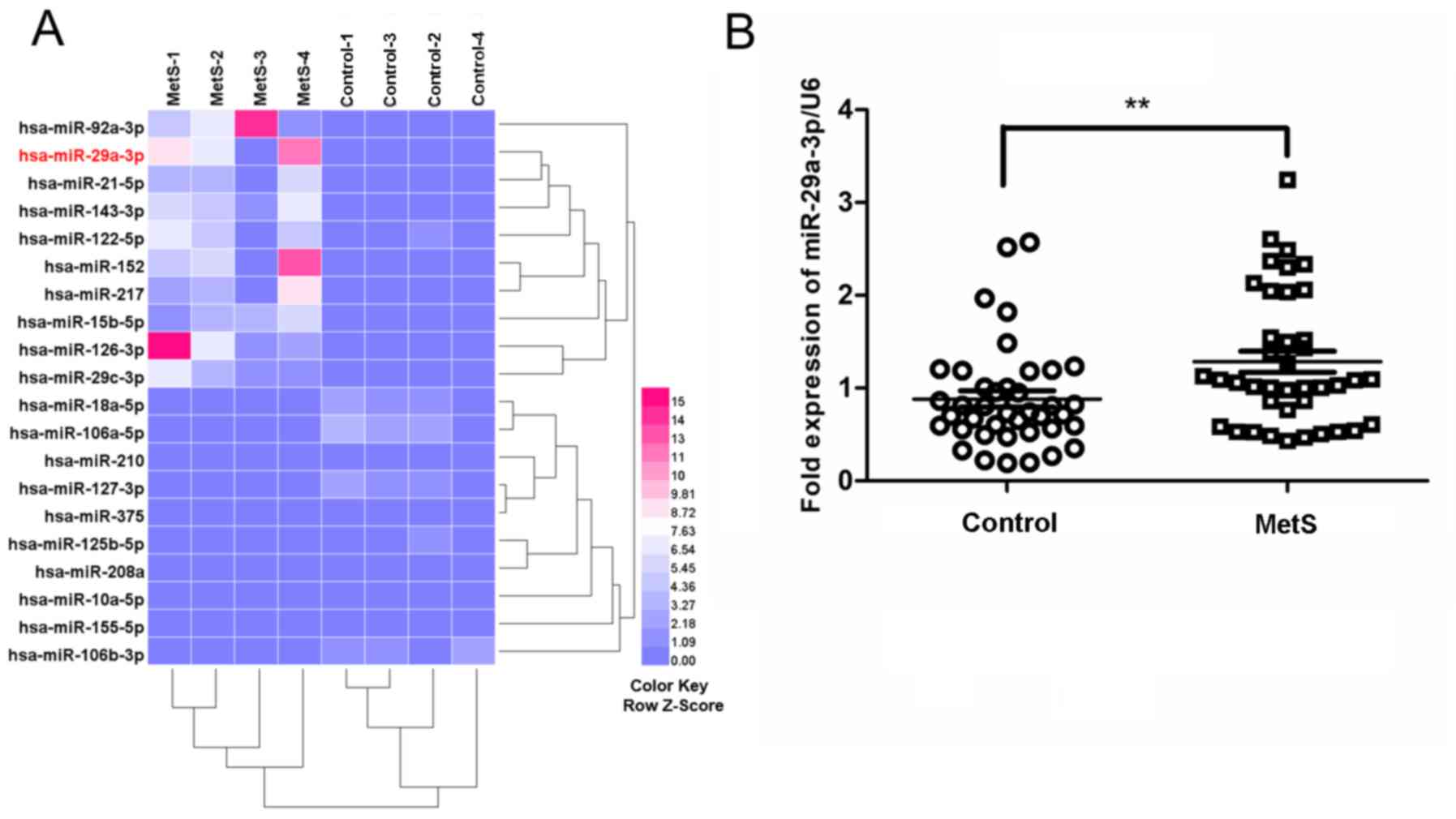
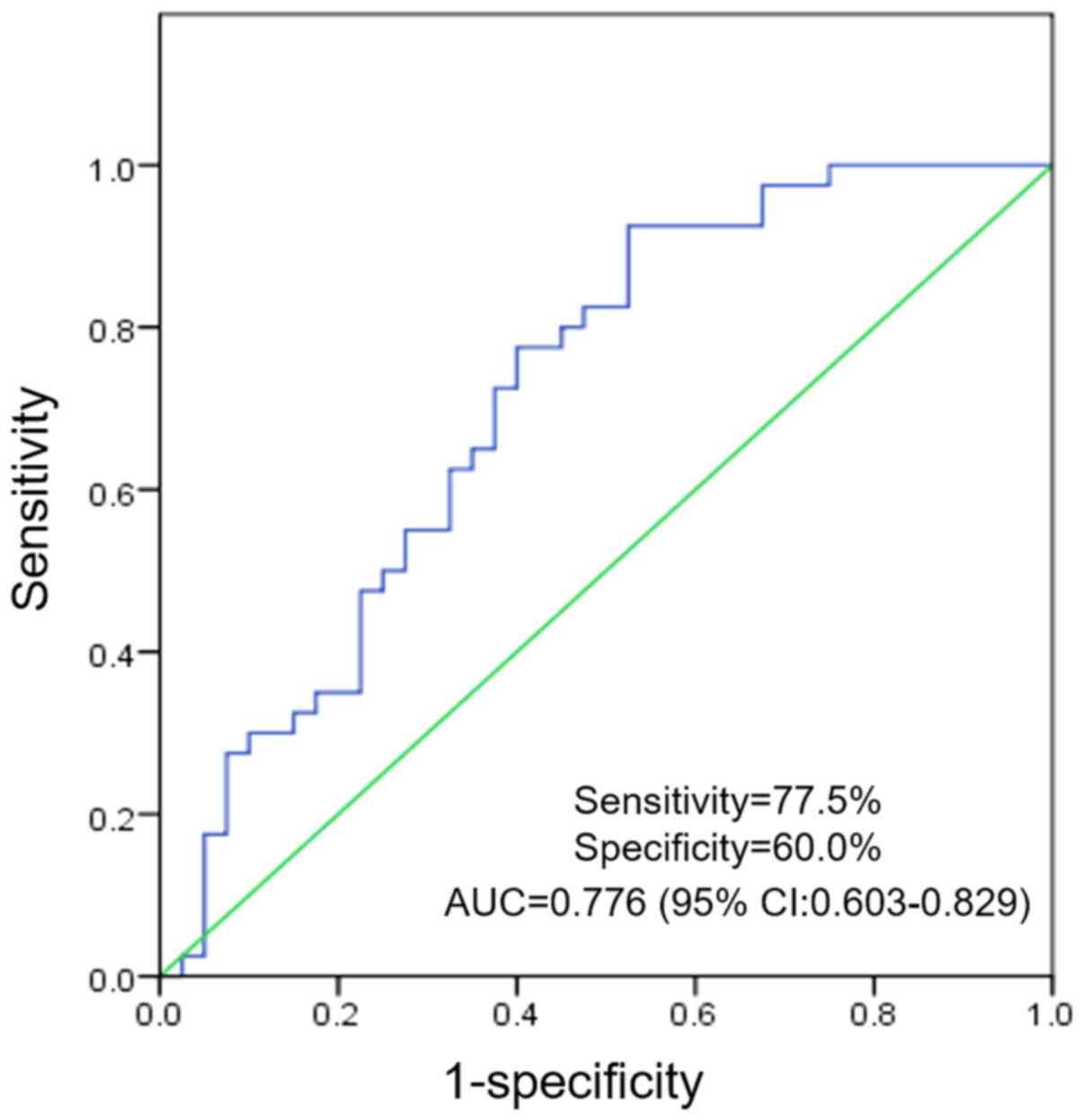
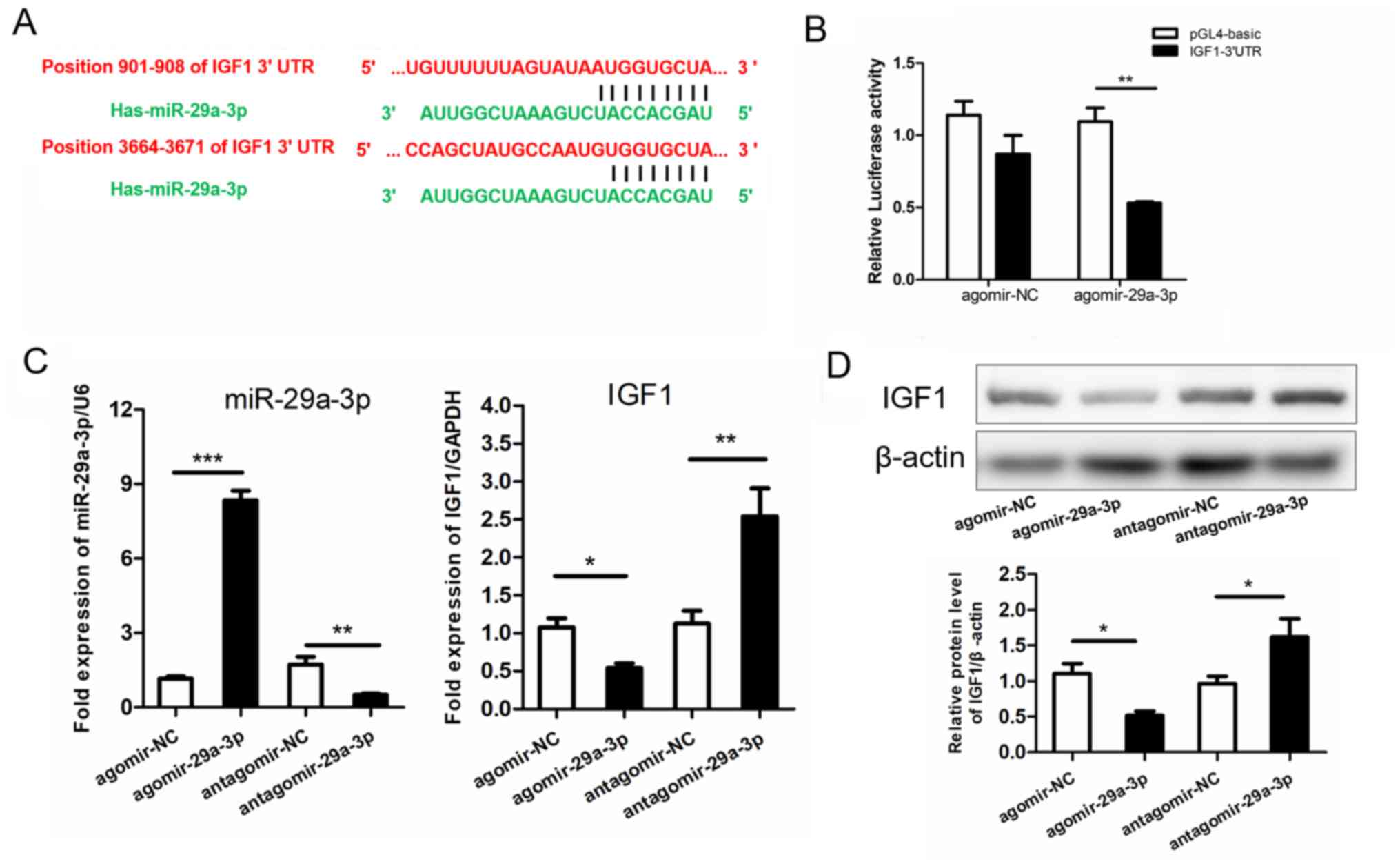
|
1
|
Shab-Bidar S, Golzarand M, Hajimohammadi M
and Mansouri S: A posteriori dietary patterns and metabolic
syndrome in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis of
observational studies. Public Health Nutr. 21:1681–1692.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Krützfeldt J and Stoffel M: MicroRNAs: A
new class of regulatory genes affecting metabolism. Cell Metab.
4:9–12. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Dehwah MA, Xu A and Huang Q: MicroRNAs and
type 2 diabetes/obesity. J Genet Genomics. 39:11–18.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Carreras-Badosa G, Bonmatí A, Ortega FJ,
Mercader JM, Guindo-Martínez M, Torrents D, Prats-Puig A,
Martinez-Calcerrada JM, Platero-Gutierrez E, De Zegher F, et al:
Altered Circulating miRNA Expression Profile in Pregestational and
Gestational Obesity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 100:E1446–E1456.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Liang Z, Gao KP, Wang YX, Liu ZC, Tian L,
Yang XZ, Ding JY, Wu WT, Yang WH, Li YL, et al: RNA sequencing
identified specific circulating miRNA biomarkers for early
detection of diabetes retinopathy. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab.
315:E374:–Ε385. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Rayner KJ and Hennessy EJ: Extracellular
communication via microRNA: Lipid particles have a new message. J
Lipid Res. 54:1174–1181. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
van de Vrie M, Deegens JK, Eikmans M, van
der Vlag J and Hilbrands LB: Urinary MicroRNA as Biomarker in Renal
Transplantation. Am J Transplant. 17:1160–1166. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Endzeliņš E, Berger A, Melne V,
Bajo-Santos C, Soboļevska K, Ābols A, Rodriguez M, Šantare D,
Rudņickiha A, Lietuvietis V, et al: Detection of circulating
miRNAs: Comparative analysis of extracellular vesicle-incorporated
miRNAs and cell-free miRNAs in whole plasma of prostate cancer
patients. BMC Cancer. 17(730)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Xie Y, Jia Y, Xie C, Hu F, Xue M and Xue
Y: Corrigendum to Urinary Exosomal MicroRNA Profiling in Incipient
Type 2 Diabetic Kidney Disease. J Diabetes Res.
2018(5969714)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Mitchell PS, Parkin RK, Kroh EM, Fritz BR,
Wyman SK, Pogosova-Agadjanyan EL, Peterson A, Noteboom J, O'Briant
KC, Allen A, et al: Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based
markers for cancer detection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
105:10513–10518. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Redova M, Sana J and Slaby O: Circulating
miRNAs as new blood-based biomarkers for solid cancers. Future
Oncol. 9:387–402. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
He A, Zhu L, Gupta N, Chang Y and Fang F:
Overexpression of micro ribonucleic acid 29, highly up-regulated in
diabetic rats, leads to insulin resistance in 3T3-L1 adipocytes.
Mol Endocrinol. 21:2785–2794. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Song H, Ding L, Zhang S and Wang W: miR-29
family members interact with SPARC to regulate glucose metabolism.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 497:667–674. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Bagge A, Clausen TR, Larsen S, Ladefoged
M, Rosenstierne MW, Larsen L, Vang O, Nielsen JH and Dalgaard LT:
MicroRNA-29a is up-regulated in beta-cells by glucose and decreases
glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
426:266–272. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Herrera BM, Lockstone HE, Taylor JM, Wills
QF, Kaisaki PJ, Barrett A, Camps C, Fernandez C, Ragoussis J,
Gauguier D, et al: MicroRNA-125a is over-expressed in insulin
target tissues in a spontaneous rat model of Type 2 Diabetes. BMC
Med Genomics. 2(54)2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Pandey AK, Verma G, Vig S, Srivastava S,
Srivastava AK and Datta M: miR-29a levels are elevated in the db/db
mice liver and its overexpression leads to attenuation of insulin
action on PEPCK gene expression in HepG2 cells. Mol Cell
Endocrinol. 332:125–133. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Liang J, Liu C, Qiao A, Cui Y, Zhang H,
Cui A, Zhang S, Yang Y, Xiao X, Chen Y, et al: MicroRNA-29a-c
decrease fasting blood glucose levels by negatively regulating
hepatic gluconeogenesis. J Hepatol. 58:535–542. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Ślusarz A and Pulakat L: The two faces of
miR-29. J Cardiovasc Med (Hagerstown). 16:480–490. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Xueyao Y, Saifei Z, Dan Y, Qianqian P,
Xuehong D, Jiaqiang Z, Fenping Z and Hong L: Circulating
fractalkine levels predict the development of the metabolic
syndrome. Int J Endocrinol. 2014(715148)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Xihua L, Shengjie T, Weiwei G, Matro E,
Tingting T, Lin L, Fang W, Jiaqiang Z, Fenping Z and Hong L:
Circulating miR 143 3p inhibition protects against insulin
resistance in Metabolic Syndrome via targeting of the insulin like
growth factor 2 receptor. Transl Res. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Chinese guidelines on prevention treatment
of dyslipidemia in adults. Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi 35:
390 419, 2007 (In Chinese).
|
|
22
|
Yin XY, Zheng FP, Zhou JQ, Du Y, Pan QQ,
Zhang SF, Yu D and Li H: Central obesity and metabolic risk factors
in middle-aged Chinese. Biomed Environ Sci. 27:343–352.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Emoto M, Nishizawa Y, Maekawa K, Hiura Y,
Kanda H, Kawagishi T, Shoji T, Okuno Y and Morii H: Homeostasis
model assessment as a clinical index of insulin resistance in type
2 diabetic patients treated with sulfonylureas. Diabetes Care.
22:818–822. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Jaisson S, Leroy N, Guillard E, Desmons A
and Gillery P: Analytical performances of the D-100TM hemoglobin
testing system (Bio-Rad) for HbA1c assay. Clin Chem Lab Med.
53:1473–1479. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Liu S, Li W, Xu M, Huang H, Wang J and
Chen X: Micro-RNA 21Targets dual specific phosphatase 8 to promote
collagen synthesis in high glucose-treated primary cardiac
fibroblasts. Can J Cardiol. 30:1689–1699. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Hu XX, Xu XN, He BS, Sun HL, Xu T, Liu XX,
Chen XX, Zeng KX, Wang SK and Pan YQ: MicroRNA-485-5p Functions as
a Tumor Suppressor in Colorectal Cancer Cells by Targeting CD147. J
Cancer. 9:2603–2611. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Dennis G Jr, Sherman BT, Hosack DA, Yang
J, Gao W, Lane HC and Lempicki RA: DAVID: Database for Annotation,
Visualization, and Integrated Discovery. Genome Biol.
4(3)2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Delić D, Eisele C, Schmid R, Baum P, Wiech
F, Gerl M, Zimdahl H, Pullen SS and Urquhart R: Urinary Exosomal
miRNA Signature in Type II Diabetic Nephropathy Patients. PLoS One.
11(e0150154)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Eissa S, Matboli M, Aboushahba R, Bekhet
MM and Soliman Y: Urinary exosomal microRNA panel unravels novel
biomarkers for diagnosis of type 2 diabetic kidney disease. J
Diabetes Complications. 30:1585–1592. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Park S, Moon S, Lee K, Park IB, Lee DH and
Nam S: Urinary and Blood MicroRNA-126 and -770 are Potential
Noninvasive Biomarker Candidates for Diabetic Nephropathy: A
Meta-Analysis. Cell Physiol Biochem. 46:1331–1340. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Peng H, Zhong M, Zhao W, Wang C, Zhang J,
Liu X, Li Y, Paudel SD, Wang Q and Lou T: Urinary miR-29 correlates
with albuminuria and carotid intima-media thickness in type 2
diabetes patients. PLoS One. 8(e82607)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Liu Y, Taylor NE, Lu L, Usa K, Cowley AW
Jr, Ferreri NR, Yeo NC and Liang M: Renal medullary microRNAs in
Dahl salt-sensitive rats: miR-29b regulates several collagens and
related genes. Hypertension. 55:974–982. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Zavesky L, Jandakova E, Turyna R,
Langmeierova L, Weinberger V, Minar L and Kohoutova M: New
perspectives in diagnosis of gynaecological cancers: Emerging role
of circulating microRNAs as novel biomarkers. Neoplasma.
62:509–520. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Campion CG, Sanchez-Ferras O and Batchu
SN: Potential Role of Serum and Urinary Biomarkers in Diagnosis and
Prognosis of Diabetic Nephropathy. Can J Kidney Health Dis.
4(2054358117705371)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Mall C, Rocke DM, Durbin-Johnson B and
Weiss RH: Stability of miRNA in human urine supports its biomarker
potential. Biomarkers Med. 7:623–631. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Ben-Dov IZ, Tan YC Morozov P, Wilson PD,
Rennert H, Blumenfeld JD and Tuschl T: Urine microRNA as potential
biomarkers of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease
progression: Description of miRNA profiles at baseline. PLoS One.
9(e86856)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Abulaban KM, Fall N, Nunna R, Ying J,
Devarajan P, Grom A, Bennett M, Ardoin SP and Brunner HI:
Relationship of cell-free urine MicroRNA with lupus nephritis in
children. Pediatr Rheumatol Online J. 14(4)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Lv LL, Cao Y, Liu D, Xu M, Liu H, Tang RN,
Ma KL and Liu BC: Isolation and quantification of microRNAs from
urinary exosomes/microvesicles for biomarker discovery. Int J Biol
Sci. 9:1021–1031. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Lelbach A, Muzes G and Feher J: The
insulin-like growth factor system: IGFs, IGF-binding proteins and
IGFBP-proteases. Acta Physiol Hung. 92:97–107. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
van Bunderen CC, Oosterwerff MM, van
Schoor NM, Deeg DJ, Lips P and Drent ML: Serum IGF1, metabolic
syndrome, and incident cardiovascular disease in older people: A
population-based study. Eur J Endocrinol. 168:393–401.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
van Nieuwpoort IC, Vlot MC, Schaap LA,
Lips P and Drent ML: The relationship between serum IGF-1, handgrip
strength, physical performance and falls in elderly men and women.
Eur J Endocrinol. 179:73–84. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Lam CS, Chen MH, Lacey SM, Yang Q,
Sullivan LM, Xanthakis V, Safa R, Smith HM, Peng X, Sawyer DB, et
al: Circulating insulin-like growth factor-1 and its binding
protein-3: Metabolic and genetic correlates in the community.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 30:1479–1484. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Saydah S, Ballard-Barbash R and Potischman
N: Association of metabolic syndrome with insulin-like growth
factors among adults in the US. Cancer Causes Control.
20:1309–1316. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|