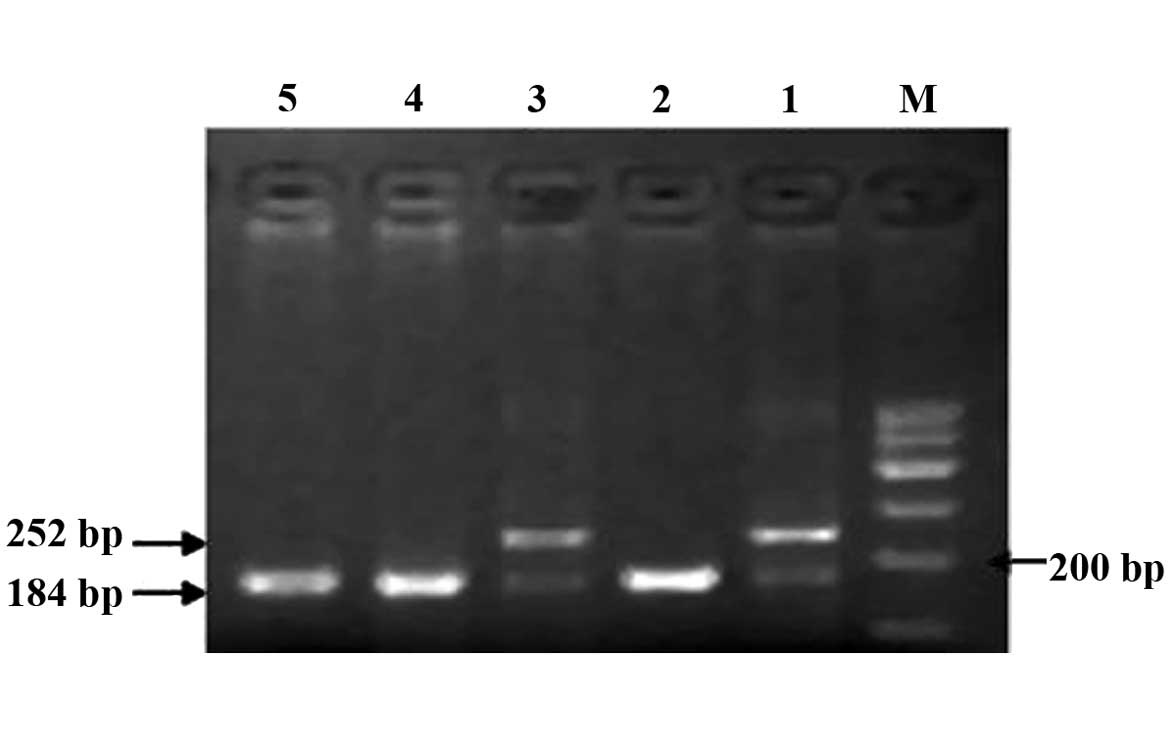
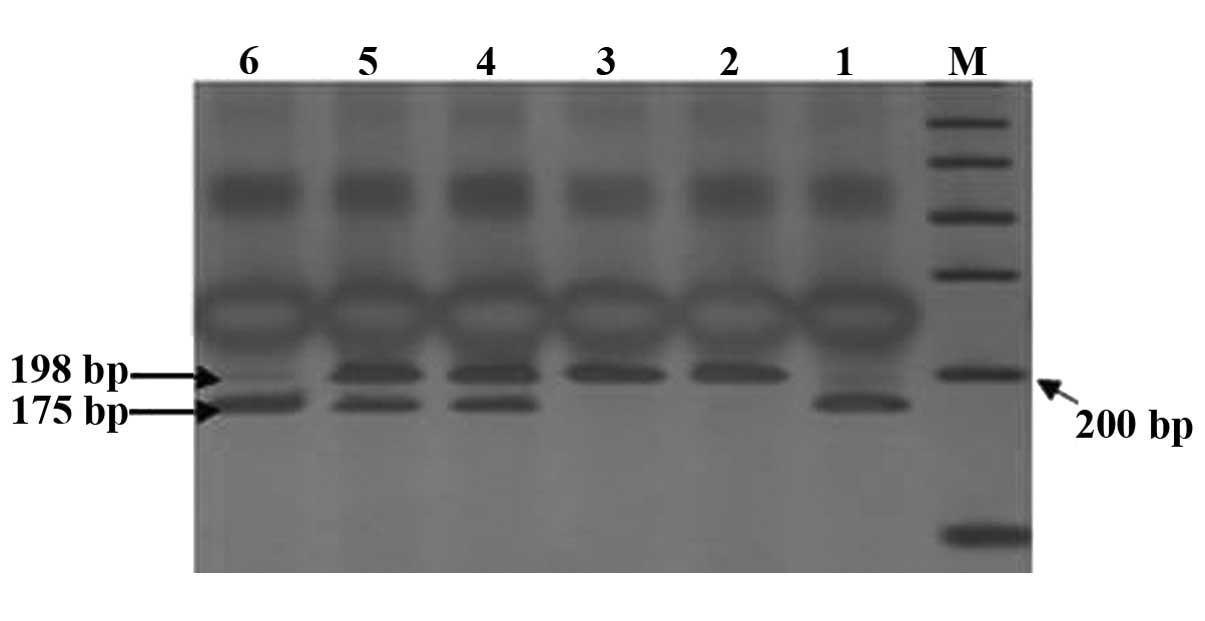
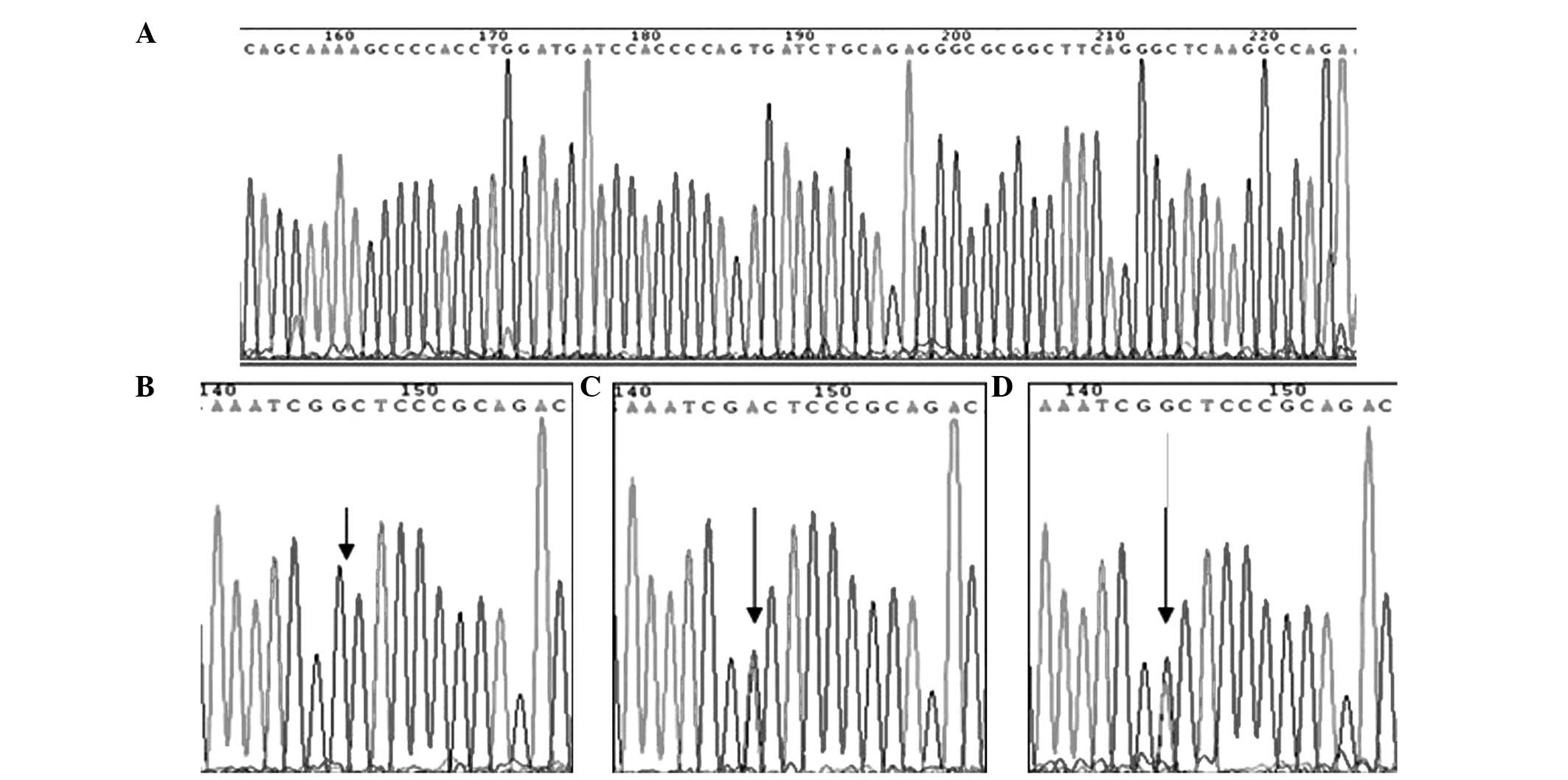
|
1
|
Petramala L, Acca M, Francucci CM and
D’Erasmo E: Hyperhomocysteinemia: a biochemical link between bone
and cardiovascular system diseases? J Endocrinol Invest. 32(Suppl
4): 10–14. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lu D and Lu XC: Research progress of
homocysteine and its metabolic enzyme gene polymorphisms and
cardiovascular disease. Lab Med Clin. 9:844–845. 2012.(In
Chinese).
|
|
3
|
Zhang L, Yin RX, Liu WY, Miao L, et al:
Association of methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase C677T
polymorphism and serum lipid levels in the Guangxi Bai Ku Yao and
Han populations. Lipids Health Dis. 9:1232010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Fowdar JY, Lason MV, Szvetko AL, Lea RA,
et al: Investigation of homocysteine-pathway-related variants in
essential hypertension. Int J Hypertens 2012.
1909:232012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yang B, Liu Y, Li Y, Fan S, et al:
Geographical distribution of MTHFR C677T, A1298C and MTRR A66G gene
polymorphisms in China: findings from 15357 adults of Han
nationality. PLoS One. 8:e579172013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Alghasham A, Settin AA, Ali A, Dowaidar M,
et al: Association of MTHFR C677T and A1298C gene polymorphisms
with hypertension. Int J Health Sci (Qassim). 6:3–11. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lucock M, Yates Z, Martin C, Choi JH, et
al: Hydrogen sulphide-related thiol metabolism and nutrigenetics in
relation to hypertension in an elderly population. Genes Nutr.
8:221–229. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yakub M, Moti N, Parveen S, Chaudhry B, et
al: Polymorphisms in MTHFR, MS and CBS genes and homocysteine
levels in a Pakistani population. PLoS One. 7:e332222012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li AF, Zheng H, Xu YM, Zhao XJ, et al: The
association between gene polymorphisms of homocysteine
metabolism-related enzymes and ischemic cerebrovascular diseases in
Chinese Henan Han population. Life Sci J. 9:403–408. 2012.
|
|
10
|
The National Blood Pressure Survey
Cooperative Group. Prevalence and variation trends of hypertension
in China. J Hypertens. 23(S1)1995.(In Chinese).
|
|
11
|
Kawamura H, Jumabay M, Mitsubayashi H,
Izumi Y, et al: 24-hour blood pressure in Uygur, Kazakh and Han
elderly subjects in China. Hypertens Res. 23:177–185. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Whitworth JA; World Health Organization,
International Society of Hypertension Writing Group. 2003 World
Health Organization (WHO)/International Society of Hypertension
(ISH) statement on management of hypertension. J Hypertens.
21:1983–1992. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tang K, Fu DJ, Julien D, Braun A, et al:
Chip-based genotyping by mass spectrometry. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
96:10016–10020. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Olivieri O, Friso S, Trabetti E, Girelli
D, et al: Homocysteine and atheromatous renal artery stenosis. Clin
Exp Med. 1:211–218. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Le Marchand L, Donlon T, Hankin JH,
Kolonel LN, Wilkens LR and Seifried A: B-vitamin intake, metabolic
genes, and colorectal cancer risk (United States). Cancer Causes
Control. 13:239–248. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bi XH, Zhao HL, Zhang ZX, Liu Q, et al:
Association analysis of CbetaS 844ins68 and MTHFD1 G1958A
polymorphisms with Alzheimer’s disease in Chinese. J Neural Transm.
117:499–503. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ott N, Geddert H and Sarbia M:
Polymorphisms in methionine synthase (A2756G) and cystathionine
beta-synthase (844ins68) and susceptibility to carcinomas of the
upper gastrointestinal tract. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 134:405–410.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Orendác M, Musková B, Richterová E,
Zvárová J, et al: Is the common 844ins68 polymorphism in the
cystathionine beta-synthase gene associated with atherosclerosis? J
Inherit Metab Dis. 22:674–675. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mitrou PN, Watson MA, Loktionov AS, et al:
MTHFR (C677T and A1298C) polymorphisms and risk of sporadic distal
colorectal adenoma in the UK Flexible Sigmoidoscopy Screening Trial
(United Kingdom). Cancer Causes Control. 17:793–801. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Poduri A, Mukherjee D, Sud K, Kohli HS, et
al: MTHFR A1298C polymorphism is associated with cardiovascular
risk in end stage renal disease in North Indians. Mol Cell Biochem.
308:43–50. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Onrat ST, Akci O, Söylemez Z, Onrat E and
Avşar A: Prevalence of myocardial infarction polymorphisms in
Afyonkarahisar, Western Turkey. Mol Biol Rep. 39:9257–9264. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Cui LH, Shin MH, Kweon SS, Kim HN, Song
HR, et al: Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase C677T polymorphism
in patients with gastric and colorectal cancer in a Korean
population. BMC Cancer. 10:2362010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|