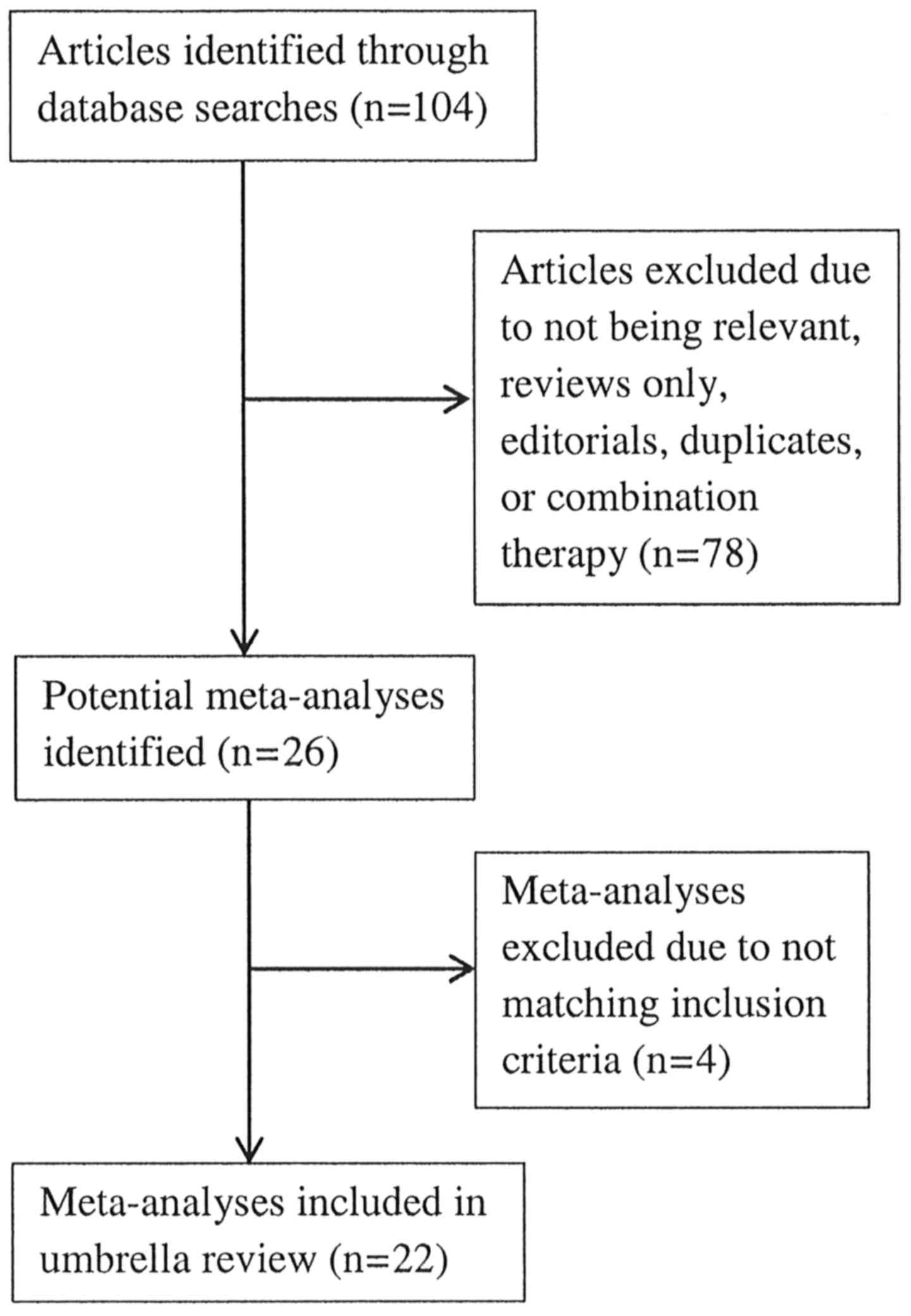
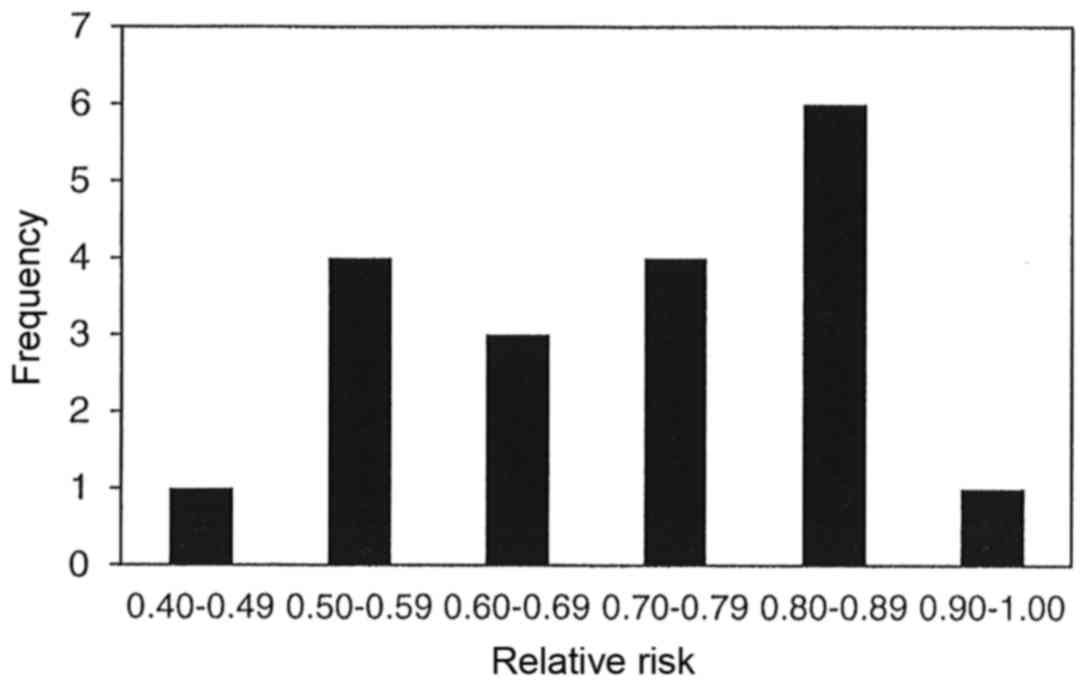
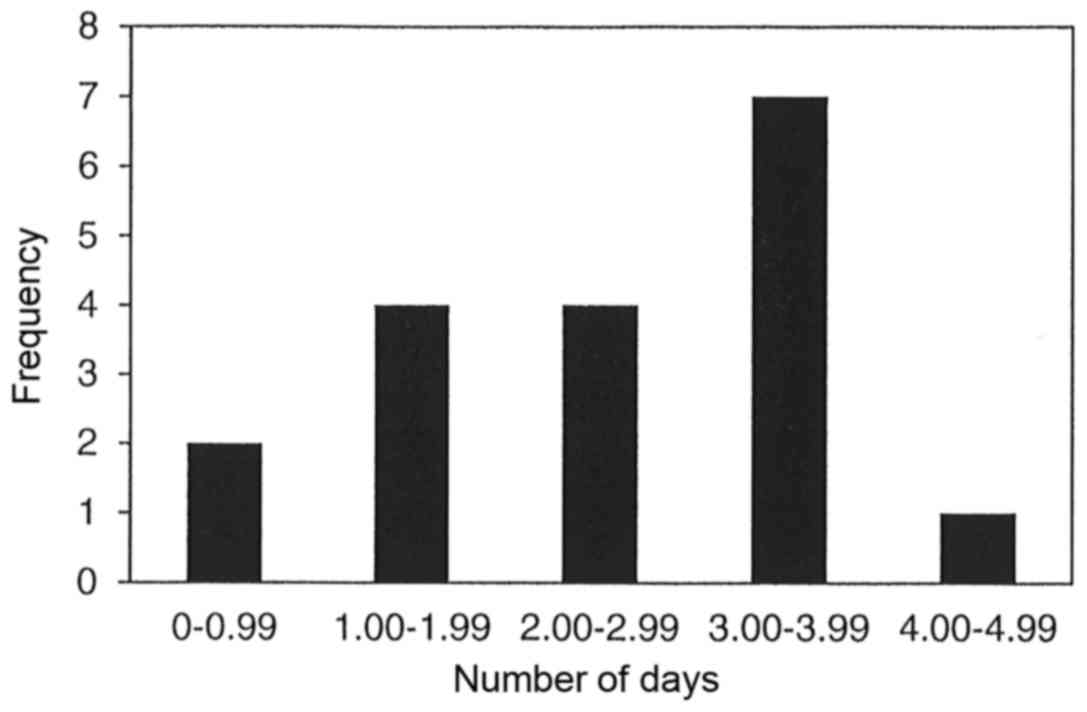
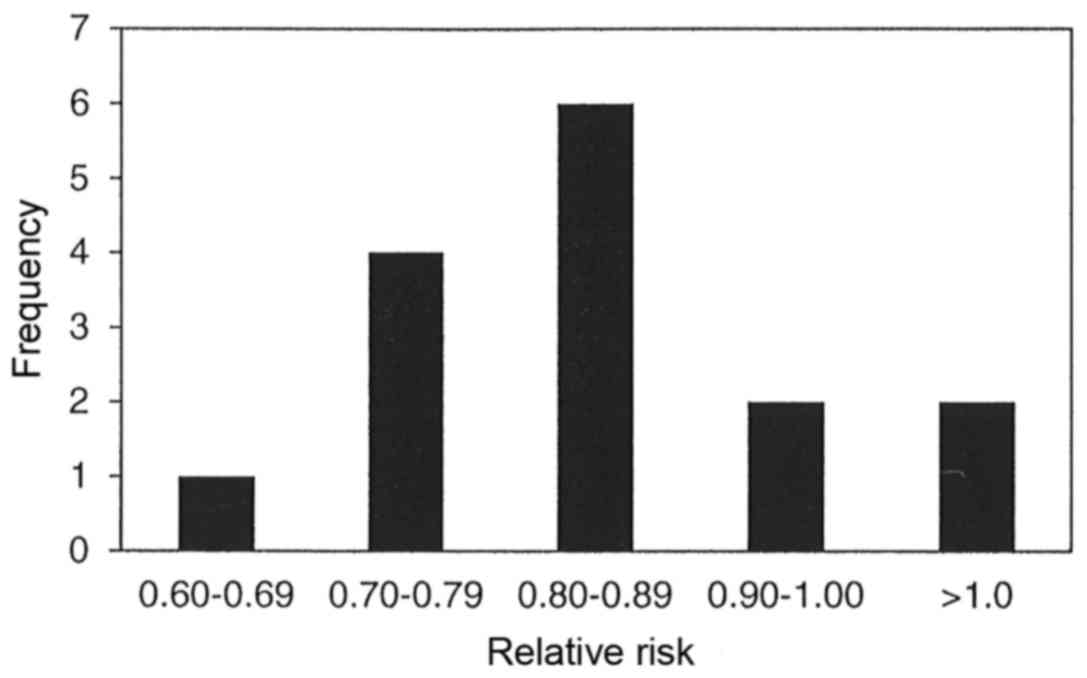
|
1
|
Wischmeyer PE: Glutamine: Mode of action
in critical illness. Crit Care Med. 35 Suppl 9:S541–S544. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wischmeyer PE: Glutamine: Role in critical
illness and ongoing clinical trials. Curr Opin Gastroenterol.
24:190–197. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wischmeyer PE: Glutamine: Role in gut
protection in critical illness. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care.
9:607–612. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
van Zanten AR: Glutamine and antioxidants:
Status of their use in critical illness. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab
Care. 18:179–186. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cynober L and De Bandt JP: Glutamine in
the intensive care unit. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 17:98–104.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mundi MS, Shah M and Hurt RT: When is it
appropriate to use glutamine in critical illness? Nutr Clin Pract.
31:445–450. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Aromataris E, Fernandez R, Godfrey CM,
Holly C, Khalil H and Tungpunkom P: Summarizing systematic reviews:
Methodological development, conduct and reporting of an umbrella
review approach. Int J Evid Based Healthc. 13:132–140. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jiang ZM and Jiang H: The clinical
efficacy of glutamine dipeptides on postoperative patients: An
updated systematic review of randomized controlled trials from
Europe and Asia (1997–2005). Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 86:1610–1614.
2006.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jiang H, Chen W, Hu W, Cai B and Liao RJ:
The impact of glutamine-enhanced enteral nutrition on clinical
outcome of patients with critical illness: A systematic review of
randomized controlled trials. Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi.
25:325–330. 2009.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Moe-Byrne T, Brown JV and McGuire W:
Glutamine supplementation to prevent morbidity and mortality in
preterm infants. Cochrane Database Syst Rev.
4:CD0014572016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Castro-Gutiérrez V and Rada G: Is there a
role for glutamine supplementation in the management of acute
pancreatitis? Medwave. 16(Suppl 3): e65122016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Novak F, Heyland DK, Avenell A, Drover JW
and Su X: Glutamine supplementation in serious illness: A
systematic review of the evidence. Crit Care Med. 30:2022–2029.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Avenell A: Glutamine in critical care:
Current evidence from systematic reviews. Proc Nutr Soc.
65:236–241. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Avenell A: Hot topics in parenteral
nutrition. Current evidence and ongoing trials on the use of
glutamine in critically-ill patients and patients undergoing
surgery. Proc Nutr Soc. 68:261–268. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bollhalder L, Pfeil AM, Tomonaga Y and
Schwenkglenks M: A systematic literature review and meta-analysis
of randomized clinical trials of parenteral glutamine
supplementation. Clin Nutr. 32:213–223. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen QH, Yang Y, He HL, Xie JF, Cai SX,
Liu AR, Wang HL and Qiu HB: The effect of glutamine therapy on
outcomes in critically ill patients: A meta-analysis of randomized
controlled trials. Crit Care. 18:R82014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Crowther M, Avenell A and Culligan DJ:
Systematic review and meta-analyses of studies of glutamine
supplementation in haematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Bone
Marrow Transplant. 44:413–425. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Asrani V, Chang WK, Dong Z, Hardy G,
Windsor JA and Petrov MS: Glutamine supplementation in acute
pancreatitis: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.
Pancreatology. 13:468–474. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhong X, Liang CP and Gong S: Intravenous
glutamine for severe acute pancreatitis: A meta-analysis. World J
Crit Care Med. 2:4–8. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tao KM, Li XQ, Yang LQ, Yu WF, Lu ZJ, Sun
YM and Wu FX: Glutamine supplementation for critically ill adults.
Cochrane Database Syst Rev. CD0100502014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wischmeyer PE, Dhaliwal R, McCall M,
Ziegler TR and Heyland DK: Parenteral glutamine supplementation in
critical illness: A systematic review. Crit Care. 18:R762014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Oldani M, Sandini M, Nespoli L, Coppola S,
Bernasconi DP and Gianotti L: Glutamine supplementation in
intensive care patients: A meta-analysis of randomized clinical
trials. Medicine (Baltimore). 94:e13192015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yong L, Lu QP, Liu SH and Fan H: Efficacy
of glutamine-enriched nutrition support for patients with severe
acute pancreatitis: A meta-analysis. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr.
40:83–94. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
van Zanten AR, Dhaliwal R, Garrel D and
Heyland DK: Enteral glutamine supplementation in critically ill
patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit Care.
19:2942015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jiang Z, Jiang H and Fürst P: The impact
of glutamine dipeptides on outcomes of surgical patients:
Systematic review of randomized controlled trials from Europe and
Asia. Clin Nutr Suppl. 1:17–23. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Zheng YM, Li F, Zhang MM and Wu XT:
Glutamine dipeptide for parenteral nutrition in abdominal surgery:
A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. World J
Gastroenterol. 12:7537–7541. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang Y, Jiang ZM, Nolan MT, Jiang H, Han
HR, Yu K, Li HL, Jie B and Liang XK: The impact of glutamine
dipeptide-supplemented parenteral nutrition on outcomes of surgical
patients: A meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. JPEN J
Parenter Enteral Nutr. 34:521–529. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yue C, Tian W, Wang W, Huang Q, Zhao R, Li
Q and Li J: The impact of perioperative glutamine-supplemented
parenteral nutrition on outcomes of patients undergoing abdominal
surgery: A meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Am Surg.
79:506–513. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kang K, Shu XL, Zhang YS, Liu XL and Zhao
J: Effect of glutamine enriched nutrition support on surgical
patients with gastrointestinal tumor: A meta-analysis of randomized
controlled trials. Chinese Med J (Engl). 128:245–251. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Sandini M, Nespoli L, Oldani M, Bernasconi
DP and Gianotti L: Effect of glutamine dipeptide supplementation on
primary outcomes for elective major surgery: Systematic review and
meta-analysis. Nutrients. 7:481–499. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lin JJ, Chung XJ, Yang CY and Lau HL: A
meta-analysis of trials using the intention to treat principle for
glutamine supplementation in critically ill patients with burn.
Burns. 39:565–570. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Mottaghi A, Yeganeh MZ, Golzarand M,
Jambarsang S and Mirmiran P: Efficacy of glutamine-enriched enteral
feeding formulae in critically ill patients: A systematic review
and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Asia Pac J Clin
Nutr. 25:504–512. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Heyland DK, Dhaliwal R, Drover JW,
Gramlich L and Dodek P; Canadian Critical Care Clinical Practice
Guidelines Committee, : Canadian clinical practice guidelines for
nutrition support in mechanically ventilated, critically ill adult
patients. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 27:355–373. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Newsholme P: Why is L-glutamine metabolism
important to cells of the immune system in health, postinjury,
surgery or infection? J Nutr. 131(9 Suppl): 2515S–2524S.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Shu XL, Yu TT, Kang K and Zhao J: Effects
of glutamine on markers of intestinal inflammatory response and
mucosal permeability in abdominal surgery patients: A
meta-analysis. Exp Ther Med. 12:3499–3506. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Oliveira GP, Dias CM, Pelosi P and Rocco
PR: Understanding the mechanisms of glutamine action in critically
ill patients. An Acad Bras Cienc. 82:417–430. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Pradelli L, Povero M, Muscaritoli M and
Eandi M: Updated cost-effectiveness analysis of supplemental
glutamine for parenteral nutrition of intensive-care patients. Eur
J Clin Nutr. 69:546–551. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Rodas PC, Rooyackers O, Hebert C, Norberg
Å and Wernerman J: Glutamine and glutathione at ICU admission in
relation to outcome. Clin Sci (Lond). 122:591–597. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Baker GR, Norton PG, Flintoft V, Blais R,
Brown A, Cox J, Etchells E, Ghali WA, Hébert P, Majumdar SR, et al:
The Canadian adverse events study: The incidence of adverse events
among hospital patients in Canada. CMAJ. 170:1678–1686. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Magill SS, Edwards JR, Bamberg W, Beldavs
ZG, Dumyati G, Kainer MA, Lynfield R, Maloney M, McAllister-Hollod
L, Nadle J, et al: Multistate point-prevalence survey of health
care-associated infections. N Engl J Med. 370:1198–1208. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Klevens RM, Edwards JR, Richards CL
Jr..Horan TC, Gaynes RP, Pollock DA and Cardo DM: Estimating health
care-associated infections and deaths in U.S. hospitals, 2002.
Public Health Rep. 122:160–166. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Heyland DK, Elke G, Cook D, Berger MM,
Wischmeyer PE, Albert M, Muscedere J, Jones G and Day AG; Canadian
Critical Care Trials Group, : Glutamine and antioxidants in the
critically ill patient: A post hoc analysis of a large-scale
randomized trial. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 39:401–409. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Vanek VW, Matarese LE, Robinson M, Sacks
GS, Young LS and Kochevar M; Novel Nutrient Task Force, Parenteral
Glutamine Workgroup; American Society for Parenteral and Enteral
Nutrition (A.S.P.E.N.) Board of Directors, : A.S.P.E.N. position
paper: Parenteral nutrition glutamine supplementation. Nutr Clin
Pract. 26:479–494. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|