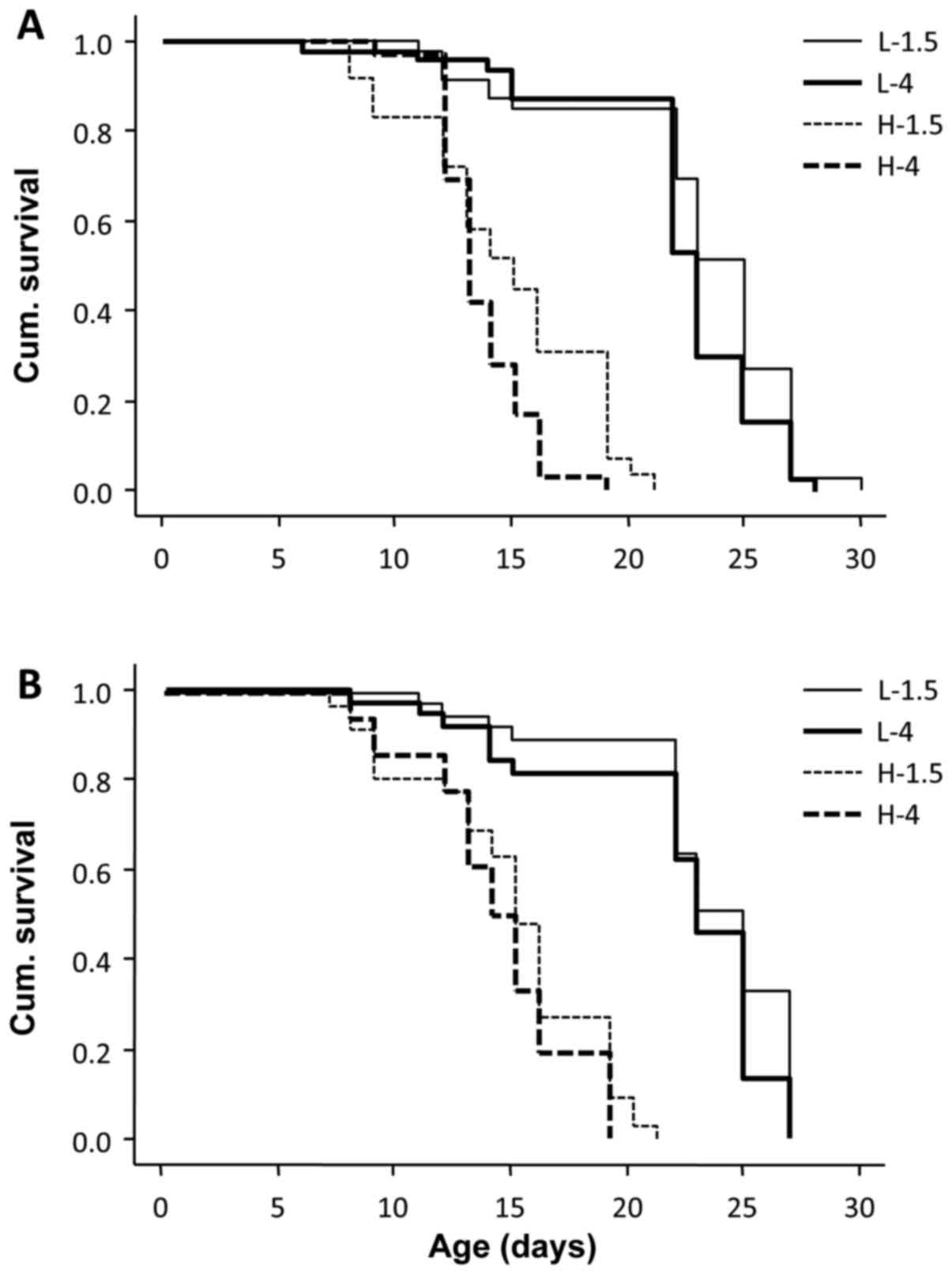
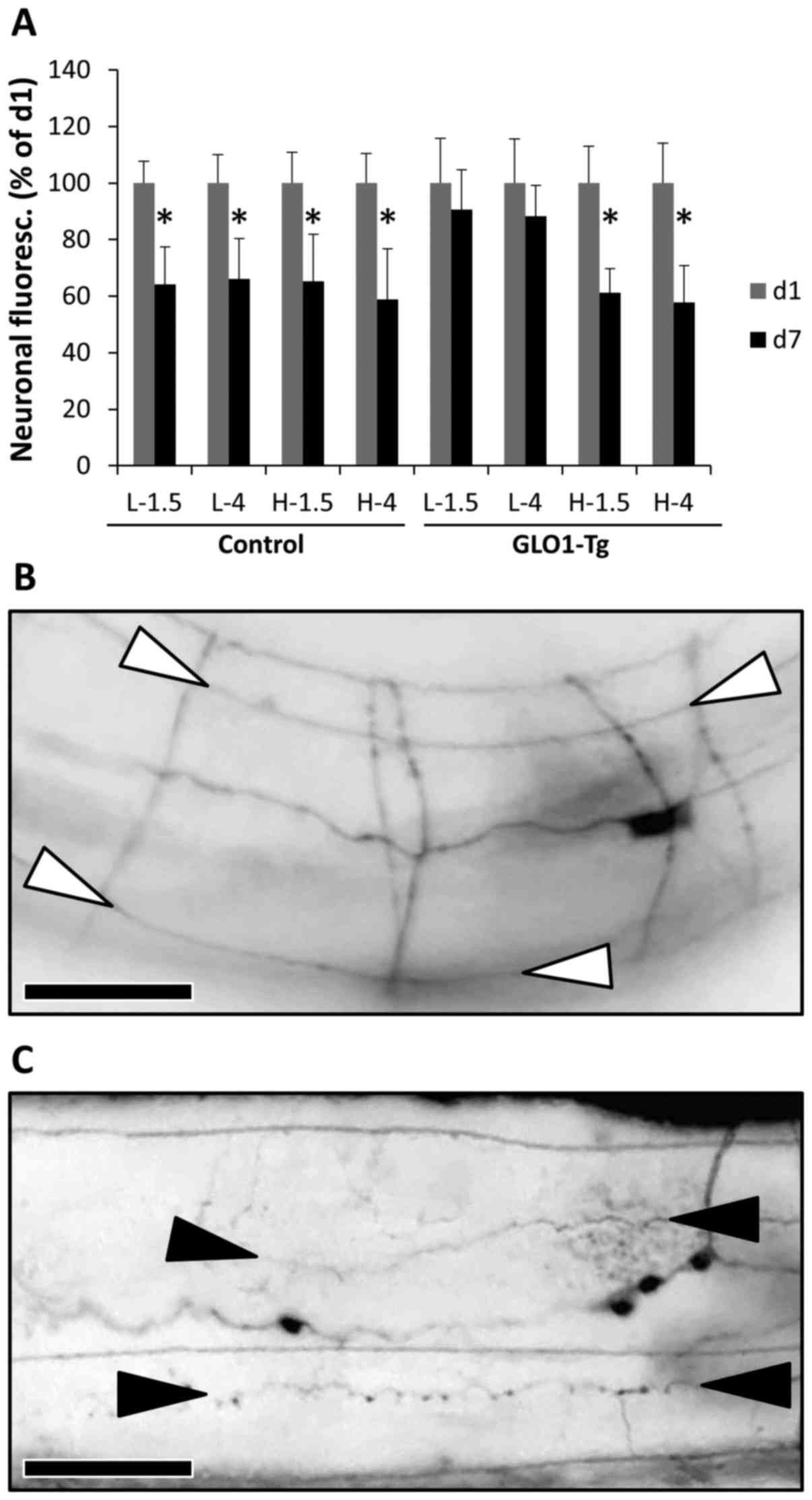
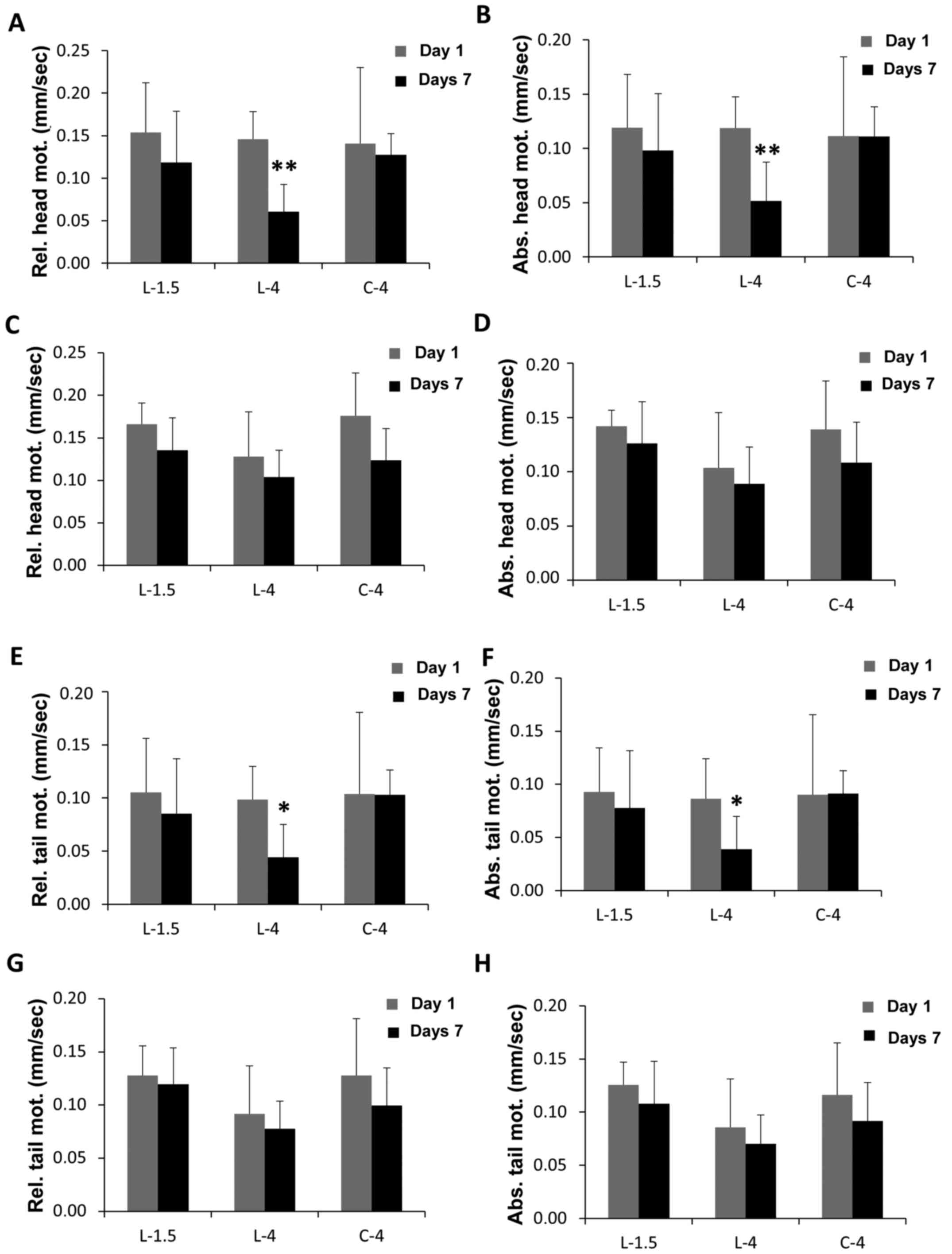
|
1
|
Davis KE, Prasad C, Vijayagopal P, Juma S
and Imrhan V: Advanced glycation end products, inflammation, and
chronic metabolic diseases: Links in a chain? Crit Rev Food Sci
Nutr. 56:989–998. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Vlassara H and Uribarri J: Advanced
glycation end products (AGE) and diabetes: Cause, effect, or both?
Curr Diab Rep. 14:4532014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hellwig M and Henle T: Baking, ageing,
diabetes: A short history of the Maillard reaction. Angew Chem Int
Ed Engl. 53:10316–10329. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Uribarri J, del Castillo MD, de la Maza
MP, Filip R, Gugliucci A, Luevano-Contreras C, Macías-Cervantes MH,
Bastos Markowicz DH, Medrano A, Menini T, et al: Dietary advanced
glycation end products and their role in health and disease. Adv
Nutr. 6:461–473. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ott C, Jacobs K, Haucke E, Santos
Navarrete A, Grune T and Simm A: Role of advanced glycation end
products in cellular signaling. Redox Biol. 2:411–429. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Johnson DW, Dent H, Hawley CM, McDonald
SP, Rosman JB, Brown FG, Bannister K and Wiggins KJ: Association of
dialysis modality and cardiovascular mortality in incident dialysis
patients. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 4:1620–1628. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Borazan A, Ustün H, Ustundag Y, Aydemir S,
Bayraktaroglu T, Sert M and Yilmaz A: The effects of peritoneal
dialysis and hemodialysis on serum tumor necrosis factor-alpha,
interleukin-6, interleukin-10 and C-reactive-protein levels.
Mediators Inflamm. 13:201–204. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chung SH, Heimbürger O, Stenvinkel P,
Bergström J and Lindholm B: Association between inflammation and
changes in residual renal function and peritoneal transport rate
during the first year of dialysis. Nephrol Dial Transplant.
16:2240–2245. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jörres A, Witowski J and Bender TO: PD and
loss of peritoneal function. Prilozi. 28:275–281. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Erixon M, Wieslander A, Lindén T, Carlsson
O, Forsbäck G, Svensson E, Jönsson JA and Kjellstrand P: How to
avoid glucose degradation products in peritoneal dialysis fluids.
Perit Dial Int. 26:490–497. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Linden T, Forsback G, Deppisch R, Henle T
and Wieslander A: 3-Deoxyglucosone, a promoter of advanced
glycation end products in fluids for peritoneal dialysis. Perit
Dial Int. 18:290–293. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Miyata T, Horie K, Ueda Y, Fujita Y,
Izuhara Y, Hirano H, Uchida K, Saito A, van Ypersele de Strihou C
and Kurokawa K: Advanced glycation and lipidoxidation of the
peritoneal membrane: Respective roles of serum and peritoneal fluid
reactive carbonyl compounds. Kidney Int. 58:425–435. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Schwenger V, Morath C, Salava A, Amann K,
Seregin Y, Deppisch R, Ritz E, Bierhaus A, Nawroth PP and Zeier M:
Damage to the peritoneal membrane by glucose degradation products
is mediated by the receptor for advanced glycation end-products. J
Am Soc Nephrol. 17:199–207. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Cooker LA, Luneburg P, Holmes CJ, Jones S
and Topley N; Bicarbonate/Lactate Study Group: Interleukin-6 levels
decrease in effluent from patients dialyzed with
bicarbonate/lactate-based peritoneal dialysis solutions, . Perit
Dial Int. 21 Suppl 3:S102–107. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Szeto CC, Chow KM, Lam CW, Leung CB, Kwan
BC, Chung KY, Law MC and Li PK: Clinical biocompatibility of a
neutral peritoneal dialysis solution with minimal
glucose-degradation products - a 1-year randomized control trial.
Nephrol Dial Transplant. 22:552–559. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Schmitt CP, von Heyl D, Rieger S, Arbeiter
K, Bonzel KE, Fischbach M, Misselwitz J, Pieper AK and Schaefer F:
Mid European Pediatric Peritoneal Dialysis Study Group (MEPPS):
Reduced systemic advanced glycation end products in children
receiving peritoneal dialysis with low glucose degradation product
content. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 22:2038–2044. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Thornalley PJ: Dietary AGEs and ALEs and
risk to human health by their interaction with the receptor for
advanced glycation endproducts (RAGE) - an introduction. Mol Nutr
Food Res. 51:1107–1110. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Thornalley PJ: Endogenous
alpha-oxoaldehydes and formation of protein and nucleotide advanced
glycation endproducts in tissue damage. Novartis Found Symp.
285:229–243; discussion 243–246. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Thornalley PJ: Glyoxalase I - structure,
function and a critical role in the enzymatic defence against
glycation. Biochem Soc Trans. 31:1343–1348. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Thornalley PJ: Protein and nucleotide
damage by glyoxal and methylglyoxal in physiological systems - role
in ageing and disease. Drug Metabol Drug Interact. 23:125–150.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Morcos M, Du X, Pfisterer F, Hutter H,
Sayed AA, Thornalley P, Ahmed N, Baynes J, Thorpe S, Kukudov G, et
al: Glyoxalase-1 prevents mitochondrial protein modification and
enhances lifespan in Caenorhabditis elegans. Aging Cell.
7:260–269. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Mendler M, Schlotterer A, Morcos M and
Nawroth PP: Understanding diabetic polyneuropathy and longevity:
What can we learn from the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans?
Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 120:182–183. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Schalkwijk CG, Posthuma N, ten Brink HJ,
ter Wee PM and Teerlink T: Induction of 1,2-dicarbonyl compounds,
intermediates in the formation of advanced glycation end-products,
during heat-sterilization of glucose-based peritoneal dialysis
fluids. Perit Dial Int. 19:325–333. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Korybalska K, Wisniewska-Elnur J,
Trómińska J, Jörres A, Breborowicz A and Witowski J: The role of
the glyoxalase pathway in reducing mesothelial toxicity of glucose
degradation products. Perit Dial Int. 26:259–265. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Altun-Gultekin Z, Andachi Y, Tsalik EL,
Pilgrim D, Kohara Y and Hobert O: A regulatory cascade of three
homeobox genes, ceh-10, ttx-3 and ceh-23, controls cell fate
specification of a defined interneuron class in C. elegans.
Development. 128:1951–1969. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zeier M, Schwenger V, Deppisch R, Haug U,
Weigel K, Bahner U, Wanner C, Schneider H, Henle T and Ritz E:
Glucose degradation products in PD fluids: Do they disappear from
the peritoneal cavity and enter the systemic circulation? Kidney
Int. 63:298–305. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hutter H: Axonale Wegfindung im ventralen
Nervenstrang von C. elegans. Tätigkeitsbericht. 2003.(In
German).
|
|
28
|
Hobert O and Loria P: Uses of GFP in
Caenorhabditis elegansGreen Fluorescent Protein: Properties,
Applications, and Protocols. Chalfie M and Kain SR: 47. 2nd
edition. John Wiley & Sons, Inc.; Hoboken, NJ: pp. 203–226.
2006
|
|
29
|
Negga R, Rudd DA, Davis NS, Justice AN,
Hatfield HE, Valente AL, Fields AS and Fitsanakis VA: Exposure to
Mn/Zn ethylene-bis-dithiocarbamate and glyphosate pesticides leads
to neurodegeneration in Caenorhabditis elegans.
Neurotoxicology. 32:331–341. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Mendler M, Schlotterer A, Ibrahim Y,
Kukudov G, Fleming T, Bierhaus A, Riedinger C, Schwenger V, Herzig
S, Hecker M, et al: daf-16/FOXO and glod-4/glyoxalase-1 are
required for the life-prolonging effect of human insulin under high
glucose conditions in Caenorhabditis elegans. Diabetologia.
58:393–401. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Schlotterer A, Greten HJ, Remppis BA,
Kukudov G, Efferth T, Machado J, Humpert P, Hammes HP and Morcos M:
Neuroprotection and antioxidative effects of Sijunzi Tang Decoction
in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Eur J Integr Med.
8:526–532. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Ortiz A, Wieslander A, Linden T,
Santamaria B, Sanz A, Justo P, Sanchez-Niño MD, Benito A and
Kjellstrand P: 3,4-DGE is important for side effects in peritoneal
dialysis what about its role in diabetes. Curr Med Chem.
13:2695–2702. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Choi HY, Kim DK, Lee TH, Moon SJ, Han SH,
Lee JE, Kim BS, Park HC, Choi KH, Ha SK, et al: The clinical
usefulness of peritoneal dialysis fluids with neutral pH and low
glucose degradation product concentration: An open randomized
prospective trial. Perit Dial Int. 28:174–182. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Schwenger V: GDP and AGE receptors:
Mechanisms of peritoneal damage. Contrib Nephrol. 150:77–83. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Müller-Krebs S, Kihm LP, Zeier B, Gross
ML, Deppisch R, Wieslander A, Henle T, Penndorf I, Oh J, Reiser J,
et al: Renal toxicity mediated by glucose degradation products in a
rat model of advanced renal failure. Eur J Clin Invest. 38:296–305.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Dengg M and van Meel JC: Caenorhabditis
elegans as model system for rapid toxicity assessment of
pharmaceutical compounds. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods. 50:209–214.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Artal-Sanz M, de Jong L and Tavernarakis
N: Caenorhabditis elegans: A versatile platform for drug
discovery. Biotechnol J. 1:1405–1418. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ailion M, Inoue T, Weaver CI, Holdcraft RW
and Thomas JH: Neurosecretory control of aging in Caenorhabditis
elegans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 96:7394–7397. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Boulianne GL: Neuronal regulation of
lifespan: Clues from flies and worms. Mech Ageing Dev. 122:883–894.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Geanacopoulos M: The determinants of
lifespan in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans: A short
primer. Sci Prog. 87:227–247. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Luo Y: Long-lived worms and aging. Redox
Rep. 9:65–69. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Paik YK, Jeong SK, Lee EY, Jeong PY and
Shim YH: C. elegans: An invaluable model organism for the
proteomics studies of the cholesterol-mediated signaling pathway.
Expert Rev Proteomics. 3:439–453. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Shen LL, Wang Y and Wang DY: Involvement
of genes required for synaptic function in aging control in C.
elegans. Neurosci Bull. 23:21–29. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Murakami S: Caenorhabditis elegans
as a model system to study aging of learning and memory. Mol
Neurobiol. 35:85–94. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Choei H, Sasaki N, Takeuchi M, Yoshida T,
Ukai W, Yamagishi S, Kikuchi S and Saito T: Glyceraldehyde-derived
advanced glycation end products in Alzheimer's disease. Acta
Neuropathol. 108:189–193. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Fatokun AA, Stone TW and Smith RA:
Oxidative stress in neurodegeneration and available means of
protection. Front Biosci. 13:3288–3311. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Deponte M: Glutathione catalysis and the
reaction mechanisms of glutathione-dependent enzymes. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1830:3217–3266. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|