|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Wallin KL, Wiklund F, Luostarinen T, et
al: A population-based prospective study of Chlamydia
trachomatis infection and cervical carcinoma. Int J Cancer.
101:371–374. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Schiffman M, Castle PE, Jeronimo J,
Rodriguez AC and Wacholder S: Human papillomavirus and cervical
cancer. Lancet. 370:890–907. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
zur Hausen H: Papillomaviruses and cancer:
from basic studies to clinical application. Nat Rev Cancer.
2:342–350. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Andera L: Signaling activated by the death
receptors of the TNFR family. Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky
Olomouc Czech Repub. 153:173–180. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kim R, Emi M, Tanabe K, Uchida Y and Toge
T: The role of Fas ligand and transforming growth factor beta in
tumor progression: molecular mechanisms of immune privilege via
Fas-mediated apoptosis and potential targets for cancer therapy.
Cancer. 100:2281–2291. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Suda T, Takahashi T, Golstein P and Nagata
S: Molecular cloning and expression of the Fas ligand, a novel
member of the tumor necrosis factor family. Cell. 75:1169–1178.
1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Huang QR, Morris D and Manolios N:
Identification and characterization of polymorphisms in the
promoter region of the human Apo-1/Fas (CD95) gene. Mol Immunol.
34:577–582. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sibley K, Rollinson S, Allan JM, et al:
Functional FAS promoter polymorphisms are associated with increased
risk of acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Res. 63:4327–4330.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wu J, Metz C, Xu X, et al: A novel
polymorphic CAAT/enhancer- binding protein beta element in the FasL
gene promoter alters Fas ligand expression: a candidate background
gene in African American systemic lupus erythematosus patients. J
Immunol. 170:132–138. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Sun T, Zhou Y, Li H, et al: FASL -844C
polymorphism is associated with increased activation-induced T cell
death and risk of cervical cancer. J Exp Med. 202:967–974. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lai HC, Lin WY, Lin YW, et al: Genetic
polymorphisms of FAS and FASL (CD95/CD95L) genes in cervical
carcinogenesis: an analysis of haplotype and gene-gene interaction.
Gynecol Oncol. 99:113–118. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zoodsma M, Nolte IM, Schipper M, et al:
Interleukin-10 and Fas polymorphisms and susceptibility for
(pre)neoplastic cervical disease. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 15(Suppl
3): 282–290. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ueda M, Terai Y, Kanda K, et al: Fas gene
promoter -670 polymorphism in gynecological cancer. Int J Gynecol
Cancer. 16(Suppl 1): 179–182. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kang S, Dong SM, Seo SS, Kim JW and Park
SY: FAS-1377 G/A polymorphism and the risk of lymph node metastasis
in cervical cancer. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 180:1–5. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zucchi F, da Silva ID, Ribalta JC, et al:
Fas/CD95 promoter polymorphism gene and its relationship with
cervical carcinoma. Eur J Gynaecol Oncol. 30:142–144.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kordi Tamandani DM, Sobti RC and Shekari
M: Association of Fas-670 gene polymorphism with risk of cervical
cancer in North Indian population. Clin Exp Obstet Gynecol.
35:183–186. 2008.
|
|
18
|
Chatterjee K, Engelmark M, Gyllensten U,
et al: Fas and FasL gene polymorphisms are not associated with
cervical cancer but differ among Black and Mixed-ancestry South
Africans. BMC Research Notes. 2:2382009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ivansson EL, Gustavsson IM, Magnusson JJ,
et al: Variants of chemokine receptor 2 and interleukin 4 receptor,
but not inter-leukin 10 or Fas ligand, increase risk of cervical
cancer. Int J Cancer. 121:2451–2457. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ueda M, Hung YC, Terai Y, et al: Fas gene
promoter -670 polymorphism (A/G) is associated with cervical
carcinogenesis. Gynecol Oncol. 98:129–133. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Engelmark MT, Renkema KY and Gyllensten
UB: No evidence of the involvement of the Fas-670 promoter
polymorphism in cervical cancer in situ. Int J Cancer.
112:1084–1085. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen YQ, Lu LG, Tian QF, et al: The
research of Fas-670 polymorphism and cervical cancer
susceptibility. Natl Med J China. 86:2792–2794. 2006.
|
|
23
|
DerSimonian R and Laird N: Meta-analysis
in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials. 7:177–188. 1986.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mantel N and Haenszel W: Statistical
aspects of the analysis of data from retrospective studies of
disease. J Natl Cancer Inst. 22:719–748. 1959.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Haber M: Exact significance levels of
goodness-of-fit tests for the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. Hum
Hered. 31:161–166. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
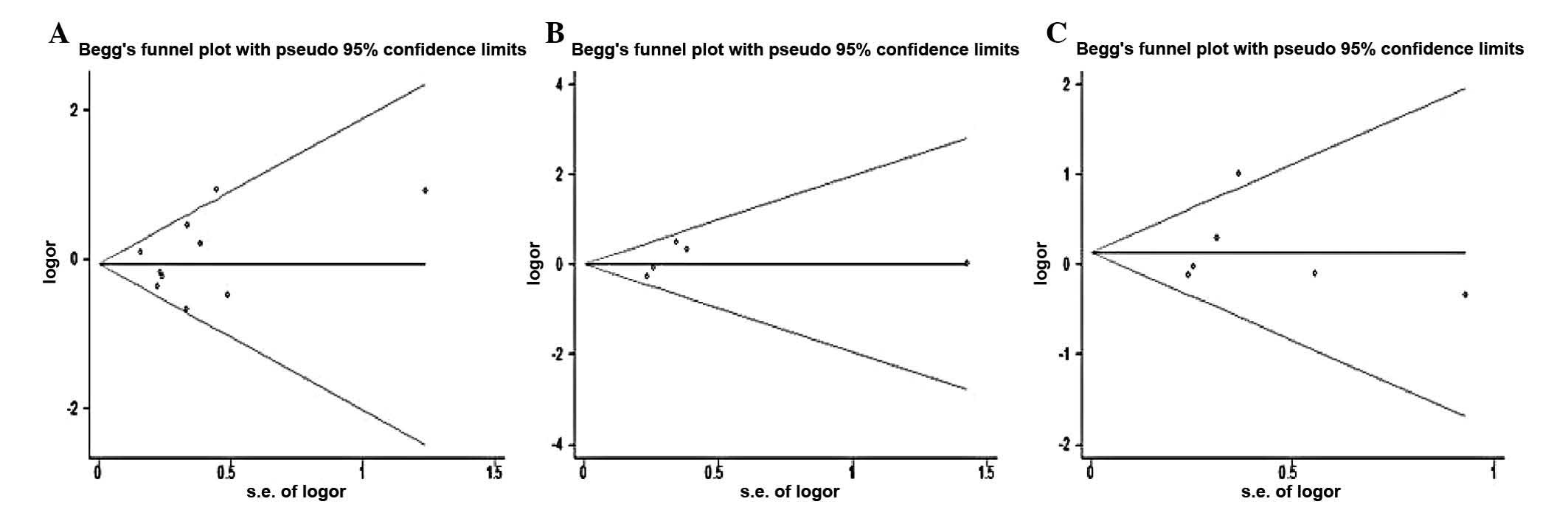
Begg CB and Mazumdar M: Operating
characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias.
Biometrics. 50:1088–1101. 1994. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M and
Minder C: Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical
test. BMJ. 315:629–634. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Reed JC: Mechanisms of apoptosis. Am J
Pathol. 157:1415–1430. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Qiu LX, Shi J, Yuan H, et al: FAS -1,377
G/A polymorphism is associated with cancer susceptibility: evidence
from 10,564 cases and 12,075 controls. Hum Gen. 125:431–435. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Liu Y, Wen Q-J, Yin Y, et al: FASLG
polymorphism is associated with cancer risk. Eur J Cancer.
45:2574–2578. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|