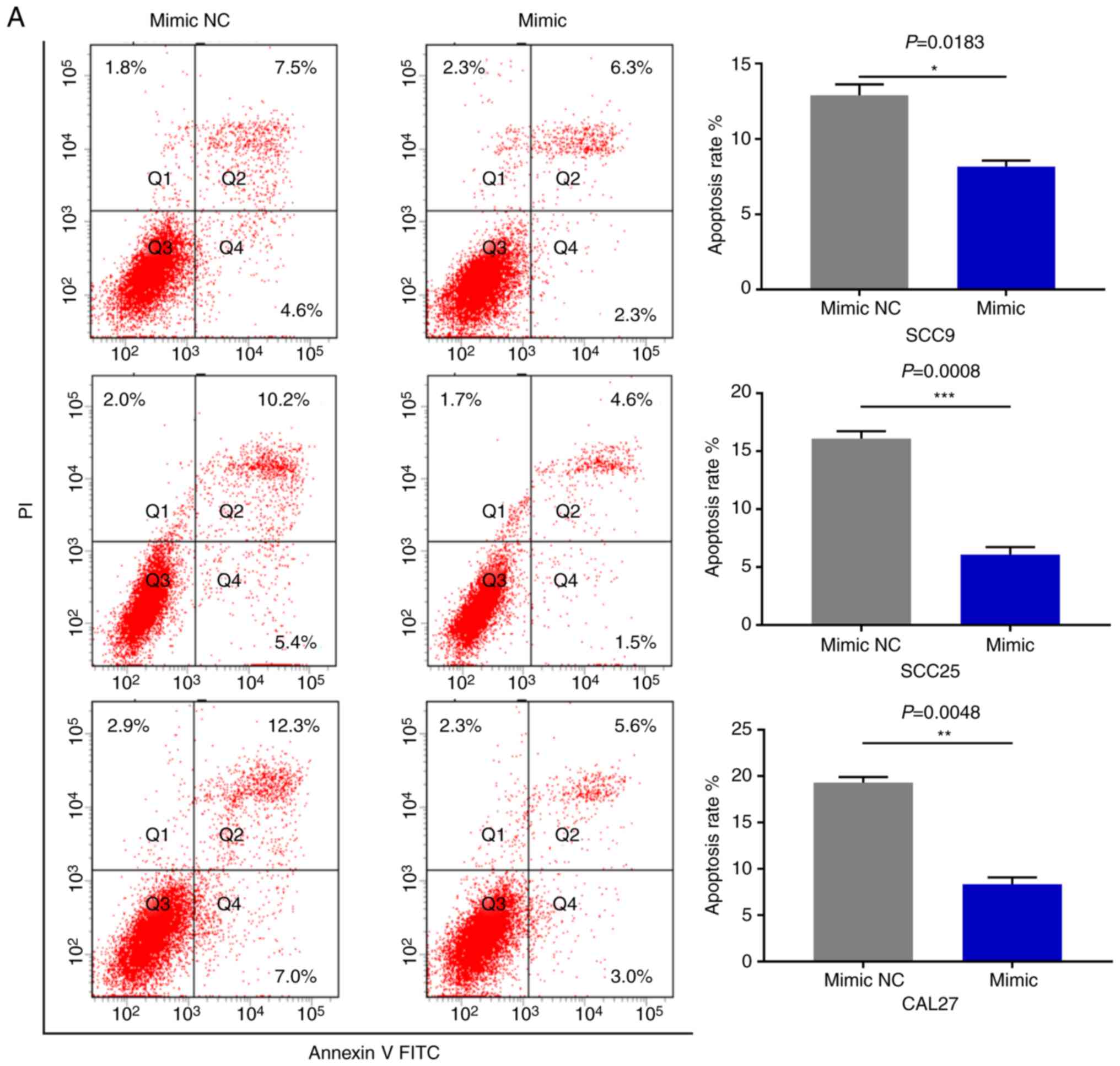
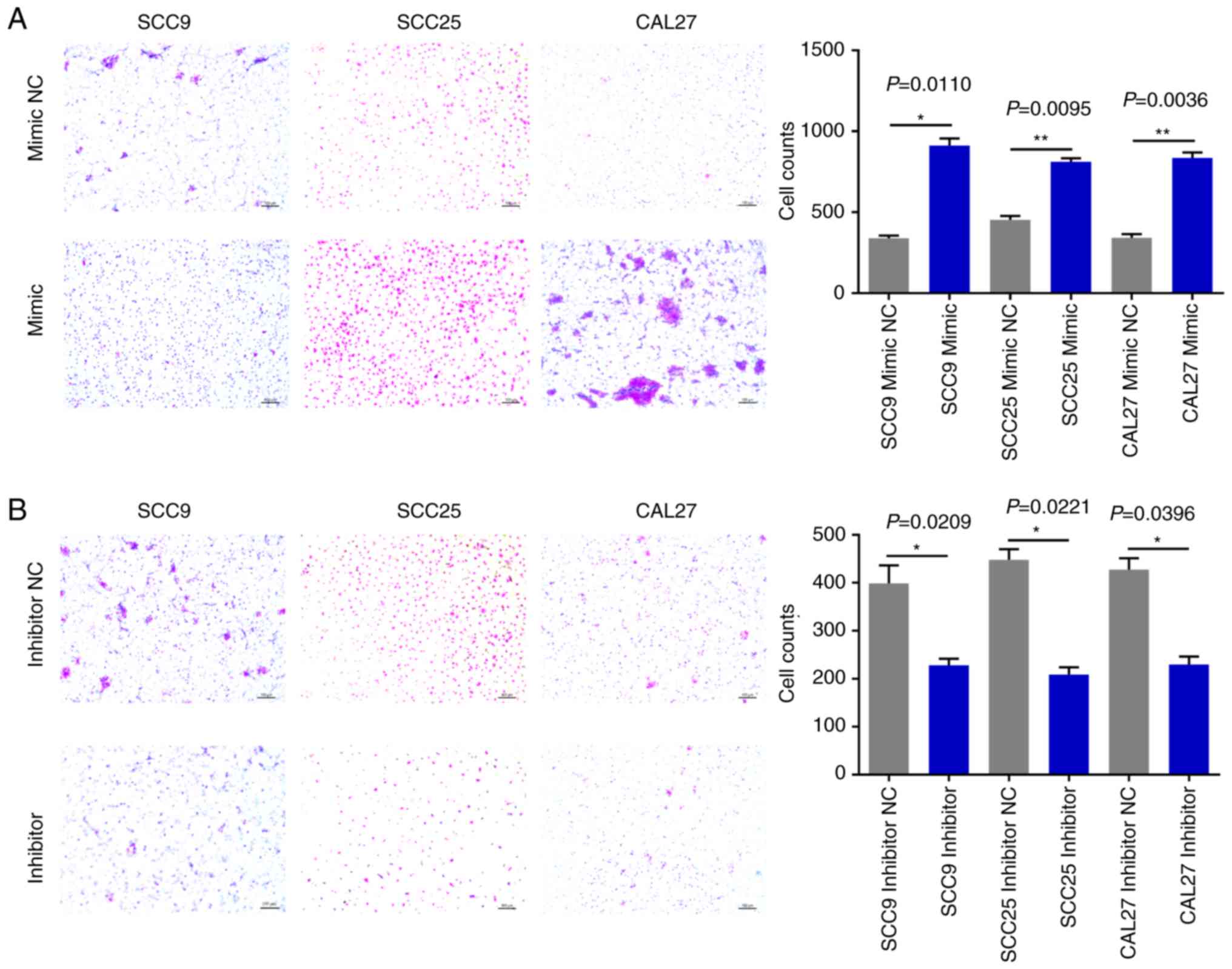
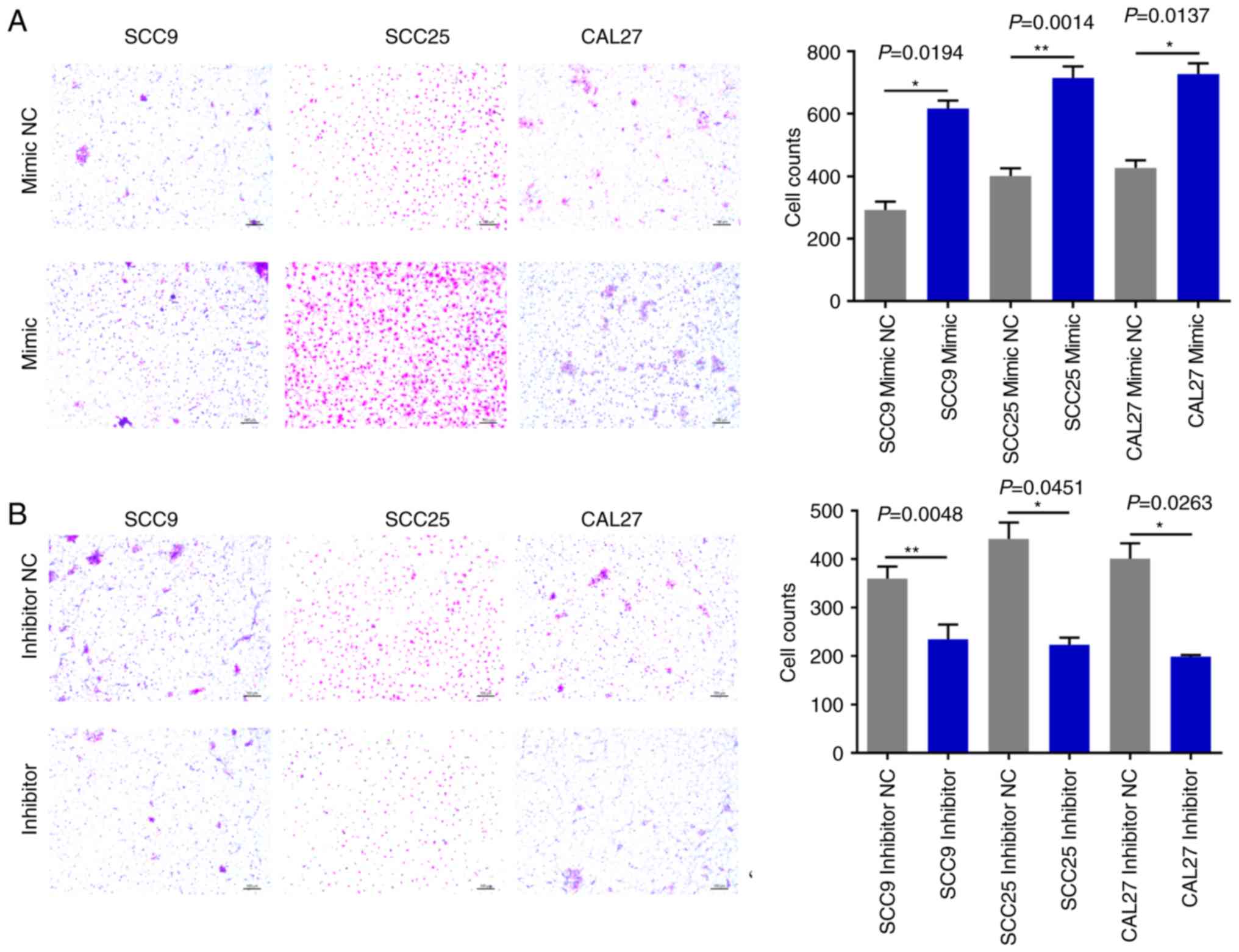
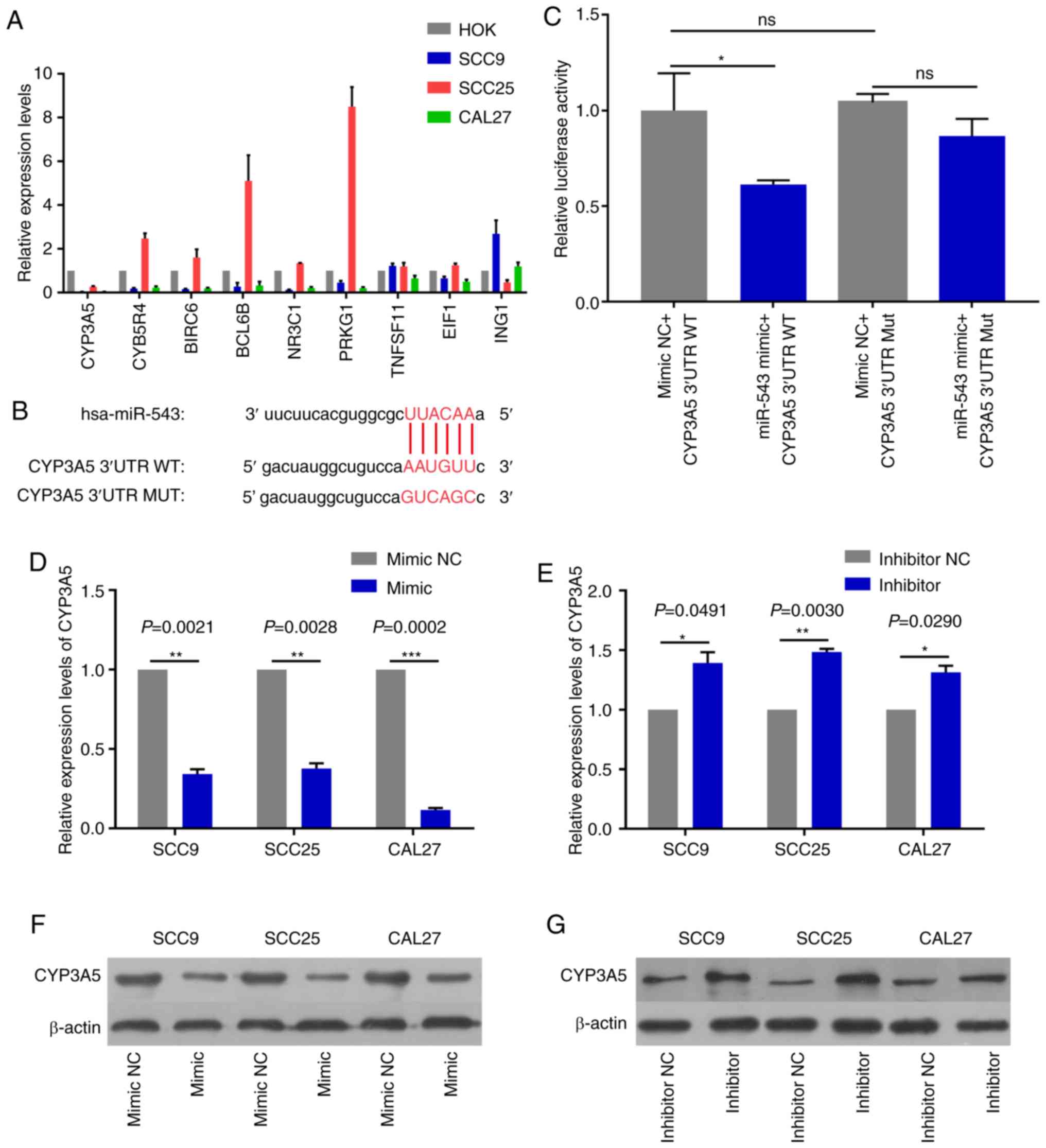
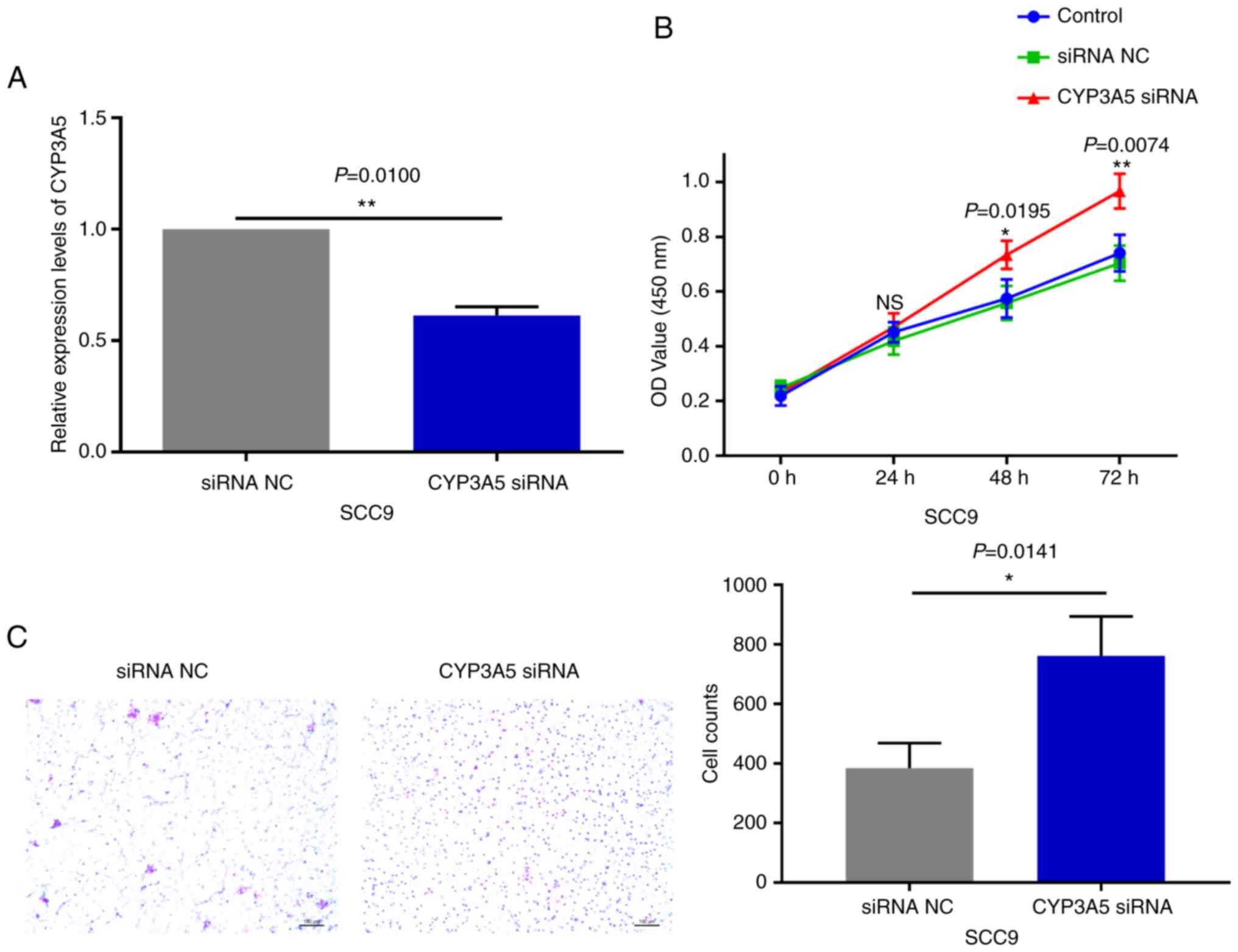
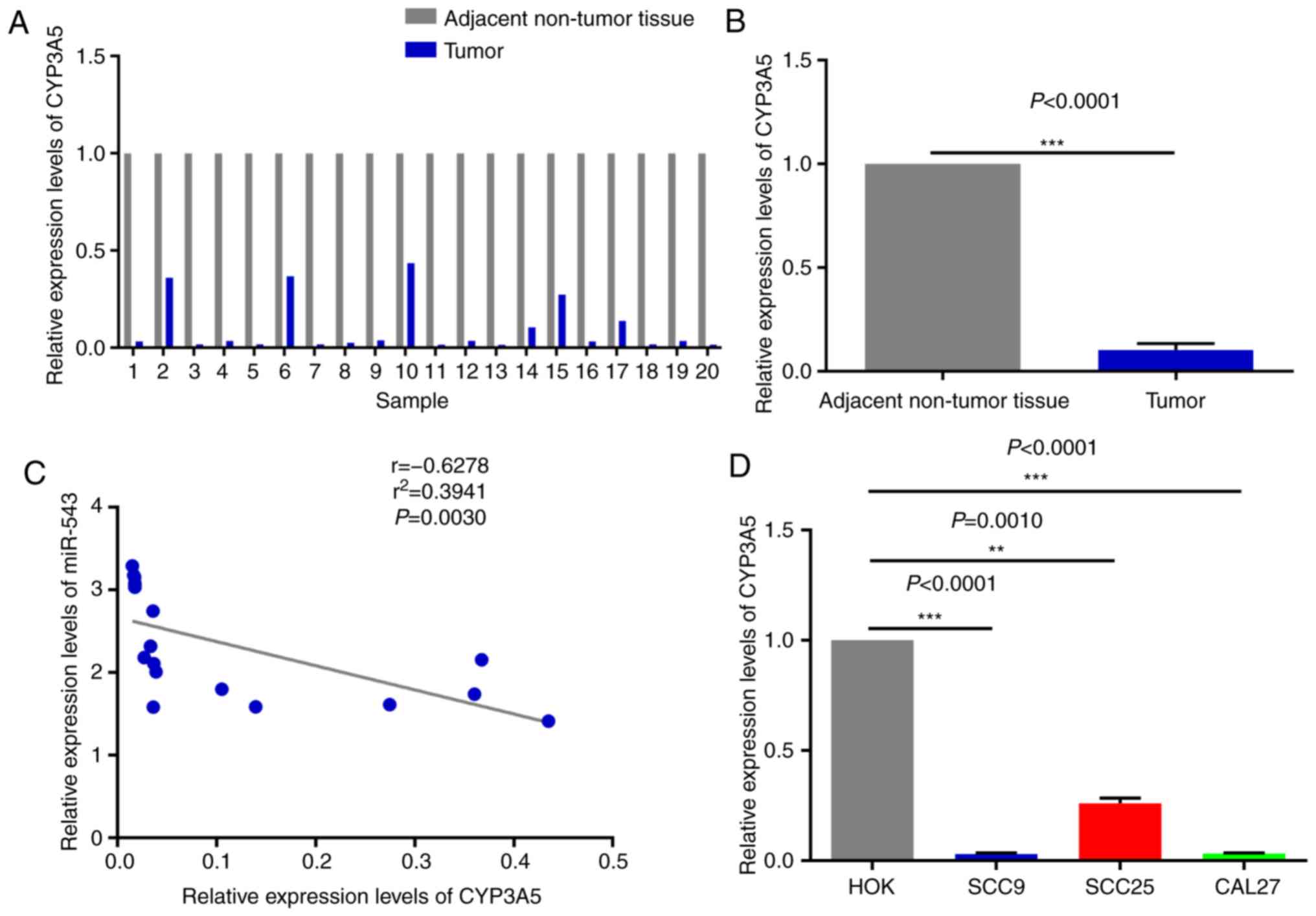
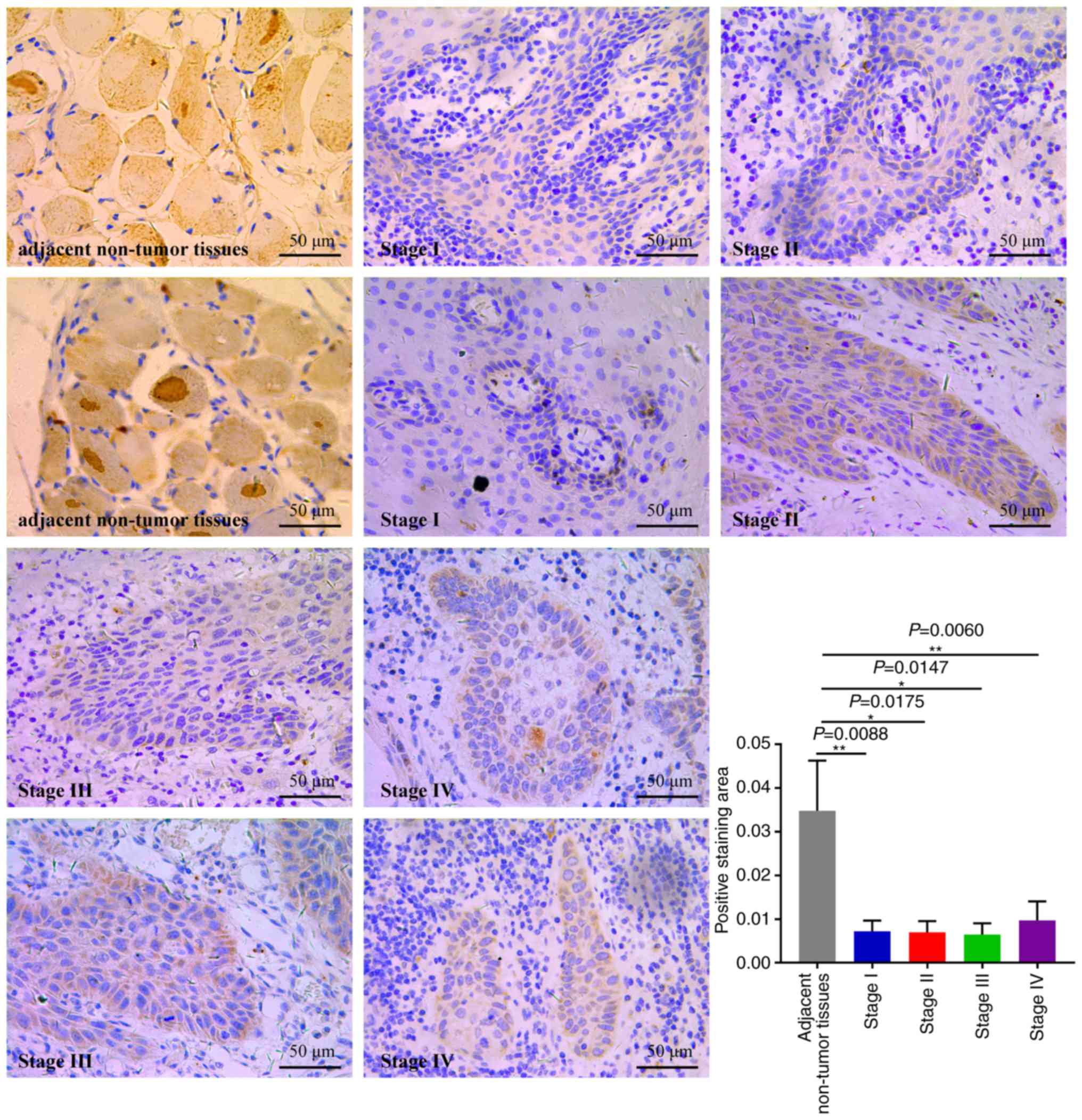
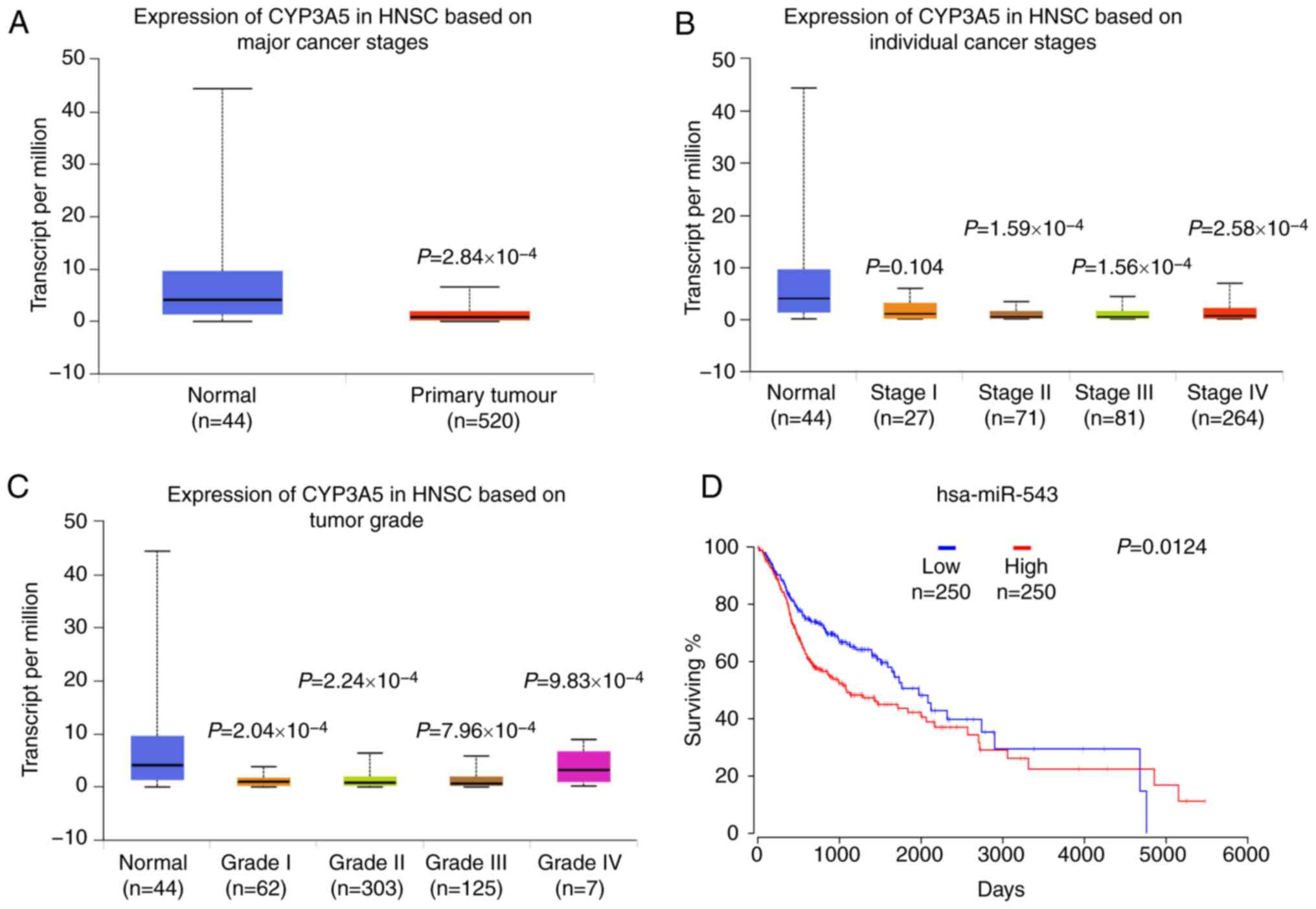
|
1
|
Warnakulasuriya S: Global epidemiology of
oral and oropharyngeal cancer. Oral Oncol. 45:309–316. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser
S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D and Bray F: Cancer
incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major
patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 136:E359–E386. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wu BH, Xiong XP, Jia J and Zhang WF:
Micrornas: New actors in the oral cancer scene. Oral Oncol.
47:314–319. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Murugan AK, Munirajan AK and Alzahrani AS:
MicroRNAs: Modulators of the ras oncogenes in oral cancer. J Cell
Physiol. 231:1424–1431. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chawla JP, Iyer N, Soodan KS, Sharma A,
Khurana SK and Priyadarshni P: Role of miRNA in cancer diagnosis,
prognosis, therapy and regulation of its expression by Epstein-Barr
virus and human papillomaviruses: With special reference to oral
cancer. Oral Oncol. 51:731–737. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kozomara A and Griffiths-Jones S: miRBase:
Annotating high confidence microRNAs using deep sequencing data.
Nucleic Acids Res. 42:D68–D73. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Shah MY and Calin GA: MicroRNAs as
therapeutic targets in human cancers. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA.
5:537–548. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mirnezamia AH, Pickard K, Zhang L,
Primrose JN and Packham G: MicroRNAs: Key players in carcinogenesis
and novel therapeutic targets. Eur J Surg Oncol. 35:339–347. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Shah MY, Ferrajoli A, Sood AK,
Lopezberestein G and Calin GA: microRNA therapeutics in cancer-an
emerging concept. Ebiomedicine. 12:34–42. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chou J, Shahi P and Werb Z:
microRNA-mediated regulation of the tumor microenvironment. Cell
Cycle. 12:3262–3271. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Esposito CL, Cerchia L, Catuogno S, Vita
GD, Dassie JP, Santamaria G, Swiderski P, Condorelli G, Giangrande
PH and de Franciscis V: Multifunctional aptamer-miRNA conjugates
for targeted cancer therapy. Mol Ther. 22:1151–1163. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bi M, Chen W, Yu H, Wang J, Ding F, Tang
DJ and Tang C: miR-543 is up-regulated in gefitinib-resistant
non-small cell lung cancer and promotes cell proliferation and
invasion via phosphatase and tensin homolog. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 480:369–374. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li J, Dong G, Wang B, Gao W and Yang Q:
miR-543 promotes gastric cancer cell proliferation by targeting
SIRT1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 469:15–21. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yu L, Zhou L, Cheng Y, Sun L, Fan J, Liang
J, Guo M, Liu N and Zhu L: MicroRNA-543 acts as an oncogene by
targeting PAQR3 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Cancer Res.
4:897–906. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen P, Xu W, Luo Y, Zhang Y, He Y, Yang S
and Yuan Z: MicroRNA 543 suppresses breast cancer cell
proliferation, blocks cell cycle and induces cell apoptosis via
direct targeting of ERK/MAPK. Onco Targets Ther. 10:1423–1431.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sun J, Zhou J, Dong M and Sheng W:
Dysregulation of MicroRNA-543 expression in colorectal cancer
promotes tumor migration and invasion. Mol Carcinog. 56:250–257.
2017. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Song N, Liu H, Ma X and Zhang S: Placental
growth factor promotes metastases of ovarian cancer through
MiR-543-regulated MMP7. Cell Physiol Biochem. 37:1104–1112. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mbatchi LC, Gassiot M, Pourquier P,
Goberna A, Mahammedi H, Mourey L, Joly F, Lumbroso S, Evrard A and
Houede N: Association of NR1I2, CYP3A5 and ABCB1 genetic
polymorphisms with variability of temsirolimus pharmacokinetics and
toxicity in patients with metastatic bladder cancer. Cancer
Chemother Pharmacol. 80:653–659. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wahlang B, Falkner KC, Cave MC and Prough
RA: Role of cytochrome P450 monooxygenase in carcinogen and
chemotherapeutic drug metabolism. Adv Pharmacol. 74:1–33. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mitra R, Guo Z, Milani M, Mesaros C,
Rodriguez M, Nguyen J, Luo X, Clarke D, Lamba J, Schuetz E, et al:
CYP3A4 mediates growth of estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer
cells in part by inducing nuclear translocation of phospho-Stat3
through biosynthesis of (±)-14,15-epoxyeicosatrienoic acid (EET). J
Biol Chem. 286:17543–17559. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fleming I: The cytochrome P450 pathway in
angiogenesis and endothelial cell biology. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
30:541–555. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jiang F, Chen L, Yang YC, Wang XM, Wang
RY, Li L, Wen W, Chang YX, Chen CY, Tang J, et al: Cyp3a5 functions
as a tumor suppressor in hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating
mTORC2/Akt signaling. Cancer Res. 75:1470–1481. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tanasubsinn P, Aung WPP, Pata S, Laopajon
W, Makeudom A, Sastraruji T, Kasinrerk W and Krisanaprakornkit S:
Overexpression of ADAM9 in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol
Lett. 15:495–502. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Li P, Wei X, Guan Y, Chen Q, Zhao T, Sun C
and Wei L: MicroRNA-1 regulates chondrocyte phenotype by repressing
histone deacetylase 4 during growth plate development. FASEB J.
28:3930–3941. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: MAnalysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liu F, Lou K, Zhao X, Zhang J, Chen W,
Qian Y, Zhao Y, Zhu Y and Zhang Y: miR-214 regulates papillary
thyroid carcinoma cell proliferation and metastasis by targeting
PSMD10. Int J Mol Med. 42:3027–3036. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chandrashekar DS, Bashel B, Balasubramanya
SAH, Creighton CJ, Poncerodriguez I, Chakravarthi BVSK and
Varambally S: Ualcan: A portal for facilitating tumor subgroup gene
expression and survival analyses. Neoplasia. 19:649–658. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Anaya J: OncoLnc: Linking TCGA survival
data to mRNAs, miRNAs, and lncRNAs. PeerJ Comput Sci. 2:e672016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Zhang GJ, Li JS, Zhou H, Xiao HX, Li Y and
Zhou T: MicroRNA-106b promotes colorectal cancer cell migration and
invasion by directly targeting DLC1. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
34:732015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Liu HN, Qie P, Yang G and Song YB:
miR-181b inhibits chemoresistance in cisplatin-resistant H446 small
cell lung cancer cells by targeting Bcl-2. Arch Med Sci.
14:745–751. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Clément T, Salone V and Rederstorff M:
Dual luciferase gene reporter assays to study miRNA function.
Methods Mol Biol. 1296:187–198. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yang Y, Huang G, Zhou Z, Fewell JG and
Kleinerman ES: miR-20a regulates Fas expression in osteosarcoma
cells by modulating Fas promoter activity and can be
therapeutically targeted to inhibit lung metastases. Mol Cancer
Ther. 17:130–139. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Pink RC, Samuel P, Massa D, Caley DP,
Brooks SA and Carter DR: The passenger strand, miR-21-3p, plays a
role in mediating cisplatin resistance in ovarian cancer cells.
Gynecol Oncol. 137:143–151. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
de Vicente JC, Rodríguez-Santamarta T,
Rosado P, Peña I and de Villalaín L: Survival after free flap
reconstruction in patients with advanced oral squamous cell
carcinoma. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 70:453–459. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Garzon R, Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNAs
in cancer. Annu Rev Med. 60:167–179. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Gorenchtein M, Poh CF, Saini R and Garnis
C: MicroRNAs in an oral cancer context-from basic biology to
clinical utility. J Dent Res. 91:440–446. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Li L and Ma HQ: MicroRNA-216a inhibits the
growth and metastasis of oral squamous cell carcinoma by targeting
eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4b. Mol Med Rep.
12:3156–3162. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kawakita A, Yanamoto S, Yamada SI, Naruse
T, Takahashi H, Kawasaki G and Umeda M: MicroRNA-21 promotes oral
cancer invasion via the Wnt/β-catenin pathway by targeting DKK2.
Pathol Oncol Res. 20:253–261. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Peng SC, Liao CT, Peng CH, Cheng AJ, Chen
SJ, Huang CG, Hsieh WP and Yen TC: MicroRNAs MiR-218, MiR-125b, and
Let-7g predict prognosis in patients with oral cavity squamous cell
carcinoma. PLoS One. 9:e1024032014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Min A, Zhu C, Peng S, Rajthala S, Costea
DE and Sapkota D: MicroRNAs as important players and biomarkers in
oral carcinogenesis. Biomed Res Int. 2015:1869042015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Tsai SC, Huang SF, Chiang JH, Chen YF,
Huang CC, Tsai MH, Tsai FJ, Kao MC and Yang JS: The differential
regulation of microRNAs is associated with oral cancer. Oncol Rep.
38:1613–1620. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Farooqi AA, Shu CW, Huang HW, Wang HR,
Chang YT, Fayyaz S, Yuan SF, Tang JY and Chang HW: TRAIL, Wnt,
sonic hedgehog, TGFβ, and miRNA signalings are potential targets
for oral cancer therapy. Int J Mol Sci. 18(pii): E15232017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Skalsky RL and Cullen BR: Reduced
expression of brain-enriched microRNAs in glioblastomas permits
targeted regulation of a cell death gene. PLoS One. 6:e242482011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhai F, Cao C, Zhang L and Zhang J:
miR-543 promotes colorectal cancer proliferation and metastasis by
targeting KLF4. Oncotarget. 8:59246–59256. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Xu L, Yu J, Wang Z, Zhu Q, Wang W and Lan
Q: miR-543 functions as a tumor suppressor in glioma in
vitro and in vivo. Oncol Rep. 38:725–734. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Fan C, Lin Y, Mao Y, Huang Z, Liu AY, Ma
H, Yu D, Maitikabili A, Xiao H, Zhang C, et al: MicroRNA-543
suppresses colorectal cancer growth and metastasis by targeting
KRAS, MTA1 and HMGA2. Oncotarget. 7:21825–21839. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zhang H, Guo X, Xing F, Wang T, Hu Z, Que
X, Tian Q, Zhu T, Guo G, Huang W and Li X: MiRNA-543 promotes
osteosarcoma cell proliferation and glycolysis by partially
suppressing PRMT9 and stabilizing HIF-1α protein. Oncotarget.
8:2342–2355. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Du Y, Liu XH, Zhu HC, Wang L, Ning JZ and
Xiao CC: MiR-543 promotes proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in prostate cancer via targeting RKIP. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 41:1135–1146. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Wacher VJ, Wu CY and Benet LZ: Overlapping
substrate specificities and tissue distribution of cytochrome P450
3A and P-glycoprotein: Implications for drug delivery and activity
in cancer chemotherapy. Mol Carcinog. 13:129–134. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Lamba JK, Lin YS, Schuetz EG and Thummel
KE: Genetic contribution to variable human CYP3A-mediated
metabolism. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 54:1271–1294. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Wojnowski L: Genetics of the variable
expression of CYP3A in humans. Ther Drug Monit. 26:192–199. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Picard N, Rouguiegmalki K, Kamar N,
Rostaing L and Marquet P: CYP3A5 genotype does not influence
everolimus in vitro metabolism and clinical pharmacokinetics in
renal transplant recipients. Transplantation. 91:652–656. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Zayed BEM and Mehaney D: The effect of
CYP3A5 polymorphism on cyclosporine plasma level in Egyptian renal
transplant recipients. Comp Clin Pathol. 23:1–5. 2014.
|
|
54
|
Islam MS, Mostofa AG, Ahmed MU, Bin Sayeed
MS, Hassan MR and Hasnat A: Association of CYP3A4, CYP3A5
polymorphisms with lung cancer risk in Bangladeshi population.
Tumor Biol. 35:1671–1678. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Ma LM, Liu HC, Ruan LH and Feng YM: CYP3A5
* 3 genetic polymorphism is associated with childhood acute
lymphoblastic leukemia risk: A meta-analysis. Biomed J. 38:428–432.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Dhaini HR, Thomas DG, Giordano TJ, Johnson
TD, Biermann JS, Leu K, Hollenberg PF and Baker LH: Cytochrome P450
CYP3A4/5 expression as a biomarker of outcome in osteosarcoma. J
Clin Oncol. 21:2481–2485. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|