|
1
|
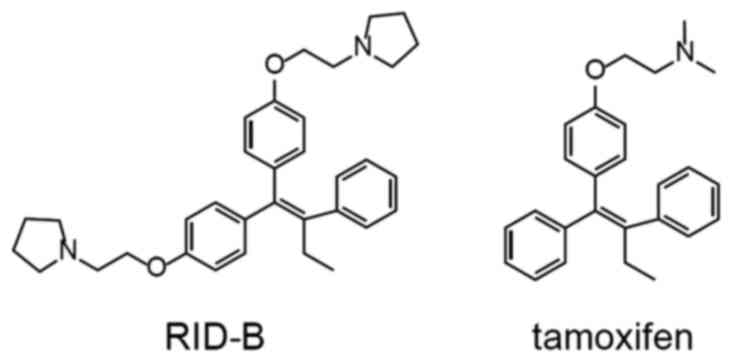
Shiina I, Sano Y, Nakata K, Kikuchi T,
Sasaki A, Ikekita M and Hasome Y: Synthesis of the new
pseudo-symmetrical tamoxifen derivatives and their anti-tumor
activity. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 17:2421–2424. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Shiina I, Sano Y, Nakata K, Kikuchi T,
Sasaki A, Ikekita M, Nagahara Y, Hasome Y, Yamori T and Yamazaki K:
Synthesis and pharmacological evaluation of the novel
pseudo-symmetrical tamoxifen derivatives as anti-tumor agents.
Biochem Pharmacol. 75:1014–1026. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Shagufta and Ahmad I: Tamoxifen a
pioneering drug: An update on the therapeutic potential of
tamoxifen derivatives. Eur J Med Chem. 143:515–531. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Guo WZ, Wang Y, Umeda E, Shiina I, Dan S
and Yamori T: Search for novel anti-tumor agents from ridaifens
using JFCR39, a panel of human cancer cell lines. Biol Pharm Bull.
36:1008–1016. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Anlifeire A, Hatori M, Morita A, Shiina I,
Nakata K, Tosaki Y, Wang Y-W, Ikekita M and Li G: Ridaifen G
induces caspase independent atypical cell death. Chin J Cell Biol.
33:635–644. 2011.
|
|
6
|
Ikeda K, Kamisuki S, Uetake S, Mizusawa A,
Ota N, Sasaki T, Tsukuda S, Kusayanagi T, Takakusagi Y, Morohashi
K, et al: Ridaifen G, tamoxifen analog, is a potent anticancer drug
working through a combinatorial association with multiple cellular
factors. Bioorg Med Chem. 23:6118–6124. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hasegawa M, Yasuda Y, Tanaka M, Nakata K,
Umeda E, Wang Y, Watanabe C, Uetake S, Kunoh T, Shionyu M, et al: A
novel tamoxifen derivative, ridaifen-F, is a nonpeptidic
small-molecule proteasome inhibitor. Eur J Med Chem. 71:290–305.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tanaka M, Zhu Y, Shionyu M, Ota N, Shibata
N, Watanabe C, Mizusawa A, Sasaki R, Mizukami T, Shiina I, et al:
Ridaifen-F conjugated with cell-penetrating peptides inhibits
intracellular proteasome activities and induces drug-resistant cell
death. Eur J Med Chem. 146:636–650. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Longley DB, Harkin DP and Johnston PG:
5-fluorouracil: Mechanisms of action and clinical strategies. Nat
Rev Cancer. 3:330–338. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Todd RC and Lippard SJ: Inhibition of
transcription by platinum antitumor compounds. Metallomics.
1:280–291. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
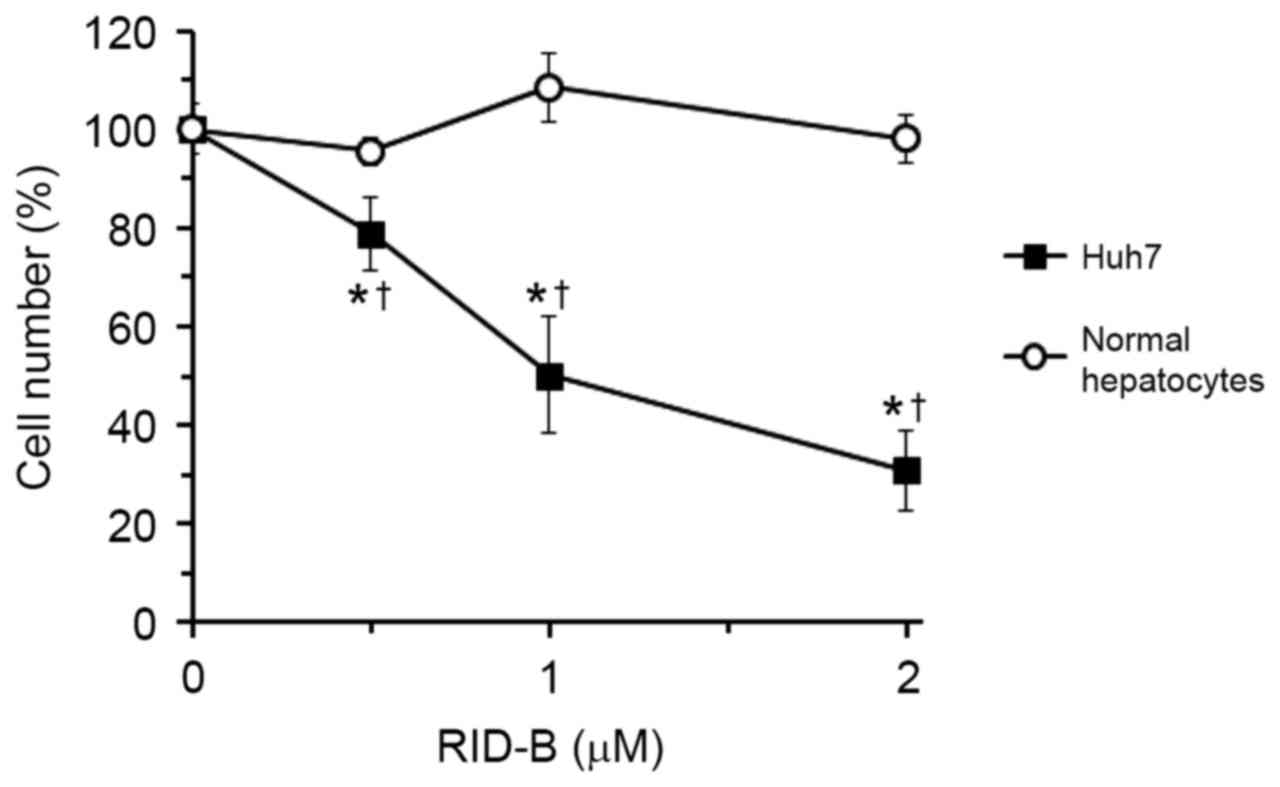
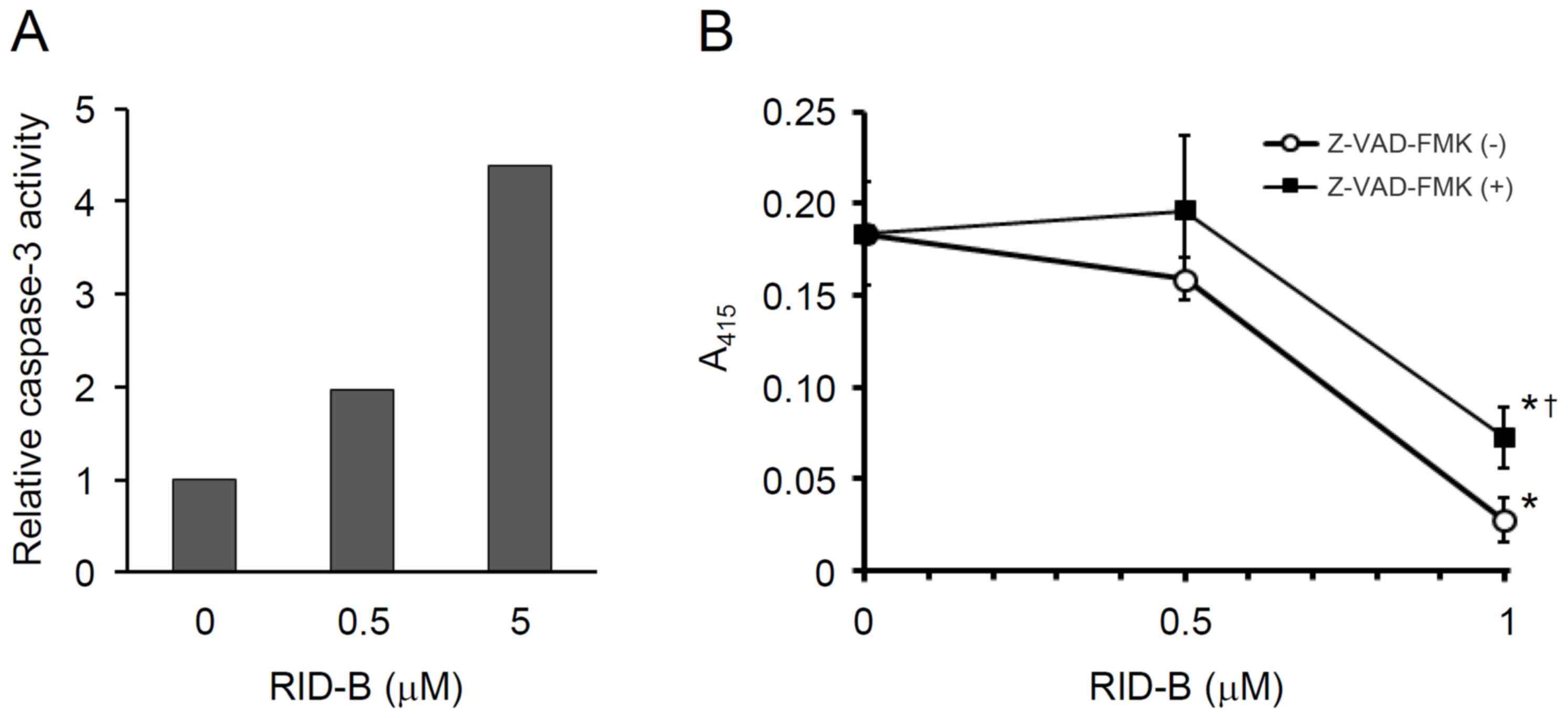
Nagahara Y, Shiina I, Nakata K, Sasaki A,
Miyamoto T and Ikekita M: Induction of mitochondria-involved
apoptosis in estrogen receptor-negative cells by a novel tamoxifen
derivative, ridaifen-B. Cancer Sci. 99:608–614. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Nagahara Y, Takeyoshi M, Sakemoto S,
Shiina I, Nakata K, Fujimori K, Wang Y, Umeda E, Watanabe C, Uetake
S, et al: Novel tamoxifen derivative Ridaifen-B induces Bcl-2
independent autophagy without estrogen receptor involvement.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 435:657–663. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
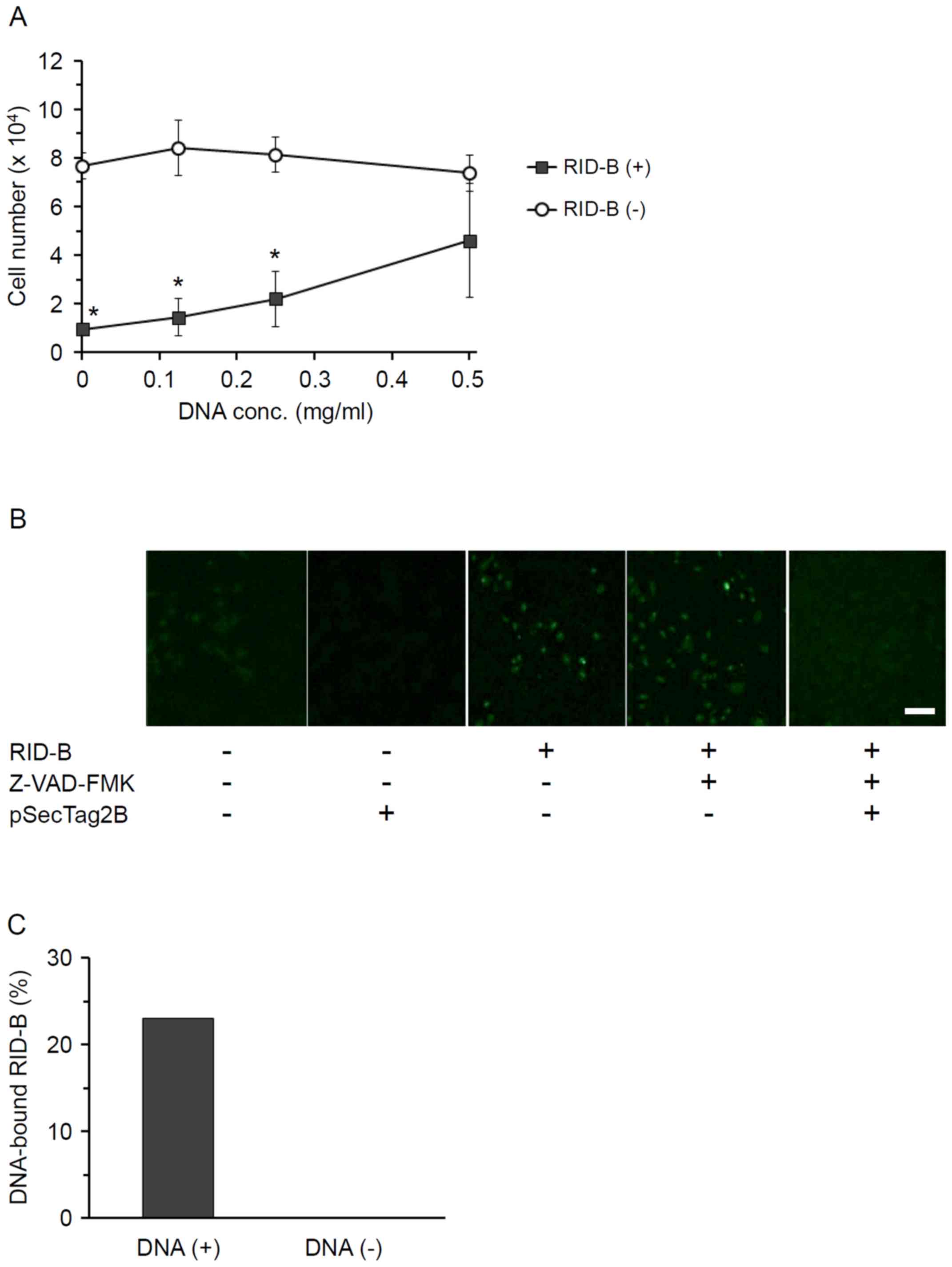
Tsukuda S, Kusayanagi T, Umeda E, Watanabe
C, Tosaki YT, Kamisuki S, Takeuchi T, Takakusagi Y, Shiina I and
Sugawara F: Ridaifen B, a tamoxifen derivative, directly binds to
Grb10 interacting GYF protein 2. Bioorg Med Chem. 21:311–320. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Seglen PO: Preparation of isolated rat
liver cells. Methods Cell Biol. 13:29–83. 1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Quistorff B, Dich J and Grunnet N:
Preparation of Isolated Rat Liver HepatocytesAnimal Cell Culture.
Walker JM and Pollard JW: Humana Press; Totowa, NJ: pp. 151–160.
1990, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Francavilla A, Ove P, Polimeno L, Sciascia
C, Coetzee ML and Starzl TE: Epidermal growth factor and
proliferation in rat hepatocytes in primary culture isolated at
different times after partial hepatectomy. Cancer Res.
46:1318–1323. 1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sebaugh JL: Guidelines for accurate
EC50/IC50 estimation. Pharm Stat. 10:128–134. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Guo WZ, Shiina I, Wang Y, Umeda E,
Watanabe C, Uetake S, Ohashi Y, Yamori T and Dan S: Ridaifen-SB8, a
novel tamoxifen derivative, induces apoptosis via reactive oxygen
species-dependent signaling pathway. Biochem Pharmacol.
86:1272–1284. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fadaka A, Ajiboye B, Ojo O, Adewale O,
Olayide I and Emuowhochere R: Biology of glucose metabolization in
cancer cells. J Oncol Sci. 3:45–51. 2017.
|
|
20
|
Jeggo PA, Pearl LH and Carr AM: DNA
repair, genome stability and cancer: A historical perspective. Nat
Rev Cancer. 16:35–42. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Pfeifer AM, Cole KE, Smoot DT, Weston A,
Groopman JD, Shields PG, Vignaud JM, Juillerat M, Lipsky MM and
Trump BF: Simian virus 40 large tumor antigen-immortalized normal
human liver epithelial cells express hepatocyte characteristics and
metabolize chemical carcinogens. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
90:5123–5127. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Reddel RR, De Silva R, Duncan EL, Rogan
EM, Whitaker NJ, Zahra DG, Ke Y, McMenamin MG, Gerwin BI and Harris
CC: SV40-induced immortalization and ras-transformation of human
bronchial epithelial cells. Int J Cancer. 61:199–205. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Martin RG and Oppenheim A: Initiation
points for DNA replication in nontransformed and simian virus
40-transformed Chinese hamster lung cells. Cell. 11:859–869. 1977.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|