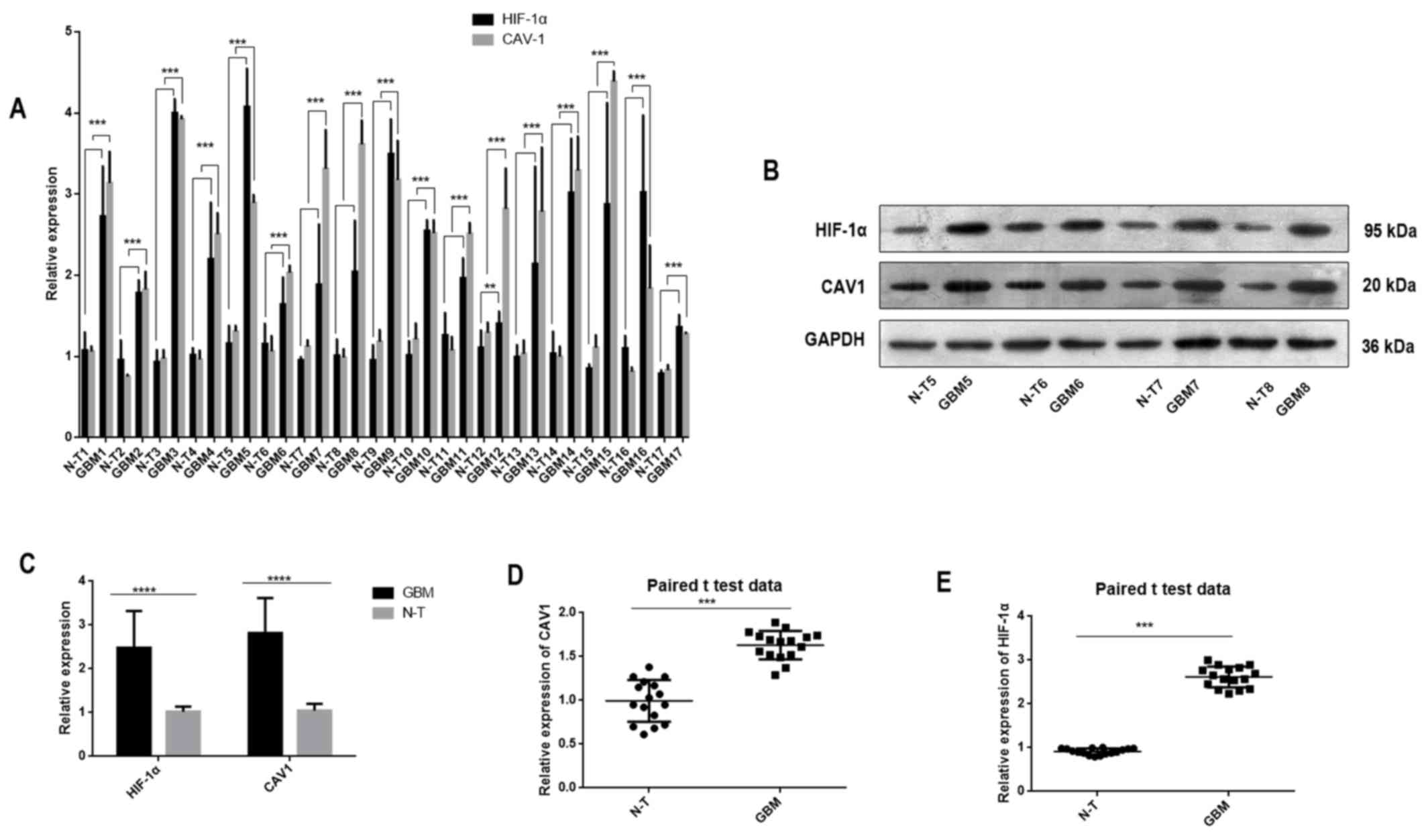
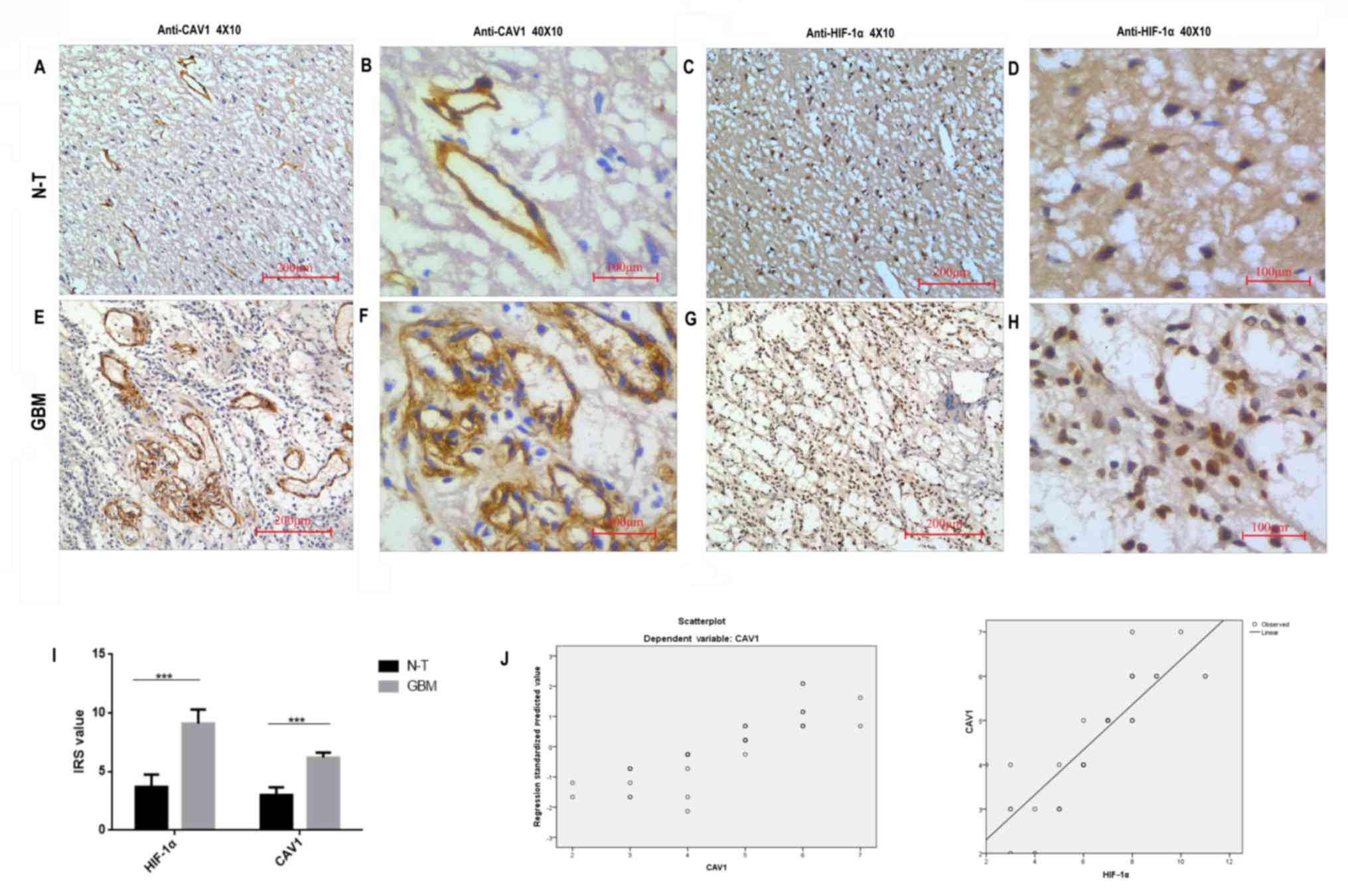
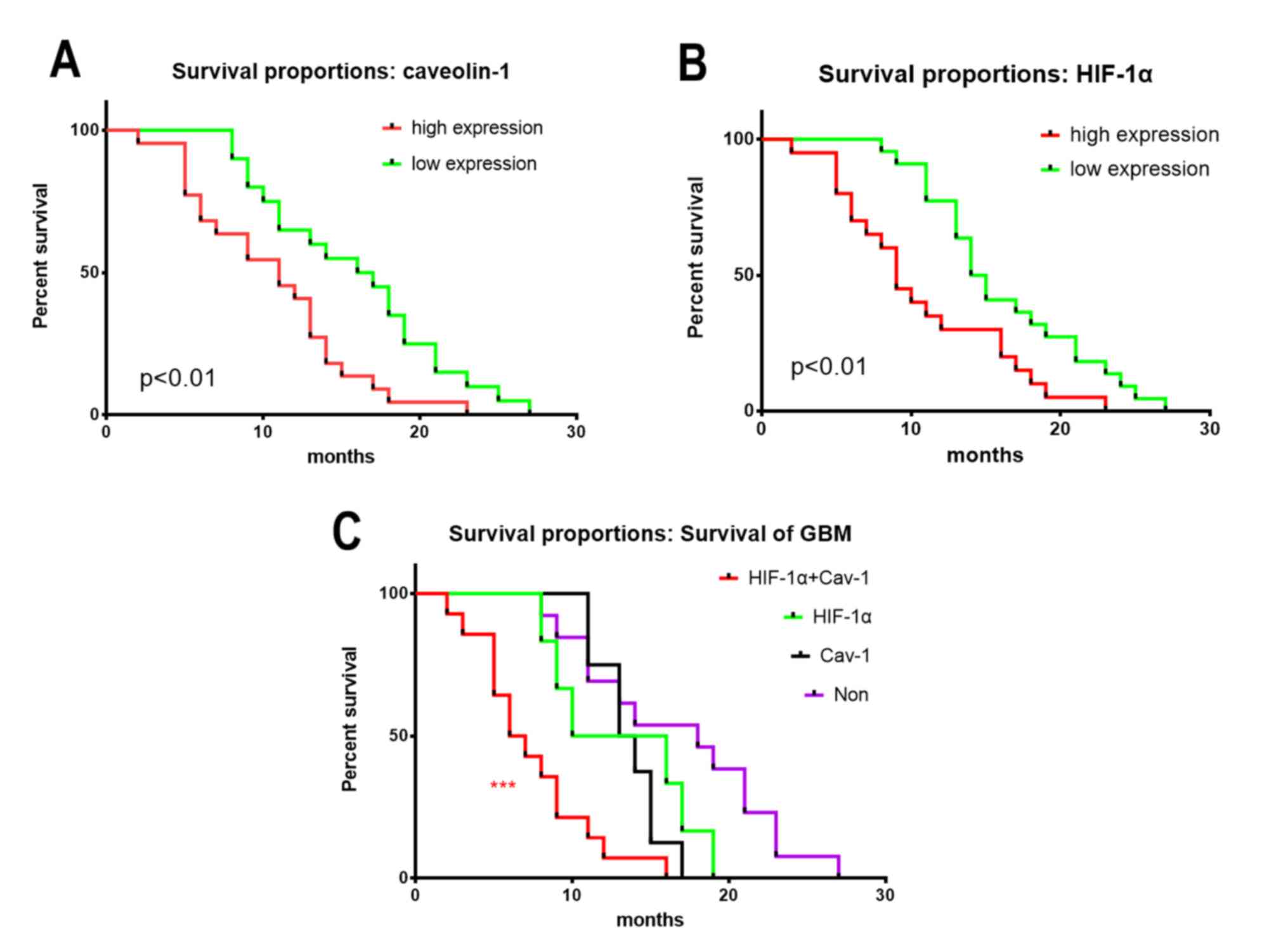
|
1
|
Kaya V, Yıldırım M, Yazıcı G, Yalçın AY,
Orhan N and Güzel A: Prognostic significance of indicators of
systemic inflammatory responses in glioblastoma multiforme
patients. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 18:3287–3291. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Koshy M, Villano JL, Dolecek TA, Howard A,
Mahmood U, Chmura SJ, Weichselbaum RR and McCarthy BJ: Improved
survival time trends for glioblastoma multiforme using the SEER 17
population-based registries. J Neurooncol. 107:207–212. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Waitkus M, Diplas B and Yan H: Isocitrate
dehydrogenase mutations in gliomas. Neuro Oncol. 18:16–26. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jun JC, Rathore A, Younas H, Gilkes D and
Polotsky VY: Hypoxia-inducible factors and cancer. Curr Sleep Med
Rep. 3:1–10. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Qin J, Liu Y, Lu Y, Liu M, Li M, Li J and
Wu L: Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha promotes cancer stem
cells-like properties in human ovarian cancer cells by upregulating
SIRT1 expression. Sci Rep. 7:105922017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Said HM, Hagemann C, Staab A, Stojic J,
Kühnel S, Vince GH, Flentje M, Roosen K and Vordermark D:
Expression patterns of the hypoxia-related genes osteopontin, CA9,
erythropoietin, VEGF and HIF-1alpha in human glioma in vitro and in
vivo. Radiother Oncol. 83:398–405. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Agrawal R, Pandey P, Jha P, Dwivedi V,
Sarkar C and Kulshreshtha R: Hypoxic signature of microRNAs in
glioblastoma: Insights from small RNA deep sequencing. BMC
Genomics. 15:6862014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kaelin WG Jr: Molecular basis of the VHL
hereditary cancer syndrome. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:673–682. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mao X, Wong SY, Tse EY, Ko FC, Tey SK,
Yeung YS, Man K, Lo RC, Ng IO and Yam JW: Mechanisms through which
hypoxia-induced caveolin-1 drives tumorigenesis and metastasis in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. 76:7242–7253. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Goetz JG, Minguet S, Navarro-Lérida I,
Lazcano JJ, Samaniego R, Calvo E, Tello M, Osteso-Ibáñez T,
Pellinen T, Echarri A, et al: Biomechanical remodeling of the
microenvironment by stromal caveolin-1 favors tumor invasion and
metastasis. Cell. 146:148–163. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang Y, Roche O, Xu C, Moriyama EH, Heir
P, Chung J, Roos FC, Chen Y, Finak G, Milosevic M, et al: Hypoxia
promotes ligand-independent EGF receptor signaling via
hypoxia-inducible factor-mediated upregulation of caveolin-1. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:4892–4897. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kannan A, Krishnan A, Ali M, Subramaniam
S, Halagowder D and Sivasithamparam ND: Caveolin-1 promotes gastric
cancer progression by up-regulating epithelial to mesenchymal
transition by crosstalk of signalling mechanisms under hypoxic
condition. Eur J Cancer. 50:204–15. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hoshide R and Jandial R: 2016 world health
organization classification of central nervous system tumors: An
Era of molecular biology. World Neurosurg. 94:561–562. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Milani M, Venturini S, Bonardi S, Allevi
G, Strina C, Cappelletti MR, Corona SP, Aguggini S, Bottini A,
Berruti A, et al: Hypoxia-related biological markers as predictors
of epirubicin-based treatment responsiveness and resistance in
locally advanced breast cancer. Oncotarget. 8:78870–78881. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Khan MN, Haggag YA, Lane ME, McCarron PA
and Tambuwala MM: Polymeric nano-encapsulation of curcumin enhances
its anti-cancer activity in breast (MDA-MB231) and lung (A549)
cancer cells through reduction in expression of HIF-1α and nuclear
p65 (Rel A). Curr Drug Deliv. 15:286–295. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li W, Zong S, Shi Q, Li H, Xu J and Hou F:
Hypoxia-induced vasculogenic mimicry formation in human colorectal
cancer cells: Involvement of HIF-1a, claudin-4, and E-cadherin and
vimentin. Sci Rep. 6:375342016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cavallo F, De Giovanni C, Nanni P, Forni G
and Lollini PL: 2011: The immune hallmarks of cancer. Cancer
Immunol Immunother. 60:319–26. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cai FF, Xu C, Pan X, Cai L, Lin XY, Chen S
and Biskup E: Prognostic value of plasma levels of HIF-1a and
PGC-1a in breast cancer. Oncotarget. 7:77793–77806. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bourseau-Guilmain E, Menard JA, Lindqvist
E, Indira Chandran V, Christianson HC, Cerezo Magaña M, Lidfeldt J,
Marko-Varga G, Welinder C and Belting M: Hypoxia regulates global
membrane protein endocytosis through caveolin-1 in cancer cells.
Nat Commun. 7:113712016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Le PU, Guay G, Altschuler Y and Nabi IR:
Caveolin-1 is a negative regulator of caveolae-mediated endocytosis
to the endoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 277:3371–3379. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Shvets E, Ludwig A and Nichols BJ: News
from the caves: Update on the structure and function of caveolae.
Curr Opin Cell Biol. 29:99–106. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Svensson KJ, Christianson HC, Wittrup A,
Bourseau-Guilmain E, Lindqvist E, Svensson LM, Mörgelin M and
Belting M: Exosome uptake depends on ERK1/2-heat shock protein 27
signaling and lipid Raft-mediated endocytosis negatively regulated
by caveolin-1. J Biol Chem. 288:17713–17724. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|