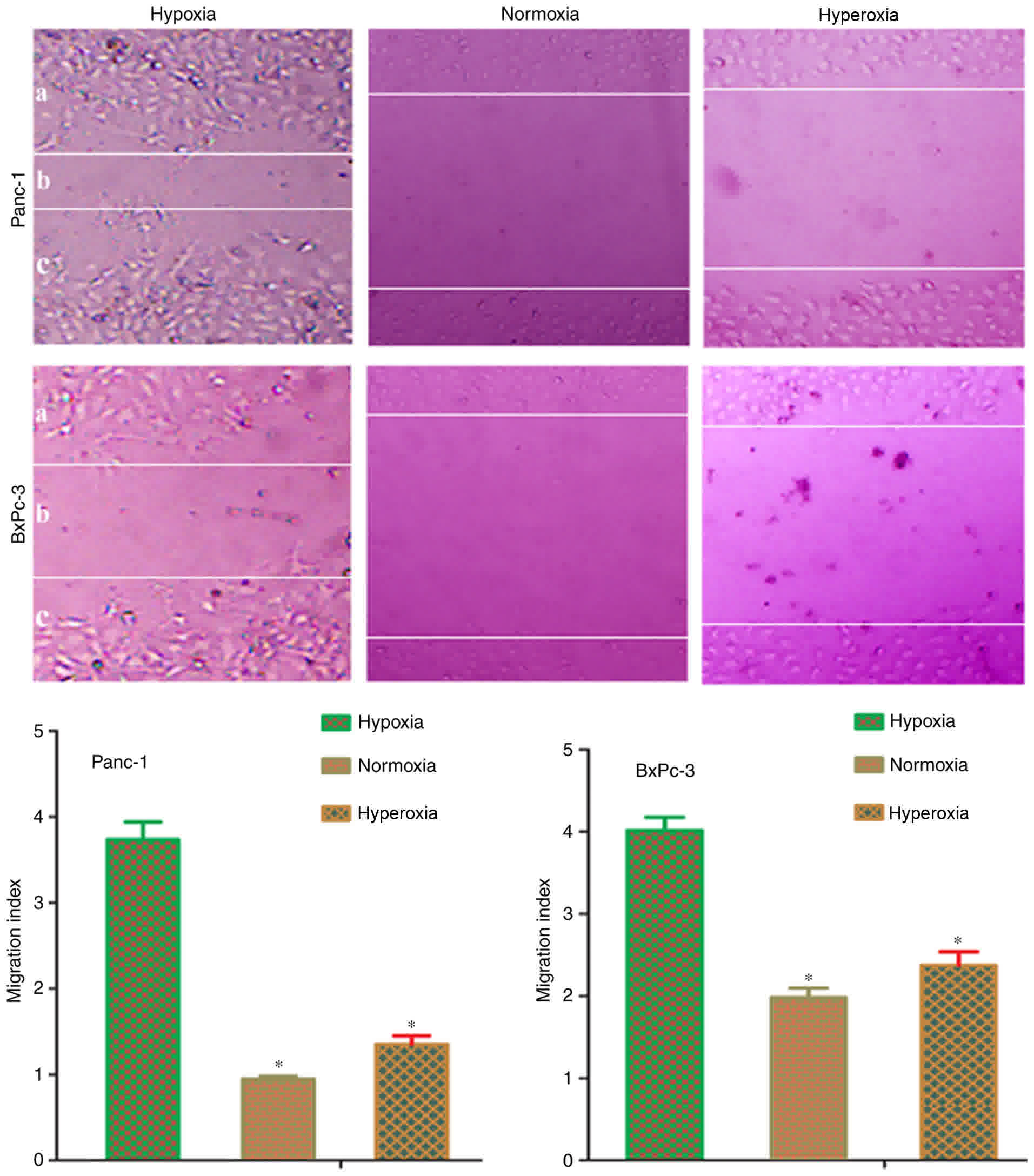
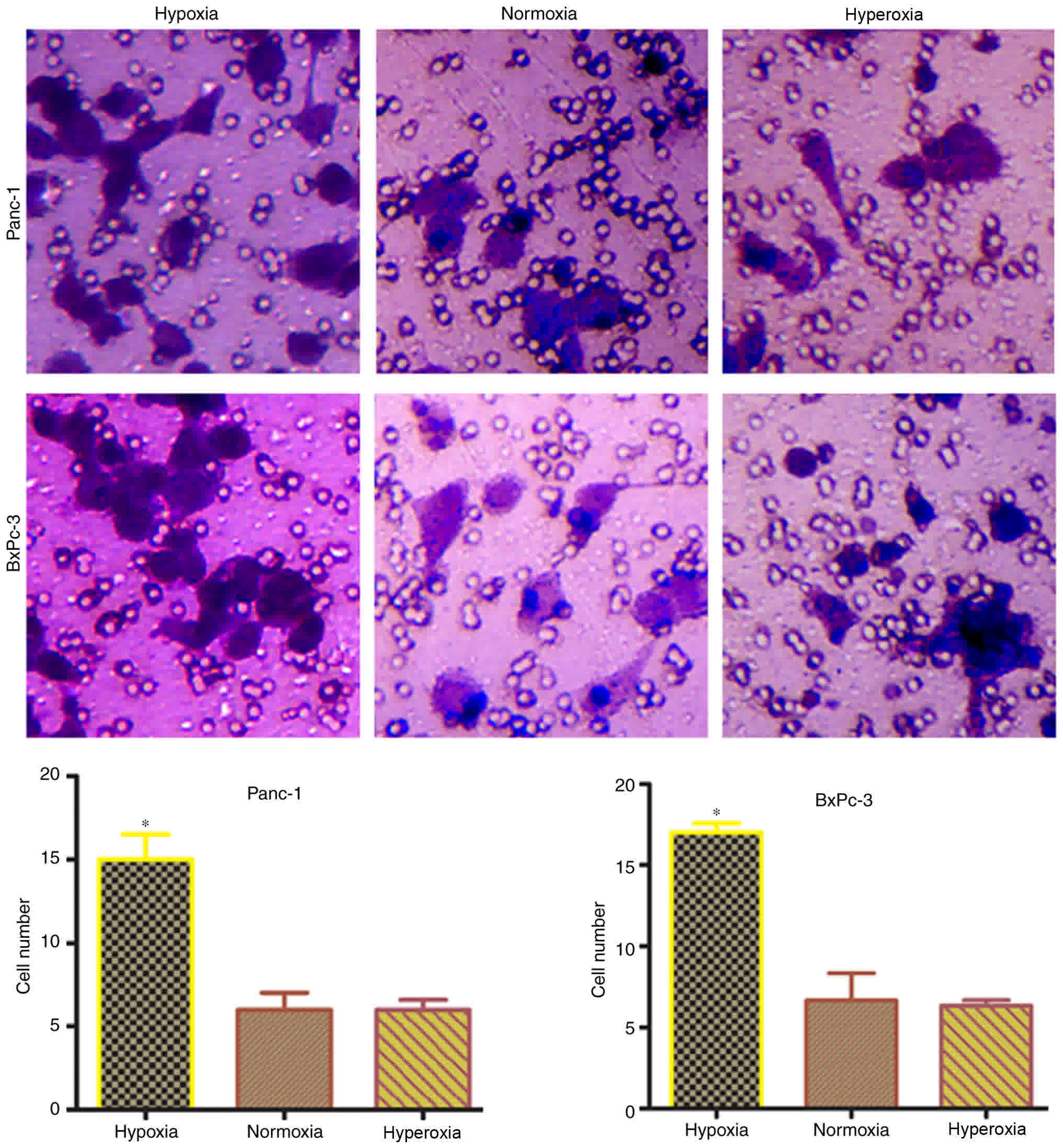
|
1
|
Shi H, Li J and Fu D: Process of hepatic
metastasis from pancreatic cancer: Biology with clinical
significance. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 142:1137–1161. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Tsai JH and Yang J: Epithelial-mesenchymal
plasticity in carcinoma metastasis. Genes Dev. 27:2192–2206. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY and Nieto
MA: Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease.
Cell. 139:871–890. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Welford SM and Giaccia AJ: Hypoxia and
senescence: The impact of oxygenation on tumor suppression. Mol
Cancer Res. 9:538–544. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ikeda Y, Hisano H, Nishikawa Y and
Nagasaki Y: Targeting and treatment of tumor hypoxia by newly
designed prodrug possessing high permeability in solid tumors. Mol
Pharm. 13:2283–2289. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yang SW, Zhang ZG, Hao YX, Zhao YL, Qian
F, Shi Y, Li PA, Liu CY and Yu PW: HIF-1α induces the
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in gastric cancer stem cells
through the Snail pathway. Oncotarget. 8:9535–9545. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sletta Yttersian K, Tveitarås MK, Lu N,
Engelsen AST, Reed RK, Garmann-Johnsen A and Stuhr L:
Oxygen-dependent regulation of tumor growth and metastasis in human
breast cancer xenografts. PloS One. 12:e01832542017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Stuhr LE, Raa A, Oyan AM, Kalland KH,
Sakariassen PO, Petersen K, Bjerkvig R and Reed RK: Hyperoxia
retards growth and induces apoptosis, changes in vascular density
and gene expression in transplanted gliomas in nude rats. J
Neurooncol. 85:191–202. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Moen I, Øyan AM, Kalland KH, Tronstad KJ,
Akslen LA, Chekenya M, Sakariassen PØ, Reed RK and Stuhr LE:
Hyperoxic treatment induces mesenchymal-to-epithelial transition in
a rat adenocarcinoma model. PloS One. 4:e63812009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chang Q, Jurisica I, Do T and Hedley DW:
Hypoxia predicts aggressive growth and spontaneous metastasis
formation from orthotopically grown primary xenografts of human
pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res. 71:3110–3120. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Maeda K, Ding Q, Yoshimitsu M, Kuwahata T,
Miyazaki Y, Tsukasa K, Hayashi T, Shinchi H, Natsugoe S and Takao
S: CD133 modulate HIF-1α expression under hypoxia in EMT phenotype
pancreatic cancer stem-like cells. Int J Mol Sci. 17:E10252016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chen S, Chen JZ, Zhang JQ, Chen HX, Yan
ML, Huang L, Tian YF, Chen YL and Wang YD: Hypoxia induces
TWIST-activated epithelial-mesenchymal transition and proliferation
of pancreatic cancer cells in vitro and in nude mice. Cancer Lett.
383:73–84. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lei J, Ma J, Ma Q, Li X, Liu H, Xu Q, Duan
W, Sun Q, Xu J, Wu Z and Wu E: Hedgehog signaling regulates hypoxia
induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition and invasion in
pancreatic cancer cells via a ligand-independent manner. Mol
Cancer. 12:662013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
De Bock K, Mazzone M and Carmeliet P:
Antiangiogenic therapy, hypoxia, and metastasis: Risky liaisons, or
not? Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 8:393–404. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Batlle E, Sancho E, Francí C, Domínguez D,
Monfar M, Baulida J and De Herreros García A: The transcription
factor snail is a repressor of E-cadherin gene expression in
epithelial tumour cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2:84–89. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Barriga EH, Maxwell PH, Reyes AE and Mayor
R: The hypoxia factor Hif-1alpha controls neural crest chemotaxis
and epithelial to mesenchymal transition. J Cell Biol. 201:759–776.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang W, Shi X, Peng Y, Wu M, Zhang P, Xie
R, Wu Y, Yan Q, Liu S and Wang J: HIF-1α promotes
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis through direct
regulation of ZEB1 in colorectal cancer. PloS One. 10:e01296032015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chen T, You Y, Jiang H and Wang ZZ:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT): A biological process in
the development, stem cell differentiation and tumorigenesis. J
Cell Physiol. 232:3261–3272. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chaffer CL, Juan San BP, Lim E and
Weinberg RA: EMT, cell plasticity and metastasis. Cancer Metast
Rev. 35:645–654. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Pradella D, Naro C, Sette C and Ghigna C:
EMT and stemness: Flexible processes tuned by alternative splicing
in development and cancer progression. Mol Cancer. 16:82017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhou P, Li B, Liu F, Zhang M, Wang Q, Liu
Y, Yao Y and Li D: The epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT)
and cancer stem cells: Implication for treatment resistance in
pancreatic cancer. Mol Cancer. 16:522017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Burdick MM, Henson KA, Delgadillo LF, Choi
YE, Goetz DJ, Tees DF and Benencia F: Expression of E-selectin
ligands on circulating tumor cells: Cross-regulation with cancer
stem cell regulatory pathways? Front Oncol. 2:1032012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yao D, Dai C and Peng S: Mechanism of the
mesenchymal-epithelial transition and its relationship with
metastatic tumor formation. Mol Cancer Res. 9:1608–1620. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Serrano-Gomez SJ, Maziveyi M and Alahari
SK: Regulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition through
epigenetic and post-translational modifications. Mol Cancer.
15:182016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Choudhry H and Harris AL: Advances in
hypoxia-inducible factor biology. Cell Metab. 27:281–298. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Huang CH, Yang WH, Chang SY, Tai SK, Tzeng
CH, Kao JY, Wu KJ and Yang MH: Regulation of membrane-type 4 matrix
metalloproteinase by SLUG contributes to hypoxia-mediated
metastasis. Neoplasia. 11:1371–1382. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Moen I and Stuhr LE: Hyperbaric oxygen
therapy and cancer-a review. Target Oncol. 7:233–242. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tsuji T, Ibaragi S, Shima K, Hu MG,
Katsurano M, Sasaki A and Hu GF: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition
induced by growth suppressor p12CDK2-AP1 promotes tumor cell local
invasion but suppresses distant colony growth. Cancer Res.
68:10377–10386. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hong Y and Zhang Q: Phenotype of
circulating tumor cell: Face-off between epithelial and mesenchymal
masks. Tumour Biol. 37:5663–5674. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|