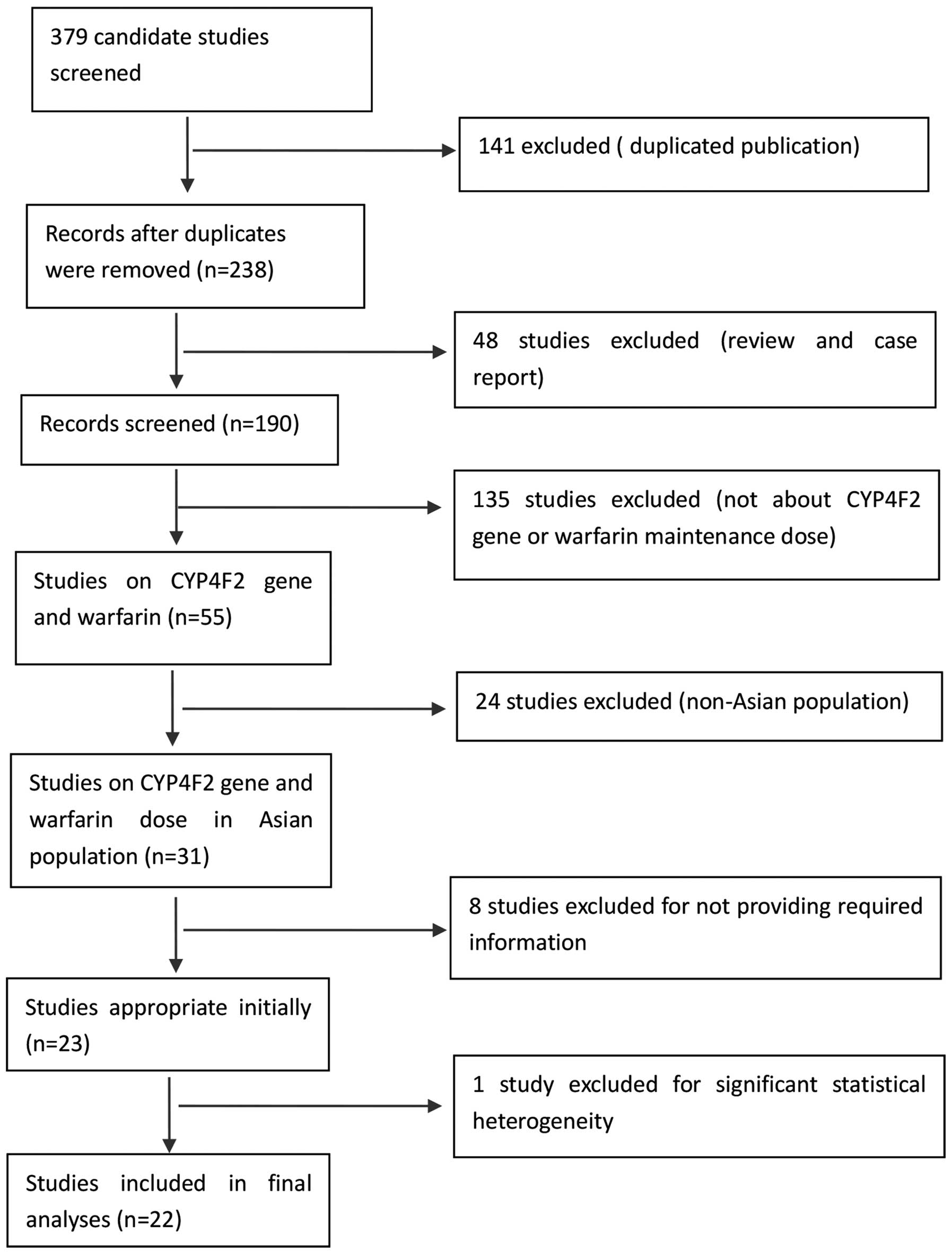
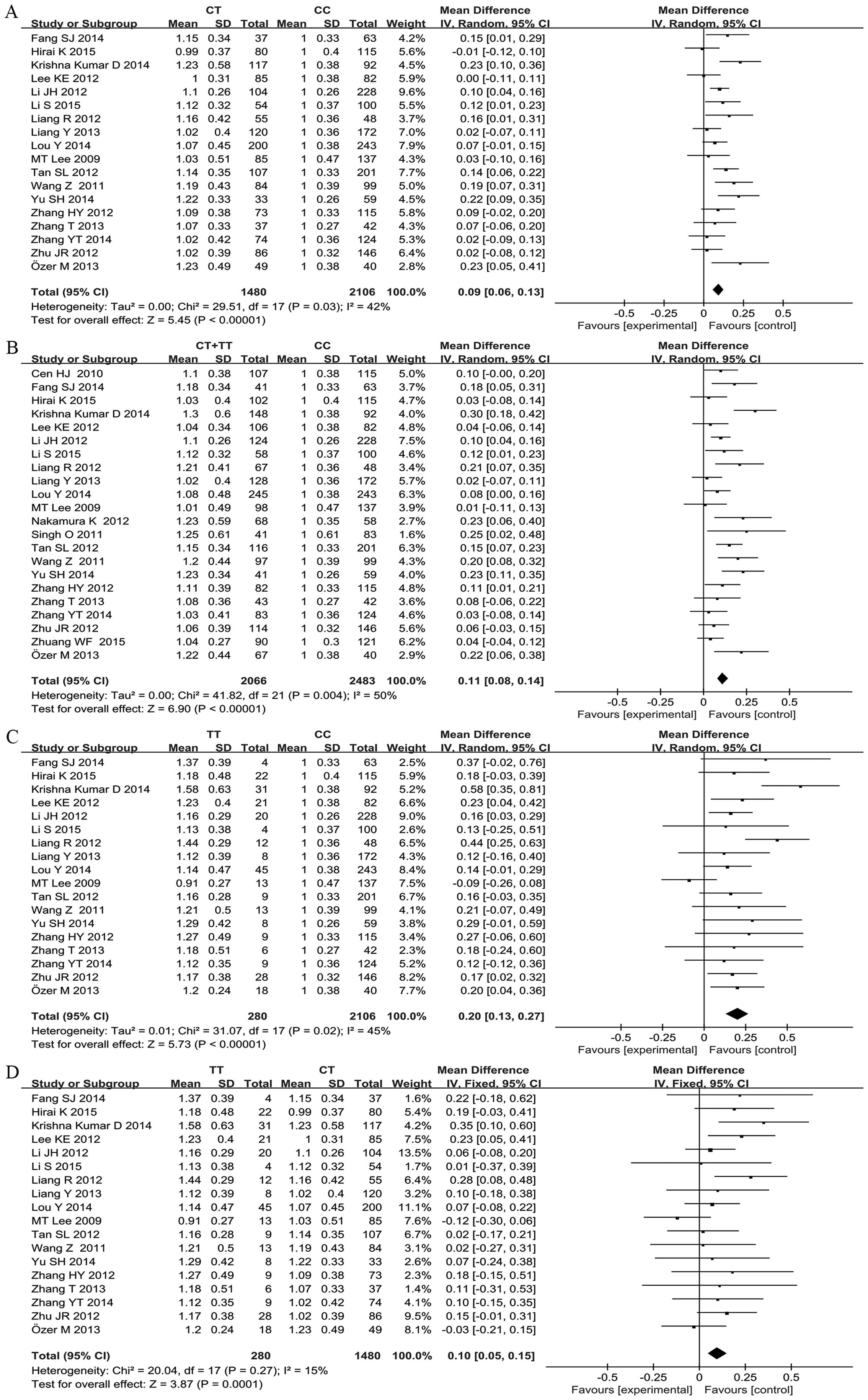
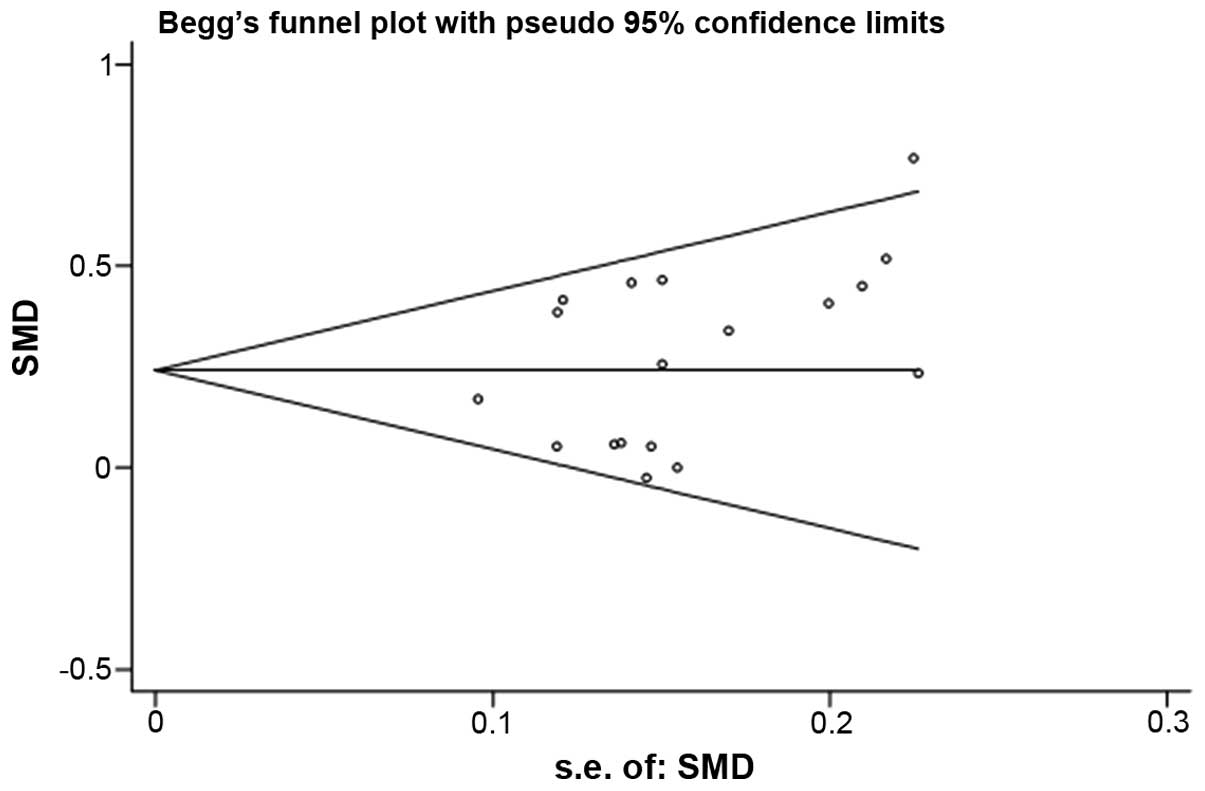
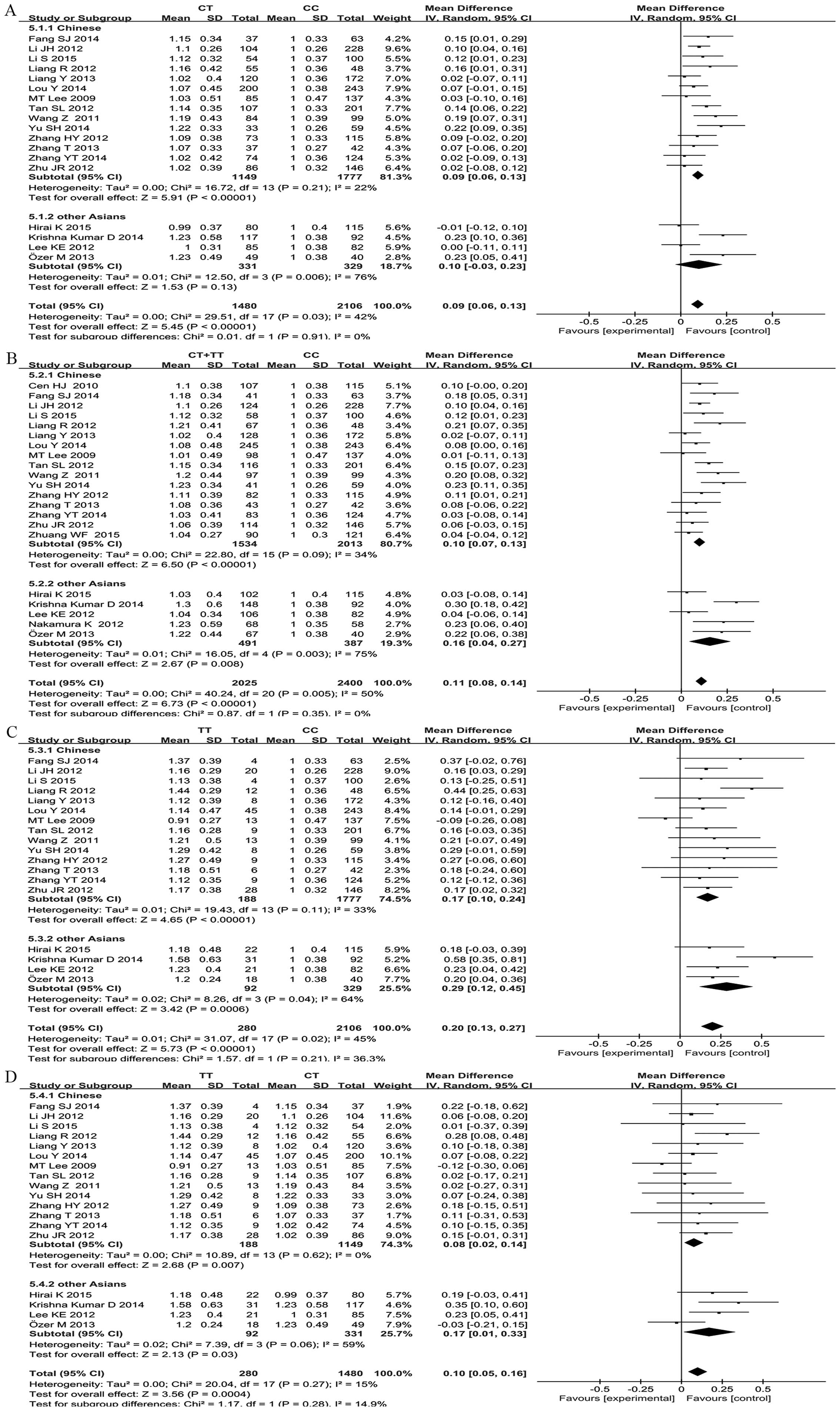
|
1
|
Klein TE, Altman RB, Eriksson N, Gage BF,
Kimmel SE, Lee MT, Limdi NA, Page D, Roden DM, Wagner MJ, et al:
International Warfarin Pharmacogenetics Consortium: Estimation of
the warfarin dose with clinical and pharmacogenetic data. N Engl J
Med. 360:753–764. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhu Y, Shennan M, Reynolds KK, Johnson NA,
Herrnberger MR, Valdes R Jr and Linder MW: Estimation of warfarin
maintenance dose based on VKORC1 (−1639 G>A) and CYP2C9
genotypes. Clin Chem. 53:1199–1205. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gage BF, Eby C, Johnson JA, Deych E,
Rieder MJ, Ridker PM, Milligan PE, Grice G, Lenzini P, Rettie AE,
et al: Use of pharmacogenetic and clinical factors to predict the
therapeutic dose of warfarin. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 84:326–331.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ohno M, Yamamoto A, Ono A, Miura G,
Funamoto M, Takemoto Y, Otsu K, Kouno Y, Tanabe T, Masunaga Y, et
al: Influence of clinical and genetic factors on warfarin dose
requirements among Japanese patients. Eur J Clin Pharmacol.
65:1097–1103. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cini M, Legnani C, Cosmi B, Guazzaloca G,
Valdrè L, Frascaro M and Palareti G: A new warfarin dosing
algorithm including VKORC1 3730 G>A polymorphism: Comparison
with results obtained by other published algorithms. Eur J Clin
Pharmacol. 68:1167–1174. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Huang SW, Chen HS, Wang XQ, Huang L, Xu
DL, Hu XJ, Huang ZH, He Y, Chen KM, Xiang DK, et al: Validation of
VKORC1 and CYP2C9 genotypes on interindividual warfarin maintenance
dose: A prospective study in Chinese patients. Pharmacogenet
Genomics. 19:226–234. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Teichert M, Eijgelsheim M, Rivadeneira F,
Uitterlinden AG, van Schaik RH, Hofman A, De Smet PA, van Gelder T,
Visser LE and Stricker BH: A genome-wide association study of
acenocoumarol maintenance dosage. Hum Mol Genet. 18:3758–3768.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
McDonald MG, Rieder MJ, Nakano M, Hsia CK
and Rettie AE: CYP4F2 is a vitamin K1 oxidase: An explanation for
altered warfarin dose in carriers of the V433M variant. Mol
Pharmacol. 75:1337–1346. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Caldwell MD, Awad T, Johnson JA, Gage BF,
Falkowski M, Gardina P, Hubbard J, Turpaz Y, Langaee TY, Eby C, et
al: CYP4F2 genetic variant alters required warfarin dose. Blood.
111:4106–4112. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lee MT, Chen CH, Chou CH, Lu LS, Chuang
HP, Chen YT, Saleem AN, Wen MS, Chen JJ, Wu JY, et al: Genetic
determinants of warfarin dosing in the Han-Chinese population.
Pharmacogenomics. 10:1905–1913. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liang R, Li L, Li C, Gao Y, Liu W, Hu D
and Sun Y: Impact of CYP2C9*3, VKORC1-1639, CYP4F2rs2108622 genetic
polymorphism and clinical factors on warfarin maintenance dose in
Han-Chinese patients. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 34:120–125. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li JH, Ma GG, Zhu SQ, Yan H, Wu YB and Xu
JJ: Correlation between single nucleotide polymorphisms in CYP4F2
and warfarin dosing in Chinese valve replacement patients. J
Cardiothorac Surg. 7:972012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liang Y, Chen Z, Guo G, Dong X, Wu C, Li
H, Wang T and Xu B: Association of genetic polymorphisms with
warfarin dose requirements in Chinese patients. Genet Test Mol
Biomarkers. 17:932–936. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li S, Zou Y, Wang X, Huang X, Sun Y, Wang
Y, Dong L and Jiang H: Warfarin dosage response related
pharmacogenetics in Chinese population. PLoS One. 10:e01164632015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhuang W, Wen W, Xuan B, Chen Y, Cao Y,
Sun Z and Ma J: Effect of CYP2C9, CYP4F2 and VKORC1 genetic
polymorphisms on pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of mean
daily maintenance dose of warfarin in Chinese patients. Blood
Coagul Fibrinolysis. 26:167–174. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Danese E, Montagnana M, Johnson JA, Rettie
AE, Zambon CF, Lubitz SA, Suarez-Kurtz G, Cavallari LH, Zhao L,
Huang M, et al: Impact of the CYP4F2 p.V433M polymorphism on
coumarin dose requirement: Systematic review and meta-analysis.
Clin Pharmacol Ther. 92:746–756. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liang R, Wang C, Zhao H, Huang J, Hu D and
Sun Y: Influence of CYP4F2 genotype on warfarin dose requirement-a
systematic review and meta-analysis. Thromb Res. 130:38–44. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Little J, Bradley L, Bray MS, Clyne M,
Dorman J, Ellsworth DL, Hanson J, Khoury M, Lau J, O'Brien TR, et
al: Reporting, appraising, and integrating data on genotype
prevalence and gene-disease associations. Am J Epidemiol.
156:300–310. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lindh JD, Holm L, Andersson ML and Rane A:
Influence of CYP2C9 genotype on warfarin dose requirements - a
systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Clin Pharmacol.
65:365–375. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cen HJ, Zeng WT, Leng XY, Huang M, Chen X,
Li JL, Huang ZY, Bi HC, Wang XD, He YL, et al: CYP4F2 rs2108622: A
minor significant genetic factor of warfarin dose in Han Chinese
patients with mechanical heart valve replacement. Br J Clin
Pharmacol. 70:234–240. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lou Y, Han L and Li Y, Zhang X, Liu Z,
Tang M, Yu H, Wang W, Xu J, Liu H and Li Y: Impact of six genetic
polymorphisms on Warfarin maintenance dose variation in Chinese Han
population. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi. 31:367–371.
2014.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang HY, Luo WW, Fang HR, Yang XQ, Xu LH
and Ma SM: Influence of VKORC1, CYP2C9, CYP4F2 and EPHX1 Gene
Polymorphisms on Warfarin Dose. China Pharmacy. 34:3201–3205.
2012.
|
|
23
|
Zhu JR, Zhu YB, Xie DJ, Ye F and Tao YF:
Effects of CYP4F2, CYP2C9 and VKORC1 genetic polymorphisms on
maintenance dosage of warfarin in Chinese Han nationality patients
with non-valve atrial fibrillation. China Pharmacy. 44:4161–4164.
2012.
|
|
24
|
Wang Z, Yang D, Li YL, et al: Influence of
CYP4F2 gene polymorphisms on warfarin dose. Guangdong Medical
Journal. 3091–3094. 2011.
|
|
25
|
Zhang YT, Liang X, Dong F, et al: Effect
of CYP4F2 polymorphism on warfarin anticoagulant in Chinese
population. Clinical Medication Journal. 41–59. 2014.
|
|
26
|
Krishna Kumar D, Shewade DG, Loriot MA,
Beaune P, Balachander J, Sai Chandran BV and Adithan C: Effect of
CYP2C9, VKORC1, CYP4F2 and GGCX genetic variants on warfarin
maintenance dose and explicating a new pharmacogenetic algorithm in
South Indian population. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 70:47–56. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Özer M, Demirci Y, Hizel C, Sarikaya S,
Karalti İ, Kaspar Ç, Alpan S and Genç E: Impact of genetic factors
(CYP2C9, VKORC1 and CYP4F2) on warfarin dose requirement in the
Turkish population. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 112:209–214.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hirai K, Yamada Y, Hayashi H, Tanaka M,
Izumiya K, Suzuki M, Yoshizawa M, Moriwaki H, Akimoto T, Tsuji D,
et al: Plasma vitamin K concentrations depend on CYP4F2
polymorphism and influence on anticoagulation in Japanese patients
with warfarin therapy. Thromb Res. 135:861–866. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Nakamura K, Obayashi K, Araki T, Aomori T,
Fujita Y, Okada Y, Kurabayashi M, Hasegawa A, Ohmori S, Nakamura T,
et al: CYP4F2 gene polymorphism as a contributor to warfarin
maintenance dose in Japanese subjects. J Clin Pharm Ther.
37:481–485. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lee KE, Chang BC, Kim HO, Yoon IK, Lee NR,
Park HY and Gwak HS: Effects of CYP4F2 gene polymorphisms on
warfarin clearance and sensitivity in Korean patients with
mechanical cardiac valves. Ther Drug Monit. 34:275–282. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Singh O, Sandanaraj E, Subramanian K, Lee
LH and Chowbay B: Influence of CYP4F2 rs2108622 (V433M) on warfarin
dose requirement in Asian patients. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet.
26:130–136. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Jorgensen AL, FitzGerald RJ, Oyee J,
Pirmohamed M and Williamson PR: Influence of CYP2C9 and VKORC1 on
patient response to warfarin: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. PLoS One. 7:e440642012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yang L, Ge W, Yu F and Zhu H: Impact of
VKORC1 gene polymorphism on interindividual and interethnic
warfarin dosage requirement - a systematic review and meta
analysis. Thromb Res. 125:e159–e166. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Jin B, Hong Y, Zhu J, Li Y and Shi HM: The
impact of VKORC1-1639G>A genetic polymorphism upon warfarin dose
requirement in different ethnic populations. Curr Med Res Opin.
30:1505–1511. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Limdi NA, Brown TM, Yan Q, Thigpen JL,
Shendre A, Liu N, Hill CE, Arnett DK and Beasley TM: Race
influences warfarin dose changes associated with genetic factors.
Blood. 126:539–545. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|