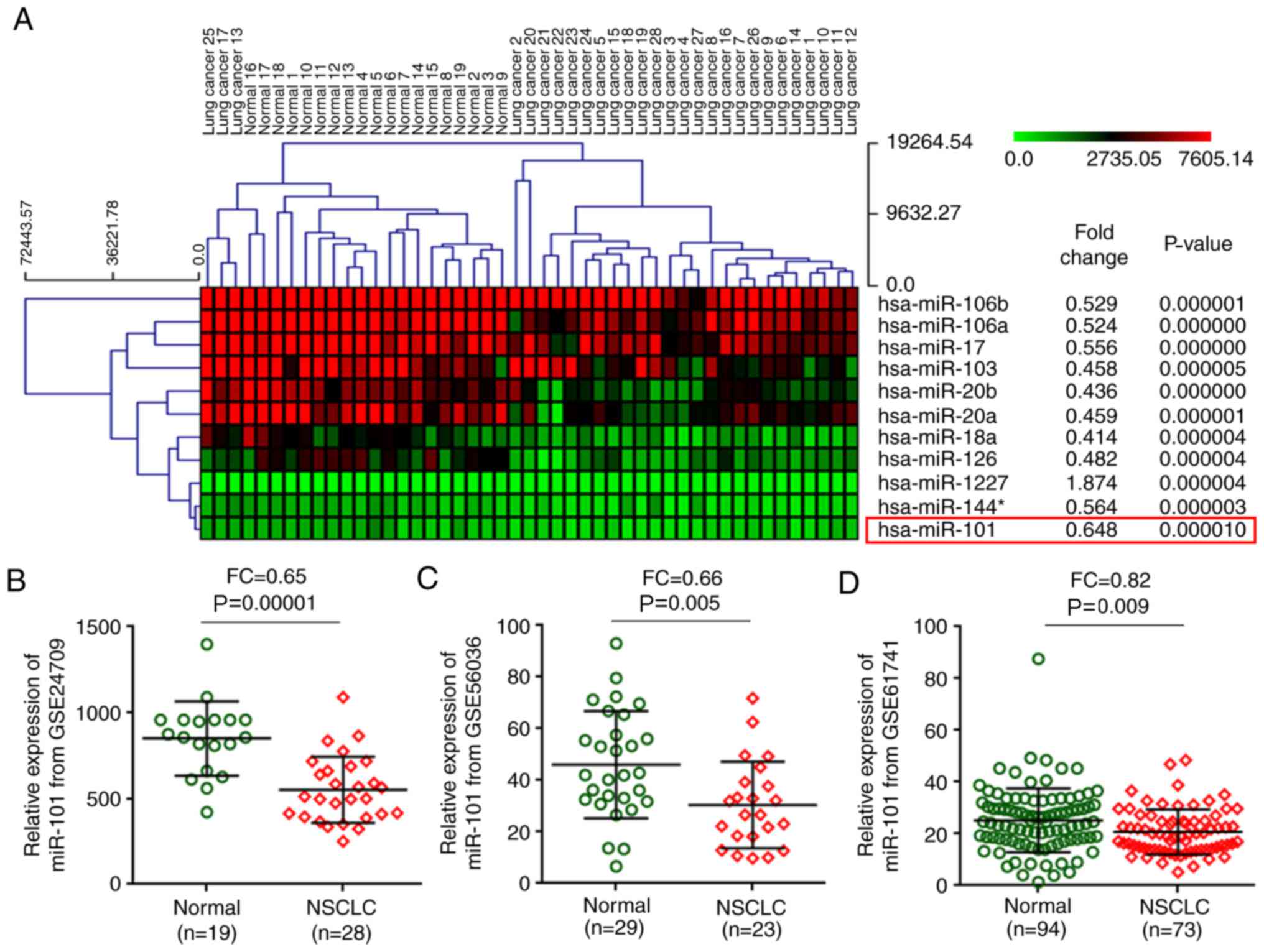
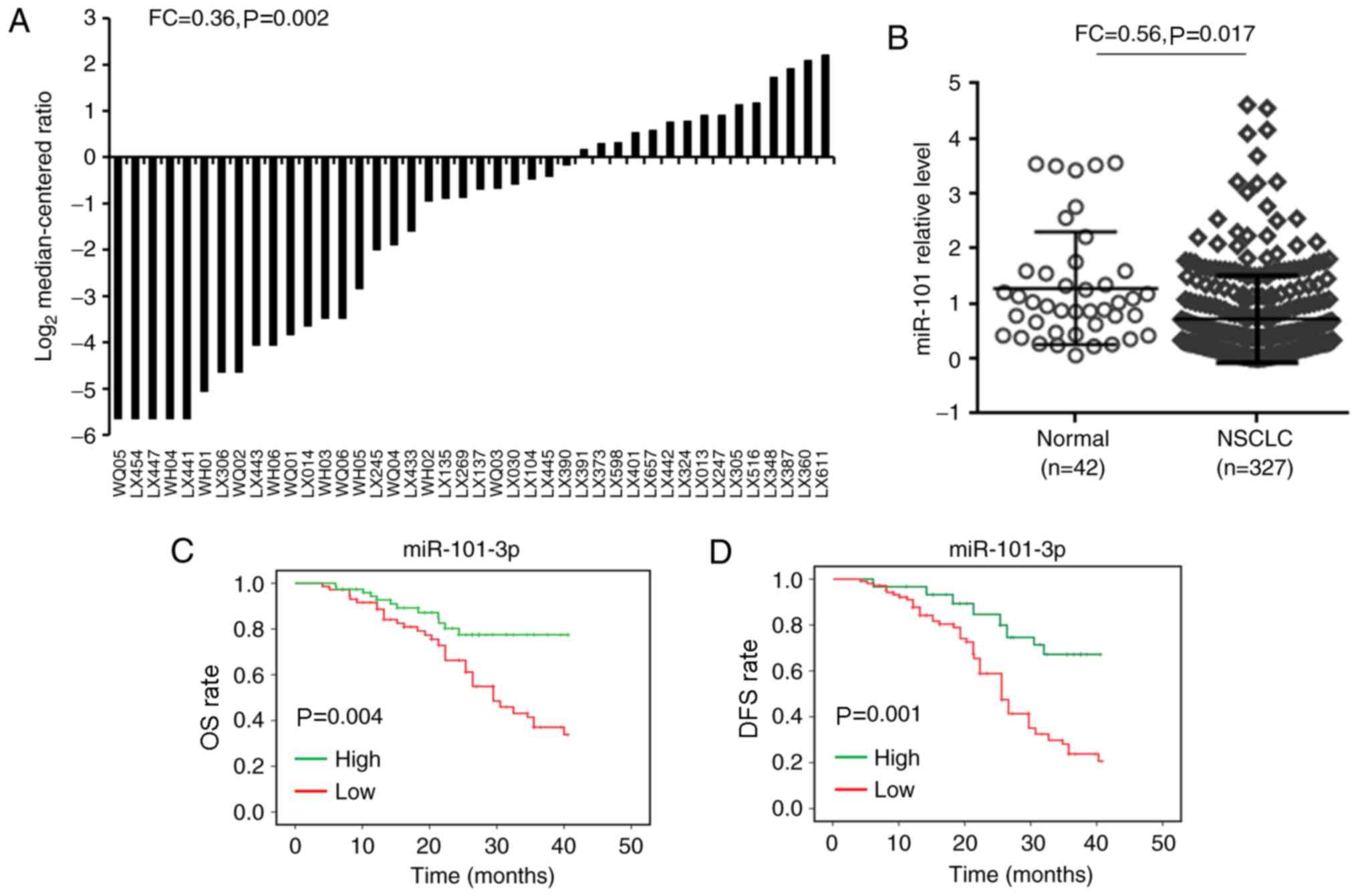
|
1
|
Lu G, Fu D, Jia C, Chai L, Han Y, Liu J,
Wu T, Xie R, Chang Z, Yang H, et al: Reduced miR-105-1 levels are
associated with poor survival of patients with non-small cell lung
cancer. Oncol Lett. 14:7842–7848. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhang T, Rong N, Chen J, Zou C, Jing H,
Zhu X and Zhang W: SIRT1 expression is associated with the
chemotherapy response and prognosis of patients with advanced
NSCLC. PLoS One. 8:e791622013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hou L, Luo P, Ma Y, Jia C, Yu F, Lv Z, Wu
C and Fu D: MicroRNA-125a-3p downregulation correlates with
tumorigenesis and poor prognosis in patients with non-small cell
lung cancer. Oncol Lett. 14:4441–4448. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hou LK, Ma YS, Han Y, Lu GX, Luo P, Chang
ZY, Xie RT, Yang HQ, Chai L, Cai MX, et al: Association of
microRNA-33a molecular signature with non-small cell lung cancer
diagnosis and prognosis after chemotherapy. PLoS One.
12:e01704312017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yu F, Liu JB, Wu ZJ, Xie WT, Zhong XJ, Hou
LK, Wu W, Lu HM, Jiang XH, Jiang JJ, et al: Tumor suppressive
microRNA-124a inhibits stemness and enhances gefitinib sensitivity
of non-small cell lung cancer cells by targeting ubiquitin-specific
protease 14. Cancer Lett. 427:74–84. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ma YS, Wu TM, Lv ZW, Lu GX, Cong XL, Xie
RT, Yang HQ, Chang ZY, Sun R, Chai L, et al: High expression of
miR-105-1 positively correlates with clinical prognosis of
hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting oncogene NCOA1. Oncotarget.
8:11896–11905. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Xu C, Haque F, Jasinski DL, Binzel DW, Shu
D and Guo P: Favorable biodistribution, specific targeting and
conditional endosomal escape of RNA nanoparticles in cancer
therapy. Cancer Lett. 414:57–70. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Salzman DW, Nakamura K, Nallur S, Dookwah
MT, Metheetrairut C, Slack FJ and Weidhaas JB: miR-34 activity is
modulated through 5′-end phosphorylation in response to DNA damage.
Nat Commun. 7:109542016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Persson H, Søkilde R, Häkkinen J, Pirona
AC, Vallon-Christersson J, Kvist A, Mertens F, Borg Å, Mitelman F,
Höglund M and Rovira C: Frequent miRNA-convergent fusion gene
events in breast cancer. Nat Commun. 8:7882017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Xie RT, Cong XL, Zhong XM, Luo P, Yang HQ,
Lu GX, Luo P, Chang ZY, Sun R, Wu TM, et al: MicroRNA-33a
downregulation is associated with tumorigenesis and poor prognosis
in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Lett.
15:4571–4577. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Mi Y, Zhang D, Jiang W, Weng J, Zhou C,
Huang K, Tang H, Yu Y, Liu X, Cui W, et al: miR-181a-5p promotes
the progression of gastric cancer via RASSF6-mediated MAPK
signalling activation. Cancer Lett. 389:11–22. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cutrona G, Matis S, Colombo M, Massucco C,
Baio G, Valdora F, Emionite L, Fabris S, Recchia AG, Gentile M, et
al: Effects of miRNA-15 and miRNA-16 expression replacement in
chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Implication for therapy. Leukemia.
31:1894–1904. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Linnstaedt SD, Gottwein E, Skalsky RL,
Luftig MA and Cullen BR: Virally induced cellular microRNA miR-155
plays a key role in B-cell immortalization by Epstein-Barr virus. J
Virol. 84:11670–11678. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yanaihara N, Caplen N, Bowman E, Seike M,
Kumamoto K, Yi M, Stephens RM, Okamoto A, Yokota J, Tanaka T, et
al: Unique microRNA molecular profiles in lung cancer diagnosis and
prognosis. Cancer Cell. 9:189–198. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Othman N and Nagoor NH: miR-608 regulates
apoptosis in human lung adenocarcinoma via regulation of AKT2. Int
J Oncol. 51:1757–1764. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang X, He X, Liu Y, Zhang H, Chen H, Guo
S and Liang Y: MiR-101-3p inhibits the growth and metastasis of
non-small cell lung cancer through blocking PI3K/AKT signal pathway
by targeting MALAT-1. Biomed Pharmacother. 93:1065–1073. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang H, Wang L, Zhang G, Lu C, Chu H, Yang
R and Zhao G: MALAT1/miR-101-3p/MCL1 axis mediates cisplatin
resistance in lung cancer. Oncotarget. 9:7501–7512. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu C, Fu H, Liu X, Lei Q, Zhang Y, She X,
Liu Q, Liu Q, Sun Y, Li G and Wu M: LINC00470 coordinates the
epigenetic regulation of ELFN2 to distract GBM cell autophagy. Mol
Ther. 26:2267–2281. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wakasugi H, Takahashi H, Niinuma T,
Kitajima H, Oikawa R, Matsumoto N, Takeba Y, Otsubo T, Takagi M,
Ariizumi Y, et al: Dysregulation of miRNA in chronic hepatitis B is
associated with hepatocellular carcinoma risk after nucleos(t)ide
analogue treatment. Cancer Lett. 434:91–100. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cao L, Chen Y, Zhang M, Xu DQ, Liu Y, Liu
T, Liu SX and Wang P: Identification of hub genes and potential
molecular mechanisms in gastric cancer by integrated bioinformatics
analysis. PeerJ. 6:e51802018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Keller A, Leidinger P, Vogel B, Backes C,
ElSharawy A, Galata V, Mueller SC, Marquart S, Schrauder MG, Strick
R, et al: miRNAs can be generally associated with human pathologies
as exemplified for miR-144. BMC Med. 12:2242014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Leidinger P, Brefort T, Backes C, Krapp M,
Galata V, Beier M, Kohlhaas J, Huwer H, Meese E and Keller A:
High-throughput qRT-PCR validation of blood microRNAs in non-small
cell lung cancer. Oncotarget. 7:4611–4623. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Fujita Y, Yagishita S, Hagiwara K,
Yoshioka Y, Kosaka N, Takeshita F, Fujiwara T, Tsuta K, Nokihara H,
Tamura T, et al: The clinical relevance of the
miR-197/CKS1B/STAT3-mediated PD-L1 network in chemoresistant
non-small-cell lung cancer. Mol Ther. 23:717–727. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chen C, Ridzon DA, Broomer AJ, Zhou Z, Lee
DH, Nguyen JT, Barbisin M, Xu NL, Mahuvakar VR, Andersen MR, et al:
Real-time quantification of microRNAs by stem-loop RT-PCR. Nucleic
Acids Res. 33:e1792005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta (T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liang Z, Kong R, He Z, Lin LY, Qin SS,
Chen CY, Xie ZQ, Yu F, Sun GQ, Li CG, et al: High expression of
miR-493-5p positively correlates with clinical prognosis of non
small cell lung cancer by targeting oncogene ITGB1. Oncotarget.
8:47389–47399. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang B, Fu D, Xu Q, Cong X, Wu C, Zhong
X, Ma Y, Lv Z, Chen F, Han L, et al: The senescence-associated
secretory phenotype is potentiated by feedforward regulatory
mechanisms involving Zscan4 and TAK1. Nat Commun. 9:17232018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Huang Q, Zhang XW, Ma YS, Lu GX, Xie RT,
Yang HQ, Lv ZW, Zhong XM, Liu T, Huang SX, et al: Up-regulated
microRNA-299 corrected with poor prognosis of glioblastoma
multiforme patients by targeting ELL2. Jpn J Clin Oncol.
47:590–596. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chang TH, Tsai MF, Gow CH, Wu SG, Liu YN,
Chang YL, Yu SL, Tsai HC, Lin SW, Chen YW, et al: Upregulation of
microRNA-137 expression by Slug promotes tumor invasion and
metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer cells through suppression
of TFAP2C. Cancer Lett. 402:190–202. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zheng HB, Zheng XG and Liu BP: miRNA-101
inhibits ovarian cancer cells proliferation and invasion by
down-regulating expression of SOCS-2. Int J Clin Exp Med.
8:20263–20270. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tsai CH, Yang DY, Lin CY, Chen TM, Tang CH
and Huang YL: Sphingosine-1-phosphate suppresses chondrosarcoma
metastasis by upregulation of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase
3 through suppressing miR-101 expression. Mol Oncol. 11:1380–1398.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang C, Lu S, Jiang J, Jia X, Dong X and
Bu P: Hsa-microRNA-101 suppresses migration and invasion by
targeting Rac1 in thyroid cancer cells. Oncol Lett. 8:1815–1821.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Li JT, Jia LT, Liu NN, Zhu XS, Liu QQ,
Wang XL, Yu F, Liu YL, Yang AG and Gao CF: MiRNA-101 inhibits
breast cancer growth and metastasis by targeting CX chemokine
receptor 7. Oncotarget. 6:30818–30830. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Shaker O, Alhelf M, Morcos G and
Elsharkawy AL: miRNA-101-1 and miRNA-221 expressions and their
polymorphisms as biomarkers for early diagnosis of hepatocellular
carcinoma. Infect Genet Evol. 51:173–181. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lv P, Zhang P, Li X and Chen Y: Micro
ribonucleic acid (RNA)-101 inhibits cell proliferation and invasion
of lung cancer by regulating cyclooxygenase-2. Thorac Cancer.
6:778–784. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lei YM, Zu YF, Wang J, Bai S, Shi YF, Shi
R, Duan J, Cui D, Chen J, Xiang Y and Dong J:
Interleukin-1β-mediated suppression of microRNA-101 and
upregulation of enhancer of zeste homolog 2 is involved in
particle-induced lung cancer. Med Oncol. 32:3872015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wan X, Kong Z, Chu K, Yi C, Hu J, Qin R,
Zhao C, Fu F, Wu H, Li Y and Huang Y: Co-expression analysis
revealed PTCH1-3′UTR promoted cell migration and invasion by
activating miR-101-3p/SLC39A6 axis in non-small cell lung cancer:
Implicating the novel function of PTCH1. Oncotarget. 9:4798–4813.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Edge SB and Compton CC: The American Joint
Committee on Cancer: The 7th edition of the AJCC cancer staging
manual and the future of TNM. Ann Surg Oncol. 17:1471–1474. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|