Introduction
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor-associated
factors (TRAFs) have emerged as the major signal transducers for
the TNF receptor (TNFR) superfamily and the interleukin-1
receptor/Toll-like receptor superfamily. TRAFs interact directly or
indirectly with TNFRs to regulate signaling events, including the
activation of nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) and c-Jun N-terminal kinase
(JNK) (1,2). TRAFs collectively play important
roles, including actions in adaptive and innate immunity, embryonic
development, the stress response and bone metabolism. These
functions are mediated by TRAFs through the induction of cell
survival, proliferation, differentiation and death (3–8).
TRAF4 shares most sequence similarity with
Drosophila TRAF1, an adapter molecule critical for JNK
activation and eye development in the fruit fly (9). Originally identified as a protein
localized in the nuclei of breast carcinoma cells, TRAF4 has also
been previously detected in the cytoplasm (10–12).
Although in vivo studies have shown that TRAF4 is involved
in important biological functions (4,8,10), how
it functions at the molecular level remains elusive.
Our previous study detected the expression of TRAF4
in normal and cancerous breast tissues. The results demonstrated
that the TRAF4 nuclei positive rate in normal breast tissue is
significantly higher than in non-invasive (P<0.01) and invasive
(P<0.05) ductal carcinomas (13).
The present study investigated the expression and
location of TRAF4 in breast cancer cells and the biological
function of TRAF4 in MCF-7 cells.
Materials and methods
Cell culture and treatment
The human normal MCF-10A breast cell line and the
human MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cell lines were obtained
from the American Type Culture Collection (Manassas, VA, USA).
Normal MCF-10A breast cells were cultured in Dulbecco’s modified
Eagle’s medium (DMEM)/F12 (1:1) supplemented with 5% equine serum,
10 μg/ml insulin and 20 ng/ml epidermal growth factor. MDA-MB-231
breast cancer cells were cultured in L15 supplemented with 10%
fetal bovine serum (FBS) and 100 units penicillin-streptomycin.
MCF-7 was routinely cultured in DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS and
100 units penicillin-streptomycin. All the cells were cultured at
37°C with 5% CO2 in a humidified incubator.
Western blot analysis
Samples (50 μg) were separated by SDS-PAGE and
transferred to a polyvinylidene fluoride membrane. The membrane was
blocked with 5% skimmed milk and incubated overnight at 4°C with
the primary antibodies. Next, the membranes were incubated in the
secondary antibodies for 2 h at room temperature with slight
agitation. The ECL western blotting detection system (Amersham
Pharmacia Biotech, Amersham, UK) was used for their detection.
Antibodies
The membranes for western blotting were incubated
with mouse anti-human monoclonal antibodies against TRAF4 (1:1,000;
BD Biosciences, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA), NF-κB p65 (1:1,000;
Beyotime Institute of Biotechnology, Haimen, China), lamin B1
(1:500; Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc., Santa Cruz, CA, USA) and
β-actin (1:1,000; Santa Cruz Biotechnology Inc.), followed by
horseradish peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibody (Santa Cruz
Biotechnology Inc.).
Immunofluorescence staining
Cells grown on glass coverslips were fixed with
ice-cold 4% paraformaldehyde for 15 min at −20°C, followed by
permeabilization with 0.2% Triton X-100. The cells were incubated
with anti-TRAF4 (1:100; Santa Cruz Biotechnology) antibodies at 4°C
overnight, followed by incubation with a secondary antibody
conjugated to rhodamine. The nuclei were counterstained with
4′6-diamidino-2-phenylindole and observations were performed with a
confocal microscope (Leica SP1 and SP2 UV; Leica, Mannheim,
Germany).
Plasmid and transfection
TRAF4 siRNA sequences (Santa Cruz Biotechnology
Inc.) were transfected with HiPerFect transfection reagent (Qiagen,
Hilden, Germany) into cells to accomplish the transient
transfection according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Control
siRNA-A (Santa Cruz Biotechnology Inc.) was used as a negative
control.
Flow cytometry
Flow cytometry was performed using an apoptosis
detection kit (KeyGen Biotech, Nanjing, China), according to the
manufacturer’s instructions, on a BD FACSCalibur™ (BD Biosciences)
flow cytometer. The percentages of cells in the various cell cycle
phases were determined using the FACSCalibur flow cytometer with
CellQuest 3.0 software (BD Biosciences). All experiments were
performed in triplicate.
Cell proliferation assay
The MCF-7 cells (1×103) were grown in
96-well plates. Following various treatments, the cells were
further incubated with MTT (0.5 mg/ml) at 37°C for 4 h, followed by
the addition of 150 μl DMSO. The absorbance values were measured at
550 nm using a microplate reader (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA).
Statistic analysis
All values are expressed as the mean ± SD. Student’s
t-test was used to analyze all results using the statistical
software package, SPSS 13.0 (SPSS, Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). For all
the tests, P<0.05 was considered to indicate a statistically
significant difference.
Results
Expression and location of TRAF4 in
breast cancer cells
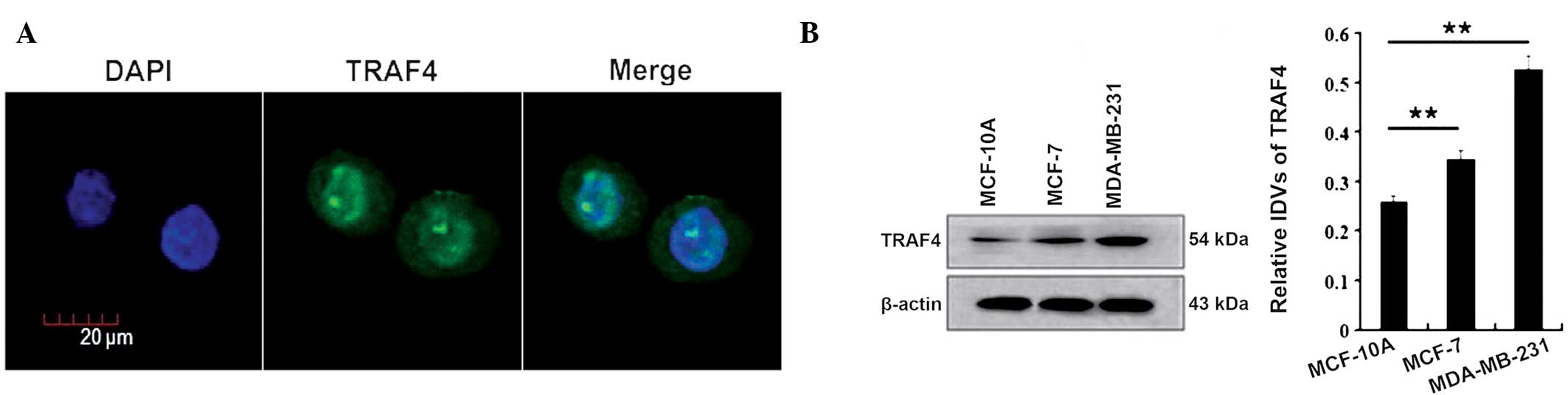
Firstly, the cellular localization of TRAF4 was
confirmed in the breast cancer MCF-7 cells through
immunofluorescence staining. The results showed that TRAF4 was
localized in the cytoplasm and nuclei of the MCF-7 cells, with its
nuclear expression stronger than its cytoplasmic expression
(Fig. 1A).
Next, the expression of TRAF4 was examined in normal
MCF-10A breast cells and the estrogen receptor-positive and
-negative breast cancer cell lines, MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231,
respectively, by western blotting. TRAF4 was found to be expressed
in all the cells, while the total expression of TRAF4 was lower in
the MCF-10A cells than in the MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 cells (P=0.002
and P=0.001, respectively; Fig.
1B).
TRAF4 suppresses the activation of NF-κB
in MCF-7 cells
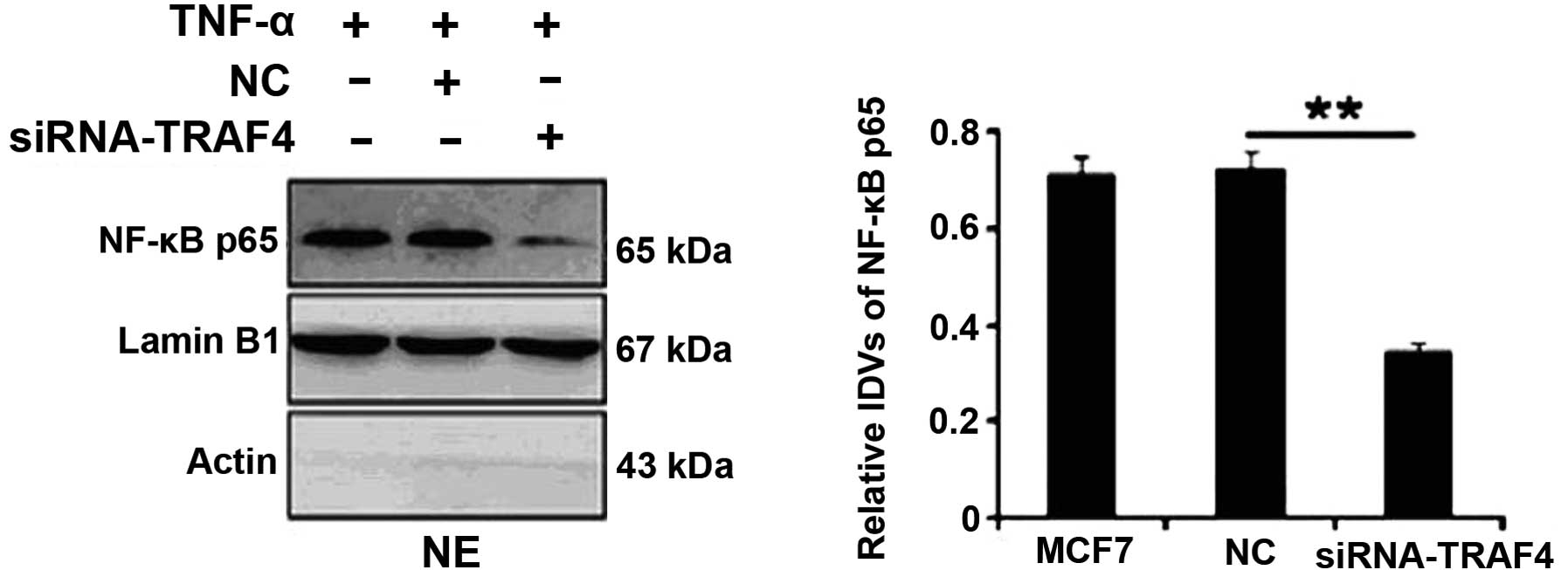
The nuclear expression of NF-κB was examined in the
estrogen receptor-positive MCF-7 breast cancer cell line by western
blotting. Following TNF-α treatment, TRAF4 depletion by siRNA in
the MCF-7 cells significantly suppressed the nuclear expression of
NF-κB (P=0.002; Fig. 2). However,
no significant differences were identified in the MCF-10A cells
(data not shown).
TRAF4 may promote cell proliferation and
suppress cell apoptosis in MCF-7 cells
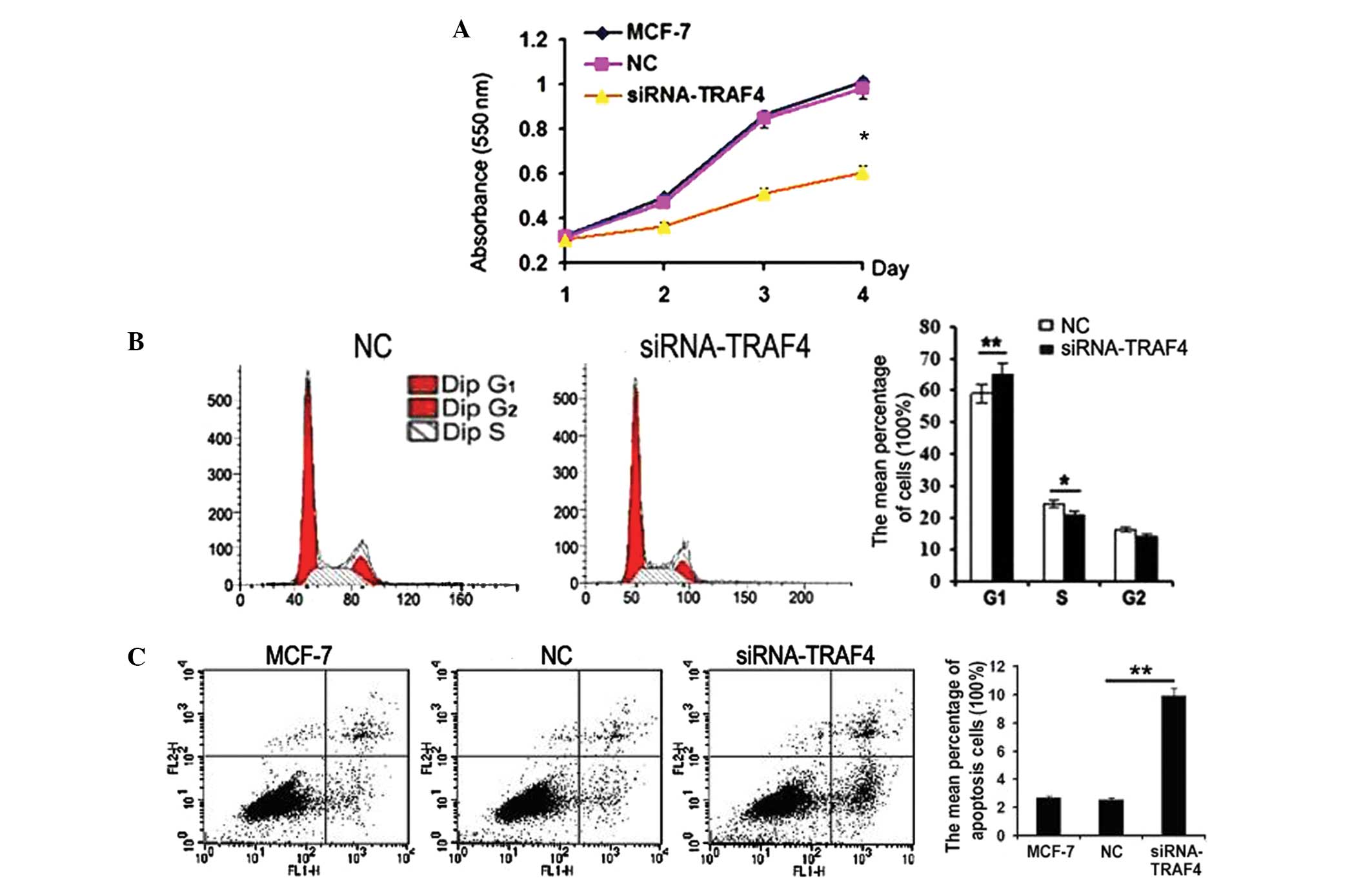
The biological function of TRAF4 was examined in the
MCF-7 cells. When TRAF4 was inhibited by siRNA in the MCF-7 cells,
the cell proliferation was effectively suppressed compared with the
negative control (P=0.02; Fig. 3A).
An increase in G1 phase cells (P=0.009) and a decrease
in S phase cells (P=0.04) was detected when TRAF4 was knocked down
(Fig. 3B). In addition, TRAF4
depletion by siRNA in the MCF-7 cells was found to markedly promote
early apoptosis (P=0.001; Fig.
3C).
Discussion
Camilleri-Broët et al previously demonstrated
that TRAF4 overexpression is a common characteristic of human
carcinomas, including lung cancer and breast, ovary, prostatic and
pancreatic adenocarcinomas (14).
The study indicated that one of the mechanisms responsible for
TRAF4 protein overexpression in human cancer was TRAF4 gene
amplification. TRAF4 is located in a region of amplification that
is devoid of known oncogenes on chromosome 17q11.2, and is commonly
overexpressed in cancer. The results of the present study showed
that, in vitro, TRAF4 exhibits higher expression in breast
cancer cells than in normal breast cells. In addition, TRAF4
expression in the estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer cell
lines was higher than in the estrogen receptor-negative breast
cancer cell lines. This is consistent with the expression of TRAF4
in breast cancer tissues reported in our previous study (13). The results of the present study in
breast cancer cells and human breast tissues may indicate that
TRAF4 has an important role in breast cancer.
Numerous TRAF family members negatively regulate
apoptotic pathways by increasing the expression of genes that
promote cell survival (15,16). Several previous studies have
hypothesized that TRAF4 may also be involved in apoptosis. However,
depending on the study, the role of TRAF4 in apoptosis is
controversial. On the one hand, Sax et al previously
demonstrated that TRAF4 may play a role in p53-mediated
proapoptotic signaling in response to cellular stress (17). Furthermore, TRAF4 has been
previously shown to suppress the ability of the common neurotrophin
receptor, p75NTR, dimers to block cell death induced by p75NTR
monomers, also indicating a proapoptotic role for TRAF4 (18). On the other hand, Fleckenstein et
al hypothesized an anti-apoptotic function for TRAF4 when the
study found that the anti-Fas antibody, CH-11, induces apoptosis in
HEK293 cells, but not when these cells are stably transfected with
TRAF4 (19). Although seemingly
paradoxical, these results may all be correct depending on the
cells examined. In the current study, following TNF-α treatment in
breast cancer MCF-7 cells, the expression of TRAF4 suppressed the
activation of NF-κB and promoted early cell apoptosis. In addition,
it was demonstrated that TRAF4 ablation resulted in a significant
increase in G1 phase cells and a reduction in S phase
cells. These results indicate that TRAF4 may promote the activation
of NF-κB induced by TNF-α in MCF-7 cells. Future studies must
clarify the roles of TRAF4 in apoptotic reactions and may
contribute to the development of a new strategy against breast
cancer.
References
|
1
|
Reinhard C, Shamoon B, Shyamala V and
Williams LT: Tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced activation of
c-jun Nterminal kinase is mediated by TRAF2. EMBO J. 16:1080–1092.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rothe M, Sarma V, Dixit VM and Goeddel DV:
TARF2-mediated activation of NF-kappa B by TNF receptor 2 and CD40.
Science. 269:1424–1427. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chung YJ, Park YC, Ye H and Wu H: All
TRAFs are not created equal common and distinct molecular
mechanisms of TRAF-mediated signal transduction. J Cell Sci.
115:679–688. 2002.
|
|
4
|
Kalkan T, Iwasaki Y, Park CY and Thomsen
GH: Tumor necrosis factor-receptor-associated factor-4 is a
positive regulator of transforming growth factor-beta signaling
that affects neural crest formation. Mol Biol Cell. 20:3436–3450.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Kedinger V, Alpy F, Tomasetto C, et al:
Spatial and temporal distribution of the traf4 genes during
zebrafish development. Gene Expr Patterns. 5:545–552. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mathew SJ, Kerridge M and Leptin M: A
small genomic region containing several loci required for
gastrulation in Drosophila. PLoS One. 4:e74372009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mathew SJ, Rembold M and Leptin M: Role
for Traf4 in polarizing adherens junctions as a prerequisite for
efficient cell shape changes. Mol Cell Biol. 31:4978–4993. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wajant H, Henkler F and Scheurich P: The
TNF-receptor-associated factor family: scaffold molecules for
cytokine receptors, kinases and their regulators. Cell Signal.
13:389–340. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cha GH, Cho KS, Lee JH, et al: Discrete
functions of TRAF1 and TRAF2 in Drosophila melanogaster mediated by
c-Jun N-terminal kinase and NF-kappaB-dependent signaling pathways.
Mol Cell Biol. 23:7982–7991. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Glauner H, Siegmund D, Motejadded H, et
al: Intracellular localization and transcriptional regulation of
tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor-associated factor 4 (TRAF4).
Eur J Biochem. 269:4819–4829. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Krajewska M, Krajewski S, Zapata JM, et
al: TRAF-4 expression in epithelial progenitor cells. Analysis in
normal adult, fetal, and tumor tissues. Am J Pathol. 152:1549–1561.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Régnier CH, Tomasetto C, Moog-Lutz C, et
al: Presence of a new conserved domain in CART1, a novel member of
the tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated protein family, which
is expressed in breast carcinoma. J Biol Chem. 27:25715–25721.
1995.
|
|
13
|
Dai WB, Zheng YW, Mi XY, et al: Expression
and significance of TRAF4 protein in breast carcinoma. Ai Zheng.
26:1095–1098. 2007.(In Chinese).
|
|
14
|
Camilleri-Broët S, Cremer I, Marmey B, et
al: TRAF4 overexpression is a common characteristic of human
carcinomas. Oncogene. 26:142–147. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Arch RH, Gedrich RW and Thompson CB: Tumor
necrosis factor receptor-associated factors (TRAFs) -a family of
adapter proteins that regulates life and death. Genes Dev.
12:2821–2830. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Dempsey PW, Doyle SE, He JQ and Cheng G:
The signaling adaptors and pathways activated by TNF superfamily.
Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 14:193–209. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sax JK and El-Deiry WS: Identification and
characterization of the cytoplasmic protein TRAF4 as a
p53-regulated proapoptotic gene. J Biol Chem. 278:36435–36444.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ye X, Mehlen P, Rabizadeh S, et al: TRAF
family proteins interact with the common neurotrophin receptor and
modulate apoptosis induction. J Biol Chem. 274:30202–30208. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fleckenstein DS, Dirks WG, Drexler HG and
Quentmeier H: Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor
(TRAF) 4 is a new binding partner for the p70S6 serine/threonine
kinase. Leuk Res. 27:687–694. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|