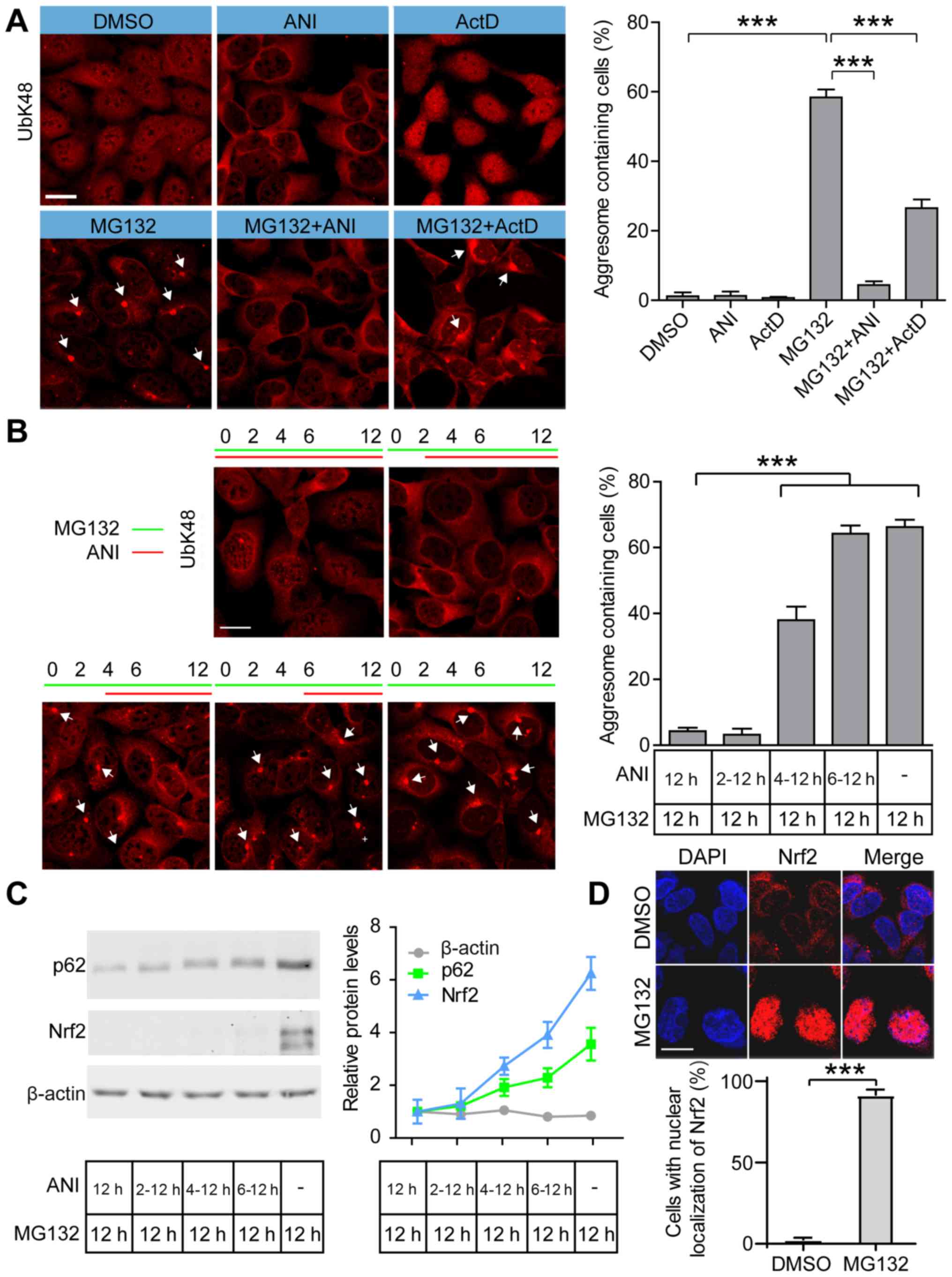
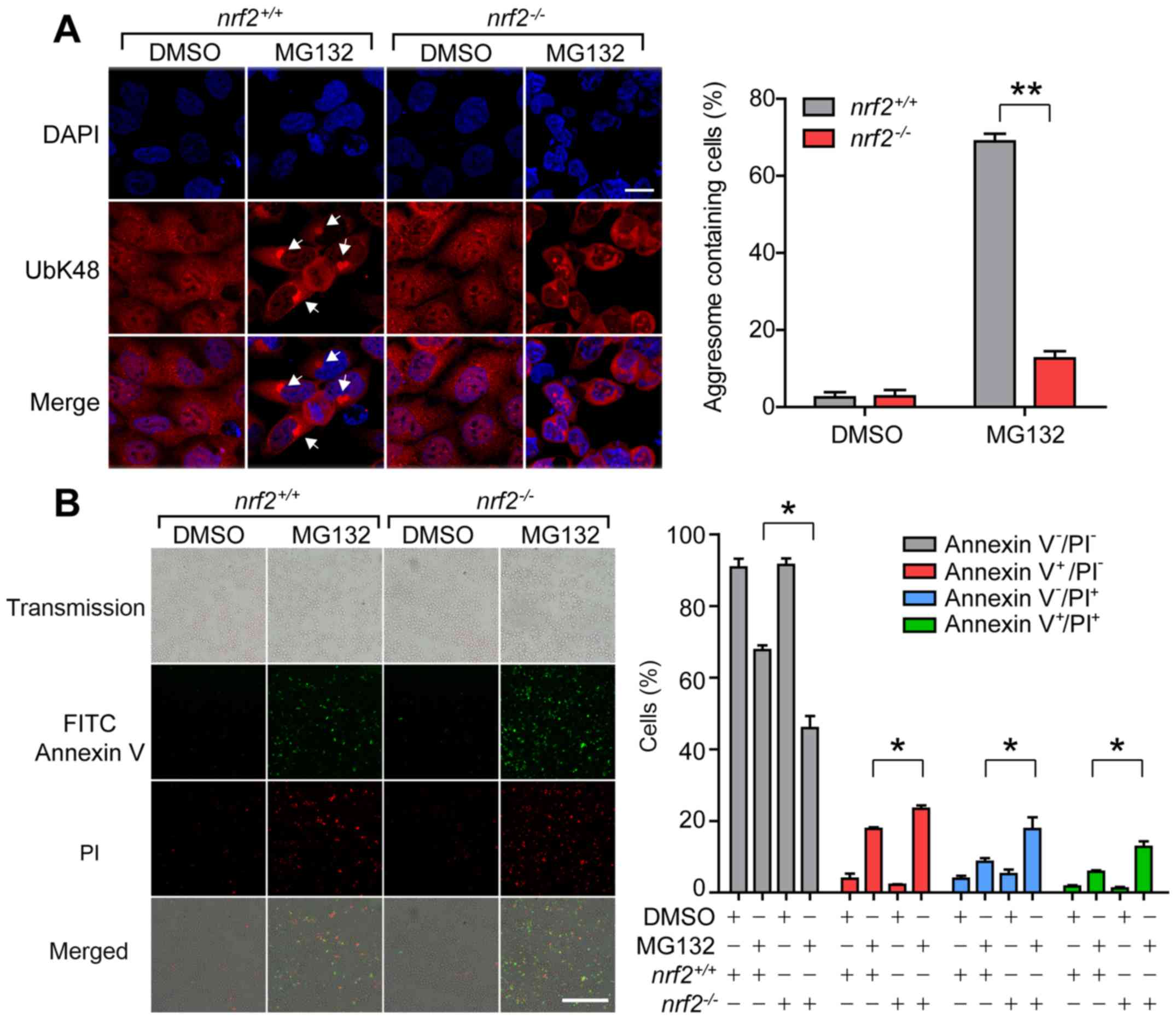
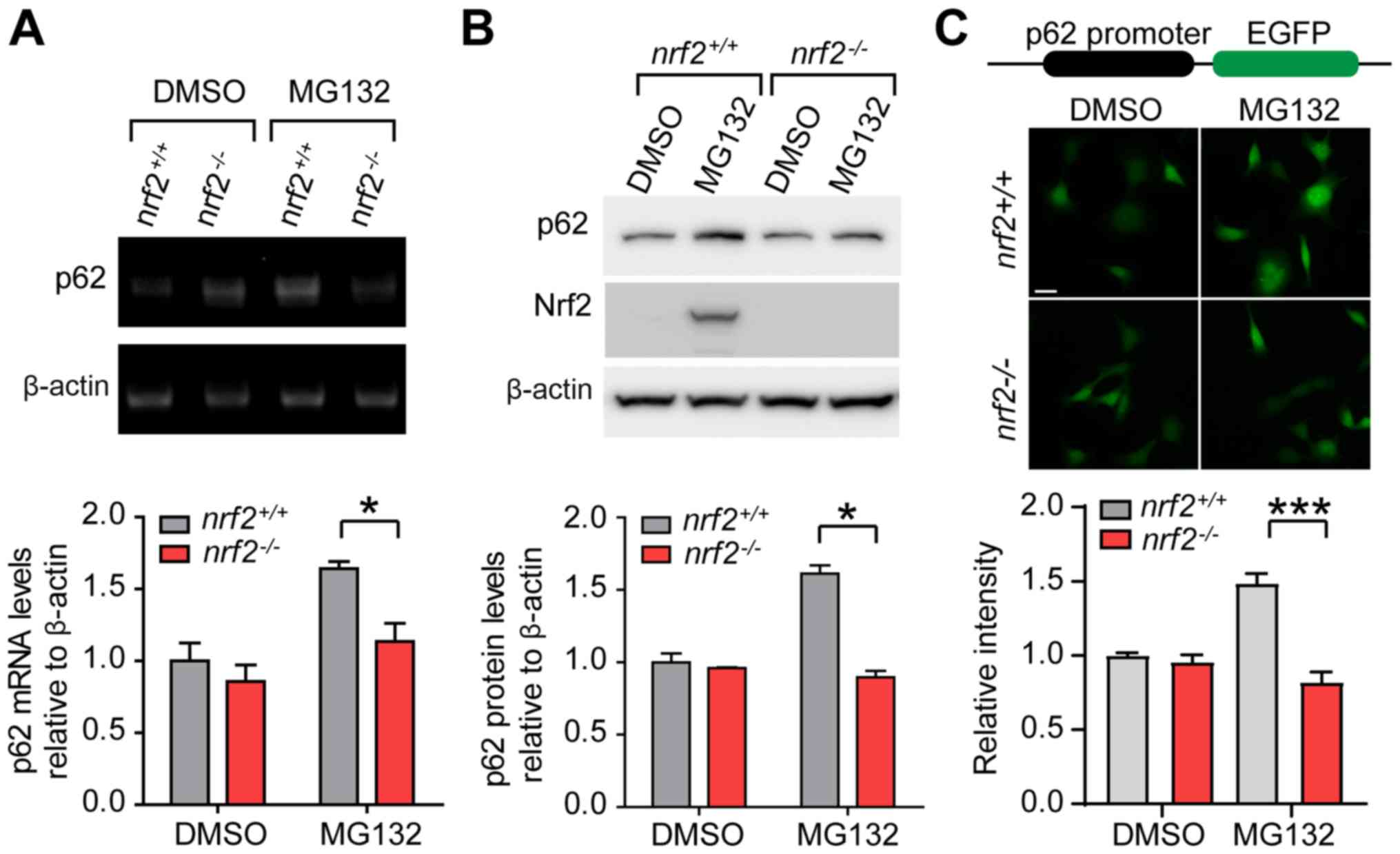
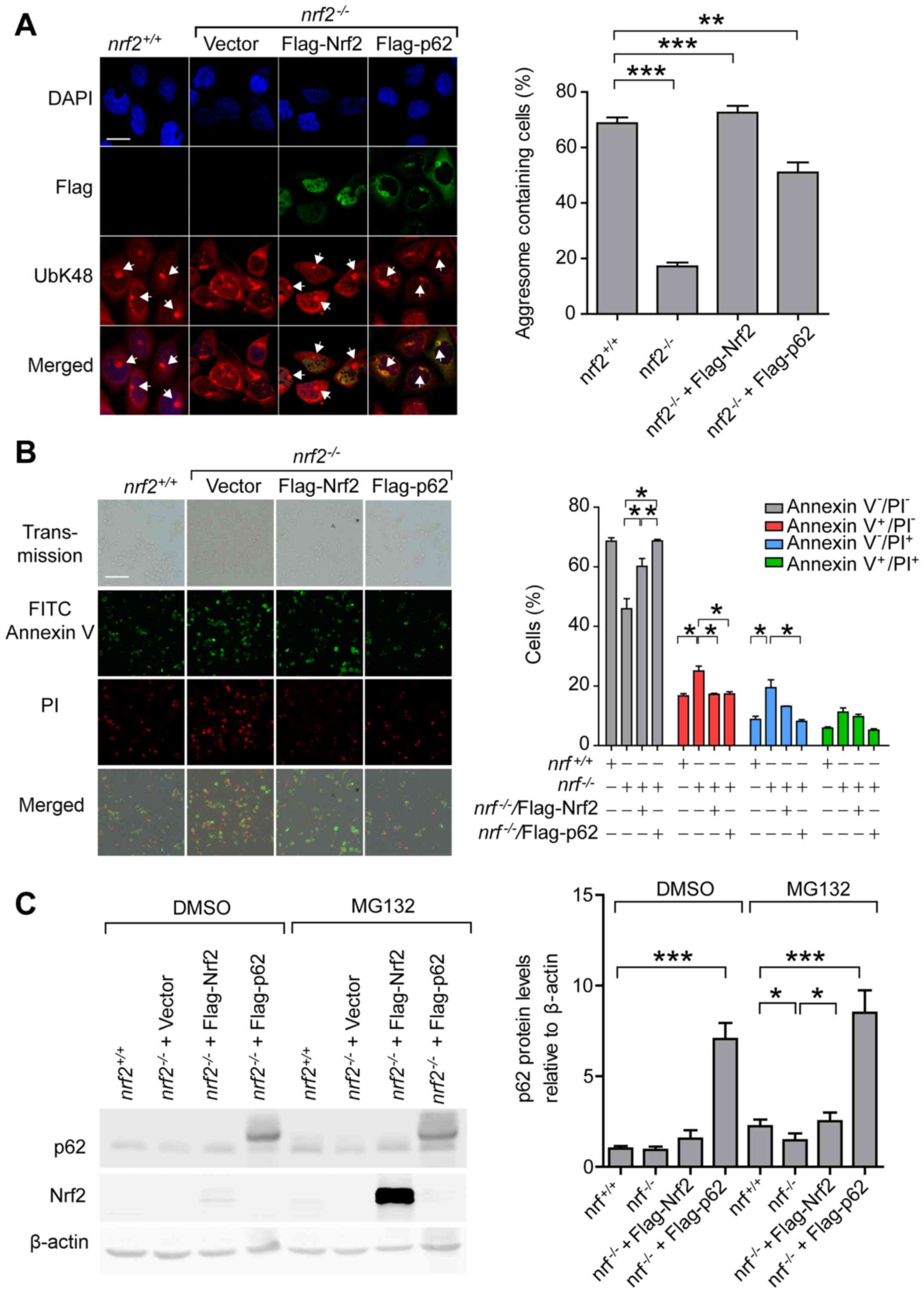
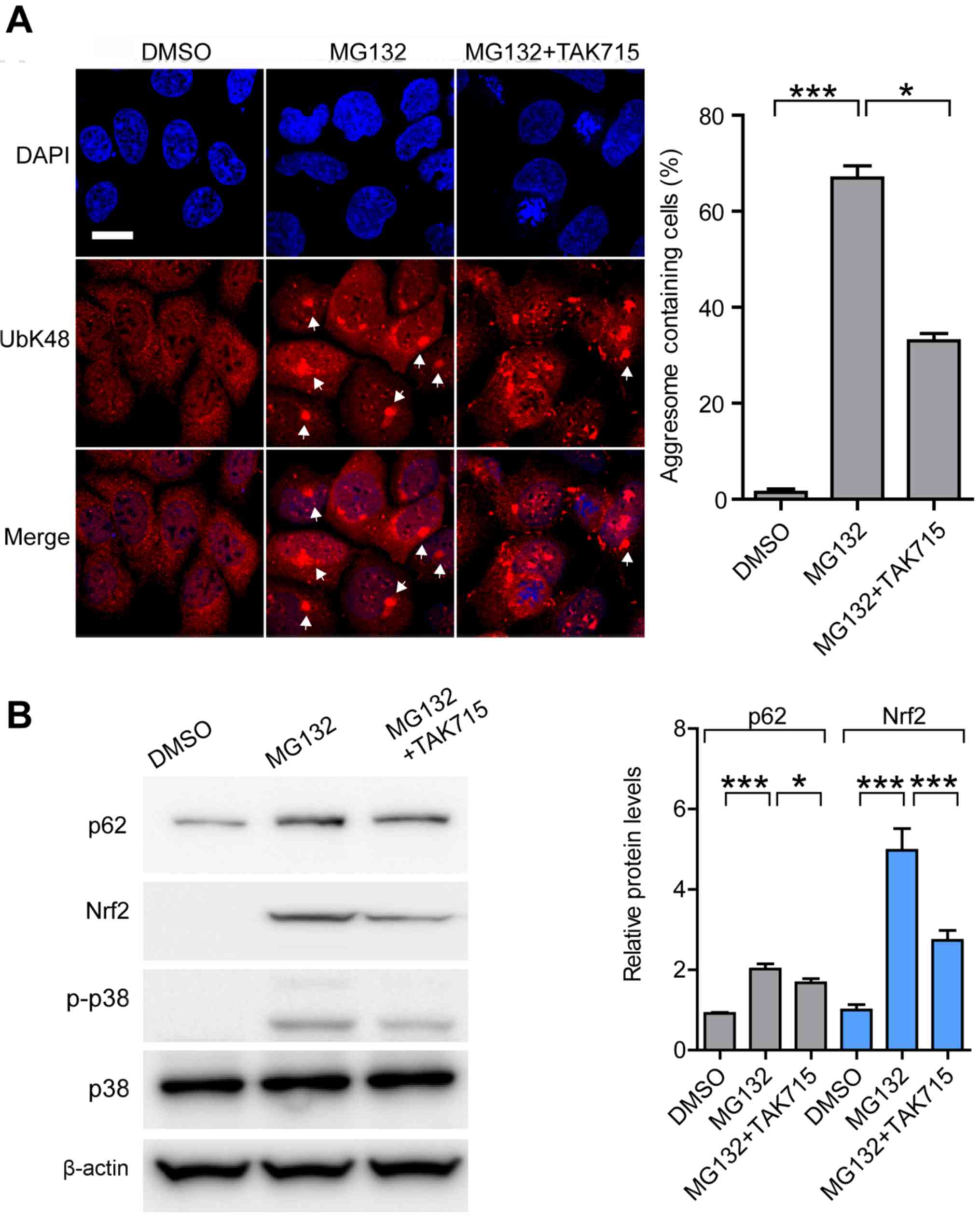
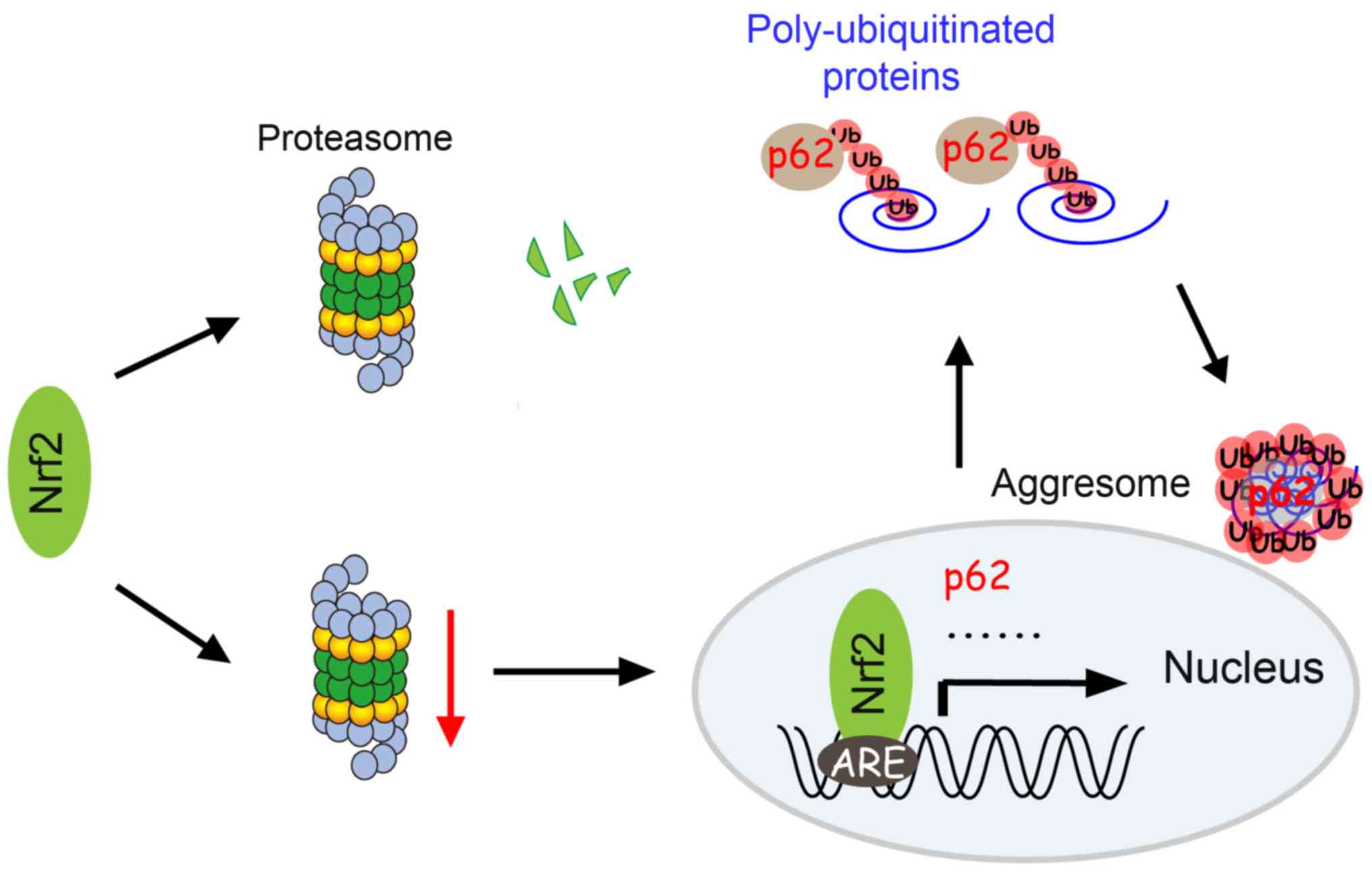
|
1
|
Corboy MJ, Thomas PJ and Wigley WC:
Aggresome formation. Methods Mol Biol. 301:305–327. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Johnston JA, Ward CL and Kopito RR:
Aggresomes: A cellular response to misfolded proteins. J Cell Biol.
143:1883–1898. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Kawaguchi Y, Kovacs JJ, McLaurin A, Vance
JM, Ito A and Yao TP: The deacetylase HDAC6 regulates aggresome
formation and cell viability in response to misfolded protein
stress. Cell. 115:727–738. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Webb JL, Ravikumar B and Rubinsztein DC:
Microtubule disruption inhibits autophagosome-lysosome fusion:
Implications for studying the roles of aggresomes in polyglutamine
diseases. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 36:2541–2550. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Tanaka M, Kim YM, Lee G, Junn E, Iwatsubo
T and Mouradian MM: Aggresomes formed by alpha-synuclein and
synphilin-1 are cytoprotective. J Biol Chem. 279:4625–4631.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Rubinsztein DC, Ravikumar B,
Acevedo-Arozena A, Imarisio S, O'Kane CJ and Brown SD: Dyneins,
autophagy, aggregation and neurodegeneration. Autophagy. 1:177–178.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Marambio P, Toro B, Sanhueza C, Troncoso
R, Parra V, Verdejo H, García L, Quiroga C, Munafo D, Díaz-Elizondo
J, et al: Glucose deprivation causes oxidative stress and
stimulates aggresome formation and autophagy in cultured cardiac
myocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1802:509–518. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Kovacs I, Lentini KM, Ingano LM and Kovacs
DM: Presenilin 1 forms aggresomal deposits in response to heat
shock. Journal of molecular neuroscience. J Mol Neurosci. 29:9–19.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Ang E, Pavlos NJ, Rea SL, Qi M, Chai T,
Walsh JP, Ratajczak T, Zheng MH and Xu J: Proteasome inhibitors
impair RANKL-induced NF-kappaB activity in osteoclast-like cells
via disruption of p62, TRAF6, CYLD, and IkappaBalpha signaling
cascades. J Cell Physiol. 220:450–459. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Kirkin V, McEwan DG, Novak I and Dikic I:
A role for ubiquitin in selective autophagy. Mol Cell. 34:259–269.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Pankiv S, Clausen TH, Lamark T, Brech A,
Bruun JA, Outzen H, Øvervatn A, Bjørkøy G and Johansen T:
p62/SQSTM1 binds directly to Atg8/LC3 to facilitate degradation of
ubiquitinated protein aggregates by autophagy. J Biol Chem.
282:24131–24145. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Gao J, Li M, Qin S, Zhang T, Jiang S, Hu
Y, Deng Y, Zhang C, You D, Li H, et al: Cytosolic PINK1 promotes
the targeting of ubiquitinated proteins to the aggresome-autophagy
pathway during proteasomal stress. Autophagy. 12:632–647.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Olzmann JA, Li L, Chudaev MV, Chen J,
Perez FA, Palmiter RD and Chin LS: Parkin-mediated K63-linked
polyubiquitination targets misfolded DJ-1 to aggresomes via binding
to HDAC6. J Cell Biol. 178:1025–1038. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Waxman EA, Covy JP, Bukh I, Li X, Dawson
TM and Giasson BI: Leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 expression leads to
aggresome formation that is not associated with alpha-synuclein
inclusions. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 68:785–796. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
McLean PJ, Ribich S and Hyman BT:
Subcellular localization of alpha-synuclein in primary neuronal
cultures: Effect of missense mutations. J Neural Transm Suppl.
58:53–63. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Harding HP, Novoa I, Zhang Y, Zeng H, Wek
R, Schapira M and Ron D: Regulated translation initiation controls
stress-induced gene expression in mammalian cells. Mol Cell.
6:1099–1108. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Jain A, Lamark T, Sjøttem E, Larsen KB,
Awuh JA, Øvervatn A, McMahon M, Hayes JD and Johansen T: p62/SQSTM1
is a target gene for transcription factor NRF2 and creates a
positive feedback loop by inducing antioxidant response
element-driven gene transcription. J Biol Chem. 285:22576–22591.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Lau A, Zheng Y, Tao S, Wang H, Whitman SA,
White E and Zhang DD: Arsenic inhibits autophagic flux, activating
the Nrf2-Keap1 pathway in a p62-dependent manner. Mol Cell Biol.
33:2436–2446. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Ichimura Y, Waguri S, Sou YS, Kageyama S,
Hasegawa J, Ishimura R, Saito T, Yang Y, Kouno T, Fukutomi T, et
al: Phosphorylation of p62 activates the Keap1-Nrf2 pathway during
selective autophagy. Mol Cell. 51:618–631. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Komatsu M, Kurokawa H, Waguri S, Taguchi
K, Kobayashi A, Ichimura Y, Sou YS, Ueno I, Sakamoto A, Tong KI, et
al: The selective autophagy substrate p62 activates the stress
responsive transcription factor Nrf2 through inactivation of Keap1.
Nat Cell Biol. 12:213–223. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Ran FA, Hsu PD, Wright J, Agarwala V,
Scott DA and Zhang F: Genome engineering using the CRISPR-Cas9
system. Nat Protoc. 8:2281–2308. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Pickart CM and Fushman D: Polyubiquitin
chains: Polymeric protein signals. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 8:610–616.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Zhang C, Gao J, Li M, Deng Y and Jiang C:
p38δ MAPK regulates aggresome biogenesis by phosphorylating SQSTM1
in response to proteasomal stress. J Cell Sci.
131(131)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Hao R, Nanduri P, Rao Y, Panichelli RS,
Ito A, Yoshida M and Yao TP: Proteasomes activate aggresome
disassembly and clearance by producing unanchored ubiquitin chains.
Mol Cell. 51:819–828. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Mekhail K, Khacho M, Carrigan A, Hache RR,
Gunaratnam L and Lee S: Regulation of ubiquitin ligase dynamics by
the nucleolus. J Cell Biol. 170:733–744. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Cui T, Lai Y, Janicki JS and Wang X:
Nuclear factor erythroid-2 related factor 2 (Nrf2)-mediated protein
quality control in cardiomyocytes. Front Biosci. 21:192–202.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hochmuth CE, Biteau B, Bohmann D and
Jasper H: Redox regulation by Keap1 and Nrf2 controls intestinal
stem cell proliferation in Drosophila. Cell Stem Cell. 8:188–199.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Kovac S, Angelova PR, Holmström KM, Zhang
Y, Dinkova-Kostova AT and Abramov AY: Nrf2 regulates ROS production
by mitochondria and NADPH oxidase. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1850:794–801. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Arakawa M and Ito Y: N-acetylcysteine and
neurodegenerative diseases: Basic and clinical pharmacology.
Cerebellum. 6:308–314. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Sheng XJ, Tu HJ, Chien WL, Kang KH, Lu DH,
Liou HH, Lee MJ and Fu WM: Antagonism of proteasome
inhibitor-induced heme oxygenase-1 expression by PINK1 mutation.
PLoS One. 12(e0183076)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Kim D, Kim SH and Li GC: Proteasome
inhibitors MG132 and lactacystin hyperphosphorylate HSF1 and induce
hsp70 and hsp27 expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
254:264–268. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Vadlamudi RK and Shin J: Genomic structure
and promoter analysis of the p62 gene encoding a non-proteasomal
multiubiquitin chain binding protein. FEBS Lett. 435:138–142.
1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Lim J, Lachenmayer ML, Wu S, Liu W, Kundu
M, Wang R, Komatsu M, Oh YJ, Zhao Y and Yue Z: Proteotoxic stress
induces phosphorylation of p62/SQSTM1 by ULK1 to regulate selective
autophagic clearance of protein aggregates. PLoS Genet.
11(e1004987)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Matsumoto G, Wada K, Okuno M, Kurosawa M
and Nukina N: Serine 403 phosphorylation of p62/SQSTM1 regulates
selective autophagic clearance of ubiquitinated proteins. Mol Cell.
44:279–289. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Du ZX, Yan Y, Zhang HY, Liu BQ, Gao YY,
Niu XF, Meng X and Wang HQ: Proteasome inhibition induces a p38
MAPK pathway-dependent antiapoptotic program via Nrf2 in thyroid
cancer cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 96:E763–E771.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Kopito RR: Aggresomes, inclusion bodies
and protein aggregation. Trends Cell Biol. 10:524–530.
2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Szebenyi G, Wigley WC, Hall B, Didier A,
Yu M, Thomas P and Krämer H: Hook2 contributes to aggresome
formation. BMC Cell Biol. 8(19)2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Bolhuis S and Richter-Landsberg C: Effect
of proteasome inhibition by MG-132 on HSP27 oligomerization,
phosphorylation, and aggresome formation in the OLN-93
oligodendroglia cell line. J Neurochem. 114:960–971.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Meriin AB, Zaarur N and Sherman MY:
Association of translation factor eEF1A with defective ribosomal
products generates a signal for aggresome formation. J Cell Sci.
125:2665–2674. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Hyttinen JM, Amadio M, Viiri J, Pascale A,
Salminen A and Kaarniranta K: Clearance of misfolded and aggregated
proteins by aggrephagy and implications for aggregation diseases.
Ageing Res Rev. 18:16–28. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Lamark T and Johansen T: Aggrephagy:
Selective disposal of protein aggregates by macroautophagy. Int J
Cell Biol. 2012(736905)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Takalo M, Salminen A, Soininen H, Hiltunen
M and Haapasalo A: Protein aggregation and degradation mechanisms
in neurodegenerative diseases. Am J Neurodegener Dis. 2:1–14.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Brüning A and Jückstock J: Misfolded
proteins: From little villains to little helpers in the fight
against cancer. Front Oncol. 5(47)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Park J, Park Y, Ryu I, Choi MH, Lee HJ, Oh
N, Kim K, Kim KM, Choe J, Lee C, et al: Misfolded polypeptides are
selectively recognized and transported toward aggresomes by a CED
complex. Nat Commun. 8(15730)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Liu B and Qian SB: Translational
reprogramming in cellular stress response. Wiley Interdiscip Rev
RNA. 5:301–315. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Sonenberg N and Hinnebusch AG: Regulation
of translation initiation in eukaryotes: Mechanisms and biological
targets. Cell. 136:731–745. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Espinosa-Diez C, Miguel V, Mennerich D,
Kietzmann T, Sánchez-Pérez P, Cadenas S and Lamas S: Antioxidant
responses and cellular adjustments to oxidative stress. Redox Biol.
6:183–197. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Baird L and Dinkova-Kostova AT: The
cytoprotective role of the Keap1-Nrf2 pathway. Arch Toxicol.
85:241–272. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
McMahon M, Thomas N, Itoh K, Yamamoto M
and Hayes JD: Redox-regulated turnover of Nrf2 is determined by at
least two separate protein domains, the redox-sensitive Neh2 degron
and the redox-insensitive Neh6 degron. J Biol Chem.
279:31556–31567. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Nguyen T, Sherratt PJ, Huang HC, Yang CS
and Pickett CB: Increased protein stability as a mechanism that
enhances Nrf2-mediated transcriptional activation of the
antioxidant response element. Degradation of Nrf2 by the 26 S
proteasome. J Biol Chem. 278:4536–4541. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Itoh K, Wakabayashi N, Katoh Y, Ishii T,
O'Connor T and Yamamoto M: Keap1 regulates both cytoplasmic-nuclear
shuttling and degradation of Nrf2 in response to electrophiles.
Genes Cells. 8:379–391. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Furukawa M and Xiong Y: BTB protein Keap1
targets antioxidant transcription factor Nrf2 for ubiquitination by
the Cullin 3-Roc1 ligase. Mol Cell Biol. 25:162–171.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Holmström KM, Baird L, Zhang Y, Hargreaves
I, Chalasani A, Land JM, Stanyer L, Yamamoto M, Dinkova-Kostova AT
and Abramov AY: Nrf2 impacts cellular bioenergetics by controlling
substrate availability for mitochondrial respiration. Biol Open.
2:761–770. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Pilecka I, Sadowski L, Kalaidzidis Y and
Miaczynska M: Recruitment of APPL1 to ubiquitin-rich aggresomes in
response to proteasomal impairment. Exp Cell Res. 317:1093–1107.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Salemi LM, Almawi AW, Lefebvre KJ and
Schild-Poulter C: Aggresome formation is regulated by RanBPM
through an interaction with HDAC6. Biol Open. 3:418–430.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Dron M, Dandoy-Dron F, Farooq Salamat MK
and Laude H: Proteasome inhibitors promote the sequestration of
PrPSc into aggresomes within the cytosol of prion-infected CAD
neuronal cells. J Gen Virol. 90:2050–2060. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Beaudoin S, Goggin K, Bissonnette C,
Grenier C and Roucou X: Aggresomes do not represent a general
cellular response to protein misfolding in mammalian cells. BMC
Cell Biol. 9(59)2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Dantuma NP and Bott LC: The
ubiquitin-proteasome system in neurodegenerative diseases:
Precipitating factor, yet part of the solution. Front Mol Neurosci.
7(70)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Cummings CJ, Mancini MA, Antalffy B,
DeFranco DB, Orr HT and Zoghbi HY: Chaperone suppression of
aggregation and altered subcellular proteasome localization imply
protein misfolding in SCA1. Nat Genet. 19:148–154. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Arrasate M, Mitra S, Schweitzer ES, Segal
MR and Finkbeiner S: Inclusion body formation reduces levels of
mutant huntingtin and the risk of neuronal death. Nature.
431:805–810. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Cummings CJ, Reinstein E, Sun Y, Antalffy
B, Jiang Y, Ciechanover A, Orr HT, Beaudet AL and Zoghbi HY:
Mutation of the E6-AP ubiquitin ligase reduces nuclear inclusion
frequency while accelerating polyglutamine-induced pathology in
SCA1 mice. Neuron. 24:879–892. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Gandhi J, Antonelli AC, Afridi A, Vatsia
S, Joshi G, Romanov V, Murray IV and Khan SA: Protein misfolding
and aggregation in neurodegenerative diseases: A review of
pathogeneses, novel detection strategies, and potential
therapeutics. Rev Neurosci. 30:339–358. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|