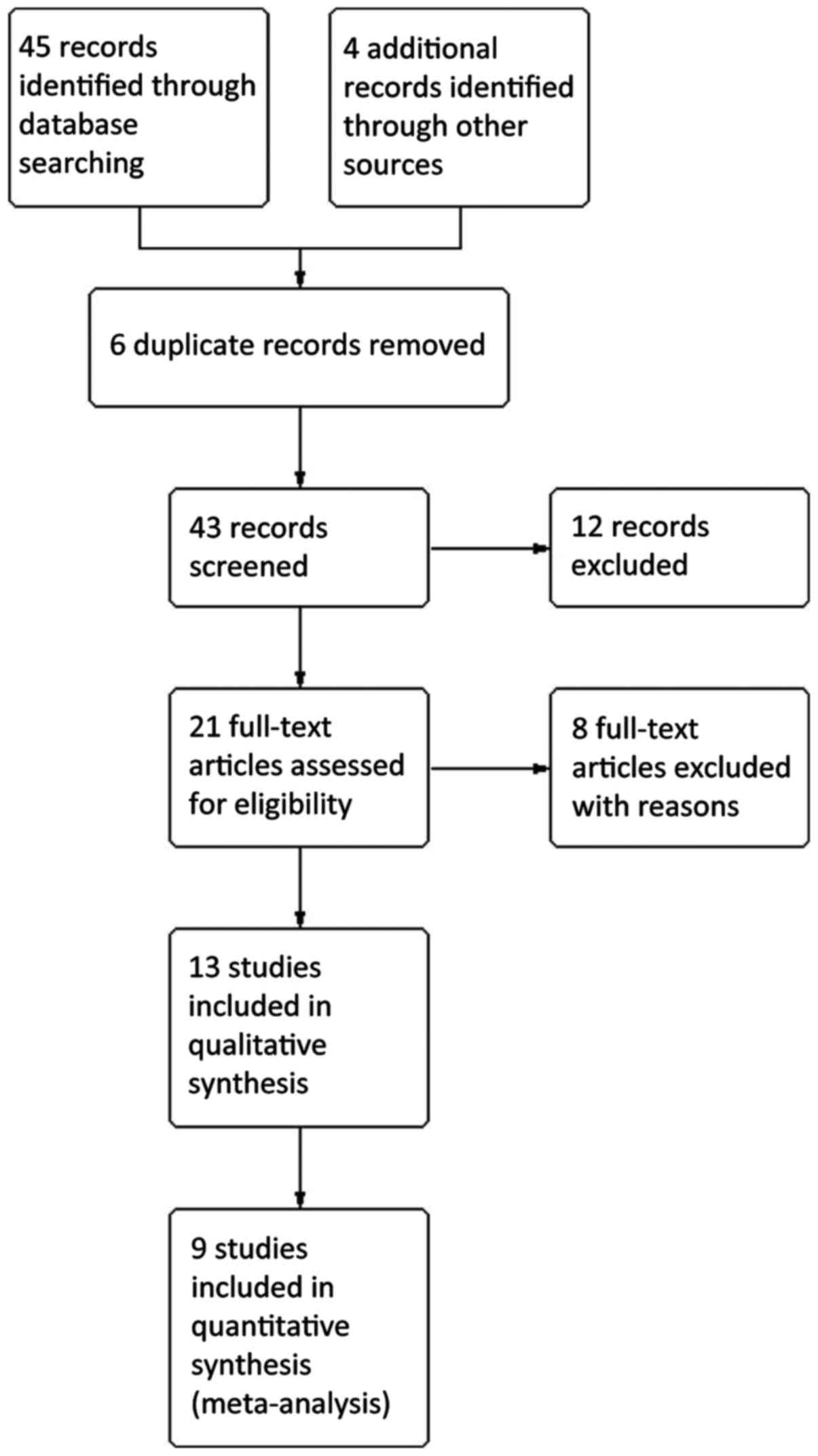
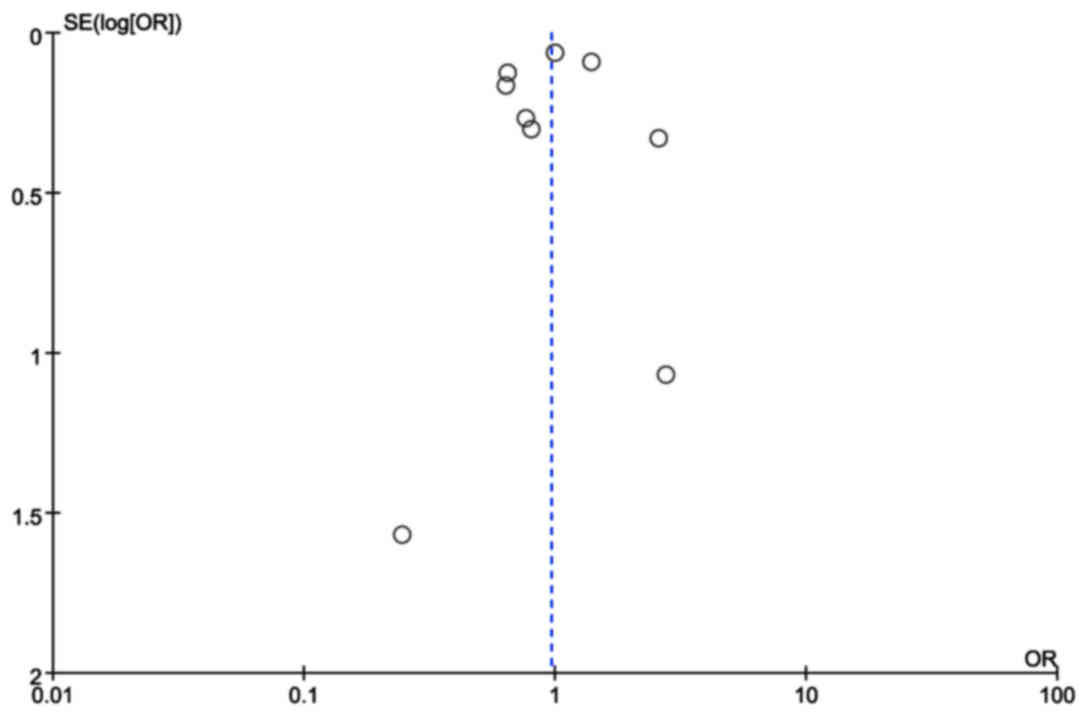
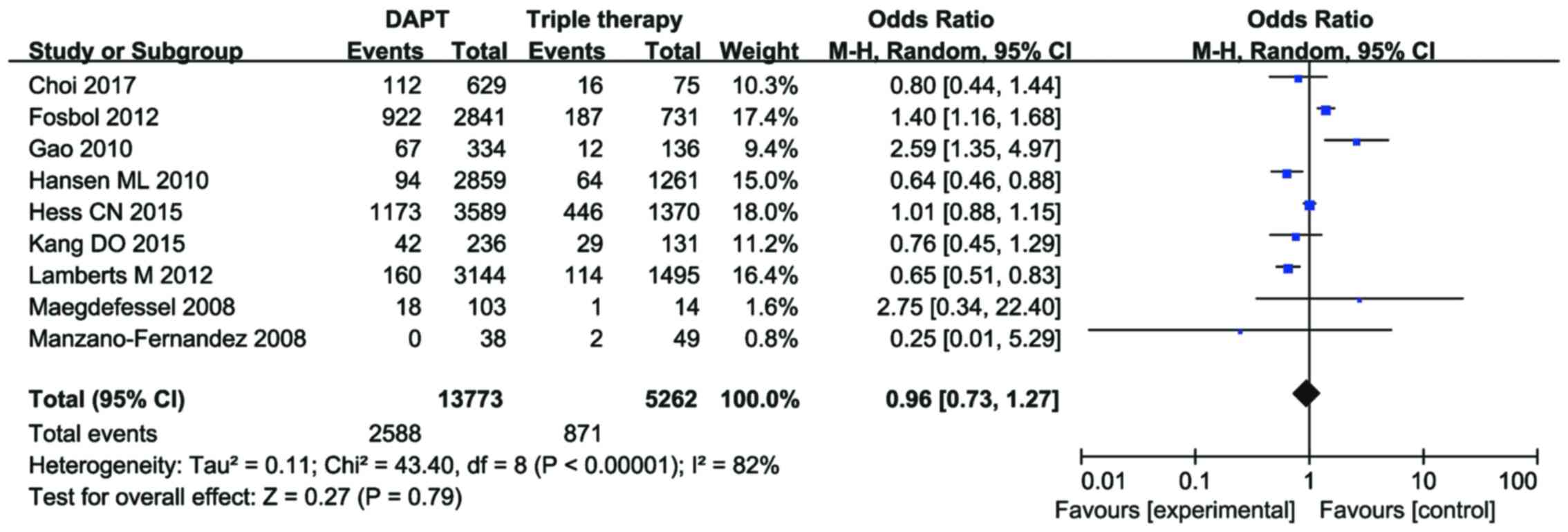
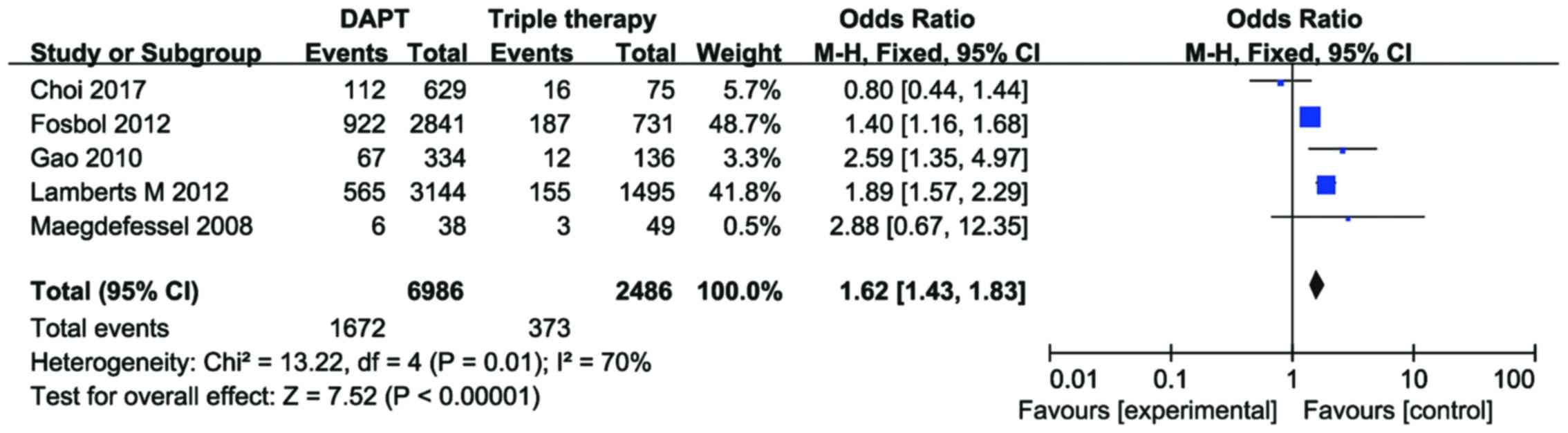
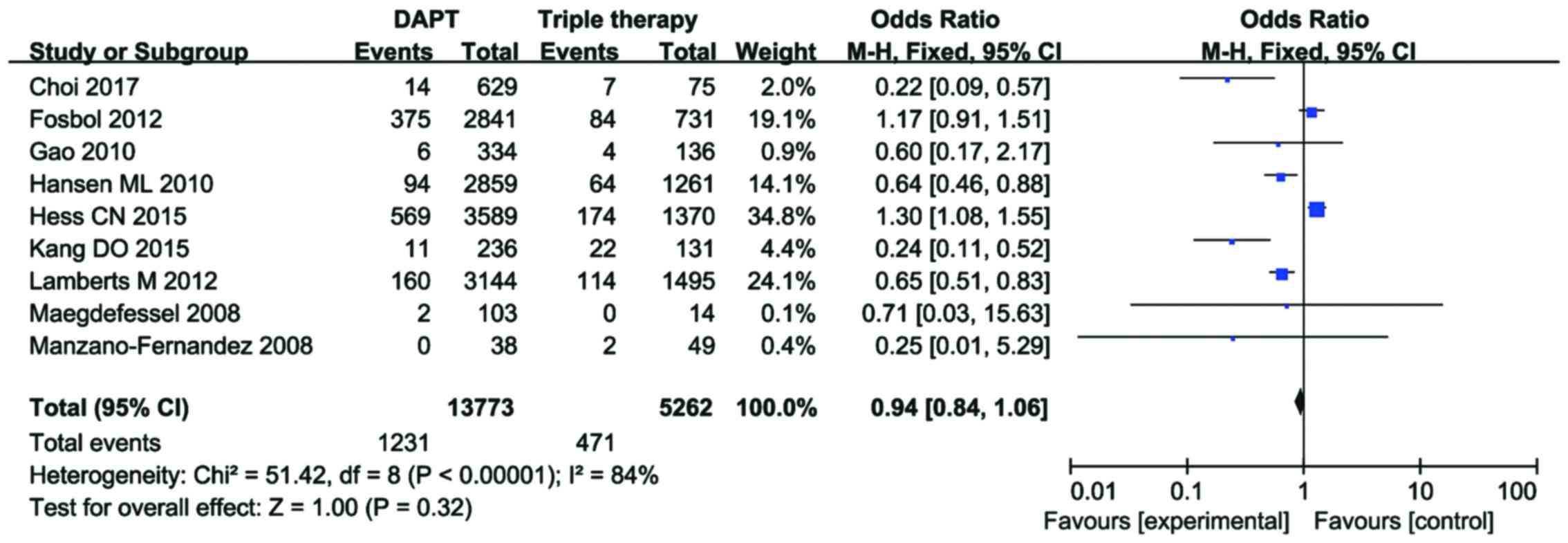
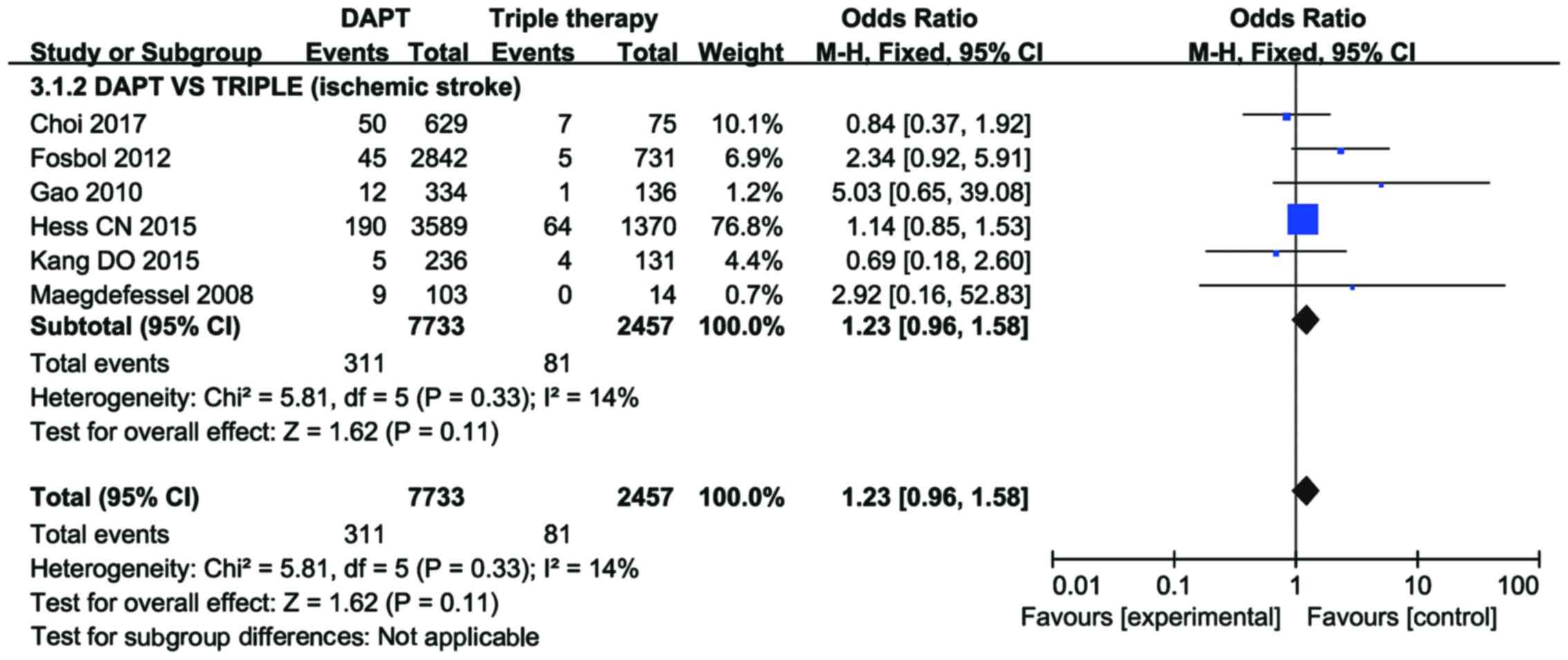
|
1
|
Kanagaratnam L, Kowey P and Whalley D:
Pharmacological therapy for rate and rhythm control for atrial
fibrillation in 2017. Heart Lung Circ. 26:926–933. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Boriani G, Botto GL, Padeletti L, Santini
M, Capucci A, Gulizia M, Ricci R, Biffi M, De Santo T, Corbucci G,
et al: Italian AT-500 registry investigators: Improving stroke risk
stratification using the CHADS2 and CHA2DS2-VASc risk scores in
patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation by continuous
arrhythmia burden monitoring. Stroke. 42:1768–1770. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mazurek M, Shantsila E, Lane DA, Wolff A,
Proietti M and Lip GYH: Guideline-adherent antithrombotic treatment
improves outcomes in patients with atrial fibrillation: Insights
from the community-based Darlington atrial fibrillation registry.
Mayo Clin Proc. 92:pp. 1203–1213. 2017; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Koene RJ, Win S, Naksuk N, Adatya SN,
Rosenbaum AN, John R and Eckman PM: HAS-BLED and CHA2DS2-VASc
scores as predictors of bleeding and thrombotic risk after
continuous-flow ventricular assist device implantation. J Card
Fail. 20:800–807. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Roldán V, Marín F, Manzano-Fernández S,
Gallego P, Vílchez JA, Valdés M, Vicente V and Lip GY: The HAS-BLED
score has better prediction accuracy for major bleeding than CHADS2
or CHA2DS2-VASc scores in anticoagulated patients with atrial
fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 62:2199–2204. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Apostolakis S, Lane DA, Buller H and Lip
GY: Comparison of the CHADS2, CHA2DS2-VASc and HAS-BLED scores for
the prediction of clinically relevant bleeding in anticoagulated
patients with atrial fibrillation: The AMADEUS trial. Thromb
Haemost. 110:1074–1079. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Angiolillo DJ, Goodman SG, Bhatt DL,
Eikelboom JW, Price MJ, Moliterno DJ, Cannon CP, Tanguay JF,
Granger CB, Mauri L, et al: Antithrombotic therapy in patients with
atrial fibrillation undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention:
A North American Perspective-2016 Update. Circ Cardiovasc Interv.
9:92016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Kralev S, Schneider K, Lang S, Süselbeck T
and Borggrefe M: Incidence and severity of coronary artery disease
in patients with atrial fibrillation undergoing first-time coronary
angiography. PLoS One. 6:e249642011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Nieuwlaat R, Capucci A, Camm AJ, Olsson
SB, Andresen D, Davies DW, Cobbe S, Breithardt G, Le Heuzey JY,
Prins MH, et al European Heart Survey Investigators, : Atrial
fibrillation management: A prospective survey in ESC member
countries: The Euro Heart Survey on Atrial Fibrillation. Eur Heart
J. 26:2422–2434. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Nabauer M, Gerth A, Limbourg T, Schneider
S, Oeff M, Kirchhof P, Goette A, Lewalter T, Ravens U, Meinertz T,
et al: The registry of the German competence NETwork on atrial
fibrillation: Patient characteristics and initial management.
Europace. 11:423–434. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Rossini R, Musumeci G, Lettieri C, Molfese
M, Mihalcsik L, Mantovani P, Sirbu V, Bass TA, Della Rovere F,
Gavazzi A, et al: Long-term outcomes in patients undergoing
coronary stenting on dual oral antiplatelet treatment requiring
oral anticoagulant therapy. Am J Cardiol. 102:1618–1623. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang TY, Robinson LA, Ou FS, Roe MT, Ohman
EM, Gibler WB, Smith SC Jr, Peterson ED and Becker RC: Discharge
antithrombotic strategies among patients with acute coronary
syndrome previously on warfarin anticoagulation: Physician practice
in the CRUSADE registry. Am Heart J. 155:361–368. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Rubboli A, Colletta M, Valencia J,
Capecchi A, Franco N, Zanolla L, La Vecchia L, Piovaccari G and Di
Pasquale G; WARfarin and Coronary STENTing (WAR-STENT) study group,
: Periprocedural management and in-hospital outcome of patients
with indication for oral anticoagulation undergoing coronary artery
stenting. J Interv Cardiol. 22:390–397. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Capodanno D and Angiolillo DJ: Management
of antiplatelet and anticoagulant therapy in patients with atrial
fibrillation in the setting of acute coronary syndromes or
percutaneous coronary interventions. Circ Cardiovasc Interv.
7:113–124. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Authors/Task Force members, ; Windecker S,
Kolh P, Alfonso F, Collet JP, Cremer J, Falk V, Filippatos G, Hamm
C, Head SJ, et al: 2014 ESC/EACTS guidelines on myocardial
revascularization: The task force on myocardial revascularization
of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European
Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS). Developed with the
special contribution of the European Association of Percutaneous
Cardiovascular Interventions (EAPCI). Eur Heart J. 35:2541–2619.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Windecker S, Kolh P, Alfonso F, Collet JP,
Cremer J, Falk V, Filippatos G, Hamm C, Head SJ, Jüniet P, et al:
2014 ESC/EACTS guidelines on myocardial revascularization. Rev Esp
Cardiol. 68:4522015.
|
|
17
|
Gurbel PA, Bliden KP, Hiatt BL and
O'Connor CM: Clopidogrel for coronary stenting: Response
variability, drug resistance, and the effect of pretreatment
platelet reactivity. Circulation. 107:2908–2913. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
James SK, Roe MT, Cannon CP, Cornel JH,
Horrow J, Husted S, Katus H, Morais J, Steg PG, Storey RF, et al
PLATO Study Group, : Ticagrelor versus clopidogrel in patients with
acute coronary syndromes intended for non-invasive management:
Substudy from prospective randomised PLATelet inhibition and
patient outcomes (PLATO) trial. BMJ. 342:35272011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Held C, Asenblad N, Bassand JP, Becker RC,
Cannon CP, Claeys MJ, Harrington RA, Horrow J, Husted S, James SK,
et al: Ticagrelor versus clopidogrel in patients with acute
coronary syndromes undergoing coronary artery bypass surgery:
Results from the PLATO (Platelet Inhibition and Patient Outcomes)
trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 57:672–684. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gwyn JCV, Thomas MR and Kirchhof P: Triple
antithrombotic therapy in patients with atrial fibrillation
undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention: A viewpoint. Eur
Heart J Cardiovasc Pharmacother. 3:157–162. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lopes RD, Rao M, Simon DN, Thomas L,
Ansell J, Fonarow GC, Gersh BJ, Go AS, Hylek EM, Kowey P, et al:
Triple vs dual antithrombotic therapy in patients with atrial
fibrillation and coronary artery disease. Am J Med. 129:592–599.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Pareek M, Bhatt DL, Ten Berg JM,
Kristensen SD and Grove EL: Antithrombotic strategies for
preventing long-term major adverse cardiovascular events in
patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation who undergo
percutaneous coronary intervention. Expert Opin Pharmacother.
18:875–883. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Choi HI, Ahn JM, Kang SH, Lee PH, Kang SJ,
Lee SW, Kim YH, Lee CW, Park SW, Park DW, et al: Prevalence,
management, and long-term (6-year) outcomes of atrial fibrillation
among patients receiving drug-eluting coronary stents. JACC
Cardiovasc Interv. 10:1075–1085. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lamberts M, Olesen JB, Ruwald MH, Hansen
CM, Karasoy D, Kristensen SL, Køber L, Torp-Pedersen C, Gislason GH
and Hansen ML: Bleeding after initiation of multiple antithrombotic
drugs, including triple therapy, in atrial fibrillation patients
following myocardial infarction and coronary intervention: A
nationwide cohort study. Circulation. 126:1185–1193. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kang DO, Yu CW, Kim HD, Cho JY, Joo HJ,
Choi RK, Park JS, Lee HJ, Kim JS, Park JH, et al: Triple
antithrombotic therapy versus dual antiplatelet therapy in patients
with atrial fibrillation undergoing drug-eluting stent
implantation. Coron Artery Dis. 26:372–380. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gao F, Zhou YJ, Wang ZJ, Shen H, Liu XL,
Nie B, Yan ZX, Yang SW, Jia de A and Yu M: Comparison of different
antithrombotic regimens for patients with atrial fibrillation
undergoing drug-eluting stent implantation. Circ J. 74:701–708.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Fosbol EL, Wang TY, Li S, Piccini JP,
Lopes RD, Shah B, Mills RM, Klaskala W, Alexander KP, Thomas L, et
al: Safety and effectiveness of antithrombotic strategies in older
adult patients with atrial fibrillation and non-ST elevation
myocardial infarction. Am Heart J. 163:720–728. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Manzano-Fernández S, Pastor FJ, Marín F,
Cambronero F, Caro C, Pascual-Figal DA, Garrido IP, Pinar E, Valdés
M and Lip GYH: Increased major bleeding complications related to
triple antithrombotic therapy usage in patients with atrial
fibrillation undergoing percutaneous coronary artery stenting.
Chest. 134:559–567. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Maegdefessel L, Schlitt A, Faerber J, Bond
SP, Messow CM, Buerke M, Raaz U, Werdan K, Muenzel T and Weiss C:
Anticoagulant and/or antiplatelet treatment in patients with atrial
fibrillation after percutaneous coronary intervention. A
single-center experience. Med Klin (Munich). 103:628–632. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hansen ML, Sørensen R, Clausen MT,
Fog-Petersen ML, Raunsø J, Gadsbøll N, Gislason GH, Folke F,
Andersen SS, Schramm TK, et al: Risk of bleeding with single, dual,
or triple therapy with warfarin, aspirin, and clopidogrel in
patients with atrial fibrillation. Arch Intern Med. 170:1433–1441.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hess CN, Peterson ED, Peng SA, de Lemos
JA, Fosbol EL, Thomas L, Bhatt DL, Saucedo JF and Wang TY: Use and
outcomes of triple therapy among older patients with acute
myocardial infarction and atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol.
66:616–627. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Rao AK, Pratt C, Berke A, Jaffe A, Ockene
I, Schreiber TL, Bell WR, Knatterud G, Robertson TL and Terrin ML:
Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction (TIMI) Trial-phase I:
Hemorrhagic manifestations and changes in plasma fibrinogen and the
fibrinolytic system in patients treated with recombinant tissue
plasminogen activator and streptokinase. J Am Coll Cardiol.
11:1–11. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Li JX, Jin EZ, Yu LH, Li Y, Liu NN, Dong
YM, Li X and Li XQ: Oral N-acetylcysteine for prophylaxis of
contrast-induced nephropathy in patients following coronary
angioplasty: A meta-analysis. Exp Ther Med. 14:1568–1576. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Stang A: Critical evaluation of the
Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of
nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur J Epidemiol.
25:603–605. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lip GY, Windecker S, Huber K, Kirchhof P,
Marin F, Ten Berg JM, Haeusler KG, Boriani G, Capodanno D, Gilard
M, et al: Document reviewers: Management of antithrombotic therapy
in atrial fibrillation patients presenting with acute coronary
syndrome and/or undergoing percutaneous coronary or valve
interventions: A joint consensus document of the European Society
of Cardiology Working Group on Thrombosis, European Heart Rhythm
Association (EHRA), European Association of Percutaneous
Cardiovascular Interventions (EAPCI) and European Association of
Acute Cardiac Care (ACCA) endorsed by the Heart Rhythm Society
(HRS) and Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society (APHRS). Eur Heart J.
35:3155–3179. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
JCS Joint Working Group, . Guidelines for
pharmacotherapy of atrial fibrillation (JCS 2013). Circ J.
78:1997–2021. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Heidenreich PA, Solis P, Estes NA III,
Fonarow GC, Jurgens CY, Marine JE, McManus DD and McNamara RL: 2016
ACC/AHA Clinical performance and quality measures for adults with
atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter: A report of the American
College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on
Performance Measures. J Am Coll Cardiol. 68:525–568. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Elewa H, Ahmed D and Barnes GD: Triple
oral antithrombotic therapy in atrial fibrillation and coronary
artery stenting: Searching for the best combination. Semin Thromb
Hemost. 42:662–670. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Camm AJ, Kirchhof P, Lip GY, Schotten U,
Savelieva I, Ernst S, Van Gelder IC, Al-Attar N, Hindricks G,
Prendergast B, et al European Heart Rhythm Association, ; European
Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery, : Guidelines for the
management of atrial fibrillation: The Task Force for the
management of Atrial Fibrillation of the European Society of
Cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J. 31:2369–2429. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Halvorsen S, Storey RF, Rocca B, Sibbing
D, Ten Berg J, Grove EL, Weiss TW, Collet JP, Andreotti F, Gulba
DC, et al ESC Working Group on Thrombosis, : Management of
antithrombotic therapy after bleeding in patients with coronary
artery disease and/or atrial fibrillation: Expert consensus paper
of the European Society of Cardiology working group on thrombosis.
Eur Heart J. 38:1455–1462. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Hart RG, Pearce LA and Aguilar MI:
Meta-analysis: Antithrombotic therapy to prevent stroke in patients
who have nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. Ann Intern Med.
146:857–867. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Peters RJ, Mehta SR, Fox KA, Zhao F, Lewis
BS, Kopecky SL, Diaz R, Commerford PJ, Valentin V and Yusuf S;
Clopidogrel in Unstable angina to prevent Recurrent Events (CURE)
Trial Investigators, : Effects of aspirin dose when used alone or
in combination with clopidogrel in patients with acute coronary
syndromes: Observations from the clopidogrel in unstable angina to
prevent recurrent events (CURE) study. Circulation. 108:1682–1687.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Sabatine MS, Cannon CP, Gibson CM,
López-Sendón JL, Montalescot G, Theroux P, Lewis BS, Murphy SA,
McCabe CH and Braunwald E; Clopidogrel as Adjunctive Reperfusion
Therapy (CLARITY)-Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction (TIMI) 28
Investigators, : Effect of clopidogrel pretreatment before
percutaneous coronary intervention in patients with ST-elevation
myocardial infarction treated with fibrinolytics: The PCI-CLARITY
study. JAMA. 294:1224–1232. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Wijns W, Kolh P, Danchin N, Di Mario C,
Falk V, Folliguet T, Garg S, Huber K, James S, Knuuti J, et al Task
Force on Myocardial Revascularization of the European Society of
Cardiology (ESC) and the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic
Surgery (EACTS), ; European Association for Percutaneous
Cardiovascular Interventions (EAPCI), : Guidelines on myocardial
revascularization. Eur Heart J. 31:2501–2555. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Wallentin L, James S, Storey RF, Armstrong
M, Barratt BJ, Horrow J, Husted S, Katus H, Steg PG, Shah SH, et
al: Effect of CYP2C19 and ABCB1 single nucleotide polymorphisms on
outcomes of treatment with ticagrelor versus clopidogrel for acute
coronary syndromes: A genetic substudy of the PLATO trial. Lancet.
376:1320–1328. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Khayata M, Gabra JN, Nasser MF, Litman GI,
Bhakta S and Raina R: Comparison of clopidogrel with prasugrel and
ticagrelor in patients with acute coronary syndrome: Clinical
outcomes from the national cardiovascular database ACTION registry.
Cardiol Res. 8:105–110. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
O'Gara PT, Kushner FG, Ascheim DD, Casey
DE Jr, Chung MK, de Lemos JA, Ettinger SM, Fang JC, Fesmire FM,
Franklin BA, et al American College of Emergency Physicians, ;
Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions, : 2013
ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of ST-elevation myocardial
infarction: A report of the American College of Cardiology
Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice
Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 61:e78–e140. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Reed GW and Cannon CP: Triple oral
antithrombotic therapy in atrial fibrillation and coronary artery
stenting. Clin Cardiol. 36:585–594. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Dzeshka MS, Brown RA and Lip GY: Patients
with atrial fibrillation undergoing percutaneous coronary
intervention. Current concepts and concerns: Part I. Pol Arch Med
Wewn. 125:73–81. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Dzeshka MS, Brown RA and Lip GY: Patients
with atrial fibrillation undergoing percutaneous coronary
intervention: Current concepts and concerns: Part II. Pol Arch Med
Wewn. 125:172–180. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Lamberts M, Gislason GH, Olesen JB,
Kristensen SL, Schjerning Olsen AM, Mikkelsen A, Christensen CB,
Lip GY, Køber L, Torp-Pedersen C, et al: Oral anticoagulation and
antiplatelets in atrial fibrillation patients after myocardial
infarction and coronary intervention. J Am Coll Cardiol.
62:981–989. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Thompson PL and Verheugt FW: Managing
antithrombotic therapy in patients with both atrial fibrillation
and coronary heart disease. Clin Ther. 36:1176–1181. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Gao F, Zhou YJ, Wang ZJ, Yang SW, Nie B,
Liu XL, Jia A and Yan ZX: Meta-analysis of the combination of
warfarin and dual antiplatelet therapy after coronary stenting in
patients with indications for chronic oral anticoagulation. Int J
Cardiol. 148:96–101. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Zhao HJ, Zheng ZT, Wang ZH, Li SH, Zhang
Y, Zhong M and Zhang W: ‘Triple therapy’ rather than ‘triple
threat’: A meta-analysis of the two antithrombotic regimens after
stent implantation in patients receiving long-term oral
anticoagulant treatment. Chest. 139:260–270. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Saheb KJ, Deng BQ, Hu QS, Xie SL, Geng DF
and Nie RQ: Triple antithrombotic therapy versus double
antiplatelet therapy after percutaneous coronary intervention with
stent implantation in patients requiring chronic oral
anticoagulation: A meta-analysis. Chin Med J (Engl). 126:2536–2542.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Andrade JG, Deyell MW, Khoo C, Lee M,
Humphries K and Cairns JA: Risk of bleeding on triple
antithrombotic therapy after percutaneous coronary
intervention/stenting: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Can J
Cardiol. 29:204–212. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|