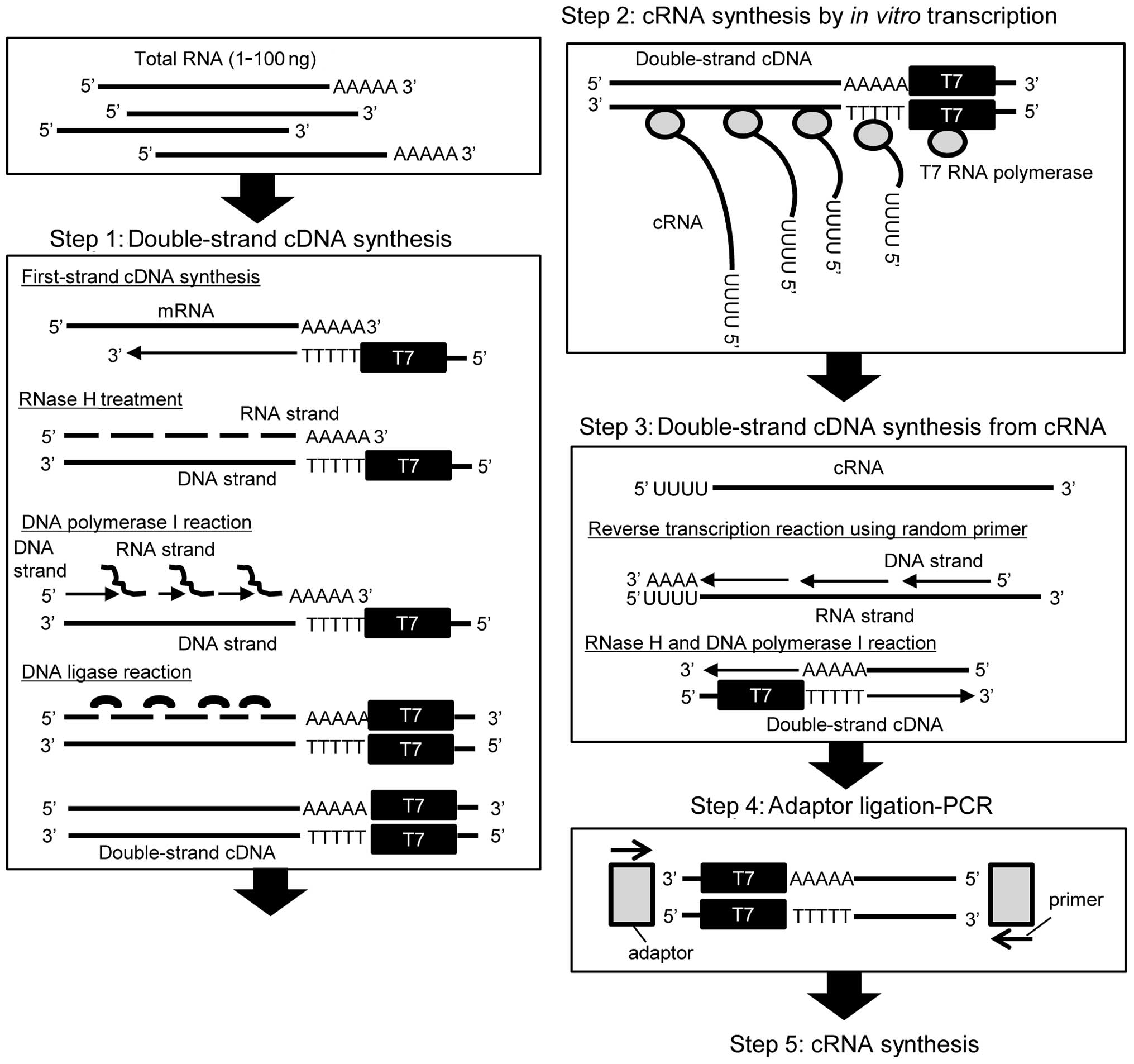
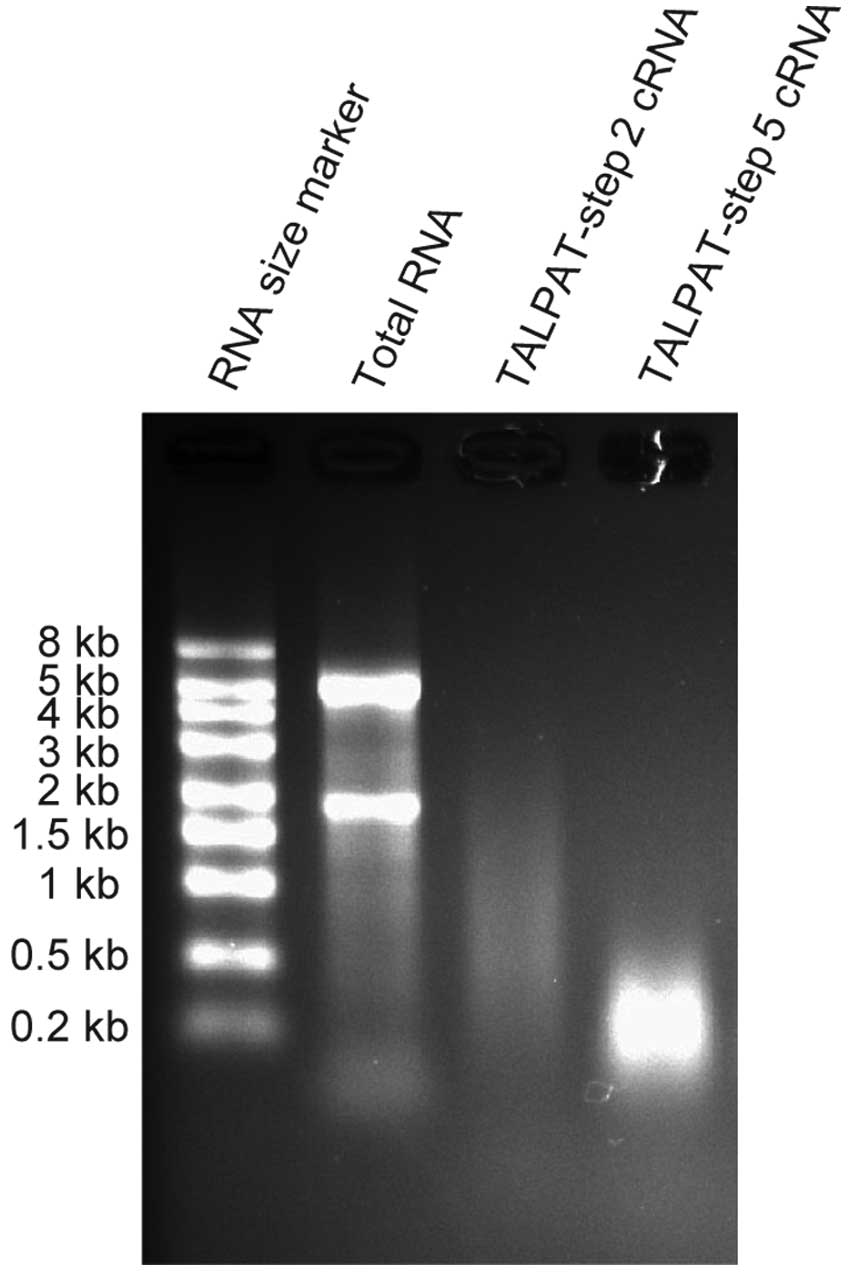
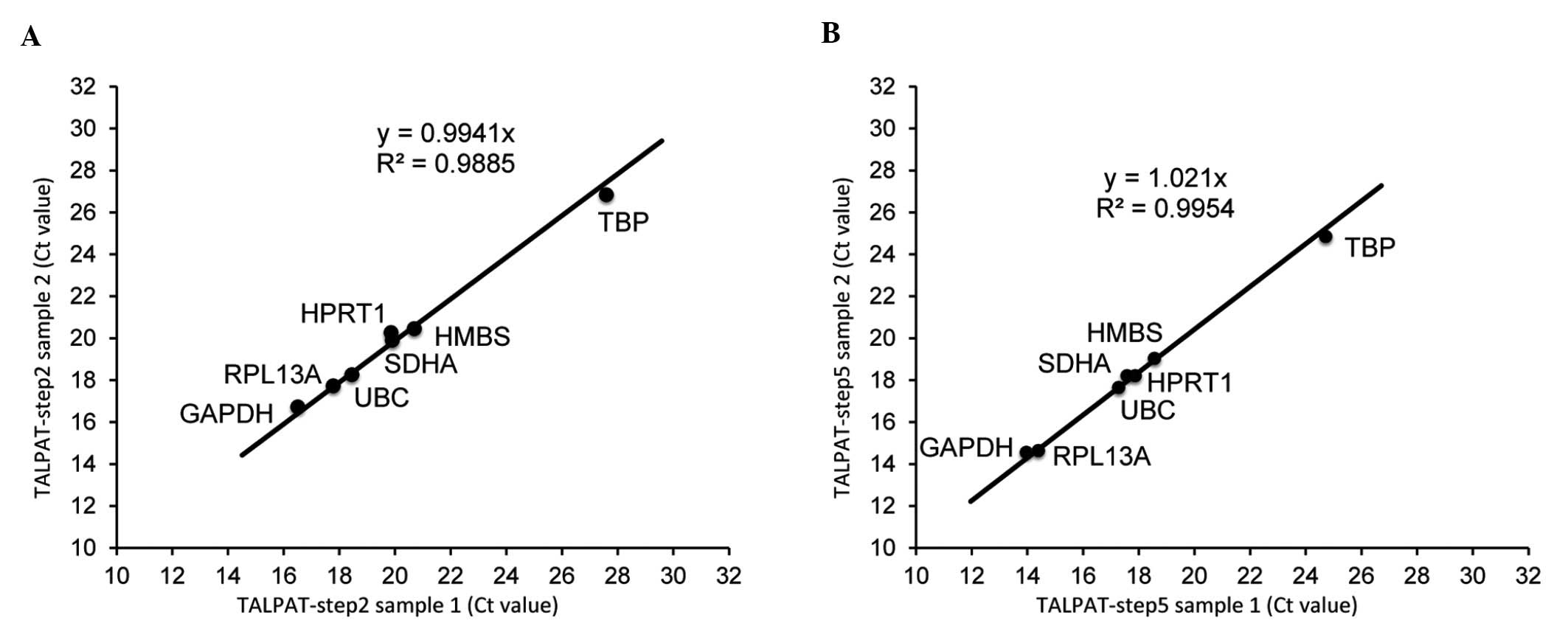
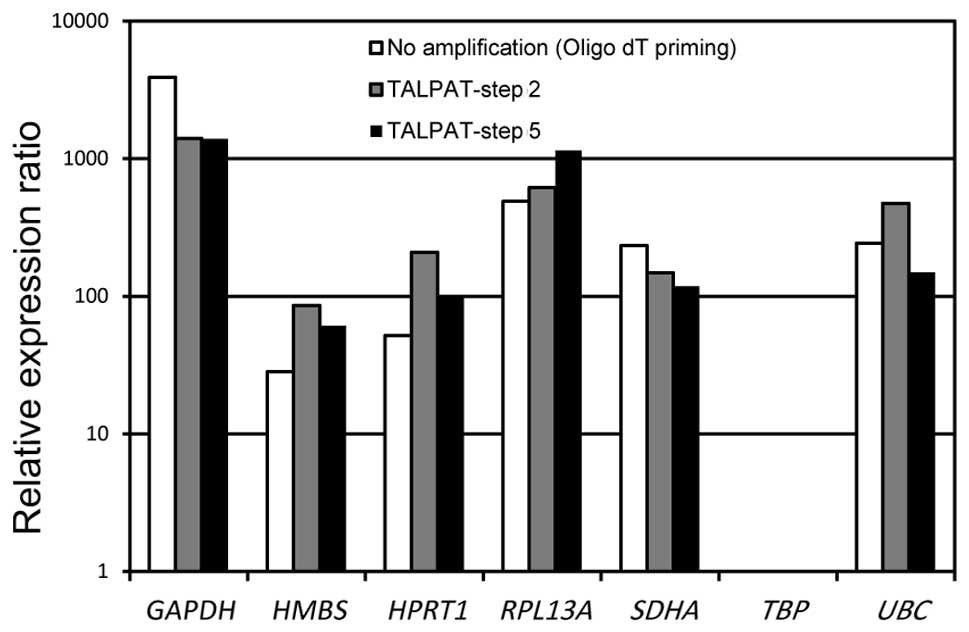
|
1.
|
Schena M, Shalon D, Davis RW and Brown PO:
Quantitative monitoring of gene expression patterns with a
complementary DNA microarray. Science. 270:467–470. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Lander ES, Linton LM, Birren B, et al:
Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature.
409:860–921. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Venter JC, Adams MD, Myers EW, et al: The
sequence of the human genome. Science. 291:1304–1351. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
International Human Genome Sequencing
Consortium: Finishing the euchromatic sequence of the human genome.
Nature. 431:931–945. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5.
|
Okazaki Y, Furuno M, Kasukawa T, et al:
Analysis of the mouse transcriptome based on functional annotation
of 60,770 full-length cDNAs. Nature. 420:563–573. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Carninci P, Kasukawa T, Katayama S, et al:
The transcriptional landscape of the mammalian genome. Science.
309:1559–1563. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Aoyagi K, Tatsuta T, Nishigaki M, et al: A
faithful method for PCR-mediated global mRNA amplification and its
integration into microarray analysis on laser-captured cells.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 300:915–920. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Isohata N, Aoyagi K, Mabuchi T, et al:
Hedgehog and epithelial-mesenchymal transition signaling in normal
and malignant epithelial cells of the esophagus. Int J Cancer.
125:1212–1221. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Wang E, Miller LD, Ohnmacht GA, Liu ET and
Marincola FM: High-fidelity mRNA amplification for gene profiling.
Nat Biotechnol. 18:457–459. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Ko MS, Ko SB, Takahashi N, Nishiguchi K
and Abe K: Unbiased amplification of a highly complex mixture of
DNA fragments by ‘lone linker’-tagged PCR. Nucleic Acids Res.
18:4293–4294. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Lucito R, Nakimura M, West JA, et al:
Genetic analysis using genomic representations. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 95:4487–4492. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Rosok O and Sioud M: Systematic
identification of sense-antisense transcripts in mammalian cells.
Nat Biotechnol. 22:104–108. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Katayama S, Tomaru Y, Kasukawa T, et al:
Antisense transcription in the mammalian transcriptome. Science.
309:1564–1566. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Bertozzi D, Iurlaro R, Sordet O, et al:
Characterization of novel antisense HIF-1α transcripts in human
cancers. Cell Cycle. 10:3189–3197. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Guttman M, Amit I, Garber M, et al:
Chromatin signature reveals over a thousand highly conserved large
non-coding RNAs in mammals. Nature. 458:223–227. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Mathivanan S, Ji H and Simpson RJ:
Exosomes: extra-cellular organelles important in intercellular
communication. J Proteomics. 73:1907–1920. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Michael A, Bajracharya SD, Yuen PS, et al:
Exosomes from human saliva as a source of microRNA biomarkers. Oral
Dis. 16:34–38. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Moon PG, You S, Lee JE, Hwang D and Baek
MC: Urinary exosomes and proteomics. Mass Spectrom Rev.
30:1185–1202. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Brase JC, Wuttig D, Kuner R and Sultmann
H: Serum microRNAs as non-invasive biomarkers for cancer. Mol
Cancer. 9:3062010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Lasser C, Alikhani VS, Ekstrom K, et al:
Human saliva, plasma and breast milk exosomes contain RNA: uptake
by macrophages. J Transl Med. 9:92011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|