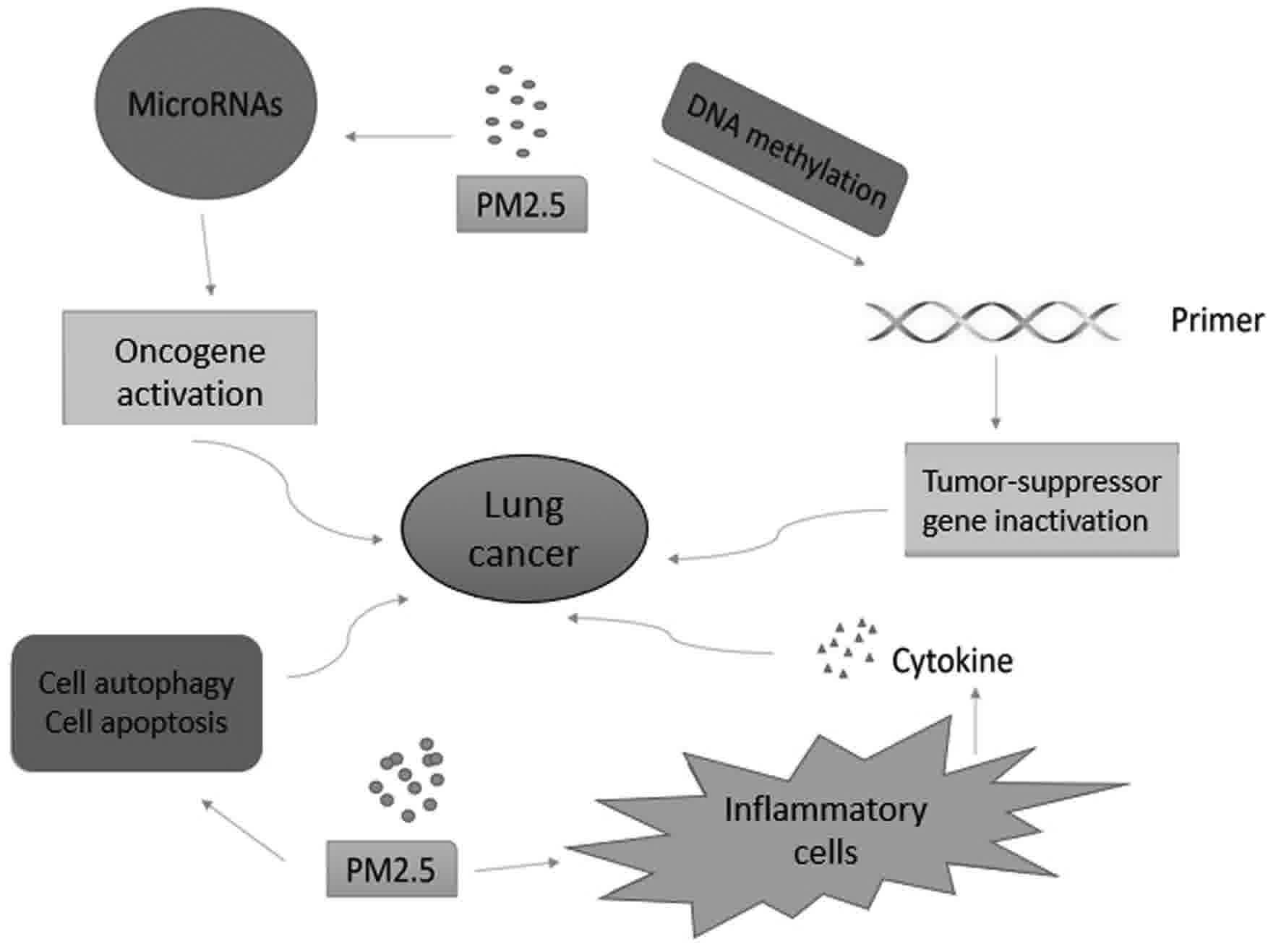
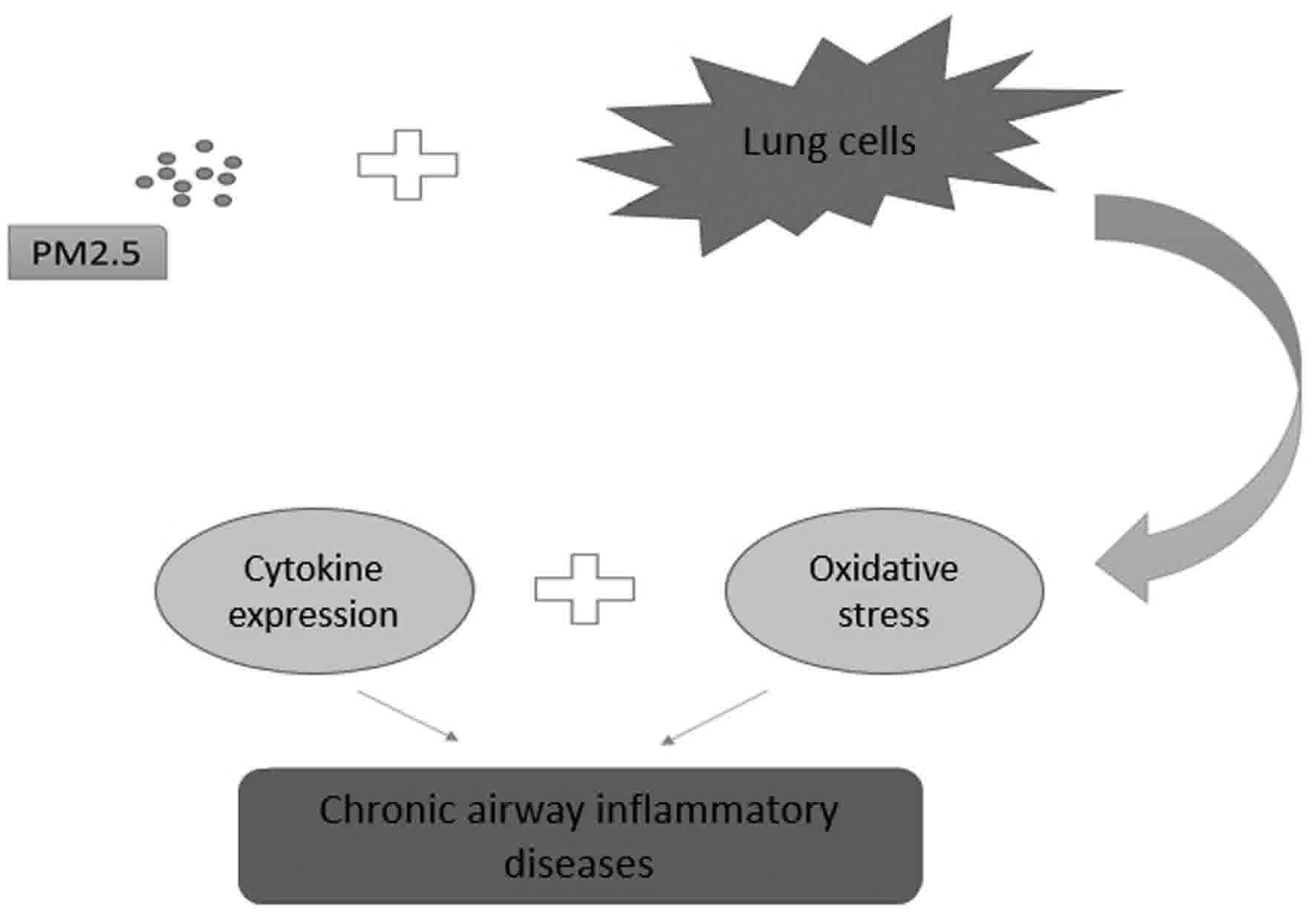
|
1
|
Li P, Xin J, Wang Y, Wang S, Li G, Pan X,
Liu Z and Wang L: The acute effects of fine particles on
respiratory mortality and morbidity in Beijing, 2004–2009. Environ
Sci Pollut Res Int. 20:6433–6444. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Du P, Du R, Ren W, Lu Z and Fu P: Seasonal
variation characteristic of inhalable microbial communities in
PM2.5 in Beijing city, China. Sci Total Environ. 610–611:308–315.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Kim Y, Seo J, Kim JY, Lee JY, Kim H and
Kim BM: Characterization of PM2.5 and identification of transported
secondary and biomass burning contribution in Seoul, Korea. Environ
Sci Pollut Res Int. 25:4330–4343. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bell ML, Dominici F, Ebisu K, Zeger SL and
Samet JM: Spatial and Temporal Variation in PM2.5 Chemical
Composition in the United States for Health Effects Studies.
Environ Health Perspect. 115:989–995. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Li Q, Liu H, Alattar M, Jiang S, Han J, Ma
Y and Jiang C: The preferential accumulation of heavy metals in
different tissues following frequent respiratory exposure to PM2.5
in rats. Sci Rep. 5:169362015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jiang S, Bo L, Du X, Liu J, Zeng X, He G,
Sun Q, Kan H, Song W, Xie Y and Zhao J: CARD9-mediated ambient PM
2.5-induced pulmonary injury is associated with Th17 cell. Toxicol
Lett. 273:36–43. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Falcon-Rodriguez CI, Osornio-Vargas AR,
Sada-Ovalle I and Segura-Medina P: Aeroparticles, composition, and
lung diseases. Front Immunol. 7:32016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jeong SC, Cho Y, Song MK, Lee E and Ryu
JC: Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-MAPK-nuclear
factor(NF)-κB-IL8: A possible mechanism of particulate matter(PM)
2.5-induced lung toxicity. Environ Toxicol. 32:1628–1636. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chen WL, Lin CY, Yan YH, Cheng KT and
Cheng TJ: Alterations in rat pulmonary phosphatidylcholines after
chronic exposure to ambient fine particulate matter. Mol Biosyst.
10:3163–3169. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Pope CA III, Bhatnagar A, Mccracken JP,
Abplanalp W, Conklin DJ and O'Toole T: Exposure to fine particulate
air pollution is associated with endothelial injury and systemic
inflammation. Circ Res. 119:12042016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gu LZ, Sun H and Chen JH: Histone
deacetylases 3 deletion restrains PM2.5-induced mice lung injury by
regulating NF-κB and TGF-β/Smad2/3 signaling pathways. Biomed
Pharmacother. 85:756–762. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Raaschou-Nielsen O, Andersen ZJ, Beelen R,
Samoli E, Stafoggia M, Weinmayr G, Hoffmann B, Fischer P,
Nieuwenhuijsen MJ, Brunekreef B, et al: Air pollution and lung
cancer incidence in 17 European cohorts: Prospective analyses from
the European Study of Cohorts for Air Pollution Effects (ESCAPE).
Lancet Oncol. 14:813–822. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
de P Pablo-Romero M, Román R, Limón JM and
Praena-Crespo M: Effects of fine particles on children's hospital
admissions for respiratory health in Seville, Spain. J Air Waste
Manage Assoc. 65:436–444. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Xu Q, Wang S, Guo Y, Wang C, Huang F, Li
X, Gao Q, Wu L, Tao L, Guo J, et al: Acute exposure to fine
particulate matter and cardiovascular hospital emergency room
visits in Beijing, China. Environ Pollut. 220:317–327. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tsai SS, Chiu HF, Liou SH and Yang CY:
Short-term effects of fine particulate air pollution on hospital
admissions for respiratory diseases: A case-crossover study in a
tropical city. J Toxicol Environ Health A. 77:1091–1101. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kravchenko J, Akushevich I, Abernethy AP,
Ross WG Jr and Lyerly HK: Long-term dynamics of death rates of
emphysema, asthma, and pneumonia and improving air quality. Int J
Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 9:613–627. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li R, Jiang N, Liu Q, Huang J, Guo X, Liu
F and Gao Z: Impact of air pollutants on outpatient visits for
acute respiratory outcomes. Int J Environ Res Public Health.
14:pii:E472017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Lin H, Wang X, Liu T, Li X, Xiao J, Zeng W
and Ma W: Air Pollution and Mortality in China. Adv Exp Med Biol.
1017:103–121. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Vahedian M, Khanjani N, Mirzaee M and
Koolivand A: Ambient air pollution and daily hospital admissions
for cardiovascular diseases in Arak, Iran. ARYA Atheroscler.
13:117–134. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Song C, He J, Wu L, Jin T, Chen X, Li R,
Ren P, Zhang L and Mao H: Health burden attributable to ambient
PM2.5 in China. Environ Pollut. 223:575–586. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kloog I: Fine particulate matter (PM2.5)
association with peripheral artery disease admissions in
northeastern United States. Int J Environ Health Res. 26:572–577.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Qin X, Xia L, Wang S, Chao W, Huang F, Qi
G, Wu L, Tao L, Jin G and Wei W: Fine particulate air pollution and
hospital emergency room visits for respiratory disease in Urban
areas in Beijing, China, in 2013. PLoS One. 11:e01530992016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Turner MC, Cohen A, Burnett RT, Jerrett M,
Diver WR, Gapstur SM, Krewski D, Samet JM and Pope CA III:
Interactions between cigarette smoking and ambient PM2.5 for
cardiovascular mortality. Environ Res. 154:304–310. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Shao Q, Liu T, Korantzopoulos P, Zhang Z,
Zhao J and Li G: Association between air pollution and development
of atrial fibrillation: A meta-analysis of observational studies.
Heart Lung. 45:557–562. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Pope CA III, Burnett RT, Turner MC, Cohen
A, Krewski D, Jerrett M, Gapstur SM and Thun MJ: Lung cancer and
cardiovascular disease mortality associated with ambient air
pollution and cigarette smoke: Shape of the exposure-response
relationships. Environ Health Perspect. 119:1616–1621. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Mao G, Nachman RM, Sun Q, Zhang X, Koehler
K, Chen Z, Hong X, Wang G, Caruso D and Zong G: Individual and
Joint Effects of Early-Life Ambient PM2.5 Exposure and Maternal
Pre-Pregnancy Obesity on Childhood Overweight or Obesity. Environ
Health Perspect. 2016. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yang YR, Chen YM, Chen SY and Chan CC:
Associations between long-term particulate matter exposure and
adult renal function in the taipei metropolis. Environ Health
Perspect. 125:602–607. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ramalingam S, Pawlish K, Gadgeel S, Demers
R and Kalemkerian GP: Lung cancer in young patients: Analysis of a
Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results database. J Clin Oncol.
16:651–657. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang N, Liang H, Zhou Y, Wang C, Zhang S,
Pan Y, Wang Y, Yan X, Zhang J, Zhang CY, et al: miR-203 suppresses
the proliferation and migration and promotes the apoptosis of lung
cancer cells by targeting SRC. PLoS One. 9:e1055702014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Harrison RM, Smith DJ and Kibble AJ: What
Is Responsible for the Carcinogenicity of PM2.5? Occup Environ Med.
61:799–805. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li J, Li WX, Bai C and Song Y: Particulate
matter-induced epigenetic changes and lung cancer. Clin Respir J.
11:539–546. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Vinikoor-Imler LC, Allen DJ and Luben TJ:
An ecologic analysis of county-level PM2.5 concentrations and lung
cancer incidence and mortality. Int J Environ Res Public Health.
8:1865–1671. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Eckel SP, Cockburn M, Shu YH, Deng H,
Lurmann FW, Liu L and Gilliland FD: Air pollution affects lung
cancer survival. Thorax. 71:891–898. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Xie Y, Zhao B, Zhao Y, Luo Q, Wang S, Zhao
B and Bai S: Reduction in population exposure to PM2.5 and cancer
risk due to PM2.5-bound PAHs exposure in Beijing, China during the
APEC meeting. Environ Pollut. 225:338–345. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Fabian MR, Sonenberg N and Filipowicz W:
Regulation of mRNA translation and stability by microRNAs. Annu Rev
Biochem. 79:351–379. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Papoutsidakis N, Deftereos S, Kaoukis A,
Bouras G, Giannopoulos G, Theodorakis A, Angelidis C, Hatzis G and
Stefanadis C: MicroRNAs and the heart: Small things do matter. Curr
Top Med Chem. 13:216–230. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Liu C, Guo H, Cheng X, Shao M, Wu C, Wang
S, Li H, Wei L, Gao Y, Tan W, et al: Exposure to airborne PM2.5
suppresses microRNA expression and deregulates target oncogenes
that cause neoplastic transformation in NIH3T3 cells. Oncotarget.
6:29428–29439. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Li X, Lv Y, Gao N, Sun H, Lu R, Yang H,
Zhang C, Meng Q, Wu S, Li AQ, et al: microRNA-802/Rnd3 pathway
imposes on carcinogenesis and metastasis of fine particulate matter
exposure. Oncotarget. 7:35026–35043. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ding X, Wang M, Chu H, Chu M, Na T, Wen Y,
Wu D, Han B, Bai Z, Chen W, et al: Global gene expression profiling
of human bronchial epithelial cells exposed to airborne fine
particulate matter collected from Wuhan, China. Toxicol Lett.
228:25–33. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Sancini G, Farina F, Battaglia C, Cifola
I, Mangano E, Mantecca P, Camatini M and Palestini P: Health risk
assessment for air pollutants: Alterations in lung and cardiac gene
expression in mice exposed to Milano winter fine particulate matter
(PM2.5). PLoS One. 9:e1096852014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zhou Z, Liu Y, Duan F, Qin M, Wu F, Sheng
W, Yang L, Liu J and He K: Transcriptomic analyses of the
biological effects of airborne PM2.5 exposure on human bronchial
epithelial cells. PLoS One. 10:e01382672015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Deng X, Feng N, Zheng M, Ye X, Lin H, Yu
X, Gan Z, Fang Z, Zhang H, Gao M, et al: PM 2.5 exposure-induced
autophagy is mediated by lncRNA loc146880 which also promotes the
migration and invasion of lung cancer cells. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1861:112–125. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Cai W, Li Q, Yang Z, Miao X, Wen Y, Huang
S and Ouyang J: Expression of p53 upregulated modulator of
apoptosis (PUMA) and C-myb in gallbladder adenocarcinoma and their
pathological significance. Clin Transl Oncol. 15:818–824. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ellis P, Lonning PE, Borresen-Dale A, Aas
T, Geisler S, Akslen LA, Salter I, Smith IE and Dowsett M: Absence
of p21 expression is associated with abnormal p53 in human breast
carcinomas. Br J Cancer. 76:480–485. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Deben C, Van den Bossche J, Van Der Steen
N, Lardon F, Wouters A, de Beeck KO, Hermans C, Jacobs J, Peeters
M, Van Camp G, et al: Deep sequencing of the TP53 gene reveals a
potential risk allele for non-small cell lung cancer and supports
the negative prognostic value of TP53 variants. Tumour Biol.
39:10104283176943272017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhou W, Tian D, He J, Wang Y, Zhang L, Cui
L, Jia L, Zhang L, Li L, Shu Y, et al: Repeated PM2.5 exposure
inhibits BEAS-2B cell P53 expression through ROS-Akt-DNMT3B
pathway-mediated promoter hypermethylation. Oncotarget.
7:20691–20703. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Heßelbach K, Kim GJ, Flemming S, Häupl T,
Bonin M, Dornhof R, Günther S, Merfort I and Humar M: Disease
relevant modifications of the methylome and transcriptome by
particulate matter (PM2.5) from biomass combustion. Epigenetics.
12:779–792. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Ding R, Jin Y, Liu X, Zhu Z, Zhang Y, Wang
T and Xu Y: Characteristics of DNA methylation changes induced by
traffic-related air pollution. Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ
Mutagen. 796:46–53. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Guo L, Byun HM, Zhong J, Motta V, Barupal
J, Zheng Y, Dou C, Zhang F, Mccracken JP, Diaz A, et al: Effects of
short-term exposure to inhalable particulate matter on DNA
methylation of tandem repeats. Environ Mol Mutagen. 55:322–335.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Hou L, Zhang X, Zheng Y, Wang S, Dou C,
Guo L, Byun HM, Motta V, Mccracken J, Díaz A, et al: Altered
methylation in tandem repeat element and elemental component levels
in inhalable air particles. Environ Mol Mutagen. 55:256–265. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Graves EE, Maity A and Le QT: The tumor
microenvironment in non-small cell lung cancer. Semin Radiat Oncol.
20:156–163. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Vendramini-Costa DB and Carvalho JE:
Molecular link mechanisms between inflammation and cancer. Curr
Pharm Des. 18:38312012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Cho WC, Kwan CK, Yau S, So PP, Poon PC and
Au JS: The role of inflammation in the pathogenesis of lung cancer.
Expert Opin Ther Targets. 15:1127–1237. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Yang B, Chen D, Hui Z and Xiao C: The
effects for PM2.5 exposure on non-small-cell lung cancer induced
motility and proliferation. Springerplus. 5:20592016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Almatroodi SA, McDonald CF and Pouniotis
DS: Alveolar macrophage polarisation in lung cancer. Lung Cancer
Int. 2014:7210872014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Baulig A, Blanchet S, Rumelhard M, Lacroix
G, Marano F and Baeza-Squiban A: Fine urban atmospheric particulate
matter modulates inflammatory gene and protein expression in human
bronchial epithelial cells. Front Biosci. 12:771–782. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Gualtieri M, Mantecca P, Cetta F and
Camatini M: Organic compounds in tire particle induce reactive
oxygen species and heat-shock proteins in the human alveolar cell
line A549. Environ Int. 34:437–442. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Jiang M, Wei Q, Dong G, Komatsu M, Su Y
and Dong Z: Autophagy in proximal tubules protects against acute
kidney injury. Kidney Int. 82:1271–1283. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Viry E, Paggetti J, Baginska J,
Mgrditchian T, Berchem G, Moussay E and Janji B: Autophagy: An
adaptive metabolic response to stress shaping the antitumor
immunity. Biochem Pharmacol. 92:31–42. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Taylor R, Cullen S and Martin S:
Apoptosis: Controlled demolition at the cellular level. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 9:231–241. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Kim R, Emi M and Tanabe K: Role of
mitochondria as the gardens of cell death. Cancer Chemother
Pharmacol. 57:545–553. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Mohseni N, McMillan S, Chaudhary R, Mok J
and Reed B: Autophagy promotes caspase-dependent cell death during
Drosophila development. Autophagy. 5:329–338. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Joubert PE, Werneke SW, de la Calle C,
Guivel-Benhassine F, Giodini A, Peduto L, Levine B, Schwartz O,
Lenschow DJ and Albert ML: Chikungunya virus-induced autophagy
delays caspase-dependent cell death. J Exp Med. 209:1029–1047.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
You M, Savaraj N, Kuo MT, Wangpaichitr M,
Varona-Santos J, Wu C, Nguyen DM and Feun L: TRAIL induces
autophagic protein cleavage through caspase activation in melanoma
cell lines under arginine deprivation. Mol Cell Biochem.
374:181–190. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Cho D, Jo Y, Hwang JJ, Lee YM, Roh SA and
Kim JC: Caspase-mediated cleavage of ATG6/Beclin-1 links apoptosis
to autophagy in HeLa cells. Cancer Lett. 274:95–100. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Hou W, Han J, Lu C, Goldstein LA and
Rabinowich H: Autophagic degradation of active caspase-8: A
crosstalk mechanism between autophagy and apoptosis. Autophagy.
6:891–900. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Xu X, Wang H, Liu S, Xing C, Liu Y,
Aodengqimuge, Zhou W, Yuan X, Ma Y, Hu M, et al: TP53-dependent
autophagy links the ATR-CHEK1 axis activation to proinflammatory
VEGFA production in human bronchial epithelial cells exposed to
fine particulate matter (PM2.5). Autophagy. 12:18322016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Liu T, Wu B, Wang Y, He H, Lin Z, Tan J,
Yang L, Kamp DW, Zhou X, Tang J, et al: Particulate matter 2.5
induces autophagy via inhibition of the phosphatidylinositol
3-kinase/Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin kinase signaling pathway
in human bronchial epithelial cells. Mol Med Report. 12:1914–1922.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Wang Y, Lin Z, Huang H, He H, Yang L, Chen
T, Yang T, Ren N, Jiang Y, Xu W, et al: AMPK is required for
PM2.5-induced autophagy in human lung epithelial A549 cells. Int J
Clin Exp Med. 8:58–72. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Zhou Z, Shao T, Qin M, Miao X, Chang Y,
Sheng W, Wu F and Yu Y: The effects of autophagy on vascular
endothelial cells induced by airborne PM2.5. J Environ Sci.
2017.(In Press).
|
|
71
|
Longhin E, Holme JA, Gutzkow KB, Arlt VM,
Kucab JE, Camatini M and Gualtieri M: Cell cycle alterations
induced by urban PM2.5 in bronchial epithelial cells:
Characterization of the process and possible mechanisms involved.
Part Fibre Toxicol. 10:632013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Gualtieri M, Ovrevik J, Mollerup S, Asare
N, Longhin E, Dahlman HJ, Camatini M and Holme JA: Airborne urban
particles (Milan winter-PM2.5) cause mitotic arrest and cell death:
Effects on DNA, mitochondria, AhR binding and spindle organization.
Mutat Res. 713:18–31. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Abbas I, Verdin A, Escande F,
Saint-Georges F, Cazier F, Mulliez P, Courcot D, Shirali P, Gosset
P and Garçon G: In vitro short-term exposure to air pollution
PM2.5-0.3 induced cell cycle alterations and genetic instability in
a human lung cell coculture model. Environ Res. 147:146–158. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Deng X, Zhang F, Wang L, Rui W, Long F,
Zhao Y, Chen D and Ding W: Airborne fine particulate matter induces
multiple cell death pathways in human lung epithelial cells.
Apoptosis. 19:1099–1112. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Dagher Z, Garcon G, Billet S, Gosset P,
Ledoux F, Courcot D, Aboukais A and Shirali P: Activation of
different pathways of apoptosis by air pollution particulate matter
(PM2.5) in human epithelial lung cells (L132) in culture.
Toxicology. 225:12–24. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Ezegbunam W and Foronjy R:
Posttranscriptional control of airway inflammation. Wiley
Interdiscip Rev RNA. 9:e14552018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Su N, Lin J, Chen P, Li J, Wu C, Yin K,
Liu C, Chen Y, Zhou X and Yuan Y: Evaluation of asthma control and
patient's perception of asthma: findings and analysis of a
nationwide questionnaire-based survey in China. J Asthma.
50:861–870. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Tecer LH, Alagha O, Karaca F, Tuncel G and
Eldes N: Particulate matter (PM(2.5), PM(10-2.5), and PM(10)) and
children's hospital admissions for asthma and respiratory diseases:
A bidirectional case-crossover study. J Toxicol Environ Health A.
71:512–520. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Jalaludin B, Khalaj B, Sheppeard V and
Morgan G: Air pollution and ED visits for asthma in Australian
children: A case-crossover analysis. Int Arch Occup Environ Health.
81:967–974. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Jacquemin B, Siroux V, Sanchez M, Carsin
AE, Schikowski T, Adam M, Bellisario V, Buschka A, Bono R,
Brunekreef B, et al: Ambient air pollution and adult asthma
incidence in six European cohorts (ESCAPE). Environ Health
Perspect. 123:613–621. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Kim H, Kim H, Park YH and Lee JT:
Assessment of temporal variation for the risk of particulate
matters on asthma hospitalization. Environ Res. 156:542–550. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Yan C, Wong GW and Jing L: Environmental
exposure and genetic predisposition as risk factors for Asthma in
China. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 8:92–100. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Maestrelli P, Canova C, Scapellato ML,
Visentin A, Tessari R, Bartolucci GB, Simonato L and Lotti M:
Personal exposure to particulate matter is associated with worse
health perception in adult asthma. J Investig Allergol Clin
Immunol. 21:120–128. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Wagner JG, Morishita M, Keeler GJ and
Harkema JR: Divergent effects of urban particulate air pollution on
allergic airway responses in experimental asthma: A comparison of
field exposure studies. Environ Health. 11:452012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Xiang Z, Xu X, Zheng X, Reponen T, Chen A
and Xia H: Heavy metals in PM 2.5 and in blood, and children's
respiratory symptoms and asthma from an e-waste recycling area.
Environ Pollut. 210:346–353. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Yao W, Wang C, Zhong N, Han X, Wu C, Yan
X, Chen P, Yang W, Henley M and Kramer B: Effect of once-daily
indacaterol in a predominantly Chinese population with chronic
obstructive pulmonary disease: A 26-week Asia-Pacific study.
Respirology. 19:231–238. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Montoya-Estrada A, Torres-Ramos YD,
Flores-Pliego A, Ramirez-Venegas A, Ceballos-Reyes GM,
Guzman-Grenfell AM and Hicks JJ: Urban PM2.5 activates GAPDH and
induces RBC damage in COPD patients. Front Biosci (Schol Ed).
5:638–649. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Cortezlugo M, Ramírezaguilar M,
Pérezpadilla R, Sansoresmartínez R, Ramírezvenegas A and
Barrazavillarreal A: Effect of personal exposure to PM2.5 on
respiratory health in a mexican panel of patients with COPD. Int J
Environ Res Public Health. 12:10635–10647. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Rice MB, Ljungman PL, Wilker EH, Dorans
KS, Gold DR, Schwartz J, Koutrakis P, Washko GR, O'Connor GT and
Mittleman MA: Long-term exposure to traffic emissions and fine
particulate matter and lung function decline in the Framingham
heart study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 191:656–664. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Ren J, Li B, Yu D, Liu J and Ma Z:
Approaches to prevent the patients with chronic airway diseases
from exacerbation in the haze weather. J Thorac Dis. 8:E1–E7.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Rahman I and Adcock I: Oxidative stress
and redox regulation of lung inflammation in COPD. Eur Respir J.
28:219–242. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Watterson TL, Sorenson J, Martin R and
Coulombe RA Jr: Effects of PM2.5 Collected from Cache Valley Utah
in Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells. Annual Meeting of the Society
of Toxicology. 2006.
|
|
93
|
Li R, Kou X, Xie L, Cheng F and Geng H:
Effects of ambient PM2.5 on pathological injury, inflammation,
oxidative stress, metabolic enzyme activity, and expression of
c-fos and c-jun in lungs of rats. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int.
22:20167–20176. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Riva DR, Magalhães CB, Lopes AA, Lanças T,
Mauad T, Malm O, Valença SS, Saldiva PH, Faffe DS and Zin WA: Low
dose of fine particulate matter (PM2.5) can induce acute oxidative
stress, inflammation and pulmonary impairment in healthy mice.
Inhal Toxicol. 23:57–67. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
95
|
Zhao QJ, Liu XJ, Zeng XL and Bao HR:
Effect of PM2.5 on the level of nuclear factor erythroid-2 related
factor 2 in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease mice and its
relationship with oxidative stress. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi.
96:2241–2245. 2016.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Yan Z, Wang J, Li J, Jiang N, Zhang R,
Yang W, Yao W and Wu W: Oxidative stress and endocytosis are
involved in upregulation of interleukin-8 expression in airway
cells exposed to PM2.5. Environ Toxicol. 31:1869–1878. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Xu D, Huang N, Wang Q and Liu H: Study of
ambient PM2.5 on the influence of the inflammation injury and the
immune function of subchronic exposure rats. Wei Sheng Yan Jiu.
37:423–428. 2008.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Shu J, Liu X, Chu X, Qiu J, Zeng X and Bao
H: Effects of PM2.5 on phagocytic function of alveolar macrophages
in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease mice. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za
Zhi. 96:301–305. 2016.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Gu XY, Chu X, Zeng XL, Bao HR and Liu XJ:
Effects of PM2.5 exposure on the Notch signaling pathway and immune
imbalance in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Environ Pollut.
226:163–173. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Hong Z, Guo Z, Zhang R, Xu J, Dong W,
Zhuang G and Deng C: Airborne fine particulate matter induces
oxidative stress and inflammation in human nasal epithelial cells.
Tohoku J Exp Med. 239:117–125. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Bekki K, Ito T, Yoshida Y, He C,
Arashidani K, He M, Sun G, Zeng Y, Sone H and Kunugita N: PM2.5
collected in China causes inflammatory and oxidative stress
responses in macrophages through the multiple pathways. Environ
Toxicol Pharmacol. 45:362–369. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Liu Q, Baumgartner J, Zhang Y, Liu Y, Sun
Y and Zhang M: Oxidative potential and inflammatory impacts of
source apportioned ambient air pollution in Beijing. Environ Sci
Technol. 48:12920–12929. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Zhang X, Zhong W, Meng Q, Lin Q, Fang C,
Huang X, Li C, Huang Y and Tan J: Ambient PM2.5 exposure
exacerbates severity of allergic asthma in previously sensitized
mice. J Asthma. 52:785–794. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Zhao C, Liao J, Chu W, Wang S, Yang T, Tao
Y and Wang G: Involvement of TLR2 and TLR4 and Th1/Th2 shift in
inflammatory responses induced by fine ambient particulate matter
in mice. Inhal Toxicol. 24:918–927. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Huang KL, Liu SY, Chou CC, Lee YH and
Cheng TJ: The effect of size-segregated ambient particulate matter
on Th1/Th2-like immune responses in mice. PLoS One.
12:e01731582017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Xie X, Chen J, Li F, Tian J, Gao JS and
Zhang D: A T-cell-based enzyme-linked immunospot assay for
tuberculosis screening in Chinese patients with rheumatic diseases
receiving infliximab therapy. Clin Exp Med. 11:155–161. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Jassal MS, Bakman I and Jones B:
Correlation of ambient pollution levels and heavily-trafficked
roadway proximity on the prevalence of smear-positive tuberculosis.
Public Health. 127:268–274. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Lai TC, Chiang CY, Wu CF, Yang SL, Liu DP,
Chan CC and Lin HH: Ambient air pollution and risk of tuberculosis:
A cohort study. Occup Environ Med. 73:56–61. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Nicola I, Cerutti F, Grego E, Bertone I,
Gianella P, D'Angelo A, Peletto S and Bellino C: Characterization
of the upper and lower respiratory tract microbiota in Piedmontese
calves. Microbiome. 5:1522017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Rivas-Santiago CE, Sarkar S, Cantarella P
IV, Osornio-Vargas Á, Quintana-Belmares R, Meng Q, Kirn TJ,
Strickland Ohman P, Chow JC, Watson JG, et al: Air pollution
particulate matter alters antimycobacterial respiratory epithelium
innate immunity. Infect Immun. 83:2507–2517. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
MacIntyre EA, Gehring U, Mölter A, Fuertes
E, Klümper C, Krämer U, Quass U, Hoffmann B, Gascon M, Brunekreef
B, et al: Air pollution and respiratory infections during early
childhood: An analysis of 10 European birth cohorts within the
ESCAPE Project. Environ Health Perspect. 122:107–113.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Darrow LA, Klein M, Flanders WD,
Mulholland JA, Tolbert PE and Strickland MJ: Air pollution and
acute respiratory infections among children 0–4 years of age: An
18-year time-series study. Am J Epidemiol. 180:968–977. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Ghosh R, Rossner P, Honkova K, Dostal M,
Sram RJ and Hertzpicciotto I: Air pollution and childhood
bronchitis: Interaction with xenobiotic, immune regulatory and DNA
repair genes. Environ Int. 87:94–100. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|