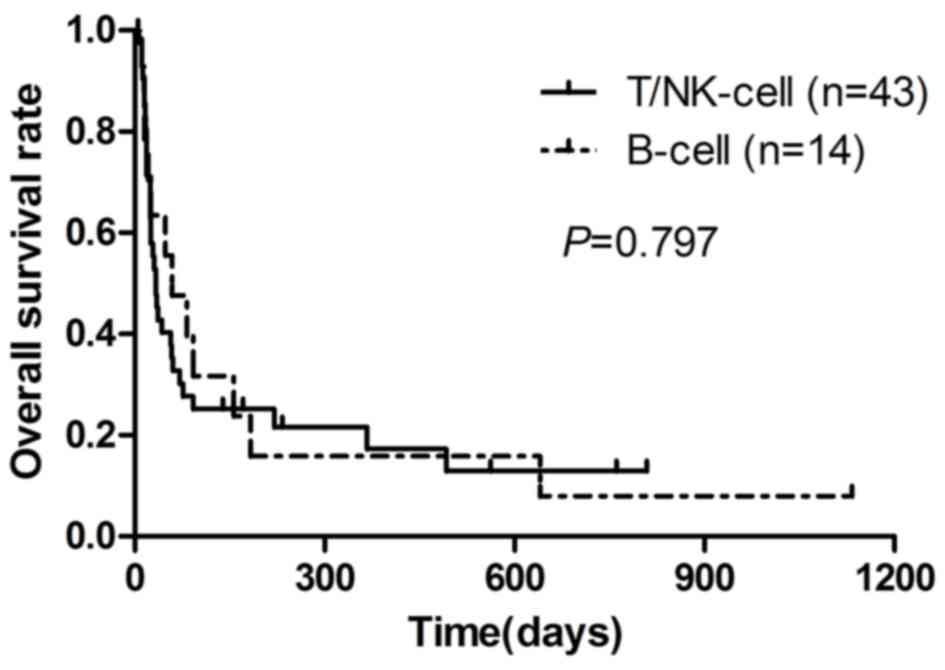
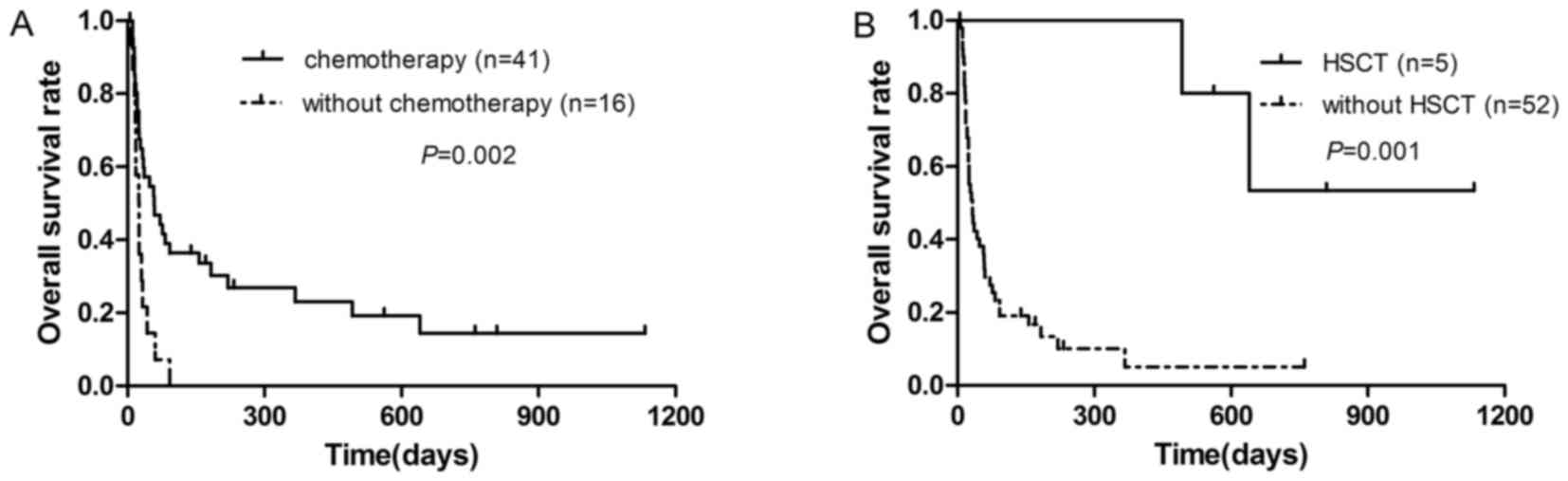
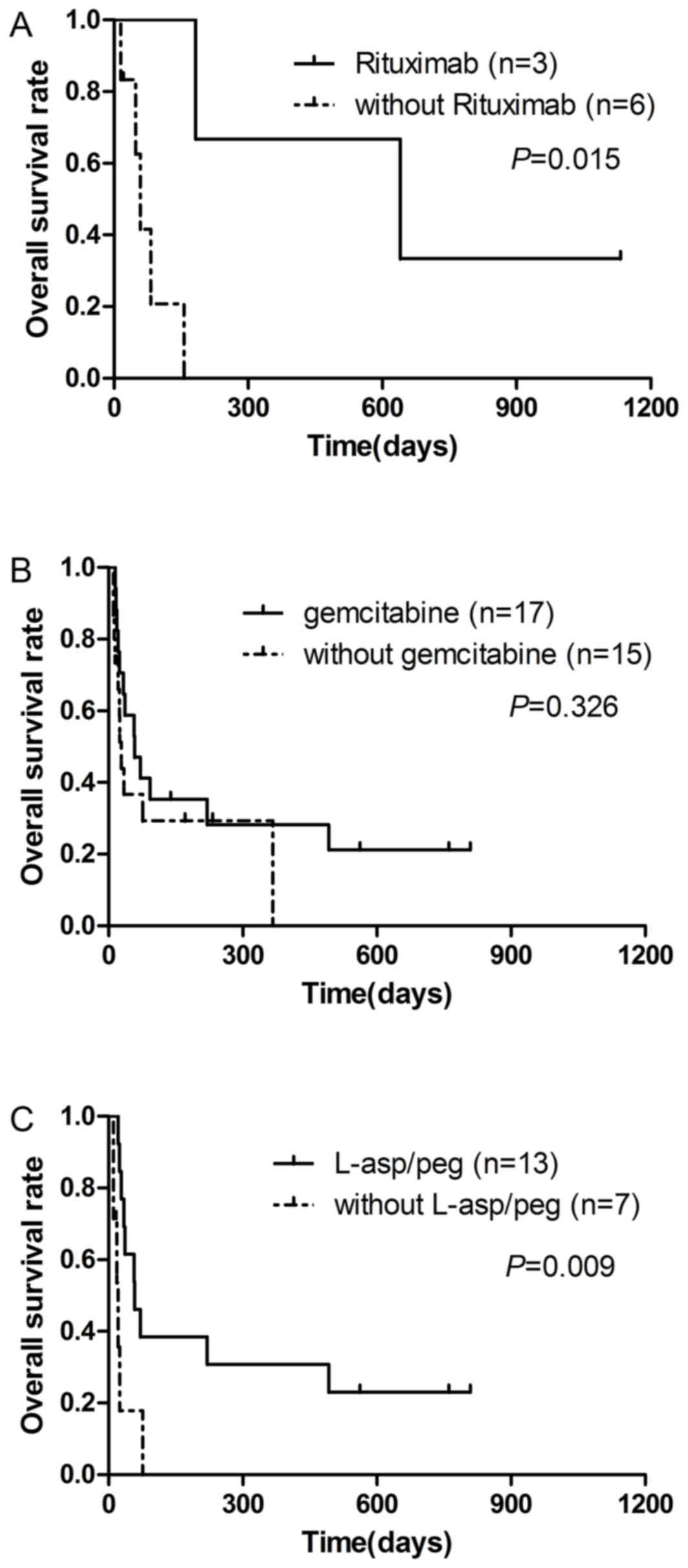
|
1
|
Risdall RJ, McKenna RW, Nesbit ME, Krivit
W, Balfour HJ, Simmons RL and Brunning RD: Virus-associated
hemophagocytic syndrome: A benign histiocytic proliferation
distinct from malignant histiocytosis. Cancer. 3:993–1002. 1979.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Szyper-Kravitz M: The hemophagocytic
syndrome/macrophage activation syndrome: A final common pathway of
a cytokine storm. Isr Med Assoc J. 10:633–634. 2009.
|
|
3
|
Janka GE and Lehmberg K: Hemophagocytic
lymphohistiocytosis: Pathogenesis and treatment. Hematology Am Soc
Hematol Educ Program. 2013:605–611. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Rouphael NG, Talati NJ, Vaughan C,
Cunningham K, Moreira R and Gould C: Infections associated with
haemophagocytic syndrome. Lancet Infect Dis. 12:814–822. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Janka GE and Lehmberg K: Hemophagocytic
syndromes-an update. Blood Rev. 4:135–142. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Han L, Li L, Wu J, Li X, Zhang L, Wang X,
Fu X, Ma W, Sun Z, Zhang X, et al: Clinical features and treatment
of natural killer/T cell lymphoma associated with hemophagocytic
syndrome: Comparison with other T cell lymphoma associated with
hemophagocytic syndrome. Leuk Lymphoma. 9:2048–2055. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Parikh SA, Kapoor P, Letendre L, Kumar S
and Wolanskyj AP: Prognostic factors and outcomes of adults with
hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Mayo Clin Proc. 89:484–492.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Han AR, Lee HR, Park BB, Hwang IG, Park S,
Lee SC, Kim K, Lim HY, Ko YH, Kim SH and Kim WS:
Lymphoma-associated hemophagocytic syndrome: Clinical features and
treatment outcome. Ann Hematol. 86:493–498. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sano H, Kobayashi R, Tanaka J, Hashino S,
Ota S, Torimoto Y, Kakinoki Y, Yamamoto S, Kurosawa M, Hatakeyama
N, et al: Risk factor analysis of non-Hodgkin lymphoma-associated
haemophagocytic syndromes: A multicentre study. Br J Haematol.
165:786–792. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tabata C and Tabata R: Possible prediction
of underlying lymphoma by high sIL-2R/ferritin ratio in
hemophagocytic syndrome. Ann Hematol. 91:63–71. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Seo JJ: Hematopoietic cell transplantation
for hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: Recent advances and
controversies. Blood Res. 50:131–139. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sabattini E, Bacci F, Sagramoso C and
Pileri SA: WHO classification of tumours of haematopoietic and
lymphoid tissues in 2008: An overview. Pathologica. 102:83–87.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Henter JI, Horne A, Arico M, Egeler RM,
Filipovich AH, Imashuku S, Ladisch S, McClain K, Webb D, Winiarski
J and Janka G: HLH-2004: Diagnostic and therapeutic guidelines for
hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Pediatr Blood Cancer.
48:124–131. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Olweny CL: Cotswolds modification of the
Ann Arbor staging system for Hodgkin's disease. J Clin Oncol.
9:15981990.
|
|
15
|
Oken MM, Creech RH, Tormey DC, Horton J,
Davis TE, McFadden ET and Carbone PP: Toxicity and response
criteria of the Eastern cooperative oncology group. Am J Clin
Oncol. 5:649–655. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cheson BD, Pfistner B, Juweid ME, Gascoyne
RD, Specht L, Horning SJ, Coiffier B, Fisher RI, Hagenbeek A, Zucca
E, et al: Revised response criteria for malignant lymphoma. J Clin
Oncol. 25:579–586. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Takahashi N, Chubachi A, Miura I, Nakamura
S and Miura AB: Lymphoma-associated hemophagocytic syndrome in
Japan. Rinsho Ketsueki. 40:542–549. 1999.(In Japanese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yu JT, Wang CY, Yang Y, Wang RC, Chang KH,
Hwang WL and Teng CL: Lymphoma-associated hemophagocytic
lymphohistiocytosis: Experience in adults from a single
institution. Ann Hematol. 11:1529–1536. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Tong H, Ren Y, Liu H, Xiao F, Mai W, Meng
H, Qian W, Huang J, Mao L, Tong Y, et al: Clinical characteristics
of T-cell lymphoma associated with hemophagocytic syndrome:
Comparison of T-cell lymphoma with and without hemophagocytic
syndrome. Leuk Lymphoma. 49:81–87. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Allen CE, Yu X, Kozinetz CA and McClain
KL: Highly elevated ferritin levels and the diagnosis of
hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Pediatr Blood Cancer.
50:1227–1235. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chen YP, Jones D, Chen TY and Chang KC:
Epstein-Barr virus present in T cells or B cells shows differential
effects on hemophagocytic symptoms associated with outcome in
T-cell lymphomas. Leuk Lymphoma. 55:2038–2047. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kwong YL, Pang AW, Leung AY, Chim CS and
Tse E: Quantification of circulating Epstein-Barr virus DNA in
NK/T-cell lymphoma treated with the SMILE protocol: Diagnostic and
prognostic significance. Leukemia. 28:865–870. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Suzuki R, Yamaguchi M, Izutsu K, Yamamoto
G, Takada K, Harabuchi Y, Isobe Y, Gomyo H, Koike T, Okamoto M, et
al: Prospective measurement of Epstein-Barr virus-DNA in plasma and
peripheral blood mononuclear cells of extranodal NK/T-cell
lymphoma, nasal type. Blood. 118:6018–6022. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ohno T, Ueda Y, Nagai K, Takahashi T,
Konaka Y, Takamatsu T, Suzuki T, Sasada M and Uchiyama T; Kyoto
University Hematology/Oncology Study Group: The serum cytokine
profiles of lymphoma-associated hemophagocytic syndrome: A
comparative analysis of B-cell and T-cell/natural killer cell
lymphomas. Int J Hematol. 77:286–294. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chuang HC, Lay JD, Hsieh WC and Su IJ:
Pathogenesis and mechanism of disease progression from
hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis to Epstein-Barr virus-associated
T-cell lymphoma: Nuclear factor-kappa B pathway as a potential
therapeutic target. Cancer Sci. 98:1281–1287. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Barba T, Maucort-Boulch D, Iwaz J, Bohé J,
Ninet J, Hot A, Lega JC, Guérin C, Argaud L, Broussolle C, et al:
Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis in intensive care unit: A
71-case strobe-compliant retrospective study. Medicine (Baltimore).
94:e23182015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Cattaneo C, Oberti M, Skert C, Passi A,
Farina M, Re A, Tozzi P, Borlenghi E and Rossi G: Adult onset
hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis prognosis is affected by
underlying disease and coexisting viral infection: Analysis of a
single institution series of 35 patients. Hematol Oncol.
35:828–834. 2017. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yiu CR, Kao YH, Phipps C and Tan D:
Positron emission tomography findings in patients with
lymphoma-associated haemophagocytic syndrome. Singapore Med J.
7:e156–e159. 2011.
|
|
29
|
Zhang LJ, Xu J, Liu P, Ding CY, Li JY, Qiu
HX and Zhang SJ: The significance of 18F-FDG PET/CT in secondary
hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. J Hematol Oncol. 5:402012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yang YQ, Ding CY, Xu J, Fan L, Wang L,
Tian T, Li TN, Li JY and Xu W: Exploring the role of bone marrow
increased FDG uptake on PET/CT in patients with lymphoma-associated
hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: A reflection of bone marrow
involvement or cytokine storm? Leuk Lymphoma: Jun 19, 1–8, 2015
(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
31
|
Maruoka H, Inoue D, Takiuchi Y, Nagano S,
Arima H, Tabata S, Matsushita A, Ishikawa T, Oita T and Takahashi
T: IP-10/CXCL10 and MIG/CXCL9 as novel markers for the diagnosis of
lymphoma-associated hemophagocytic syndrome. Ann Hematol.
3:393–401. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Henter JI, Arico M, Egeler RM, Elinder G,
Favara BE, Filipovich AH, Gadner H, Imashuku S, Janka-Schaub G,
Komp D, et al: HLH-94: A treatment protocol for hemophagocytic
lymphohistiocytosis. HLH study group of the histiocyte society. Med
Pediatr Oncol. 28:342–347. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Park BB, Kim WS, Suh C, Shin DY, Kim JA,
Kim HG and Lee WS: Salvage chemotherapy of gemcitabine,
dexamethasone, and cisplatin (GDP) for patients with relapsed or
refractory peripheral T-cell lymphomas: A consortium for improving
survival of lymphoma (CISL) trial. Ann Hematol. 94:1845–1851. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Pellegrini C, Dodero A, Chiappella A,
Monaco F, Degl'Innocenti D, Salvi F, Vitolo U, Argnani L, Corradini
P and Zinzani PL; Italian Lymphoma Foundation (Fondazione Italiana
Linfomi Onlus, FIL): A phase II study on the role of gemcitabine
plus romidepsin (GEMRO regimen) in the treatment of
relapsed/refractory peripheral T-cell lymphoma patients. J Hematol
Oncol. 9:382016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Li X, Cui Y, Sun Z, Zhang L, Li L, Wang X,
Wu J, Fu X, Ma W, Zhang X, et al: DDGP versus SMILE in newly
diagnosed advanced natural Killer/T cell lymphoma: A randomized
controlled, multicenter, Open-label study in China. Clin Cancer
Res. 22:5223–5228. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Li L, Zhang C, Zhang L, Li X, Wu JJ, Sun
ZC, Fu XR, Wang XH, Chang Y, Wang R, et al: Efficacy of a
pegaspargase-based regimen in the treatment of newly-diagnosed
extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma. Neoplasma. 61:225–232.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhou Z, Li X, Chen C, Li X, Zhang L, Li L,
Wang X, Ma W, Fu X, Wu J, et al: Effectiveness of gemcitabine,
pegaspargase, cisplatin, and dexamethasone (DDGP) combination
chemotherapy in the treatment of relapsed/refractory extranodal
NK/T cell lymphoma: A retrospective study of 17 patients. Ann
Hematol. 93:1889–1894. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kwong YL, Kim WS, Lim ST, Kim SJ, Tang T,
Tse E, Leung AY and Chim CS: SMILE for natural killer/T-cell
lymphoma: Analysis of safety and efficacy from the Asia lymphoma
study group. Blood. 120:2973–2980. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Trottestam H, Horne A, Arico M, Egeler RM,
Filipovich AH, Gadner H, Imashuku S, Ladisch S, Webb D, Janka G, et
al: Chemoimmunotherapy for hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis:
Long-term results of the HLH-94 treatment protocol. Blood.
118:4577–4584. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Marsh RA, Vaughn G, Kim MO, Li D, Jodele
S, Joshi S, Mehta PA, Davies SM, Jordan MB, Bleesing JJ and
Filipovich AH: Reduced-intensity conditioning significantly
improves survival of patients with hemophagocytic
lymphohistiocytosis undergoing allogeneic hematopoietic cell
transplantation. Blood. 116:5824–5831. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Machaczka M, Nahi H, Karbach H, Klimkowska
M and Hagglund H: Successful treatment of recurrent
malignancy-associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis with a
modified HLH-94 immunochemotherapy and allogeneic stem cell
transplantation. Med Oncol. 29:1231–1236. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Inoue D, Nagai Y, Takiuchi Y, Nagano S,
Arima H, Kimura T, Shimoji S, Mori M, Togami K, Tabata S, et al:
Successful treatment of extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma,
nasal type, complicated by severe hemophagocytic syndrome, with
dexamethasone, methotrexate, ifosfamide, L-asparaginase, and
etoposide chemotherapy followed by autologous stem cell transplant.
Leuk Lymphoma. 51:720–723. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
George MR: Hemophagocytic
lymphohistiocytosis: Review of etiologies and management. J Blood
Med. 5:69–86. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|