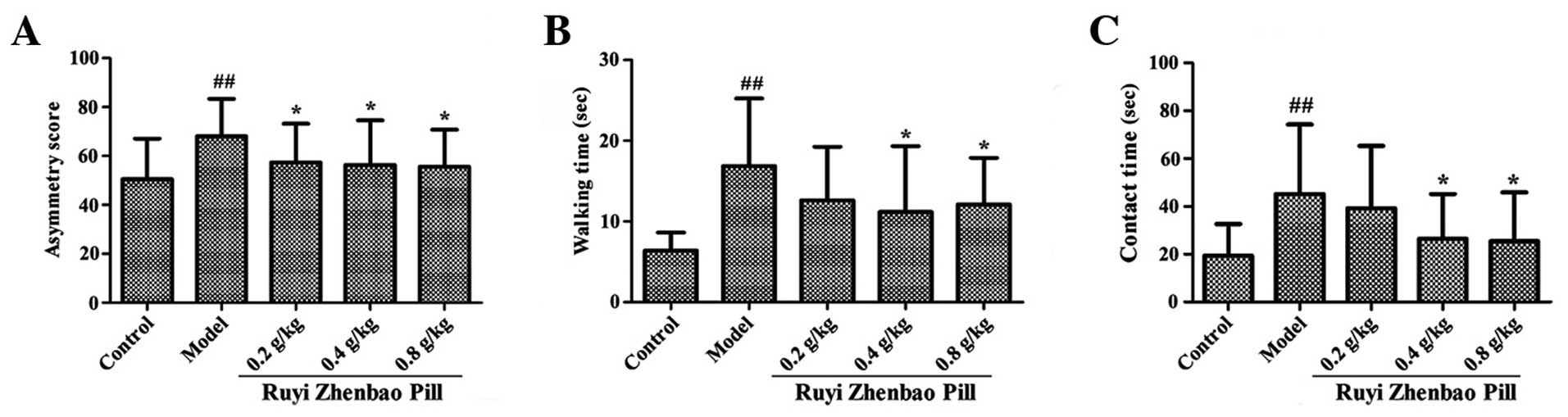
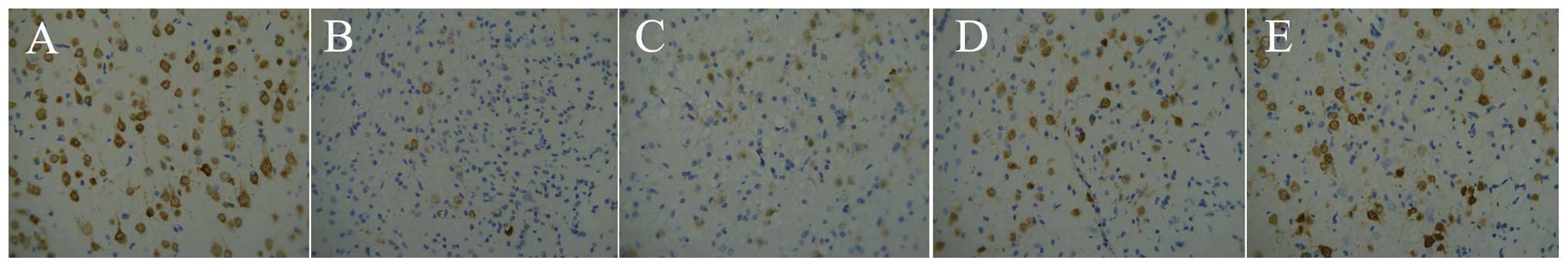
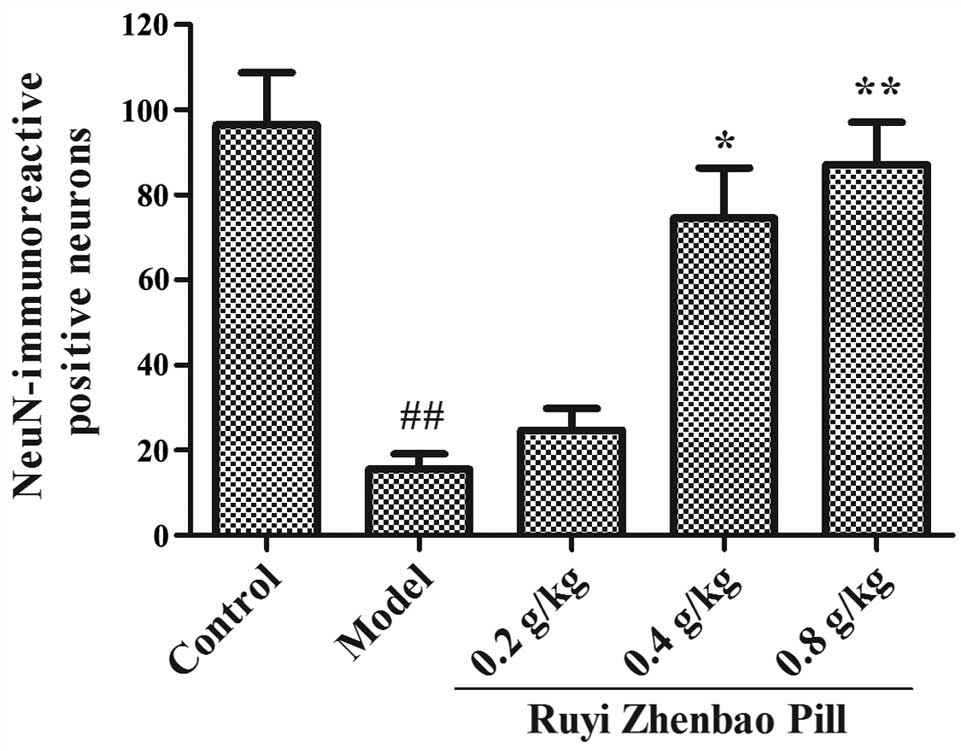
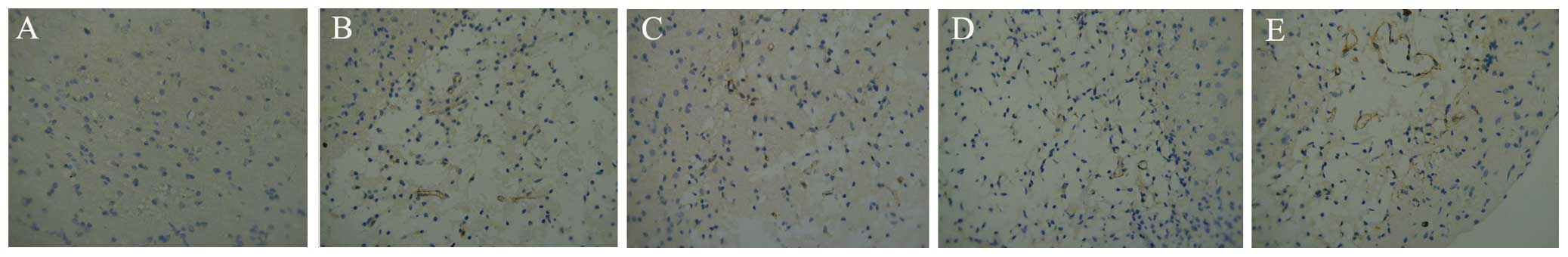
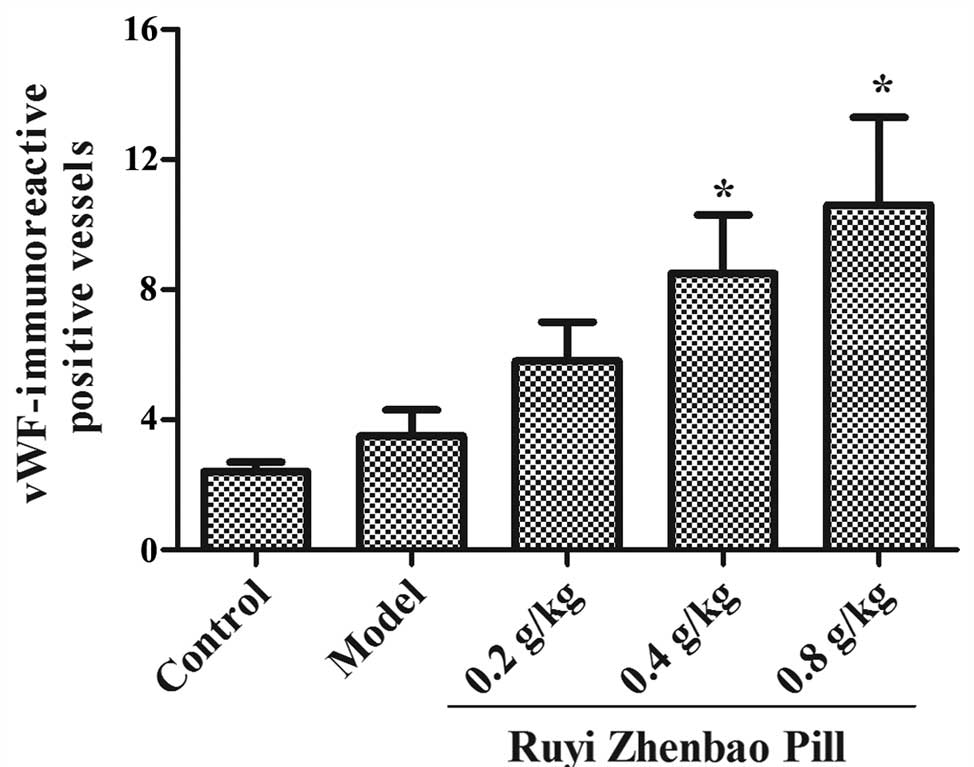
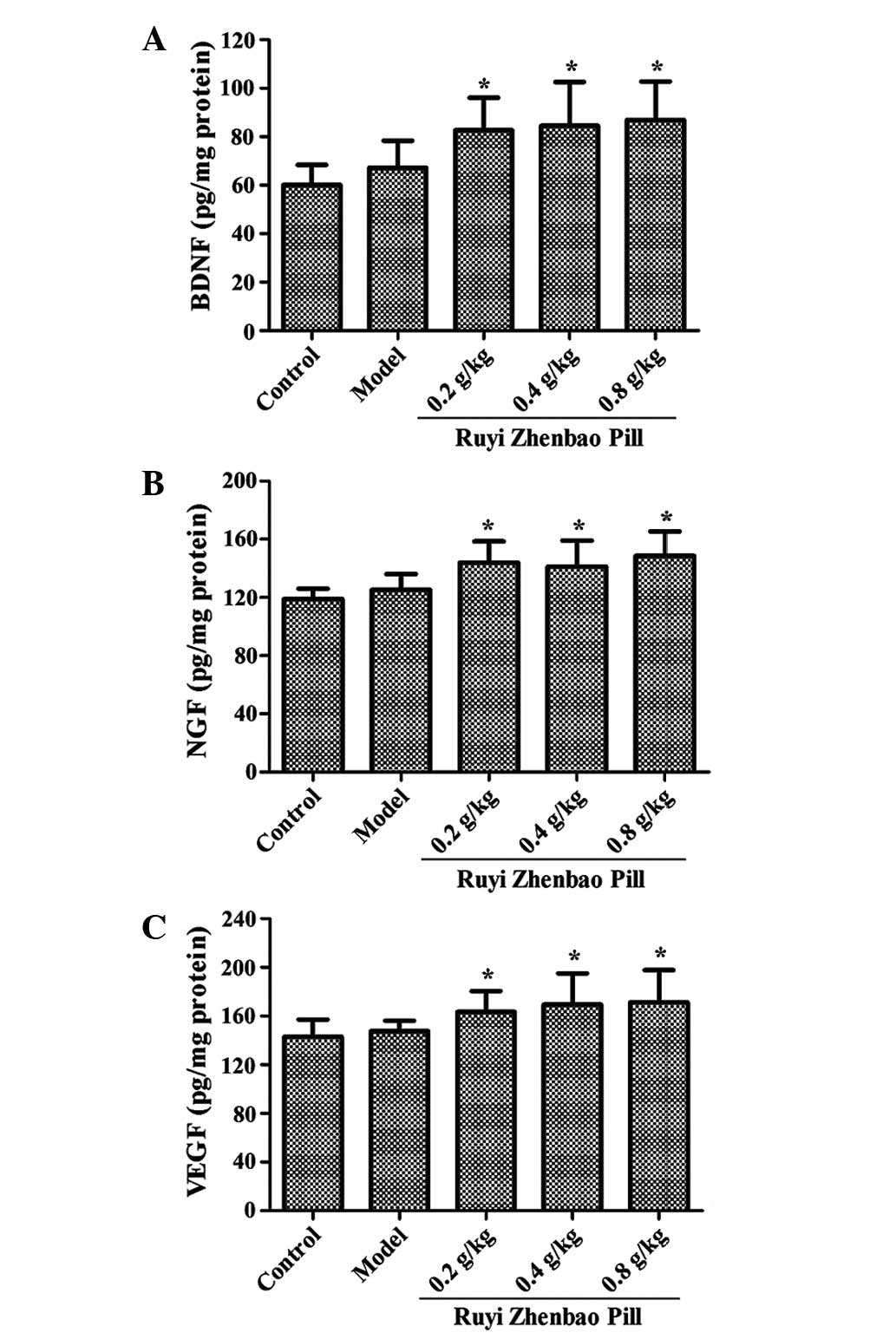
|
1
|
Johnston SC, Mendis S and Mathers CD:
Global variation in stroke burden and mortality: Estimates from
monitoring, surveillance and modelling. Lancet Neurol. 8:345–354.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Young AR, Ali C, Duretête A and Vivien D:
Neuroprotection and stroke: Time for a compromise. J Neurochem.
103:1302–1309. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wong CH and Crack PJ: Modulation of
neuro-inflammation and vascular response by oxidative stress
following cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Curr Med Chem.
15:1–14. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Eltzschig HK and Eckle T: Ischemia and
reperfusion-from mechanism to translation. Nat Med. 17:1391–1401.
2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Huang J, Upadhyay UM and Tamargo RJ:
Inflammation in stroke and focal cerebral ischemia. Surg Neurol.
66:232–245. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gürsoy-Ozdemir Y, Can A and Dalkara T:
Reperfusion-induced oxidative/nitrative injury to neurovascular
unit after focal cerebral ischemia. Stroke. 35:1449–1453. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Arai K, Jin G, Navaratna D and Lo EH:
Brain angiogenesis in developmental and pathological processes:
Neurovascular injury and angiogenic recovery after stroke. FEBS J.
276:4644–4652. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Moskowitz MA, Lo EH and Iadecola C: The
science of stroke: Mechanisms in search of treatments. Neuron.
67:181–198. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Raab S and Plate KH: Different networks,
common growth factors: Shared growth factors and receptors of the
vascular and the nervous system. Acta Neuropathol. 113:607–626.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yao RQ, Zhang L, Wang W and Li L: Cornel
iridoid glycoside promotes neurogenesis and angiogenesis and
improves neurological function after focal cerebral ischemia in
rats. Brain Res Bull. 79:69–76. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gu LJ and Zhang J: Protective effect of
Ruyi Zhenbao pian on experimental cerebral ischemia in rats. Chin
Arch Tradi Chin Med. 31:1288–1290. 2013.(In Chinese).
|
|
12
|
Liu X, Wang L and Fu J: To study the
effect of Ruyi Zhenbao pill on functional recovery of post-stroke
patients. Shandong Medi. 50:882010.(In Chinese).
|
|
13
|
Pereira BM, Weinstein PR, Zea-Longa E and
el-Fiki M: Effect of blood flow rate and donor vessel diameter on
the patency of carotid venous bypass grafts in dogs. Surg Neurol.
31:195–199. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S and
Cummins R: Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without
craniectomy in rats. Stroke. 20:84–91. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shi GX, Yang CY, Wu MM, Guan LP, Wang LP
and Liu CZ: Muscle hypertonia after permanent focal cerebral
ischemia in rats: A qualitative and quantitative behavioral and
electrophysiological study. Int J Neurosci. 123:575–581. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Soleman S, Yip P, Leasure JL and Moon L:
Sustained sensorimotor impairments after endothelin-1 induced focal
cerebral ischemia (stroke) in aged rats. Exp Neurol. 222:13–24.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Allred RP, Maldonado MA, Hsu Je and Jones
TA: Training the ‘less-affected’ forelimb after unilateral cortical
infarcts interferes with functional recovery of the impaired
forelimb in rats. Restor Neurol Neurosci. 23:297–302.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Schallert T, Upchurch M, Wilcox RE and
Vaughn DM: Posture-independent sensorimotor analysis of
inter-hemispheric receptor asymmetries in neostriatum. Pharmacol
Biochem Behav. 18:753–759. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lin B, Levy S, Raval AP, Perez-Pinzon MA
and Defazio RA: Forebrain ischemia triggers GABAergic system
degeneration in substantia nigra at chronic stages in rats.
Cardiovasc Psychiatry Neurol. 2010:5069522010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Holmberg P, Liljequist S and Wägner A:
Secondary brain injuries in thalamus and hippocampus after focal
ischemia caused by mild, transient extradural compression of the
somatosensori cortex in the rat. Curr Neurovasc Res. 6:1–11. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Moro N and Sutton RL: Beneficial effects
of sodium or ethyl pyruvate after traumatic brain injury in the
rat. Exp Neurol. 225:391–401. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lyden PD, Zivin JA, Chabolla DR, Jacobs MA
and Gage FH: Quantitative effects of cerebral infarction on spatial
learning in rats. Exp Neurol. 116:122–132. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Porritt MJ, Andersson HC, Hou L, Nilsson
A, Pekna M, Pekny M and Nilsson M: Photothrombosis-induced
infarction of the mouse cerebral cortex is not affected by the
Nrf2-activator sulforaphane. PLoS One. 7:e410902012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Schallert T, Fleming SM, Leasure JL,
Tillerson JL and Bland ST: CNS plasticity and assessment of
forelimb sensorimotor outcome in unilateral rat models of stroke,
cortical ablation, parkinsonism and spinal cord injury.
Neuropharmacology. 39:777–787. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chang YS, Mu D, Wendland M, Sheldon RA,
Vexler ZS, McQuillen PS and Ferriero DM: Erythropoietin improves
functional and histological outcome in neonatal stroke. Pediatr
Res. 58:106–111. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Nomura S, Kagawa Y, Kida H, Maruta Y,
Imoto H, Fujii M and Suzuki M: Effects of intrathecal baclofen
therapy on motor and cognitive functions in a rat model of cerebral
palsy. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 9:209–215. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Park SI, Jang DK, Han YM, Sunwoo YY, Park
MS, Chung YA, Maeng LS, Im R, Kim MW, Jeun SS and Jang KS: Effect
of combination therapy with sodium ozagrel and panax ginseng on
transient cerebral ischemia model in rats. J Biomed Biotechnol.
2010:8934012010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gow WR, Campbell K, Meade AJ, Watt PM,
Milech N, Knuckey NW and Meloni BP: Lack of neuroprotection of
inhibitory peptides targeting Jun/JNK after transient focal
cerebral ischemia in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Cereb Blood
Flow Metab. 31:e1–e8. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Liu YP, Seçkin H, Izci Y, Du ZW, Yan YP
and Başkaya MK: Neuroprotective effects of mesenchymal stem cells
derived from human embryonic stem cells in transient focal cerebral
ischemia in rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 29:780–791. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang L, Zhang Z, Wang Y, Zhang R and Chopp
M: Treatment of stroke with erythropoietin enhances neurogenesis
and angiogenesis and improves neurological function in rats.
Stroke. 35:1732–1737. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Huang EJ and Reichardt LF: Neurotrophins:
Roles in neuronal development and function. Annu Rev Neurosci.
24:677–736. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Cowansage KK, LeDoux JE and Monfils MH:
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor: A dynamic gatekeeper of neural
plasticity. Curr Mol Pharmacol. 3:12–29. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kim MW, Bang MS, Han TR, Ko YJ, Yoon BW,
Kim JH, Kang LM, Lee KM and Kim MH: Exercise increased BDNF and
trkB in the contralateral hemisphere of the ischemic rat brain.
Brain Res. 1052:16–21. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Madinier A, Bertrand N, Mossiat C,
Prigent-Tessier A, Beley A, Marie C and Garnier P: Microglial
involvement in neuroplastic changes following focal brain ischemia
in rats. PLoS One. 4:e81012009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Greenberg DA and Jin K: From angiogenesis
to neuropathology. Nature. 438:954–959. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|