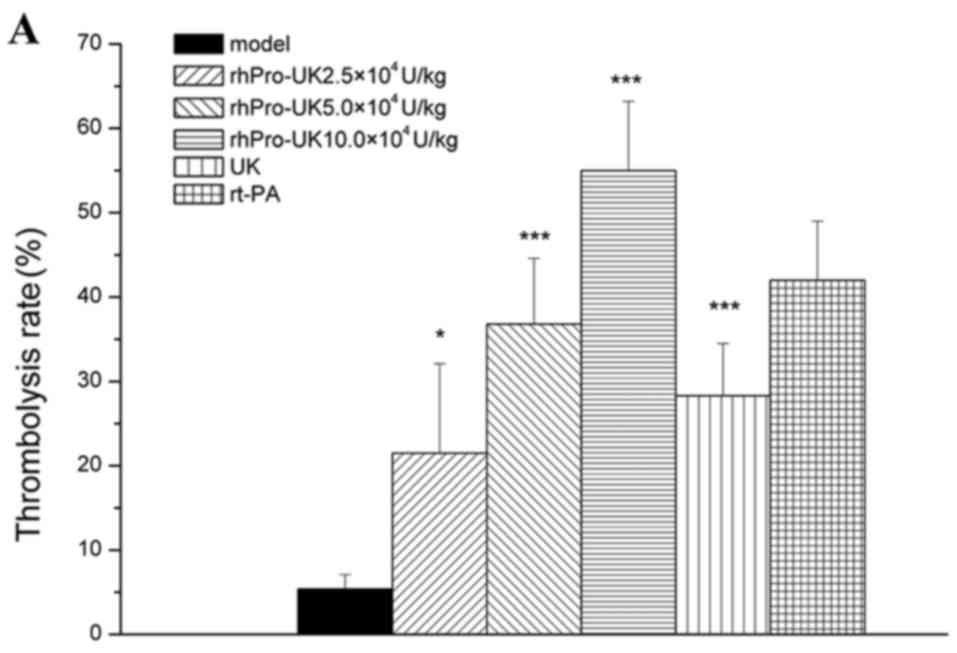
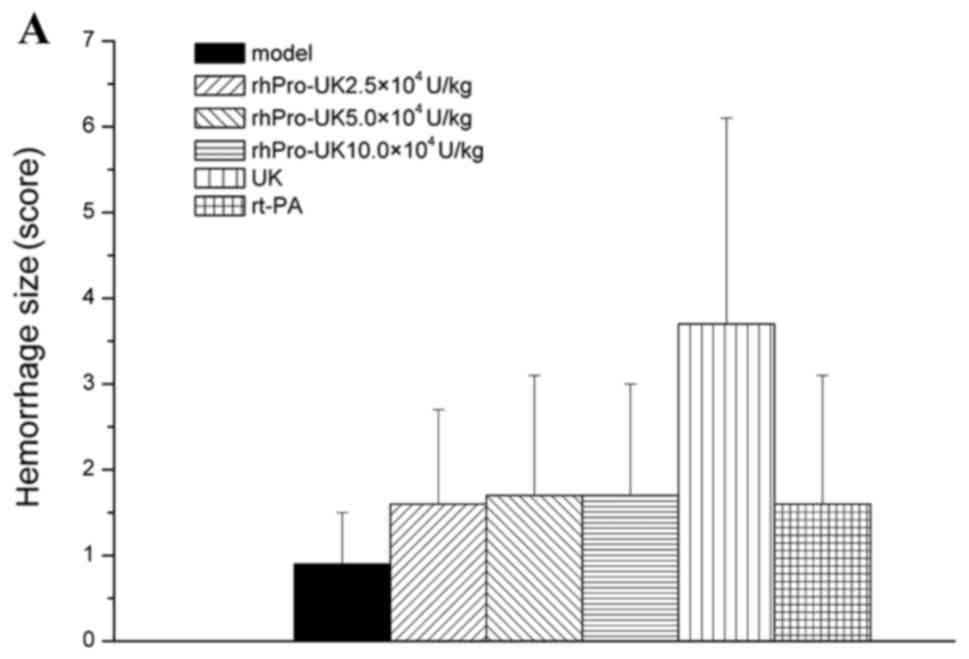
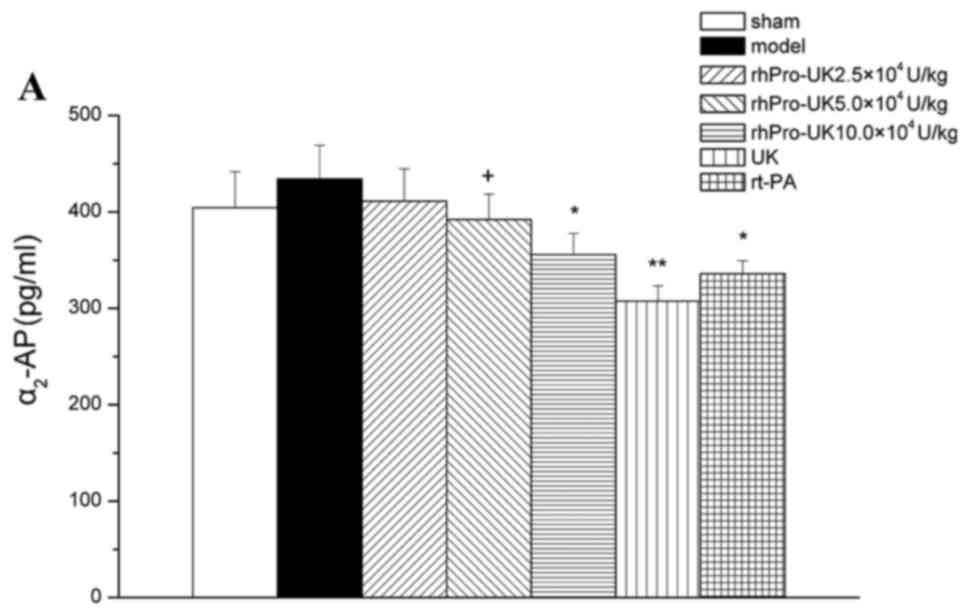
|
1
|
Furlan A, Higashida R, Wechsler L, Gent M,
Rowley H, Kase C, Pessin M, Ahuja A, Callahan F, Clark WM, et al:
Intra-arterial prourokinase for acute ischemic stroke. The PROACT
II study: A randomized controlled trial. Prolyse in acute cerebral
thromboembolism. JAMA. 282:2003–2011. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gurewich V, Pannell R, Louie S, Kelley P,
Suddith RL and Greenlee R: Effective and fibrin-specific clot lysis
by a zymogen precursor form of urokinase (pro-urokinase). A study
in vitro and in two animal species. J Clin Invest. 73:1731–1739.
1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
del Zoppo GJ, Higashida RT, Furlan AJ,
Pessin MS, Rowley HA and Gent M: PROACT: A phase II randomized
trial of recombinant pro-urokinase by direct arterial delivery in
acute middle cerebral artery stroke. PROACT investigators. Prolyse
in acute cerebral thromboembolism. Stroke. 29:4–11. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Moia M, Mannucci PM, Pini M, Prandoni P
and Gurewich V: A pilot study of pro-urokinase in the treatment of
deep vein thrombosis. Thromb Haemost. 72:430–433. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ning RX, Wang R and Cui XY: A new
thrombolytic drug: Recombinant human prourokinase. Zhongguo Xin Yao
Zazhi. 17:430–432. 2008.(In Chinese).
|
|
6
|
Liu Y and Wang L: Efficacy and safety of
thrombolytic therapy with recombinant human prourokinase for acute
myocardial infarction in 50 cases. Chin Pharm J. 15:76–78. 2015.(In
Chinese).
|
|
7
|
Thomas GR, Thibodeaux H, Bennett WF,
Refino CJ, Badillo JM, Errett CJ and Zivin JA: Optimized
thrombolysis of cerebral clots with tissue-type plasminogen
activator in a rabbit model of embolic stroke. J Pharmacol Exp
Ther. 264:67–73. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hao CH, Xu XW, Ma YZ, Zhang R, Sun SY,
Wang WT, et al: Application of 99Tcm tracer technique in rabbit
cerebral thromboembolic stroke. Yaowu Pingjia Yanjiu. 40:648–651.
2017.(In Chinese).
|
|
9
|
Zhang L, Zhang RL, Jiang Q, Ding G, Chopp
M and Zhang ZG: Focal embolic cerebral ischemia in the rat. Nat
Protoc. 10:539–547. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Feng L, Liu J, Chen J, Pan L and Feng G:
Establishing a model of middle cerebral artery occlusion in rabbits
using endovascular interventional techniques. Exp Ther Med.
6:947–952. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang Z, Zhang RL, Jiang Q, Raman SB,
Cantwell L and Chopp M: A new rat model of thrombotic focal
cerebral ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 17:123–135. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yu B, Tong J and Li HF: Thrombolytic
efficacy of rt-PA in embolic stroke of rabbits by 99Tcm trace. J
Isot. 18:160–163. 2005.
|
|
13
|
Thomas GR, Thibodeaux H, Errett CJ,
Badillo JM, Keyt BA, Refino CJ, Zivin JA, Bennett WF, et al: A
long-half-life and fibrin-specific form of tissue plasminogen
activator in rabbit models of embolic stroke and peripheral
bleeding. Stroke. 25:2072–2078. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bovill EG, Terrin ML, Stump DC, Berke AD,
Frederick M, Collen D, Feit F, Gore JM, Hillis LD, Lambrew CT, et
al: Hemorrhagic events during therapy with recombinant tissue-type
plasminogen activator, heparin, and aspirin for acute myocardial
infarction. Results of the thrombolysis in myocardial infarction
(TIMI), Phase II trial. Ann Intern Med. 115:256–265. 1991.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Clark WM, Madden KP, Lyden PD and Zivin
JA: Cerebral hemorrhagic risk of aspirin or heparin therapy with
thrombolytic treatment in rabbits. Stroke. 22:872–8761991.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Chapman DF, Lyden P, Lapchak PA, Nunez S,
Thibodeaux H and Zivin J: Comparison of TNK with wild-type tissue
plasminogen activator in a rabbit embolic stroke model. Stroke.
32:748–752. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mozaffarian D, Benjamin EJ, Go AS, Arnett
DK, Blaha MJ, Cushman M, de Ferranti S, Després JP, Fullerton HJ,
Howard VJ, et al: Heart disease and stroke statistics-2015 update:
A report from the American heart association. Circulation.
131:29–322. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Amar AP, Griffin JH and Zlokovic BV:
Combined neurothrombectomy or thrombolysis with adjunctive delivery
of 3K3A-activated protein C in acute ischemic stroke. Front Cell
Neurosci. 9:3442015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
So Relle and Ruth MP: Breaking news: The
‘biggest, baddest’ controversy in EM. Emerg Med News. 35:26–27.
2013.
|
|
20
|
Furlan AJ and Abou-Chebl A: The role of
recombinant pro-urokinase (r-pro-UK) and intra-arterial
thrombolysis in acute ischaemic stroke: The PROACT trials. Prolyse
in acute cerebral thromboembolism. Curr Med Res Opin. 18:44–47.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Prourokinase Clinical Trial Group, ; Li T,
Xiao Ch, Liu R and Liu L: Multicenter phase III study of
recombinant prourokinase for acute myocardial infarction with
ST-segment evaluation. J Med Res. 42:26–31. 2013.
|
|
22
|
Tirschwell DL, Coplin WM, Becker KJ,
Vogelzang P, Eskridge J, Haynor D, Cohen W, Newell D, Winn HR and
Longstreth WT Jr: Intra-arterial urokinase for acute ischemic
stroke: Factors associated with complications. Neurology.
57:1100–1103. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang ZG, Xiao CZ, Hu XW, Xu ZP, Liu JX,
Yang SJ, Ren JP, Liao MY, Shi XC and Wu BA: Investigation of
pharmacodynamics, pharmacology, and toxicology of domestic human
prourokinase. Sci Sin Vitae. 41:1024–1029. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|