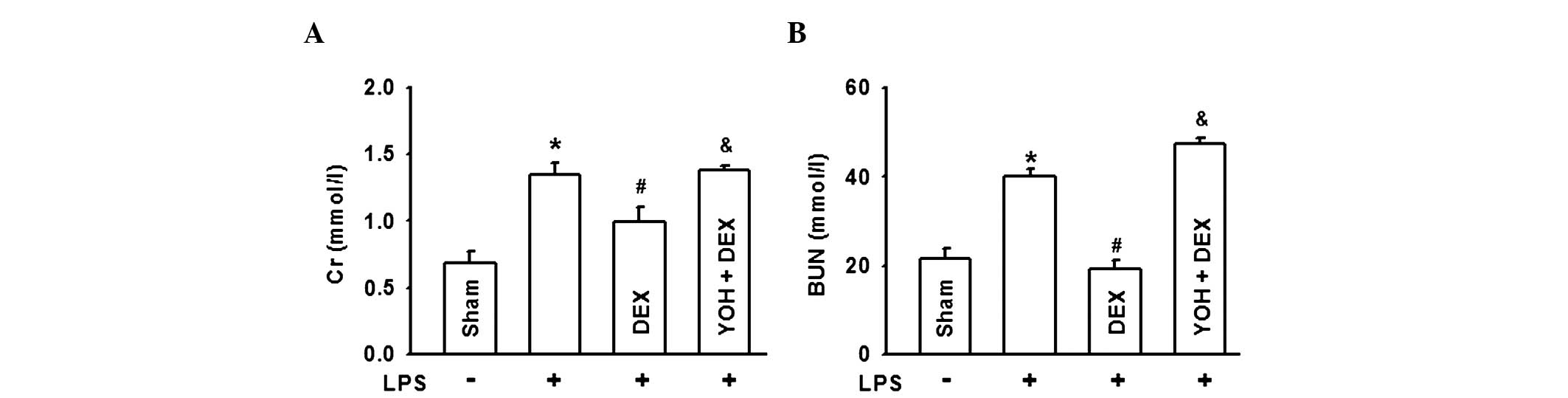
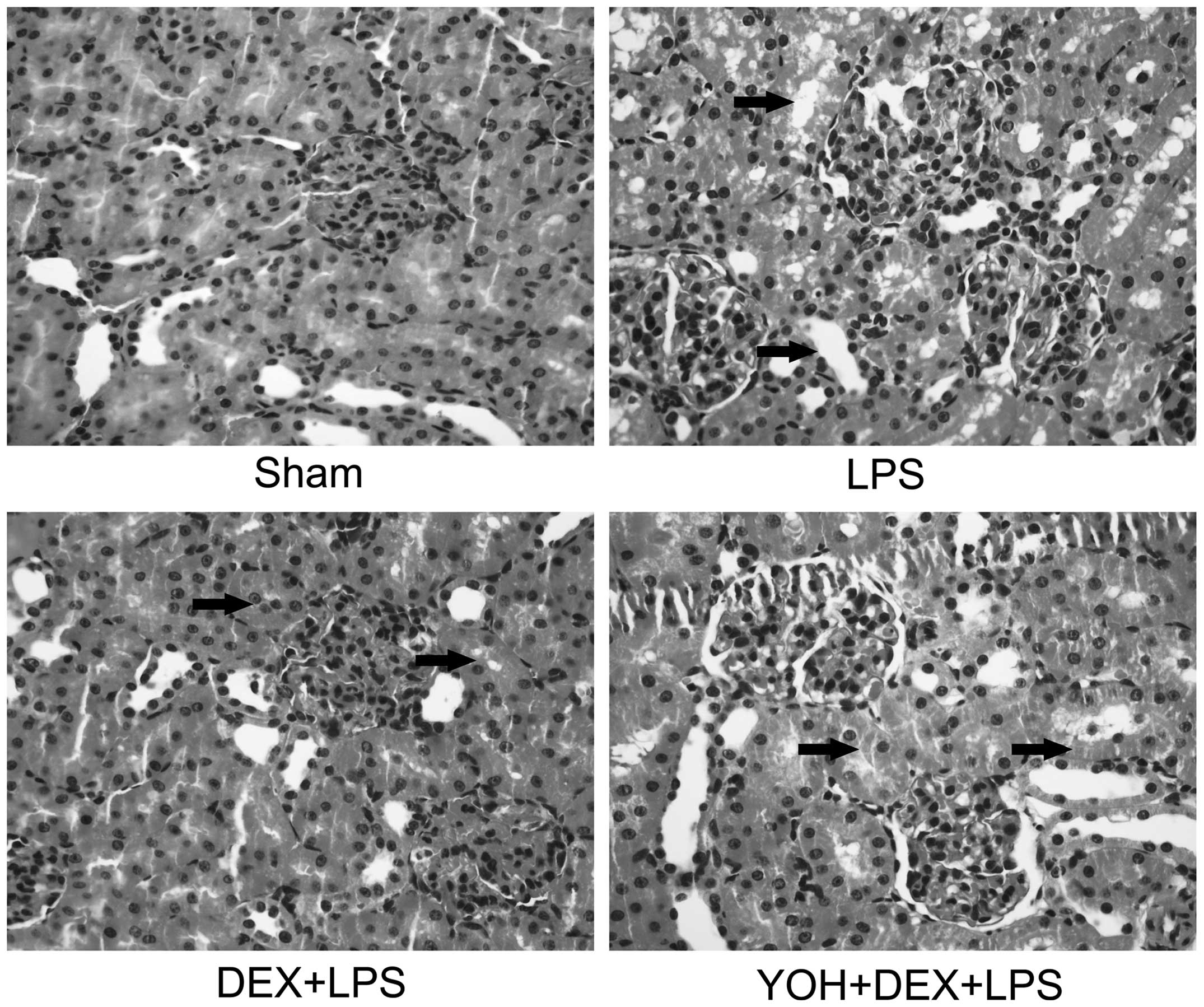
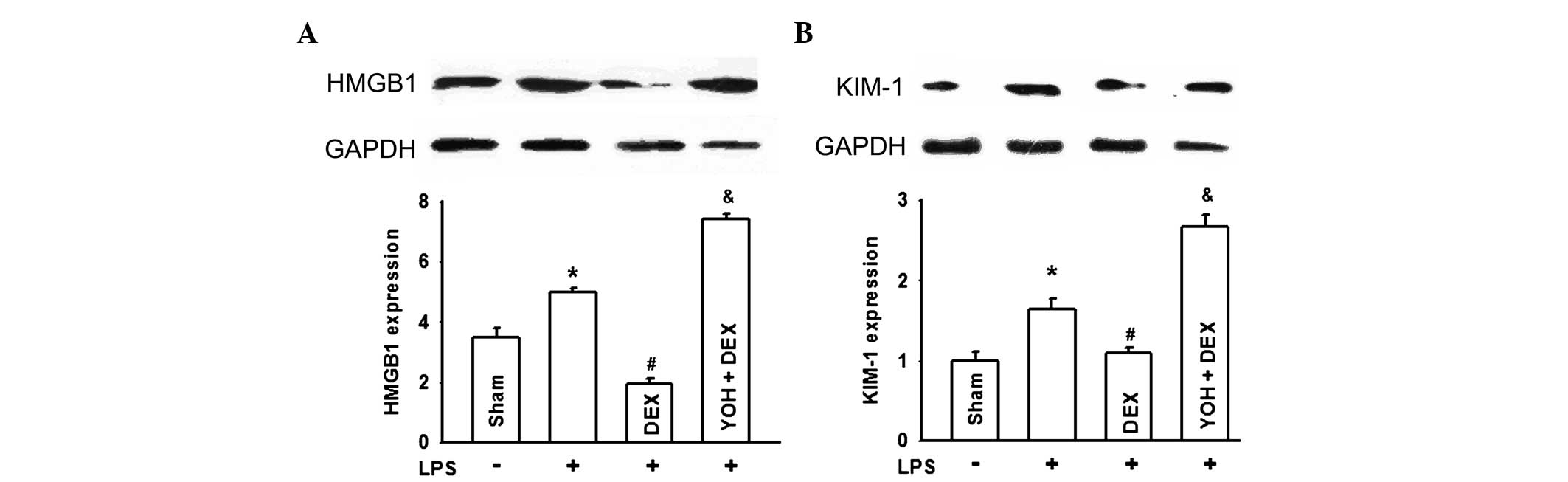
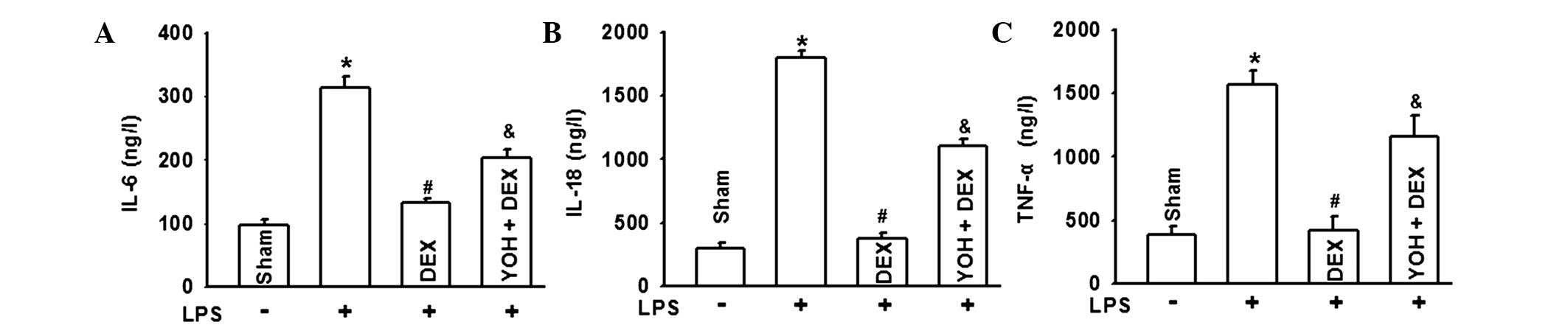
|
1
|
Puri VK: Of mice and MODS, TNF-alpha, and
sepsis. Crit Care Med. 26:11601998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Oda S, Hirasawa H, Sugai T, Shiga H,
Nakanishi K, Kitamura N, Sadahiro T and Hirano T: Comparison of
Sepsis-related Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) score and CIS
(cellular injury score) for scoring of severity for patients with
multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS). Intensive Care Med.
26:1786–1793. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bagshaw SM, George C and Bellomo R: ANZICS
Database Management Committee: Early acute kidney injury and
sepsis: A multicentre evaluation. Crit Care. 12:R472008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Schrier RW and Wang W: Acute renal failure
and sepsis. N Engl J Med. 351:159–169. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Rajapakse S, Rodrigo C, Rajapakse A,
Kirthinanda D and Wijeratne S: Renal replacement therapy in
sepsis-induced acute renal failure. Saudi J kidney Dis Transpl.
20:553–559. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Nisula S, Yang R, Poukkanen M, et al: The
FINNAKI Study Group: Predictive value of urine interleukin-18 in
the evolution and outcome of acute kidney injury in critically ill
adult patients. Br J Anaesth. Dec 3–2014.(Epub ahead of print).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yang Y, Zhang ZX, Lian D, Haig A,
Bhattacharjee RN and Jevnikar AM: IL-37 inhibits IL-18 induced
tubular epithelial cell expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines
and renal ischemia reperfusion injury. Kidney Int. 87:396–408.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Miranda ML, Balarini MM and Bouskela E:
Dexmedetomidine Attenuates the Microcirculatory Derangements Evoked
by Experimental Sepsis. Anesthesiology. Oct 13–2014.(Epub ahead of
print).
|
|
9
|
Geloen A, Chapelier K, Cividjian A,
Dantony E, Rabilloud M, May CN and Quintin L: Clonidine and
dexmedetomidine increase the pressor response to norepinephrine in
experimental sepsis: A pilot study. Crit Care Med. 41:e431–e438.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Duan X, Li Y, Zhou C, Huang L and Dong Z:
Dexmedetomidine provides neuroprotection: Impact on
ketamine-induced neuroapoptosis in the developing rat brain. Acta
Anaesthesiol Scand. 58:1121–1126. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Turan A, Bashour CA, You J, Kirkova Y,
Kurz A, Sessler DI and Saager L: Dexmedetomidine sedation after
cardiac surgery decreases atrial arrhythmias. J Clin Anesth.
26:634–642. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang ZX, Huang CY, Hua YP, Huang WQ, Deng
LH and Liu KX: Dexmedetomidine reduces intestinal and hepatic
injury after hepatectomy with inflow occlusion under general
anaesthesia: A randomized controlled trial. Br J Anaesth.
112:1055–1064. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Si YN, Bao HG, Xu L, Wang XL, Shen Y, Wang
JS and Yang XB: Dexmedetomidine protects against
ischemia/reperfusion injury in rat kidney. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol
Sci. 18:1843–1851. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bayraktar O, Tekin N, Aydın O, Akyuz F,
Musmul A and Burukoglu D: Effects of S-allyl cysteine on lung and
liver tissue in a rat model of lipopolysaccharide-induced sepsis.
Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. Dec 6–2014.(Epub ahead of
print). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Restitutti F, Laitinen MR, Raekallio MR,
Vainionpää M, O'Brien RT, Kuusela E and Vainio OM: Effect of MK-467
on organ blood flow parameters detected by contrast-enhanced
ultrasound in dogs treated with dexmedetomidine. Vet Anaesth Analg.
40:e48–e56. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang Y, Yu X, Wang F, Wang Y, Wang Y, Li
H, Lv X, Lu D and Wang H: Yohimbine promotes cardiac NE release and
prevents LPS-induced cardiac dysfunction via blockade of
presynaptic α2A-adrenergic receptor. PLoS ONE. 8:e636222013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hamar P, Song E, Kökény G, Chen A, Ouyang
N and Lieberman J: Small interfering RNA targeting Fas protects
mice against renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 101:14883–14888. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ratliff BB, Rabadi MM, Vasko R, Yasuda K
and Goligorsky MS: Messengers without borders: Mediators of
systemic inflammatory response in AKI. J Am Soc Nephrol.
24:529–536. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Westenfelder C: Programmed
anti-inflammatory macrophages protect against AKI and promote
repair through trophic actions. Kidney Int. 81:939–941. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Singbartl K and Kellum JA: AKI in the ICU:
Definition, epidemiology, risk stratification, and outcomes. Kidney
Int. 81:819–825. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Honore PM, Jacobs R, Joannes Boyau O, et
al: Septic AKI in ICU patients. Diagnosis, pathophysiology and
treatment type, dosing, and timing: A comprehensive review of
recent and future developments. Ann Intensive Care. 1:322011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Venkatachalam MA and Weinberg JM: The
conundrum of protection from AKI by adenosine in rodent clamp
ischemia models. Kidney Int. 84:16–19. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Myrvang H: Acute kidney injury: Obesity is
associated with AKI after surgery via oxidative stress. Nat Rev
Nephrol. 8:4332012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Choe JY, Park KY and Kim SK: Oxidative
stress by monosodium urate crystals promotes renal cell apoptosis
through mitochondrial caspase dependent pathway in human embryonic
kidney 293 cells: Mechanism for urate-induced nephropathy.
Apoptosis. 20:38–49. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Anjaneyulu M and Chopra K: Effect of
irbesartan on the antioxidant defence system and nitric oxide
release in diabetic rat kidney. Am J Nephrol. 24:488–496. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yatim KM and Oberbarnscheidt MH: Endotoxin
and AKI: Macrophages Protect after Preconditioning. J Am Soc
Nephrol. Nov 14–2014.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Rodríguez-Iturbe B, Johnson RJ and
Herrera-Acosta J: Tubulointerstitial damage and progression of
renal failure. Kidney Int Suppl. 99:S82–S86. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Han WK, Bailly V, Abichandani R, Thadhani
R and Bonventre JV: Kidney Injury Molecule-1 (KIM-1): A novel
biomarker for human renal proximal tubule injury. Kidney Int.
62:237–244. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Vaidya VS, Ramirez V, Ichimura T,
Bobadilla NA and Bonventre JV: Urinary kidney injury molecule-1: A
sensitive quantitative biomarker for early detection of kidney
tubular injury. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 290:F517–F529. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Liangos O, Perianayagam MC, Vaidya VS, et
al: Urinary N-acetyl-beta-(D)-glucosaminidase activity and kidney
injury molecule-1 level are associated with adverse outcomes in
acute renal failure. J Am Soc Nephrol. 18:904–912. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lameire N, Van Biesen W and Vanholder R:
Acute renal failure. Lancet. 365:417–430. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Cunningham PN, Wang Y, Guo R, He G and
Quigg RJ: Role of Toll-like receptor 4 in endotoxin-induced acute
renal failure. J Immunol. 172:2629–2635. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lu JCT, Coca SG, Patel UD, Cantley L and
Parikh CR: Translational Research Investigating Biomarkers and
Endpoints for Acute Kidney Injury (TRIBE-AKI) Consortium: Searching
for genes that matter in acute kidney injury: A systematic review.
Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 4:1020–1031. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hall IE, Yarlagadda SG, Coca SG, Wang Z,
Doshi M, Devarajan P, Han WK, Marcus RJ and Parikh CR: IL-18 and
urinary NGAL predict dialysis and graft recovery after kidney
transplantation. J Am Soc Nephrol. 21:189–197. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Villela NR, do Nascimento Júnior P, de
Carvalho LR and Teixeira A: Effects of dexmedetomidine on renal
system and on vasopressin plasma levels. Experimental study in
dogs. Rev Bras Anestesiol. 55:429–440. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hanci V, Yurdakan G, Yurtlu S, Turan IO
and Sipahi EY: Protective effect of dexmedetomidine in a rat model
of α-naphthylthiourea-induced acute lung injury. J Surg Res.
178:424–430. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Cekic B, Geze S, Ozkan G, et al: The
effect of dexmedetomidine on oxidative stress during
pneumoperitoneum. BioMed research international. 2014:7603232014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Gu J, Sun P, Zhao H, Watts HR, Sanders RD,
Terrando N, Xia P, Maze M and Ma D: Dexmedetomidine provides
renoprotection against ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice. Crit
Care. 15:R1532011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Tracey KJ: Physiology and immunology of
the cholinergic antiinflammatory pathway. J Clin Invest.
117:289–296. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Nance DM and Sanders VM: Autonomic
innervation and regulation of the immune system (1987–2007). Brain
Behav Immun. 21:736–745. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Si Y, Bao H, Han L, et al: Dexmedetomidine
protects against renal ischemia and reperfusion injury by
inhibiting the JAK/STAT signaling activation. J Transl Med.
11:1412013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|