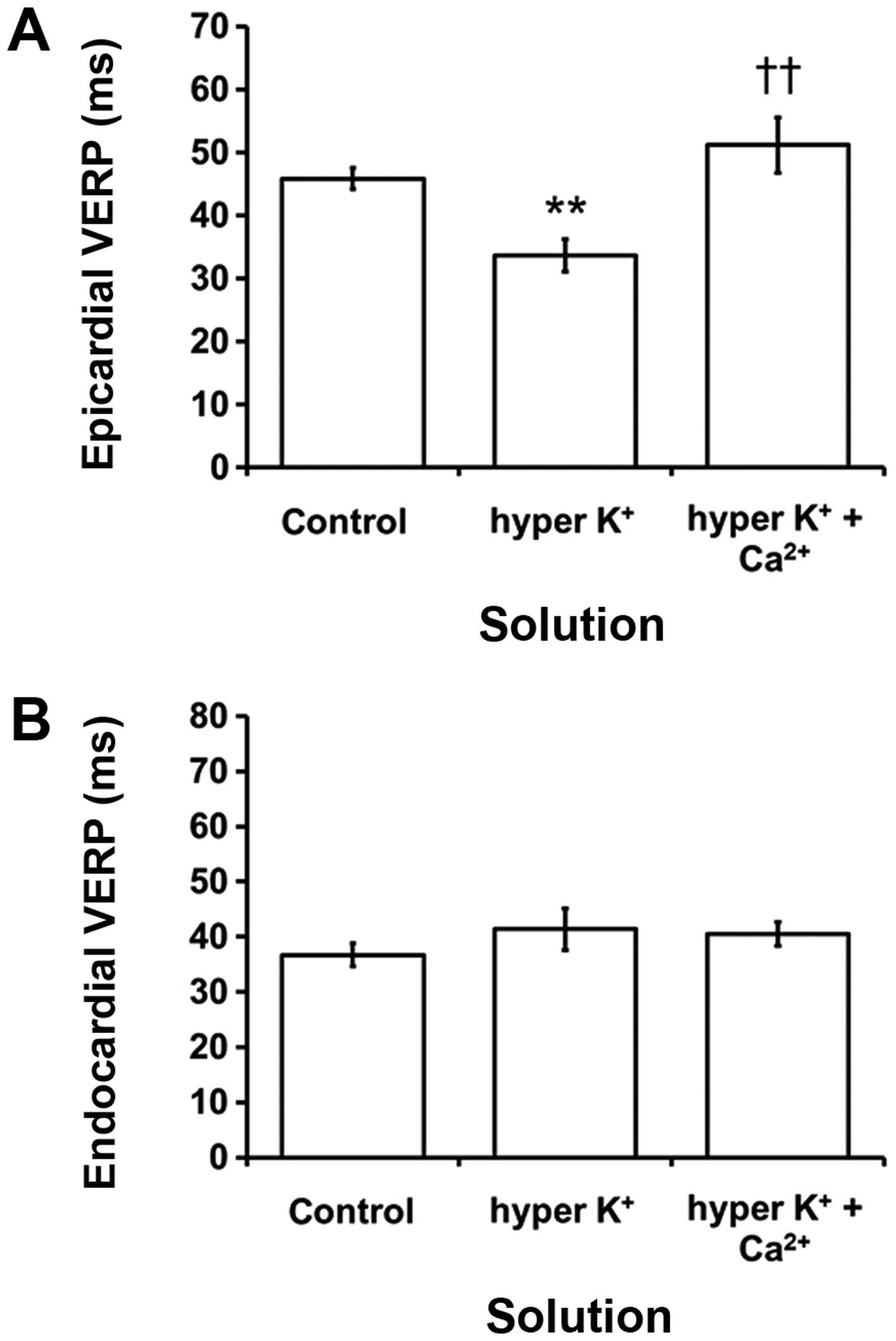
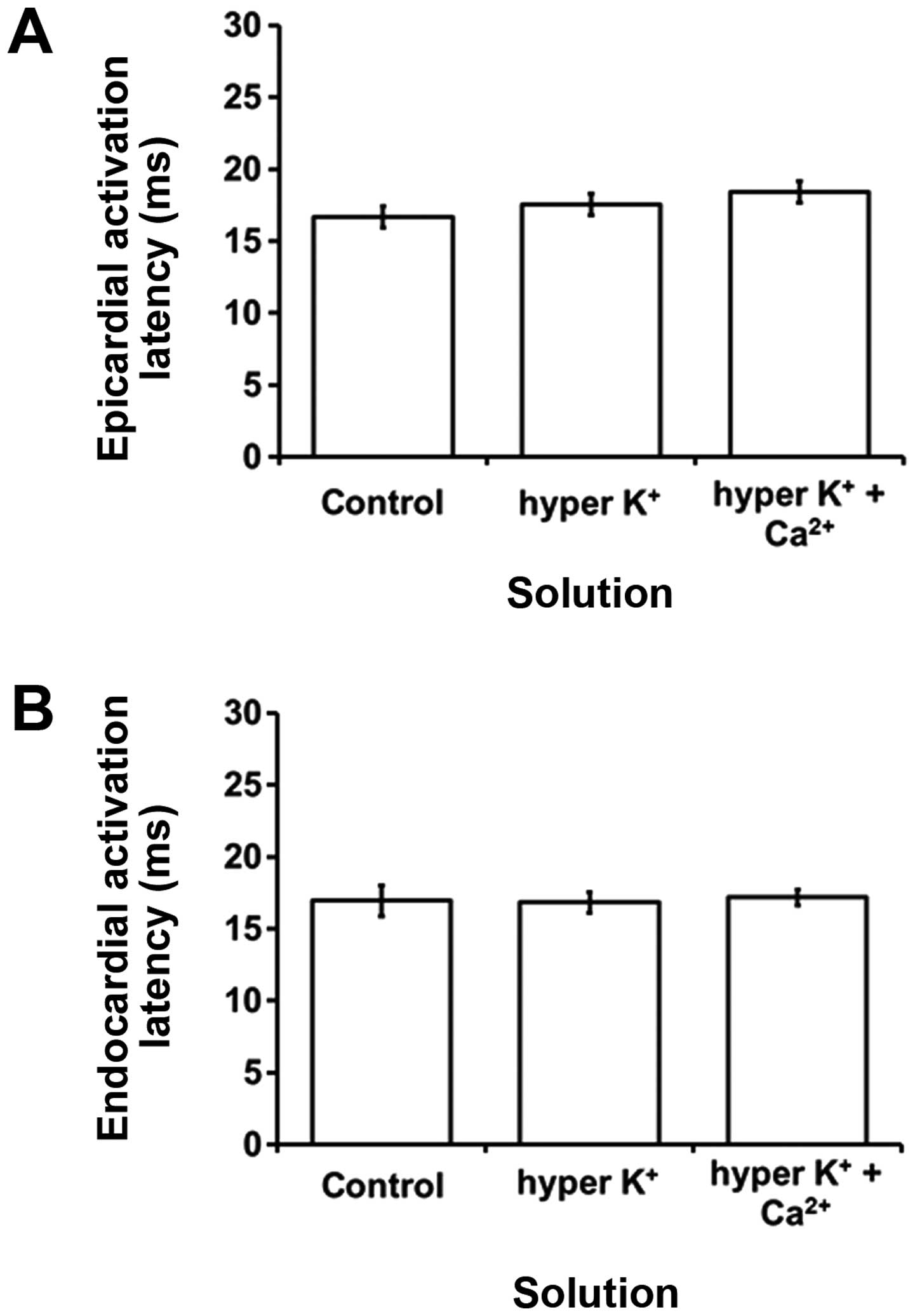
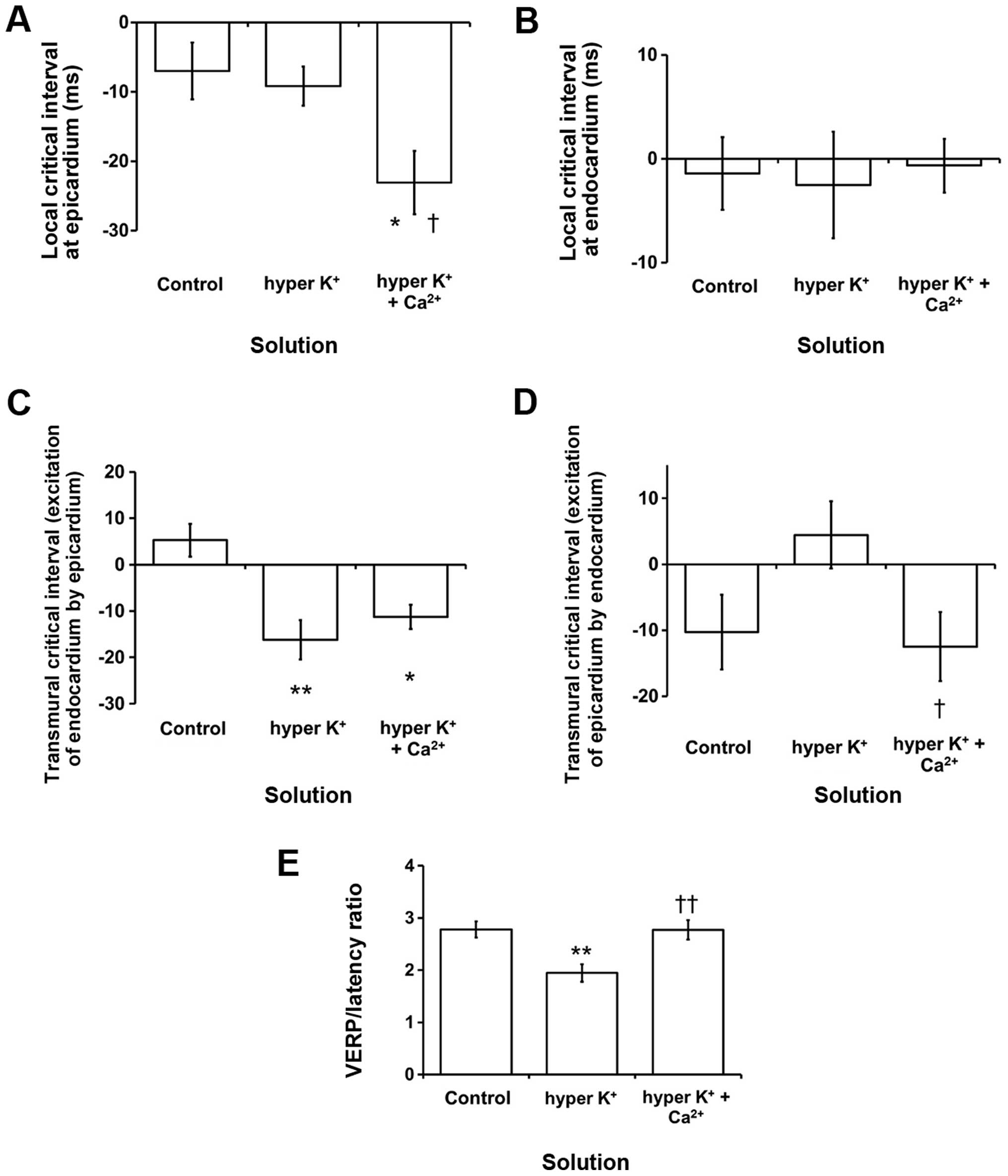
|
1
|
No authors listed, . Guidelines 2000 for
Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care.
Part 8: Advanced challenges in resuscitation: section 1:
Life-threatening electrolyte abnormalities. The American Heart
Association in collaboration with the International Liaison
Committee on Resuscitation. Circulation. 102(Suppl 8): I217–I222.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gettes LS: Electrolyte abnormalities
underlying lethal and ventricular arrhythmias. Circulation.
85(Suppl 1): I70–I76. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Friedensohn A, Faibel HE, Bairey O,
Goldbourt U and Schlesinger Z: Malignant arrhythmias in relation to
values of serum potassium in patients with acute myocardial
infarction. Int J Cardiol. 32:331–338. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ahmed MI, Ekundayo OJ, Mujib M, Campbell
RC, Sanders PW, Pitt B, Perry GJ, Bakris G, Aban I, Love TE, et al:
Mild hyperkalemia and outcomes in chronic heart failure: A
propensity matched study. Int J Cardiol. 144:383–388. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bashour TT and Cheng TO: Evidence for
specialized atrioventricular conduction in hyperkalemia. J
Electrocardiol. 8:65–68. 1975. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Dittrich KL and Walls RM: Hyperkalemia:
ECG manifestations and clinical considerations. J Emerg Med.
4:449–455. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Freeman K, Feldman JA, Mitchell P, Donovan
J, Dyer KS, Eliseo L, White LF and Temin ES: Effects of
presentation and electrocardiogram on time to treatment of
hyperkalemia. Acad Emerg Med. 15:239–249. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cooper WD, Kuan P, Reuben SR and
VandenBurg MJ: Cardiac arrhythmias following acute myocardial
infarction: Associations with the serum potassium level and prior
diuretic therapy. Eur Heart J. 5:464–469. 1984.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Weiner ID and Wingo CS: Hyperkalemia: A
potential silent killer. J Am Soc Nephrol. 9:1535–1543.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sood MM and Pauly RP: A case of severe
hyperkalemia: Fast, safe and effective treatment is required. J
Crit Care. 23:431–433. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kiewiet RM, Ponssen HH, Janssens EN and
Fels PW: Ventricular fibrillation in hypercalcaemic crisis due to
primary hyperparathyroidism. Neth J Med. 62:94–96. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Curione M, Letizia C, Amato S, Di Bona S,
Di Fazio F, Minisola S, Mazzuoli G and D'Erasmo E: Increased risk
of cardiac death in primary hyperparathyroidism: What is a role of
electrical instability? Int J Cardiol. 121:200–202. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
George SA, Sciuto KJ, Lin J, Salama ME,
Keener JP, Gourdie RG and Poelzing S: Extracellular sodium and
potassium levels modulate cardiac conduction in mice heterozygous
null for the Connexin43 gene. Pflugers Arch. 467:2287–2297. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kodama I, Wilde A, Janse MJ, Durrer D and
Yamada K: Combined effects of hypoxia, hyperkalemia and acidosis on
membrane action potential and excitability of guinea-pig
ventricular muscle. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 16:247–259. 1984.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Leitch SP and Paterson DJ: Role of Ca2+ in
protecting the heart from hyperkalemia and acidosis in the rabbit:
Implications for exercise. J Appl Physiol (1985). 77:2391–2399.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Piktel JS, Wan X, Infeld M, Rosenbaum D
and Wilson LD: Beneficial effect of calcium treatment for
hyperkalemia is mediated by calcium-dependent conduction, not
‘membrane stabilization’. Ann Emerg Med. 56:S92010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Tse G and Yeo JM: Conduction abnormalities
and ventricular arrhythmogenesis: The roles of sodium channels and
gap junctions. Int J Cardiol Heart Vasc. 9:75–82. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Choy L, Yeo JM, Tse V, Chan SP and Tse G:
Cardiac disease and arrhythmogenesis: Mechanistic insights from
mouse models. Int J Cardiol Heart Vasc. 12:1–10. 2016.
|
|
19
|
Tse G: Both transmural dispersion of
repolarization and transmural dispersion of refractoriness are poor
predictors of arrhythmogenicity: A role for the index of Cardiac
Electrophysiological Balance (QT/QRS)? J Geriatr Cardiol. (In
press). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tse G, Lai ET, Yeo JM and Yan BP:
Electrophysiological mechanisms of Bayés syndrome: Insights from
clinical and mouse studies. Front Physiol. May 31–2016.(Epub ahead
of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Tse G, Lai ET, Lee AP, Yan BP and Wong SH:
Electrophysiological mechanisms of gastrointestinal
arrhythmogenesis: Lessons from the heart. Front Physiol. (In
press).
|
|
22
|
Tse G, Lai TH, Yeo JM, Tse V and Wong SH:
Mechanisms of electrical activation and conduction in the
gastrointestinal system: Lessons from cardiac electrophysiology.
Front Physiol. May 31–2016.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Tse G, Lai ET, Tse V and Yeo JM: Molecular
and electrophysiological mechanisms underlying cardiac
arrhythmogenesis in diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes Res. (In
press).
|
|
24
|
Tse G and Yan BP: Novel arrhythmic risk
markers incorporating QRS dispersion: QRSd x (Tpeak-Tend)/QRS and
QRSd x (Tpeak-Tend)/(QT x QRS). Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. (In
press).
|
|
25
|
Tse G: Novel conduction-repolarization
indices for the stratification of arrhythmic risk. J Geriatr
Cardiol. (In press). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tse G: (Tpeak-Tend)/QRS and
(Tpeak-Tend)/(QT x QRS): Novel markers for predicting arrhythmic
risk in Brugada syndrome. Europace. (In press).
|
|
27
|
Tse G, Wong ST, Tse V, Lee YT, Lin HY and
Yeo JM: Cardiac dynamics: alternans and arrhythmogenesis. J
Arrhythm. Mar 28–2016.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tse G: Mechanisms of cardiac arrhythmias.
J Arrhythm. 32:75–81. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Tse G, Tse V and Yeo JM: Ventricular
anti-arrhythmic effects of heptanol in hypokalaemic,
Langendorff-perfused mouse hearts. Biomed Rep. 4:313–324.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Tse G, Wong ST, Tse V and Yeo JM:
Restitution analysis of alternans using dynamic pacing and its
comparison with S1S2 restitution in heptanol-treated, hypokalaemic
Langendorff-perfused mouse hearts. Biomed Rep. 4:673–680.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tse G, Hothi SS, Grace AA and Huang CL:
Ventricular arrhythmogenesis following slowed conduction in
heptanol-treated, Langendorff-perfused mouse hearts. J Physiol Sci.
62:79–92. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Tse G, Tse V, Yeo JM and Sun B: Atrial
anti-arrhythmic effects of heptanol in Langendorff-perfused mouse
hearts. PLoS One. 11:e01488582016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hogan PM and Spitzer KW: Manganese amd
electrogenic phenomena in canine Purkinje fibers. Circ Res.
36:377–391. 1975. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Balasubramaniam R, Chawla S, Mackenzie L,
Schwiening CJ, Grace AA and Huang CL: Nifedipine and diltiazem
suppress ventricular arrhythmogenesis and calcium release in mouse
hearts. Pflugers Arch. 449:150–158. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Balasubramaniam R, Grace AA, Saumarez RC,
Vandenberg JI and Huang CL: Electrogram prolongation and
nifedipine-suppressible ventricular arrhythmias in mice following
targeted disruption of KCNE1. J Physiol. 552:535–546. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Head CE, Balasubramaniam R, Thomas G,
Goddard CA, Lei M, Colledge WH, Grace AA and Huang CL: Paced
electrogram fractionation analysis of arrhythmogenic tendency in
DeltaKPQ Scn5a mice. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 16:1329–1340.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Knollmann BC, Katchman AN and Franz MR:
Monophasic action potential recordings from intact mouse heart:
Validation, regional heterogeneity, and relation to refractoriness.
J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 12:1286–1294. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Gussak I, Chaitman BR, Kopecky SL and
Nerbonne JM: Rapid ventricular repolarization in rodents:
Electrocardiographic manifestations, molecular mechanisms, and
clinical insights. J Electrocardiol. 33:159–170. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Fabritz L, Kirchhof P, Franz MR, Eckardt
L, Mönnig G, Milberg P, Breithardt G and Haverkamp W: Prolonged
action potential durations, increased dispersion of repolarization,
and polymorphic ventricular tachycardia in a mouse model of
proarrhythmia. Basic Res Cardiol. 98:25–32. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Sabir IN, Fraser JA, Killeen MJ, Grace AA
and Huang CL: The contribution of refractoriness to arrhythmic
substrate in hypokalemic Langendorff-perfused murine hearts.
Pflugers Arch. 454:209–222. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kléber AG and Rudy Y: Basic mechanisms of
cardiac impulse propagation and associated arrhythmias. Physiol
Rev. 84:431–488. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Thomas GP, Howlett SE and Ferrier GR:
Saralasin suppresses arrhythmias in an isolated guinea pig
ventricular free wall model of simulated ischemia and reperfusion.
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 274:1379–1386. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Nolan JP, Soar J, Zideman DA, Biarent D,
Bossaert LL, Deakin C, Koster RW, Wyllie J and Böttiger B: ERC
Guidelines Writing Group: European Resuscitation Council Guidelines
for Resuscitation 2010 Section 1. Executive summary. Resuscitation.
81:1219–1276. 2010.
|
|
44
|
Tse G, Wong ST, Tse V and Yeo JM:
Depolarization vs. repolarization: What is the mechanism of
ventricular arrhythmogenesis underlying sodium channel
haploinsufficiency in mouse hearts? Acta Physiol (Oxf). Apr
30–2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Chen Z, Sun B, Tse G, Jiang J and Xu W:
Reversibility of both sinus node dysfunction and reduced HCN4 mRNA
expression level in an atrial tachycardia pacing model of
tachycardia-bradycardia syndrome in rabbit hearts. Int J Clin Exp
Pathol. (In press).
|
|
46
|
Tse G, Wong ST, Tse V and Yeo JM:
Determination of action potential wavelength restitution in Scn5a
+/− mouse hearts modelling human Brugada syndrome. J Physiol. (In
press).
|
|
47
|
Antzelevitch C: Cellular basis for the
repolarization waves of the ECG. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1080:268–281.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Fisch C: Relation of electrolyte
disturbances to cardiac arrhythmias. Circulation. 47:408–419. 1973.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Sanguinetti MC and Jurkiewicz NK: Role of
external Ca2+ and K+ in gating of cardiac delayed rectifier K+
currents. Pflugers Arch. 420:180–186. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Sanguinetti MC, Jiang C, Curran ME and
Keating MT: A mechanistic link between an inherited and an acquired
cardiac arrhythmia: HERG encodes the IKr potassium channel. Cell.
81:299–307. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Kishida H, Surawicz B and Fu LT: Effects
of K+ and K+-induced polarization on (dV/dt)max, threshold
potential, and membrane input resistance in guinea pig and cat
ventricular myocardium. Circ Res. 44:800–814. 1979. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Dominguez G and Fozzard HA: Influence of
extracellular K+ concentration on cable properties and excitability
of sheep cardiac Purkinje fibers. Circ Res. 26:565–574. 1970.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Ettinger PO, Regan TJ and Oldewurtel HA:
Hyperkalemia, cardiac conduction, and the electrocardiogram: A
review. Am Heart J. 88:360–371. 1974. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Killeen MJ, Thomas G, Gurung IS, Goddard
CA, Fraser JA, MahautSmith MP, Colledge WH, Grace AA and Huang CL:
Arrhythmogenic mechanisms in the isolated perfused hypokalaemic
murine heart. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 189:33–46. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Nerbonne JM and Guo W: Heterogeneous
expression of voltage-gated potassium channels in the heart: Roles
in normal excitation and arrhythmias. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol.
13:406–409. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Antzelevitch C: Transmural dispersion of
repolarization and the T wave. Cardiovasc Res. 50:426–431. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Yan GX and Martin J: Electrocardiographic
T wave: A symbol of transmural dispersion of repolarization in the
ventricles. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 14:639–640. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Mines GR: On dynamic equilibrium in the
heart. J Physiol. 46:349–383. 1913. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Weidmann S: Effects of calcium ions and
local anesthetics on electrical properties of Purkinje fibres. J
Physiol. 129:568–582. 1955. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Hélie F, Cossette J, Vermeulen M and
Cardinal R: Differential effects of lignocaine and hypercalcaemia
on anisotropic conduction and reentry in the ischaemically damaged
canine ventricle. Cardiovasc Res. 29:359–372. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Corlew DS, Bryda SL, Bradley EL III and
DiGirolamo M: Observations on the course of untreated primary
hyperparathyroidism. Surgery. 98:1064–1071. 1985.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Rosenqvist M, Nordenström J, Andersson M
and Edhag OK: Cardiac conduction in patients with hypercalcaemia
due to primary hyperparathyroidism. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf).
37:29–33. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Parham WA, Mehdirad AA, Biermann KM and
Fredman CS: Hyperkalemia revisited. Tex Heart Inst J. 33:40–47.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Rumancik WM, Denlinger JK, Nahrwold ML and
Falk RB Jr: The QT interval and serum ionized calcium. JAMA.
240:366–368. 1978. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Scheidegger D and Drop LJ: The
relationship between duration of Q-T interval and plasma ionized
calcium concentration: Experiments with acute, steady-state [Ca++]
changes in the dog. Anesthesiology. 51:143–148. 1979. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Wortsman J and Frank S: The QT interval in
clinical hypercalcemia. Clin Cardiol. 4:87–90. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Killeen MJ, Thomas G, Sabir IN, Grace AA
and Huang CL: Mouse models of ventricular arrhythmias. Acta Physiol
(Oxf). 192:455–469. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Nerbonne JM and Kass RS: Molecular
physiology of cardiac repolarization. Physiol Rev. 85:1205–1253.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Hsieh YC, Lin JC, Hung CY, Li CH, Lin SF,
Yeh HI, Huang JL, Lo CP, Haugan K, Larsen BD, et al: Gap junction
modifier rotigaptide decreases the susceptibility to ventricular
arrhythmia by enhancing conduction velocity and suppressing
discordant alternans during therapeutic hypothermia in isolated
rabbit hearts. Heart Rhythm. 13:251–261. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Wu TJ, Lin SF, Weiss JN, Ting CT and Chen
PS: Two types of ventricular fibrillation in isolated rabbit
hearts: Importance of excitability and action potential duration
restitution. Circulation. 106:1859–1866. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Osadchii OE: Effects of ventricular pacing
protocol on electrical restitution assessments in guinea-pig heart.
Exp Physiol. 97:807–821. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Osadchii OE, Larsen AP and Olesen SP:
Predictive value of electrical restitution in hypokalemia-induced
ventricular arrhythmogenicity. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
298:H210–H220. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Osadchii OE: Mechanisms of
hypokalemia-induced ventricular arrhythmogenicity. Fundam Clin
Pharmacol. 24:547–559. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Osadchii OE, Bentzen BH and Olesen SP:
Chamber-specific effects of hypokalaemia on ventricular
arrhythmogenicity in isolated, perfused guinea-pig heart. Exp
Physiol. 94:434–446. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Osadchii OE and Olesen SP:
Electrophysiological determinants of hypokalaemia-induced
arrhythmogenicity in the guinea-pig heart. Acta Physiol (Oxf).
197:273–287. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Osadchii OE: Flecainide attenuates rate
adaptation of ventricular repolarization in guinea-pig heart. Scand
Cardiovasc J. 50:28–35. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Osadchii OE: Impact of hypokalemia on
electromechanical window, excitation wavelength and repolarization
gradients in guinea-pig and rabbit hearts. PLoS One. 9:e1055992014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Osadchii OE: Impaired epicardial
activation-repolarization coupling contributes to the proarrhythmic
effects of hypokalaemia and dofetilide in guinea pig ventricles.
Acta Physiol (Oxf). 211:48–60. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Osadchii OE: Flecainide-induced
proarrhythmia is attributed to abnormal changes in repolarization
and refractoriness in perfused guinea-pig heart. J Cardiovasc
Pharmacol. 60:456–466. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Hsieh YC, Lin SF, Lin TC, Ting CT and Wu
TJ: Therapeutic hypothermia (30 degrees C) enhances arrhythmogenic
substrates, including spatially discordant alternans, and
facilitates pacing-induced ventricular fibrillation in isolated
rabbit hearts. Circ J. 73:2214–2222. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Franz MR, Burkhoff D, Spurgeon H,
Weisfeldt ML and Lakatta EG: In vitro validation of a new cardiac
catheter technique for recording monophasic action potentials. Eur
Heart J. 7:34–41. 1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Hoffman BF, Cranefield PF, Lepeschkin E,
Surawicz B and Herrlich HC: Comparison of cardiac monophasic action
potentials recorded by intracellular and suction electrodes. Am J
Physiol. 196:1297–1301. 1959.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Tse G, Wong ST, Tse V and Yeo JM, Lin HY
and Yeo JM: Monophasic action potential recordings: Which is the
recording electrode? J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. Apr
30–2016.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Tse G, Ali A, Alpendurada F, Prasad S,
Raphael CE and Vassiliou V: Tuberculous Constrictive Pericarditis.
Res Cardiovasc Med. 4:e296142015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Tse G, Ali A, Prasad SK, Vassiliou V and
Raphael CE: Atypical case of post-partum cardiomyopathy: an overlap
syndrome with arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy?
BJR|case reports. 1:201501822015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Vassiliou V, Chin C, Perperoglou A, Tse G,
Ali A, Raphael C, Jabbour A, Newby D, Pennell D, Dweck M and Prasad
S: 93 Ejection Fraction by Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance
Predicts Adverse Outcomes Post Aortic Valve Replacement. Heart.
100(Suppl 3): A53–A54. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Kwong JS, Leithäuser B, Park JW and Yu CM:
Diagnostic value of magnetocardiography in coronary artery disease
and cardiac arrhythmias: A review of clinical data. Int J Cardiol.
167:1835–1842. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Steinhoff U, KnappeGrueneberg S, Schnabel
A, Trahms L, Smith F, Langley P, Murray A and Koch H:
Magnetocardiography for pharmacology safety studies requiring high
patient throughput and reliability. J Electrocardiol. 37(Suppl):
187–192. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Yoshida K, Ogata K, Inaba T, Nakazawa Y,
Ito Y, Yamaguchi I, Kandori A and Aonuma K: Ability of
magnetocardiography to detect regional dominant frequencies of
atrial fibrillation. J Arrhythm. 31:345–351. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Ito Y, Shiga K, Yoshida K, Ogata K,
Kandori A, Inaba T, Nakazawa Y, Sekiguchi Y, Tada H, Sekihara K, et
al: Development of a magnetocardiography-based algorithm for
discrimination between ventricular arrhythmias originating from the
right ventricular outflow tract and those originating from the
aortic sinus cusp: A pilot study. Heart Rhythm. 11:1605–1612. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Sato Y, Yoshida K, Ogata K, Inaba T, Tada
H, Sekiguchi Y, Ito Y, Ishizu T, Seo Y, Yamaguchi I, et al: An
increase in right atrial magnetic strength is a novel predictor of
recurrence of atrial fibrillation after radiofrequency catheter
ablation. Circ J. 76:1601–1608. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Tse G, Wong ST, Tse V and Yeo JM:
Variability in local action potential durations, dispersion of
repolarization and wavelength restitution in aged wild-type and
Scn5a+/− mouse hearts modelling human Brugada syndrome. Journal of
Geriatric Cardiology. (In press). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Tse G, Yeo JM, Tse V and Sun B: Gap
junction inhibition by heptanol increases ventricular
arrhythmogenicity by decreasing conduction velocity without
affecting repolarization properties or myocardial refractoriness in
Langendorff-perfused mouse hearts. MMR. (In Press).
|