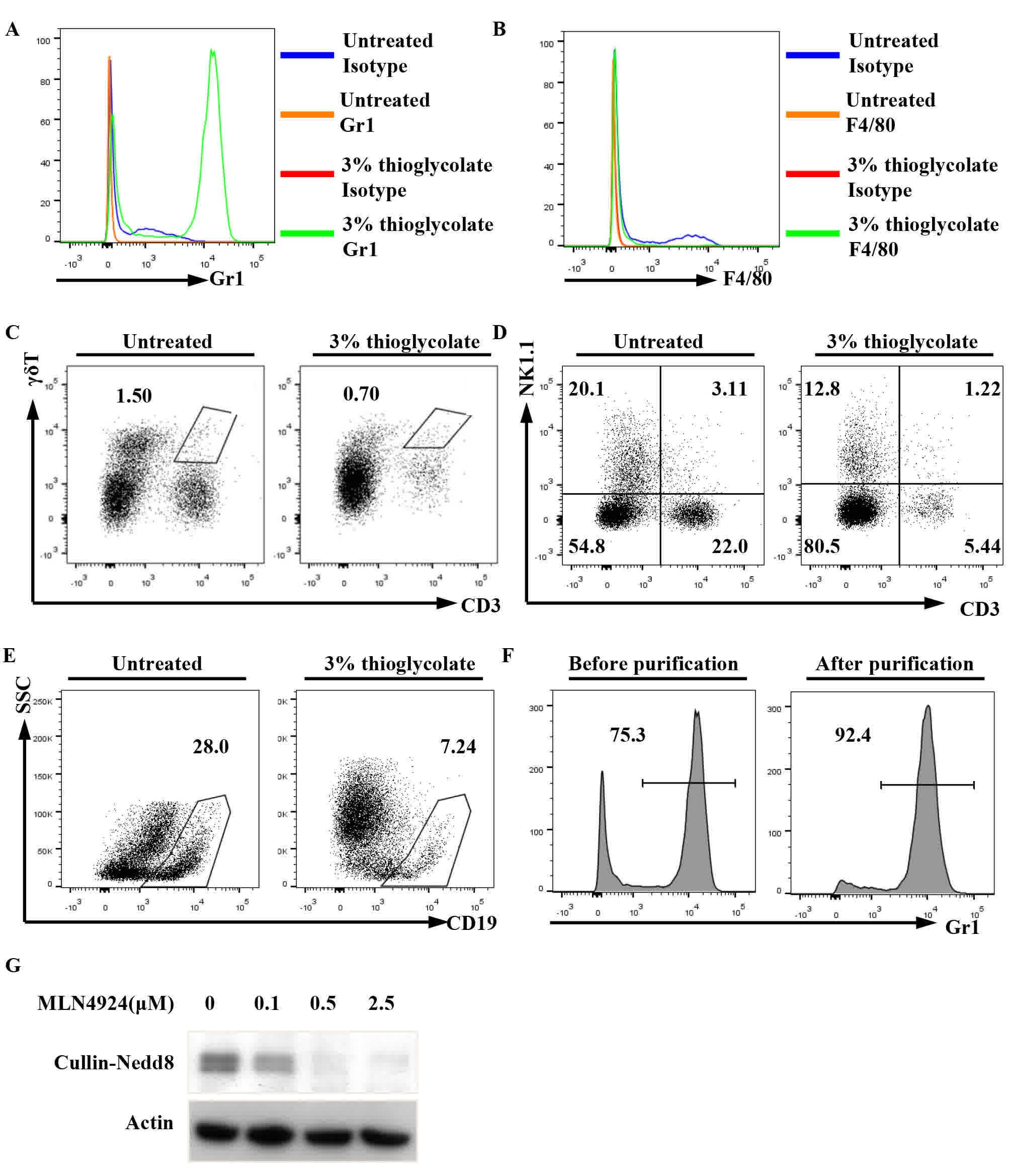
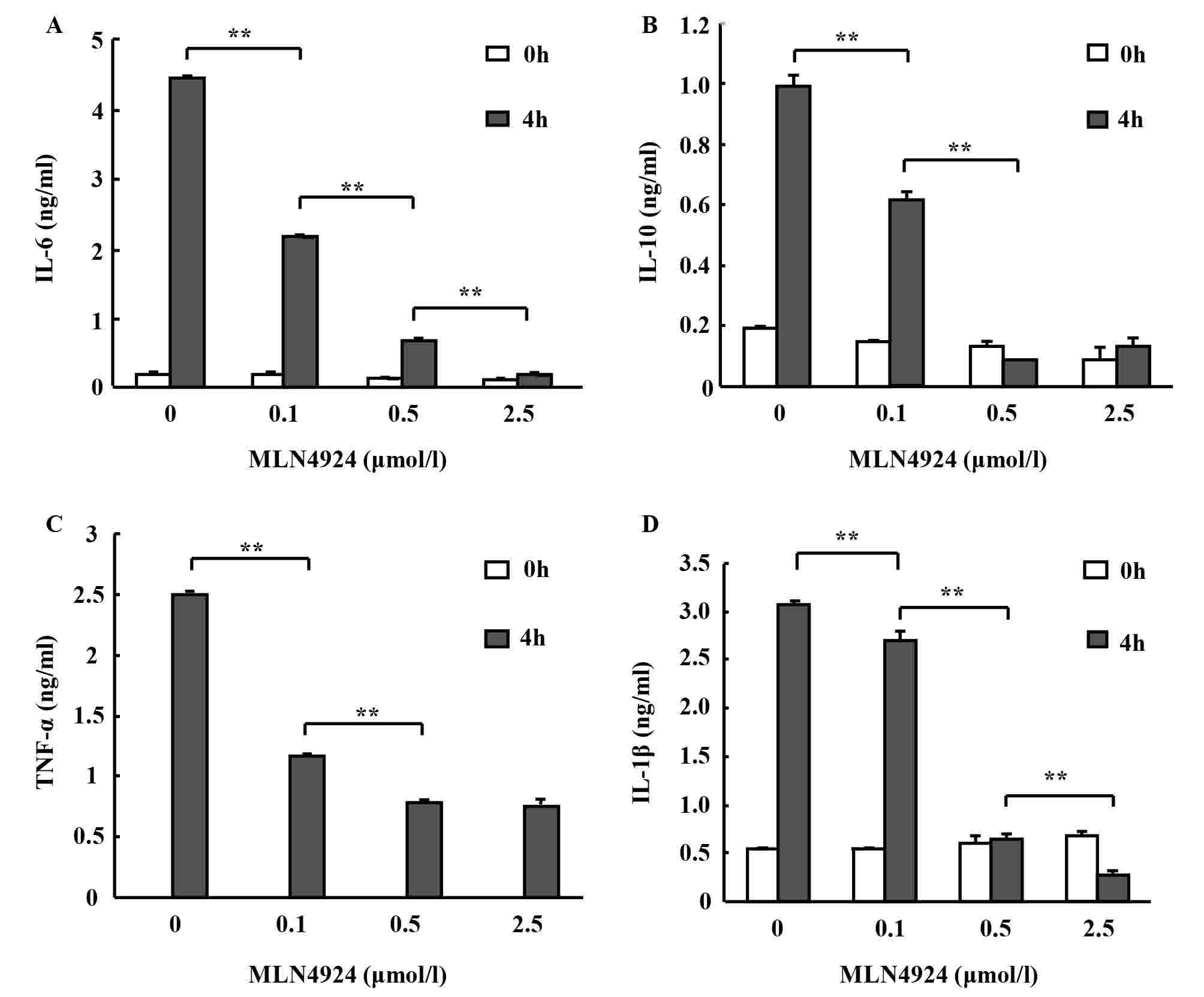
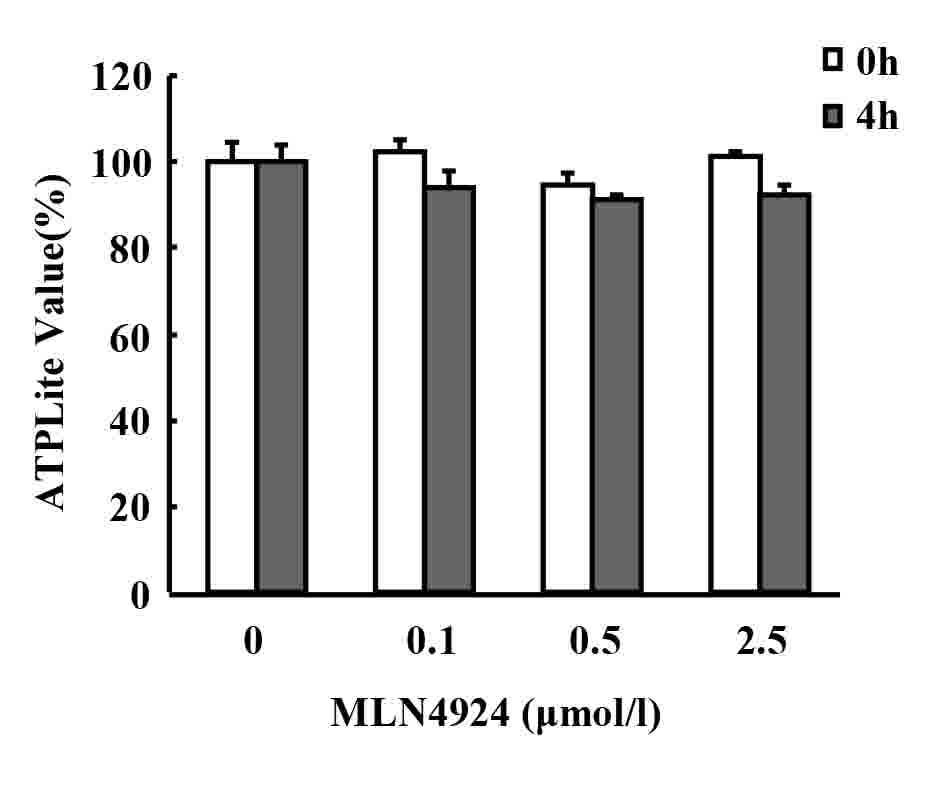
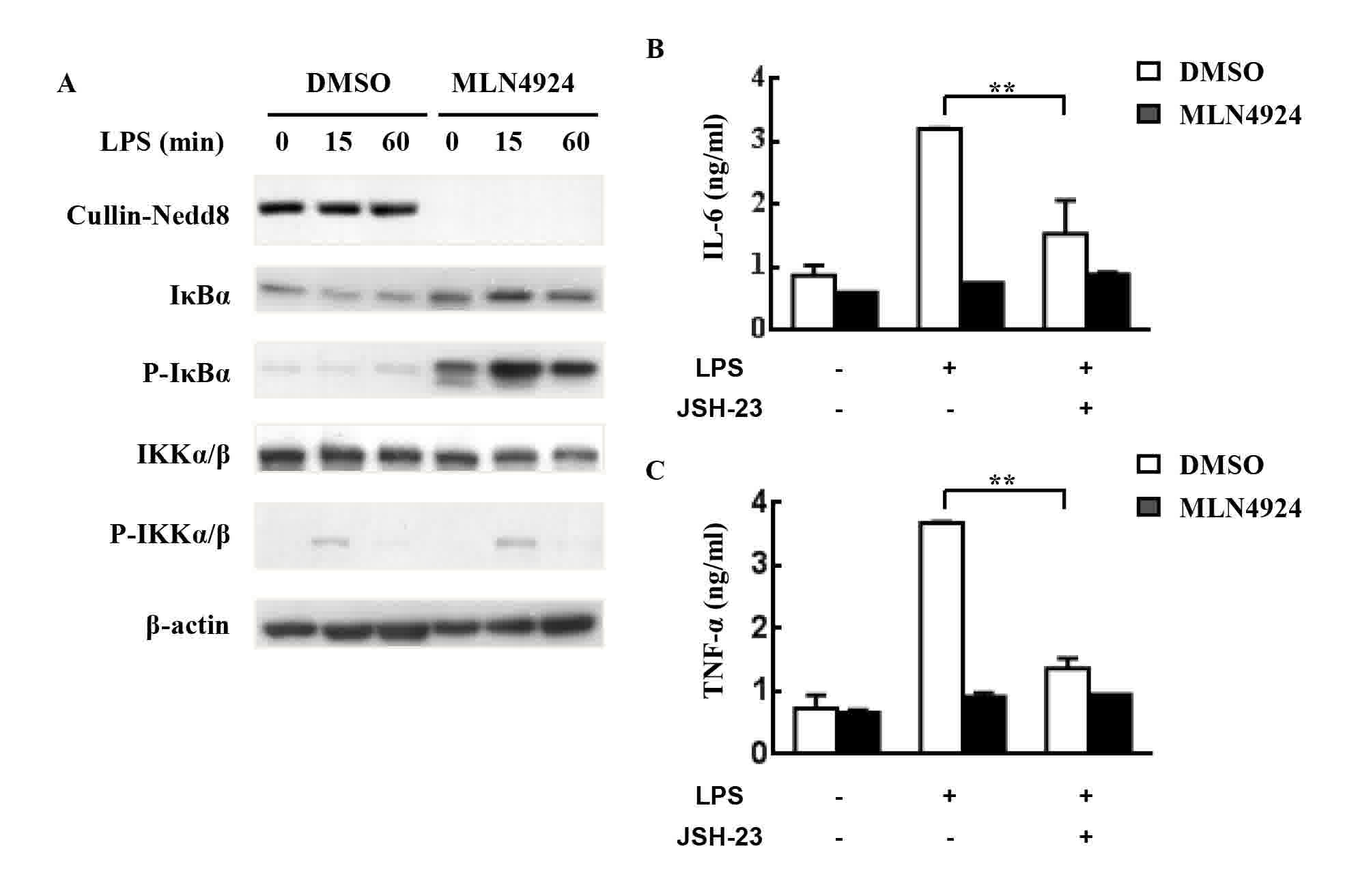
|
1
|
Futosi K, Fodor S and Mocsai A: Reprint of
Neutrophil cell surface receptors and their intracellular signal
transduction pathways. Int Immunopharmacol. 17:1185–1197. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wang Y, Wang K, Han GC, Wang RX, Xiao H,
Hou CM, Guo RF, Dou Y, Shen BF, Li Y and Chen GJ: Neutrophil
infiltration favors colitis-associated tumorigenesis by activating
the interleukin-1 (IL-1)/IL-6 axis. Mucosal Immunol. 7:1106–1115.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Rahbar A, Cederarv M, Wolmer-Solberg N,
Tammik C, Stragliotto G, Peredo I, Fornara O, Xu X, Dzabic M, Taher
C, et al: Enhanced neutrophil activity is associated with shorter
time to tumor progression in glioblastoma patients. Oncoimmunology.
5:e10756932015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sabroe I, Prince LR, Jones EC, Horsburgh
MJ, Foster SJ, Vogel SN, Dower SK and Whyte MK: Selective roles for
Toll-like receptor (TLR)2 and TLR4 in the regulation of neutrophil
activation and life span. J Immunol. 170:5268–5275. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Takeuchi O and Akira S: Pattern
recognition receptors and inflammation. Cell. 140:805–820. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chang FM, Reyna SM, Granados JC, Wei SJ,
Innis-Whitehouse W, Maffi SK, Rodriguez E, Slaga TJ and Short JD:
Inhibition of neddylation represses lipopolysaccharide-induced
proinflammatory cytokine production in macrophage cells. J Biol
Chem. 287:35756–35767. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sabroe I, Parker LC, Wilson AG, Whyte MK
and Dower SK: Toll-like receptors: Their role in allergy and
non-allergic inflammatory disease. Clin Exp Allergy. 32:984–989.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Guthrie LA, McPhail LC, Henson PM and
Johnston RB Jr: Priming of neutrophils for enhanced release of
oxygen metabolites by bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Evidence for
increased activity of the superoxide-producing enzyme. J Exp Med.
160:1656–1671. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Loftus SJ, Liu G, Carr SM, Munro S and La
Thangue NB: NEDDylation regulates E2F-1-dependent transcription.
EMBO Rep. 13:811–818. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Xirodimas DP: Novel substrates and
functions for the ubiquitin-like molecule NEDD8. Biochem Soc Trans.
36:802–806. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Xirodimas DP, Saville MK, Bourdon JC, Hay
RT and Lane DP: Mdm2-mediated NEDD8 conjugation of p53 inhibits its
transcriptional activity. Cell. 118:83–97. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zuo W, Huang F, Chiang YJ, Li M, Du J,
Ding Y, Zhang T, Lee HW, Jeong LS, Chen Y, et al: C-Cbl-mediated
neddylation antagonizes ubiquitination and degradation of the TGF-β
type II receptor. Mol Cell. 49:499–510. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Huang DT, Ayrault O, Hunt HW, Taherbhoy
AM, Duda DM, Scott DC, Borg LA, Neale G, Murray PJ, Roussel MF and
Schulman BA: E2-RING expansion of the NEDD8 cascade confers
specificity to cullin modification. Mol Cell. 33:483–495. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liakopoulos D, Doenges G, Matuschewski K
and Jentsch S: A novel protein modification pathway related to the
ubiquitin system. EMBO J. 17:2208–2214. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Osaka F, Kawasaki H, Aida N, Saeki M,
Chiba T, Kawashima S, Tanaka K and Kato S: A new NEDD8-ligating
system for cullin-4A. Genes Dev. 12:2263–2268. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Luo Z, Yu G, Lee HW, Li L, Wang L, Yang D,
Pan Y, Ding C, Qian J, Wu L, et al: The Nedd8-activating enzyme
inhibitor MLN4924 induces autophagy and apoptosis to suppress liver
cancer cell growth. Cancer Res. 72:3360–3371. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhu T, Wang J, Pei Y, Wang Q, Wu Y, Qiu G,
Zhang D, Lv M, Li W and Zhang J: Neddylation controls basal MKK7
kinase activity in breast cancer cells. Oncogene. 35:2624–2633.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gao F, Cheng J, Shi T and Yeh ET:
Neddylation of a breast cancer-associated protein recruits a class
III histone deacetylase that represses NFkappaB-dependent
transcription. Nat Cell Biol. 8:1171–1177. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mathewson N, Toubai T, Kapeles S, Sun Y,
Oravecz-Wilson K, Tamaki H, Wang Y, Hou G, Sun Y and Reddy P:
Neddylation plays an important role in the regulation of murine and
human dendritic cell function. Blood. 122:2062–2073. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cheng M, Hu S, Wang Z, Pei Y, Fan R, Liu
X, Wang L, Zhou J, Zheng S, Zhang T, et al: Inhibition of
neddylation regulates dendritic cell functions via Deptor
accumulation driven mTOR inactivation. Oncotarget. 7:35643–35654.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ajibade AA, Wang Q, Cui J, Zou J, Xia X,
Wang M, Tong Y, Hui W, Liu D, Su B, et al: TAK1 negatively
regulates NF-κB and p38 MAP kinase activation in Gr-1+CD11b+
neutrophils. Immunity. 36:43–54. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Swords RT, Kelly KR, Smith PG, Garnsey JJ,
Mahalingam D, Medina E, Oberheu K, Padmanabhan S, O'Dwyer M,
Nawrocki ST, et al: Inhibition of NEDD8-activating enzyme: A novel
approach for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia. Blood.
115:3796–3800. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hjerpe R, Thomas Y, Chen J, Zemla A,
Curran S, Shpiro N, Dick LR and Kurz T: Changes in the ratio of
free NEDD8 to ubiquitin triggers NEDDylation by ubiquitin enzymes.
Biochem J. 441:927–936. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Pelham CJ, Ketsawatsomkron P, Groh S,
Grobe JL, de Lange WJ, Ibeawuchi SR, Keen HL, Weatherford ET,
Faraci FM and Sigmund CD: Cullin-3 regulates vascular smooth muscle
function and arterial blood pressure via PPARgamma and
RhoA/Rho-kinase. Cell Metab. 16:462–472. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Guihard S, Ramolu L, Macabre C, Wasylyk B,
Noël G, Abecassis J and Jung AC: The NEDD8 conjugation pathway
regulates p53 transcriptional activity and head and neck cancer
cell sensitivity to ionizing radiation. Int J Oncol. 41:1531–1540.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Collier-Hyams LS, Sloane V, Batten BC and
Neish AS: Cutting edge: Bacterial modulation of epithelial
signaling via changes in neddylation of cullin-1. J Immunol.
175:4194–4198. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jubelin G, Taieb F, Duda DM, Hsu Y,
Samba-Louaka A, Nobe R, Penary M, Watrin C, Nougayrède JP, Schulman
BA, et al: Pathogenic bacteria target NEDD8-conjugated cullins to
hijack host-cell signaling pathways. PLoS Pathog. 6:e10011282010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Segovia JA, Tsai SY, Chang TH, Shil NK,
Weintraub ST, Short JD and Bose S: Nedd8 regulates
inflammasome-dependent caspase-1 activation. Mol Cell Biol.
35:582–597. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Vince JE and Silke J: The intersection of
cell death and inflammasome activation. Cell Mol Life Sci.
73:2349–2367. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Davis BK, Wen H and Ting JP: The
inflammasome NLRs in immunity, inflammation, and associated
diseases. Annu Rev Immunol. 29:707–735. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Franchi L, Eigenbrod T, Muñoz-Planillo R
and Nuñez G: The inflammasome: A caspase-1-activation platform that
regulates immune responses and disease pathogenesis. Nat Immunol.
10:241–247. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
McMillin DW, Jacobs HM, Delmore JE, Buon
L, Hunter ZR, Monrose V, Yu J, Smith PG, Richardson PG, Anderson
KC, et al: Molecular and cellular effects of NEDD8-activating
enzyme inhibition in myeloma. Mol Cancer Ther. 11:942–951. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Milhollen MA, Traore T, Adams-Duffy J,
Thomas MP, Berger AJ, Dang L, Dick LR, Garnsey JJ, Koenig E,
Langston SP, et al: MLN4924, a NEDD8-activating enzyme inhibitor,
is active in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma models: Rationale for
treatment of NF-{kappa}B-dependent lymphoma. Blood. 116:1515–1523.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Li L, Liu B, Dong T, Lee HW, Yu J, Zheng
Y, Gao H, Zhang Y, Chu Y, Liu G, et al: Neddylation pathway
regulates the proliferation and survival of macrophages. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 432:494–498. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Futosi K, Fodor S and Mócsai A: Neutrophil
cell surface receptors and their intracellular signal transduction
pathways. Int Immunopharmacol. 17:638–650. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Shin HM, Kim MH, Kim BH, Jung SH, Kim YS,
Park HJ, Hong JT, Min KR and Kim Y: Inhibitory action of novel
aromatic diamine compound on lipopolysaccharide-induced nuclear
translocation of NF-kappaB without affecting IkappaB degradation.
FEBS Lett. 571:50–54. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhang X, Ye Z, Pei Y, Qiu G, Wang Q, Xu Y,
Shen B and Zhang J: Neddylation is required for herpes simplex
virus type I (HSV-1)-induced early phase interferon-beta
production. Cell Mol Immunol. 13:578–83. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Guma M, Ronacher L, Liu-Bryan R, Takai S,
Karin M and Corr M: Caspase 1-independent activation of
interleukin-1beta in neutrophil-predominant inflammation. Arthritis
Rheum. 60:3642–3650. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wang M, Medeiros BC, Erba HP, DeAngelo DJ,
Giles FJ and Swords RT: Targeting protein neddylation: A novel
therapeutic strategy for the treatment of cancer. Expert Opin Ther
Targets. 15:253–264. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Soucy TA, Smith PG, Milhollen MA, Berger
AJ, Gavin JM, Adhikari S, Brownell JE, Burke KE, Cardin DP,
Critchley S, et al: An inhibitor of NEDD8-activating enzyme as a
new approach to treat cancer. Nature. 458:732–736. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Laskin DL: Macrophages and inflammatory
mediators in chemical toxicity: A battle of forces. Chem Res
Toxicol. 22:1376–1385. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Mitchell S, Vargas J and Hoffmann A:
Signaling via the NFκB system. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med.
8:227–241. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|