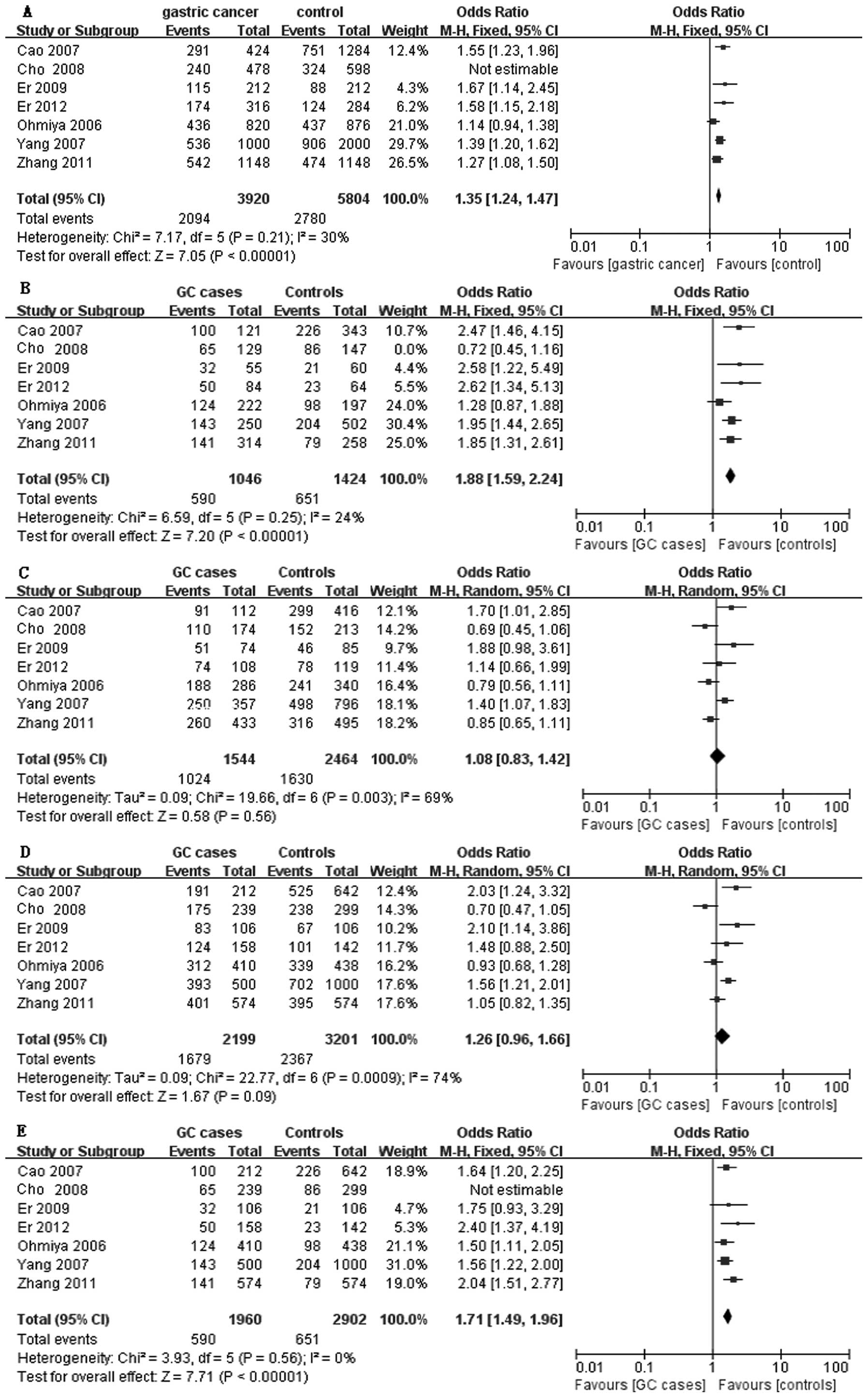
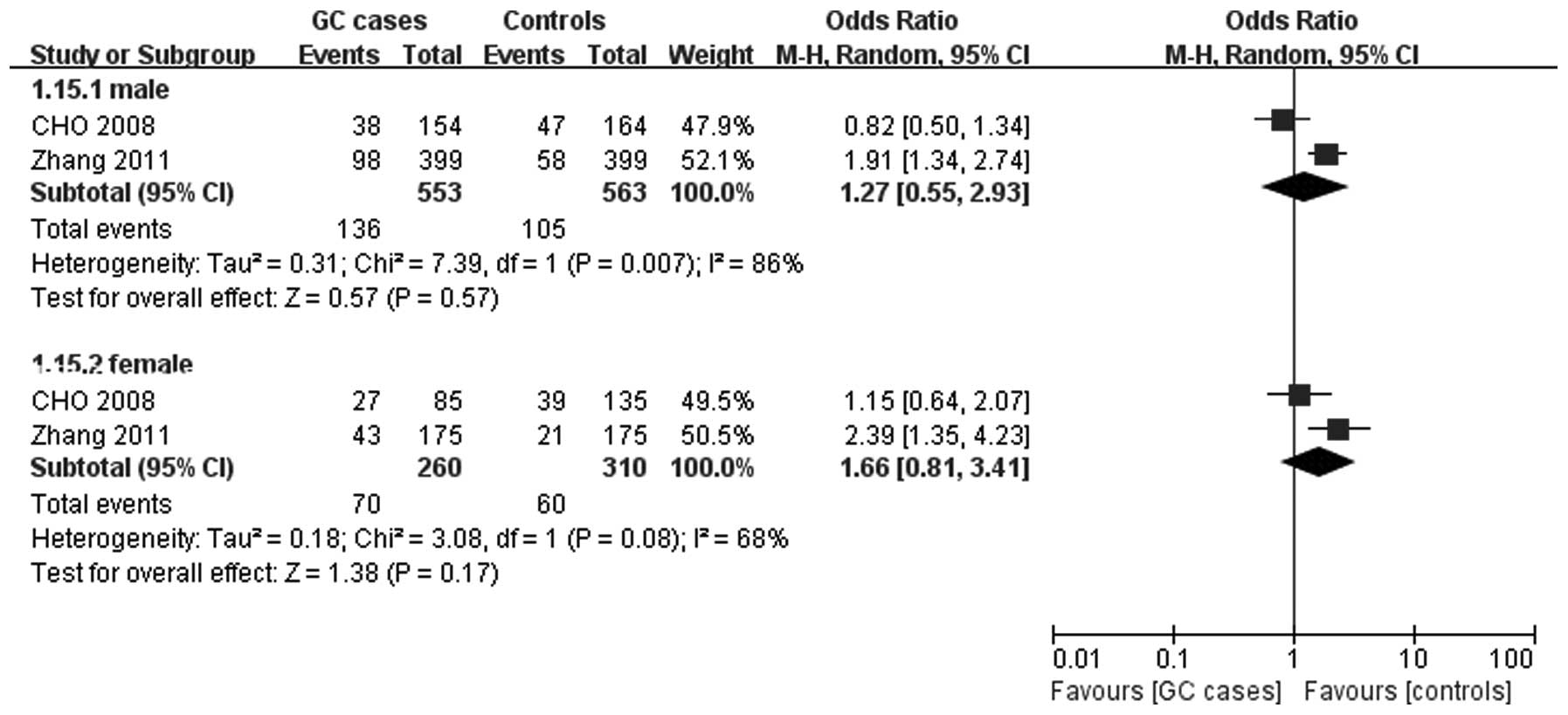
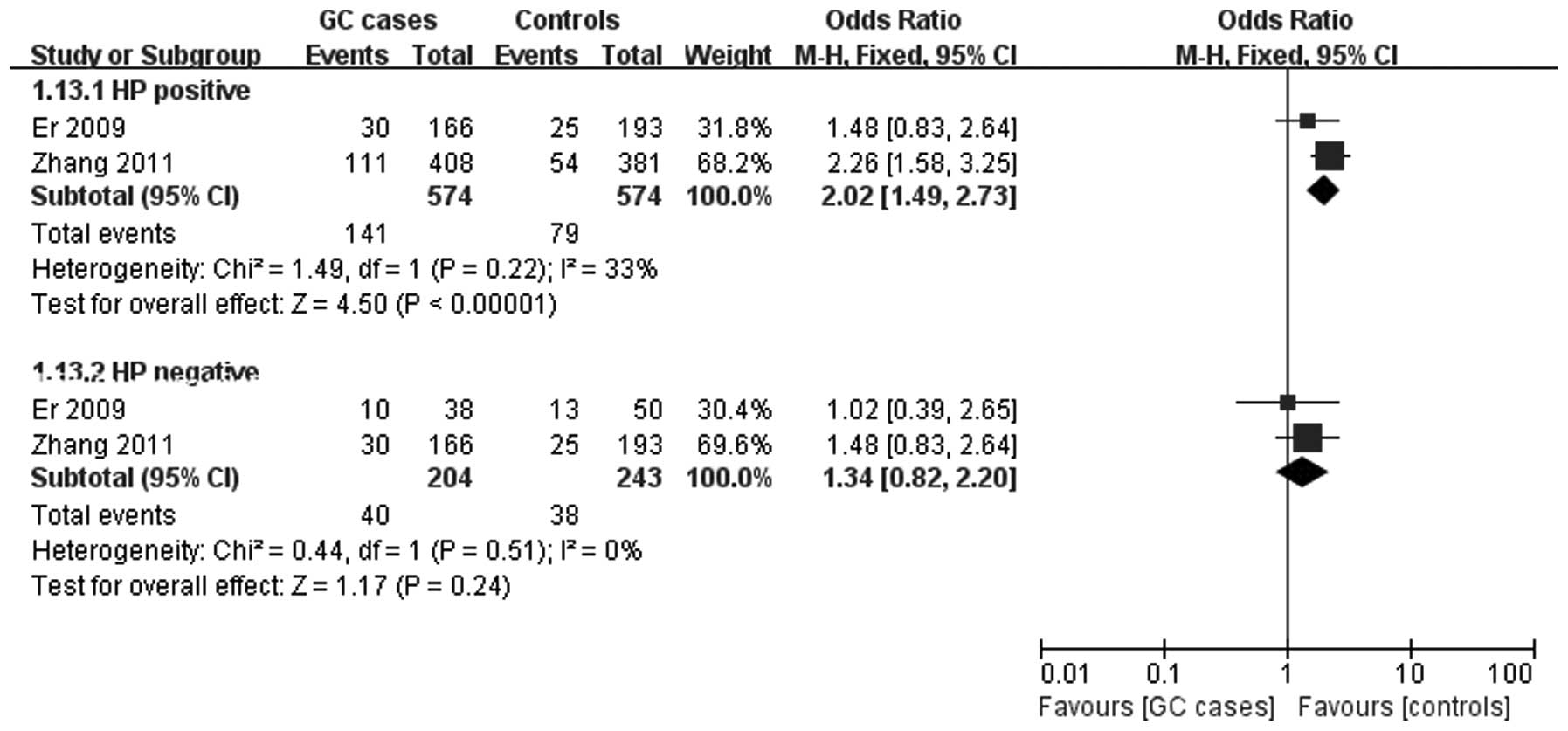
|
1
|
Nakao M, Matsuo K, Ito H, et al: ABO
genotype and the risk of gastric cancer, atrophic gastritis, and
Helicobacter pylori infection. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers
Prev. 20:1665–1672. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Duell EJ, Travier N, Lujan-Barroso L, et
al: Alcohol consumption and gastric cancer risk in the European
Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC) cohort.
Am J Clin Nutr. 94:1266–1275. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Jemal A, Center MM, DeSantis C and Ward
EM: Global patterns of cancer incidence and mortality rates and
trends. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 19:1893–1907. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ebert MP, Niemeyer D, Deininger SO, et al:
Identification and confirmation of increased fibrinopeptide a serum
protein levels in gastric cancer sera by magnet bead assisted
MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. J Proteome Res. 5:2152–2158. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cahilly-Snyder L, Yang-Feng T, Francke U
and George DL: Molecular analysis and chromosomal mapping of
amplified genes isolated from a transformed mouse 3T3 cell line.
Somat Cell Mol Genet. 13:235–244. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fakharzadeh SS, Trusko SP and George DL:
Tumorigenic potential associated with enhanced expression of a gene
that is amplified in a mouse tumor cell line. EMBO J. 10:1565–1569.
1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Piette J, Neel H and Marechal V: Mdm2:
keeping p53 under control. Oncogene. 15:1001–1010. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chen H, Xie L and Liu B: Clinical
significance of MDM2 as a tumor biomarker. Chin-Ger J Clin Oncol.
11:356–360. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Picksley SM and Lane DP: The p53-mdm2
autoregulatory feedback loop: a paradigm for the regulation of
growth control by p53? Bioessays. 15:689–690. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hirata H, Hinoda Y, Kikuno N, et al: MDM2
SNP309 polymorphism as risk factor for susceptibility and poor
prognosis in renal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 13:4123–4129.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Terry K, McGrath M, Lee IM, Buring J and
De Vivo I: MDM2 SNP309 is associated with endometrial cancer risk.
Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 17:983–986. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Olsson H, Hultman P, Rosell J, Söderkvist
P and Jahnson S: MDM2 SNP309 promoter polymorphism and p53
mutations in urinary bladder carcinoma stage T1. BMC Urol.
13:52013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang GX, Li YQ and Pan XL: Polymorphism
of MDM2 promoter, regulated by helicobacter pylori
lipopolysaccharide, is associated with both an increased
susceptibility to gastric carcinoma and poor prognosis in Chinese
patients. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 26:2802011.
|
|
14
|
Wang X, Yang J, Ho B, et al: Interaction
of Helicobacter pylori with genetic variants in the MDM2
promoter, is associated with gastric cancer susceptibility in
Chinese patients. Helicobacter. 14:114–119. 2009.
|
|
15
|
Cho YG, Choi BJ, Song JH, et al: No
association of MDM2 T309G polymorphism with susceptibility to
Korean gastric cancer patients. Neoplasma. 55:256–260.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Egger M and Smith GD: Bias in location and
selection of studies. BMJ. 316:61–66. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Pan X, Li Y, Feng J, et al: A functional
polymorphism T309G in MDM2 gene promoter, intensified by
Helicobacter pylori lipopolysaccharide, is associated with
both an increased susceptibility and poor prognosis of gastric
carcinoma in Chinese patients. BMC Cancer. 13:1262013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li Z: Association of gene polymorphisms
with helicobater pylori related gastric cancer in a Chinese
population. (unpublished masters thesis). 2011
|
|
19
|
ERL, Zhang L, Niu W, et al: Relevance of
MDM2 polymorphisms with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, gastric
adenocarcinoma and double primary cancers in esophagus and stomach.
Mod Prev Med. 39:33422012.
|
|
20
|
Er L, Zhang L, Niu W, et al: Relation of
MDM2 gene polymorphism and Helicobacter pylori infection to
gastric cardiac carcinoma. Clin Focus. 24:1594–1597. 2009.
|
|
21
|
Cao YY, Zhang XF, Guo W, Wang R, Ge H and
Zhang JH: Association of the MDM2 polymorphisms with susceptibility
of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and that of gastric cardiac
adenocarcinoma. Tumor. 27:628–632. 2007.
|
|
22
|
Yang M, Guo Y, Zhang X, et al: Interaction
of P53 Arg72Pro and MDM2 T309G polymorphisms and their associations
with risk of gastric cardia cancer. Carcinogenesis. 28:1996–2001.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ohmiya N, Taguchi A, Mabuchi N, et al:
MDM2 promoter polymorphism is associated with both an increased
susceptibility to gastric carcinoma and poor prognosis. J Clin
Oncol. 24:4434–4440. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
González CA and Agudo A: Carcinogenesis,
prevention and early detection of gastric cancer: Where we are and
where we should go. Int J Cancer. 15:745–753. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bond GL, Menin C, Bertorelle R, Alhopuro
P, Aaltonen LA and Levine AJ: MDM2 SNP309 accelerates colorectal
tumour formation in women. J Med Genet. 43:950–952. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ma HB, Huang T, Han F and Chen WY:
Association between MDM2 promoter SNP309 T/G polymorphism and liver
cancer risk - a meta-analysis. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
13:2841–2846. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ma YY, Guan TP, Yao HB, et al: The MDM2
309T>G polymorphism and ovarian cancer risk: a meta-analysis of
1534 cases and 2211 controls. PLoS One. 8:e550192013.
|
|
28
|
Zhang Y, Bai Y, Zhang Y, Guan J and Chen
L: The MDM2 309 T/G polymorphism is associated with head and neck
cancer risk especially in nasopharyngeal cancer: a meta-analysis.
Onkologie. 35:666–670. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhuo W, Zhang L, Zhu B, Ling J and Chen Z:
Association of MDM2 SNP309 variation with lung cancer risk:
evidence from 7196 cases and 8456 controls. PLoS One. 7:e415462012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Liu J, Zheng Y, Lei D, et al: MDM2
309T>G polymorphism and risk of squamous cell carcinomas of head
and neck: a meta-analysis. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 12:1899–1903.
2011.
|
|
31
|
Economopoulos KP and Sergentanis TN:
Differential effects of MDM2 SNP309 polymorphism on breast cancer
risk along with race: a meta-analysis. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
120:211–216. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wiseman M: The Second World Cancer
Research Fund/American Institute for Cancer. Proc Nutr Soc.
67:253–256. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
He W, Long J, Xian L, et al: MDM2 SNP309
polymorphism is associated with lung cancer risk in women: a
meta-analysis using METAGEN. Exp Ther Med. 4:569–576.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kodama M, Fujioka T, Murakami K, et al:
Eradication of Helicobacter pylori reduced the
immunohistochemical detection of p53 and MDM2 in gastric mucosa. J
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 20:941–946. 2005.
|