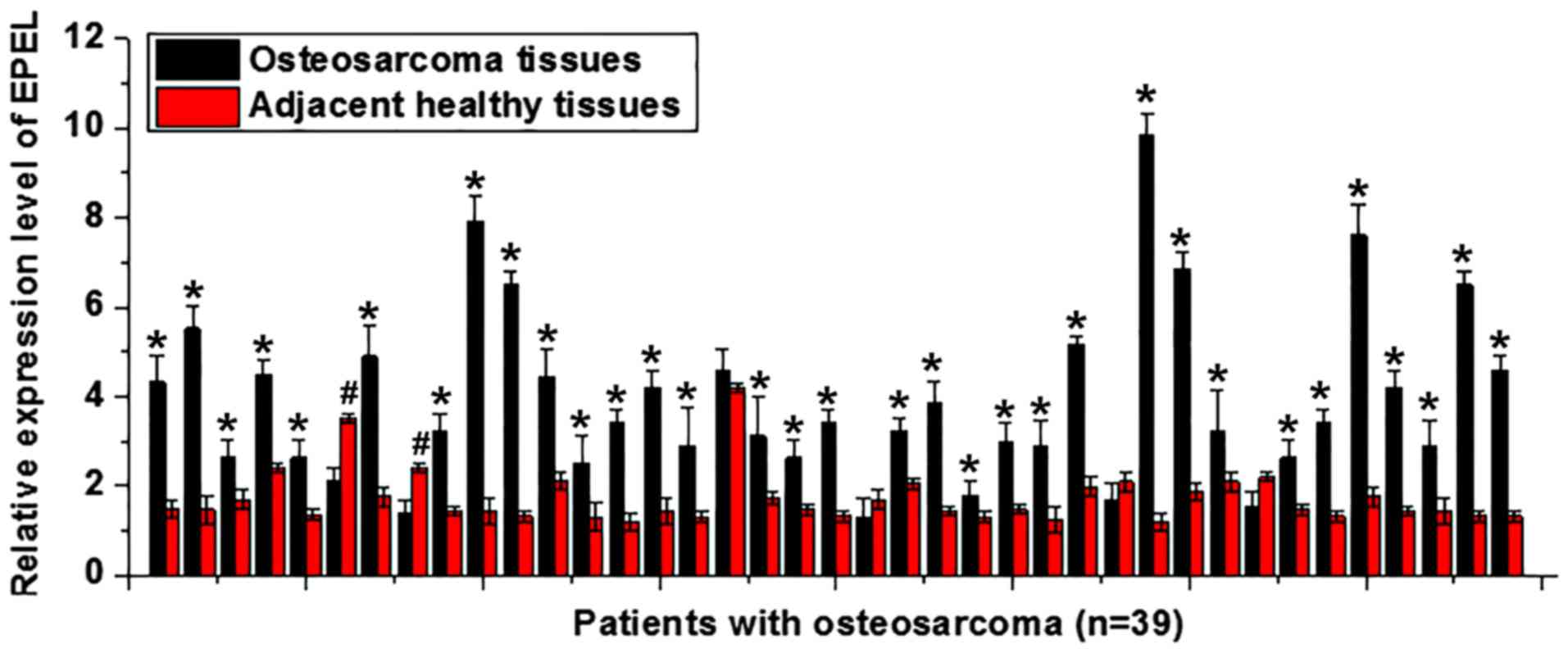
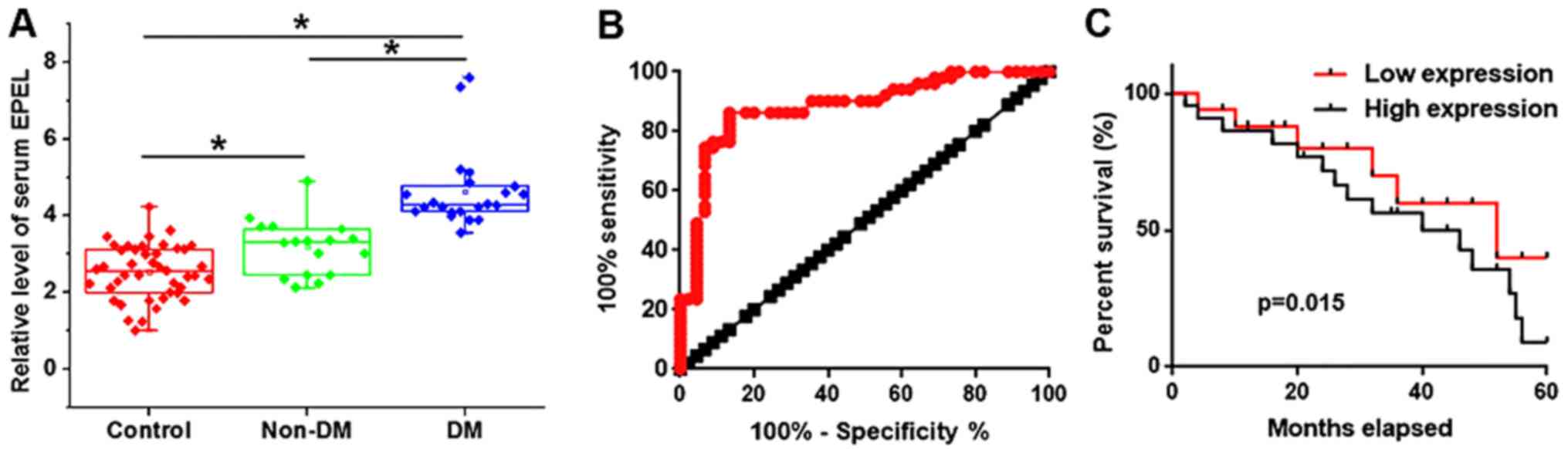
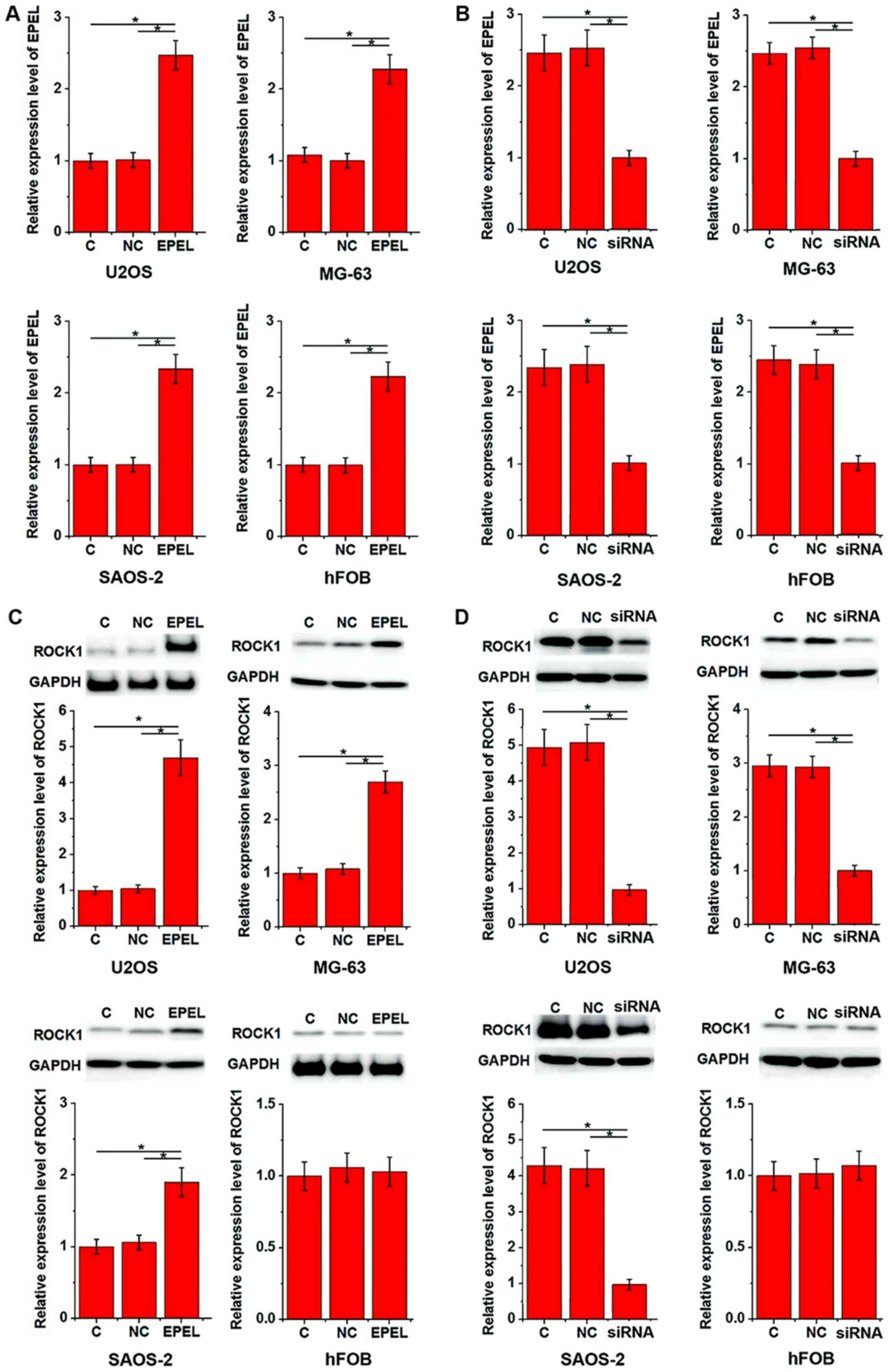
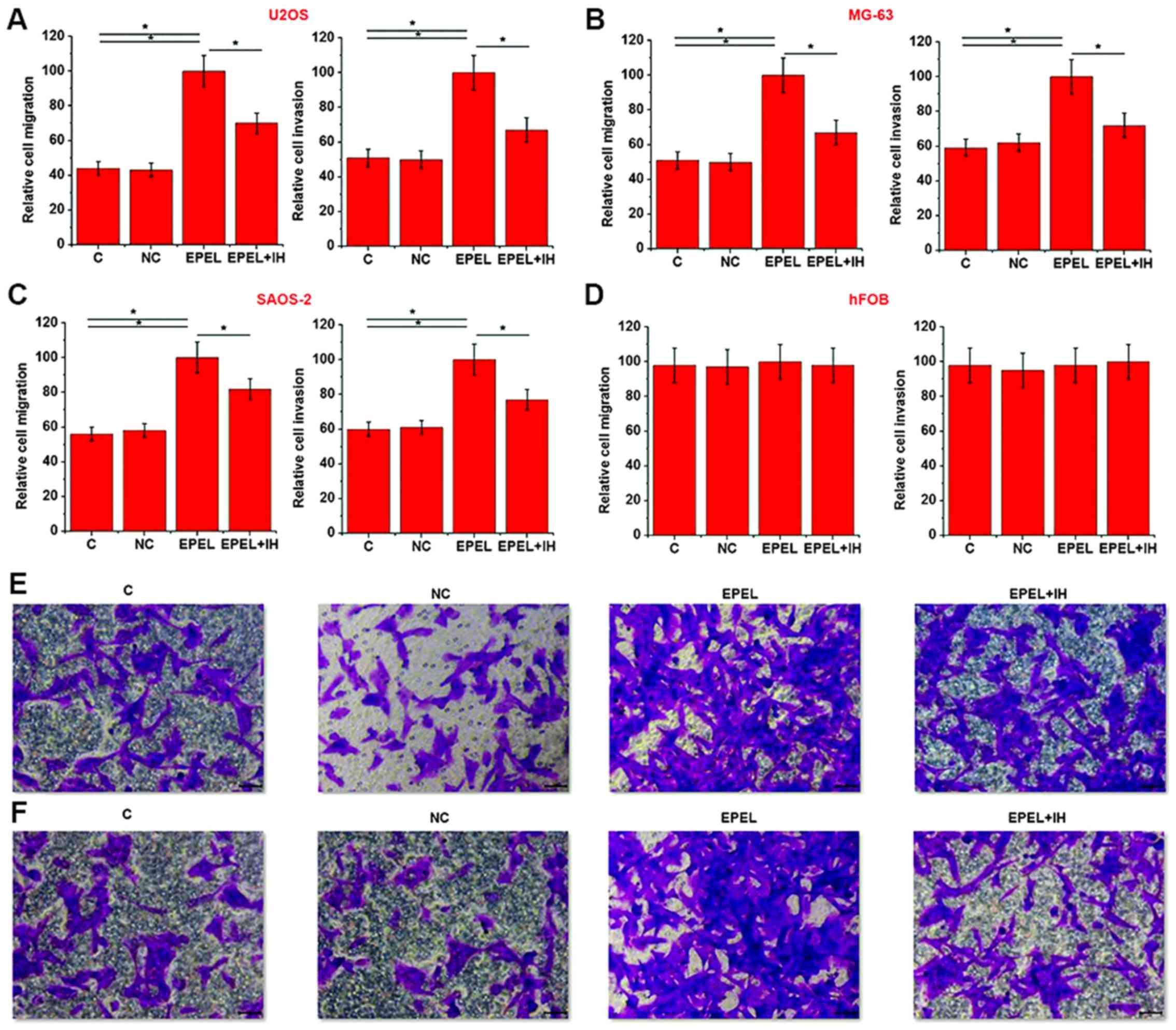
|
1
|
Botter SM, Neri D and Fuchs B: Recent
advances in osteosarcoma. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 16:15–23. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gattia M, Solari A, Pattarozzi A,
Campanella C, Thellung S, Maniscalco L, De Maria R, Würth R,
Corsaro A, Bajetto A, et al: In vitro and in vivo characterization
of stem-like cells from canine osteosarcoma and assessment of drug
sensitivity. Exp Cell Res. 363:48–64. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bielack SS, Kempf-Bielack B, Delling G,
Exner GU, Flege S, Helmke K, Kotz R, Salzer-Kuntschik M, Werner M,
Winkelmann W, et al: Prognostic factors in high-grade osteosarcoma
of the extremities or trunk: An analysis of 1,702 patients treated
on neoadjuvant cooperative osteosarcoma study group protocols. J
Clin Oncol. 20:776–790. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Luetke A, Meyers PA, Lewis I and Juergens
H: Osteosarcoma treatment-where do we stand? A state of the art
review. Cancer Treat Rev. 40:523–532. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kansara M and Thomas DM: Molecular
pathogenesis of osteosarcoma. DNA Cell Biol. 26:1–18. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Li JP, Liu LH, Li J, Chen Y, Jiang XW,
Ouyang YR, Liu YQ, Zhong H, Li H and Xiao T: Microarray expression
profile of long noncoding RNAs in human osteosarcoma. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 433:200–206. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Gao JZ, Li J, DU JL and Li XL: Long
non-coding RNA HOTAIR is a marker for hepatocellular carcinoma
progression and tumor recurrence. Oncol Lett. 11:1791–1798. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ning S, Zhang J, Wang P, Zhi H, Wang J,
Liu Y, Gao Y, Guo M, Yue M, Wang L and Li X: Lnc2Cancer: A manually
curated database of experimentally supported lncRNAs associated
with various human cancers. Nucleic Acids Res. 44:D980–D985. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Augoff K, McCue B, Plow EF and
Sossey-Alaoui K: miR-31 and its host gene lncRNA LOC554202 are
regulated by promoter hypermethylation in triple-negative breast
cancer. Mol Cancer. 11:52012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang Y, Zhao W and Fu Q: miR-335
suppresses migration and invasion by targeting ROCK1 in
osteosarcoma cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 384:105–111. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Harting MT, Blakely ML, Jaffe N, Cox CS
Jr, Hayes-Jordan A, Benjamin RS, Raymond AK, Andrassy RJ and Lally
KP: Long-term survival after aggressive resection of pulmonary
metastases among children and adolescents with osteosarcoma. J
Pediatr Surg. 41:194–199. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hori SS and Gambhir SS: Mathematical model
identifies blood biomarker-based early cancer detection strategies
and limitations. Sci Transl Med. 3:109ra–116ra. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Grammatikakis I, Panda AC, Abdelmohsen K
and Gorospe M: Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) and the molecular
hallmarks of aging. Aging (Albany NY). 6:992–1009. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mayfield RD: Emerging roles for ncRNAs in
alcohol use disorders. Alcohol. 60:31–39. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang J, Qiu M, Xu Y, Li M, Dong G, Mao Q,
Yin R and Xu L: Long noncoding RNA CCAT2 correlates with smoking in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 36:5523–5528.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Rath N and Olson MF: Rho-associated
kinases in tumorigenesis: Re-considering ROCK inhibition for cancer
therapy. EMBO Rep. 13:900–908. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhou X, Wei M and Wang W: MicroRNA-340
suppresses osteosarcoma tumor growth and metastasis by directly
targeting ROCK1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 437:653–658. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liu X, Choy E, Hornicek FJ, Yang S, Yang
C, Harmon D, Mankin H and Duan Z: ROCK1 as a potential therapeutic
target in osteosarcoma. J Orthop Res. 29:1259–1266. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li E, Zhang J, Yuan T and Ma B: MiR-145
inhibits osteosarcoma cells proliferation and invasion by targeting
ROCK1. Tumour Biol. 35:7645–7650. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|