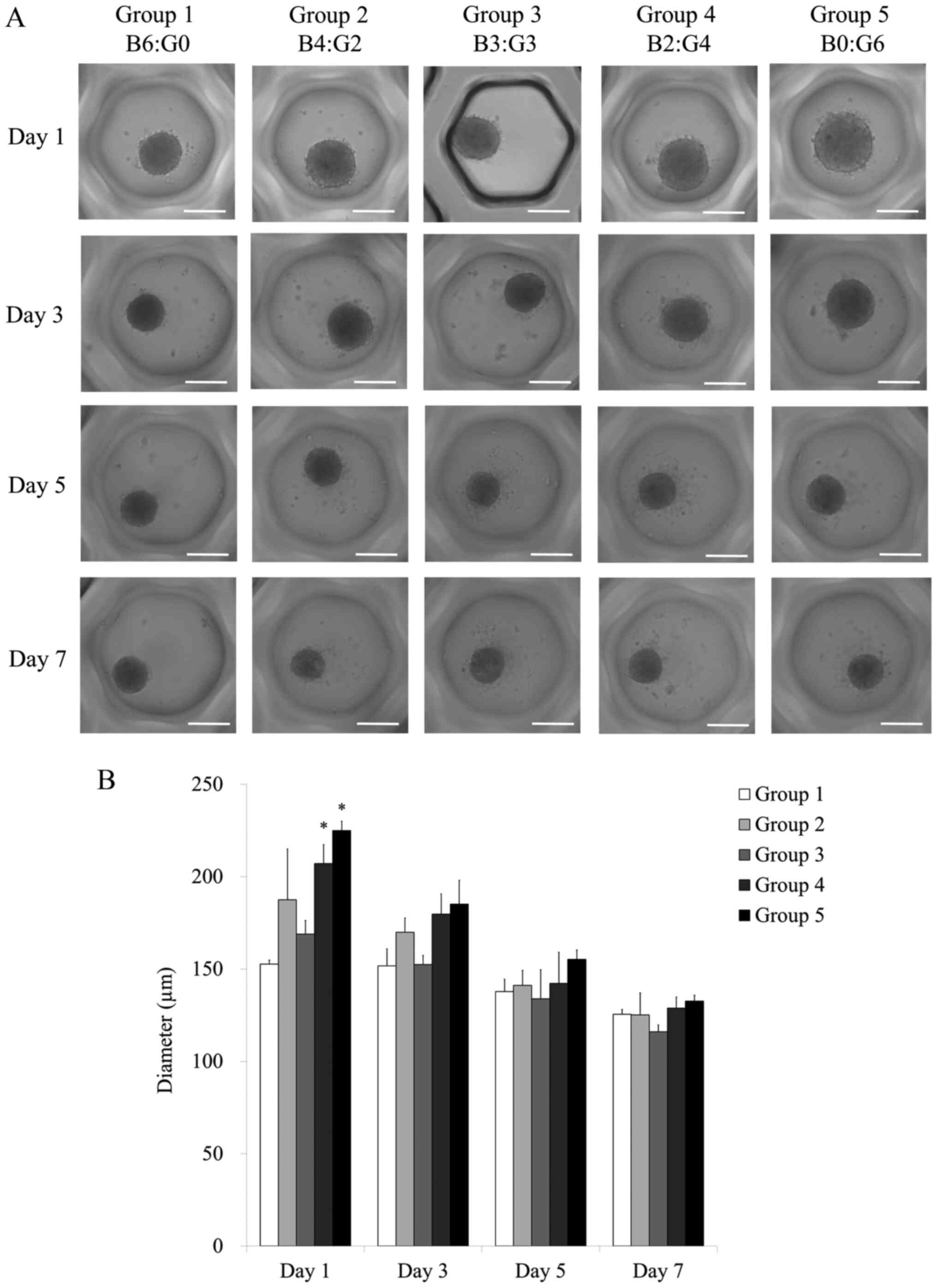
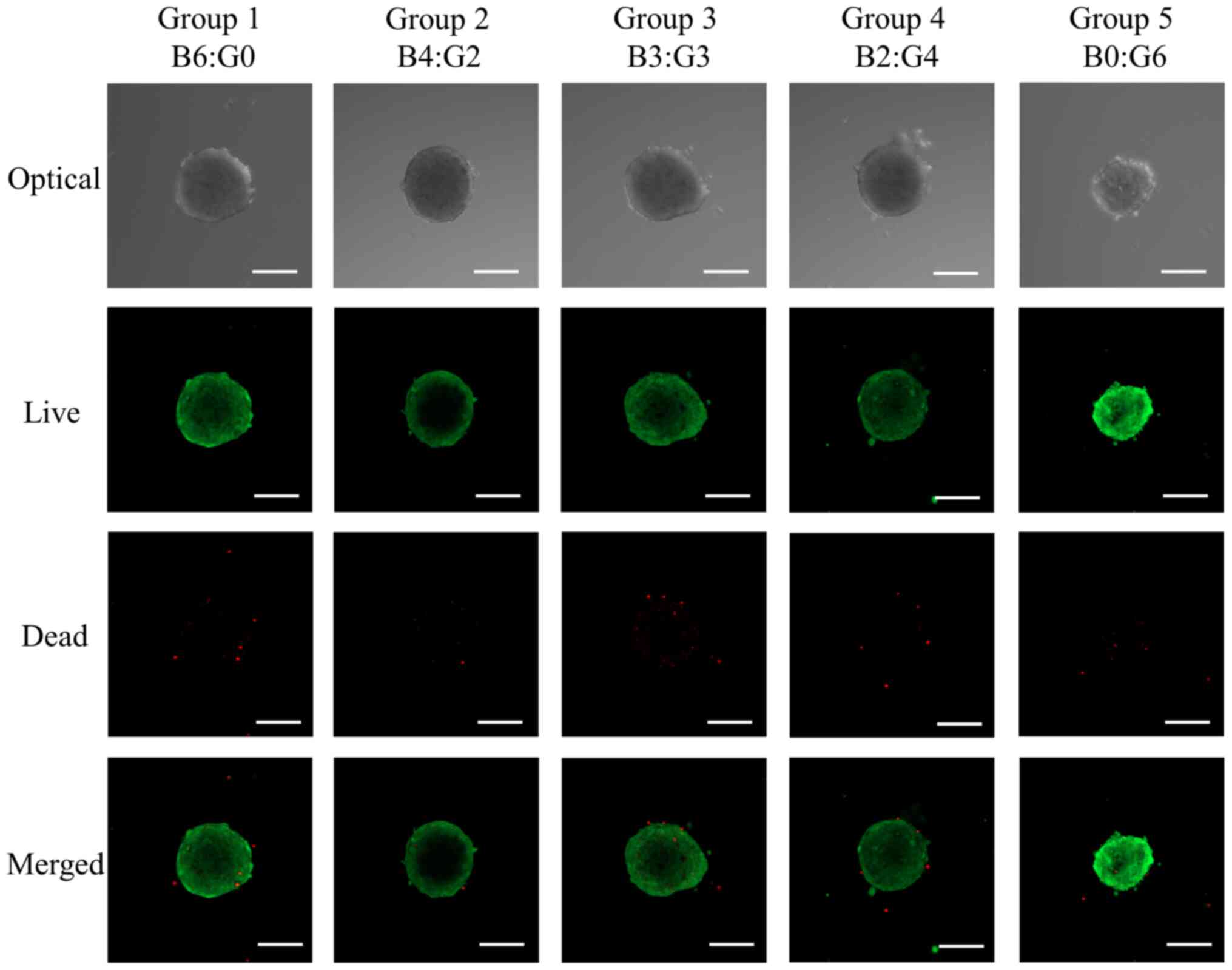
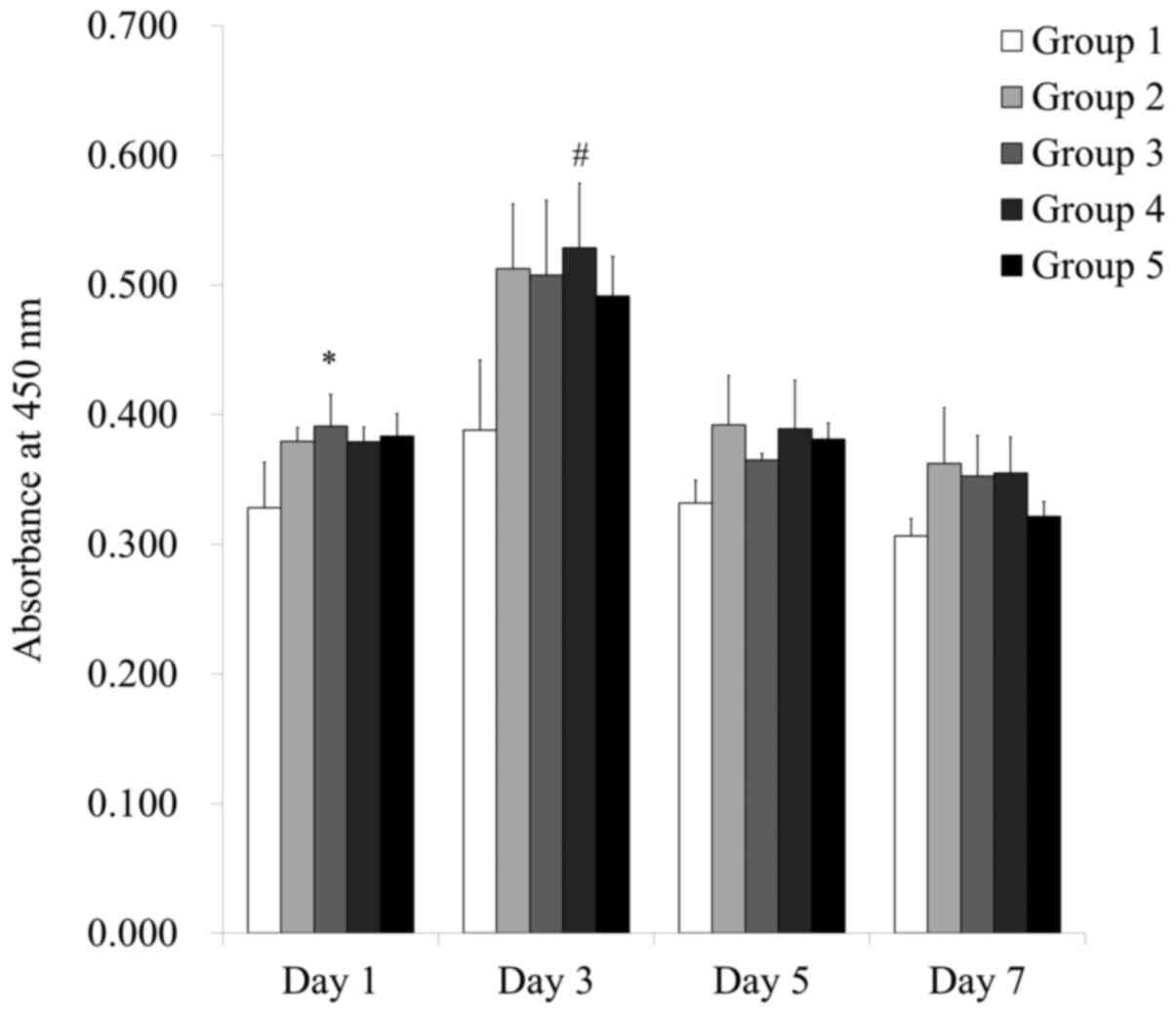
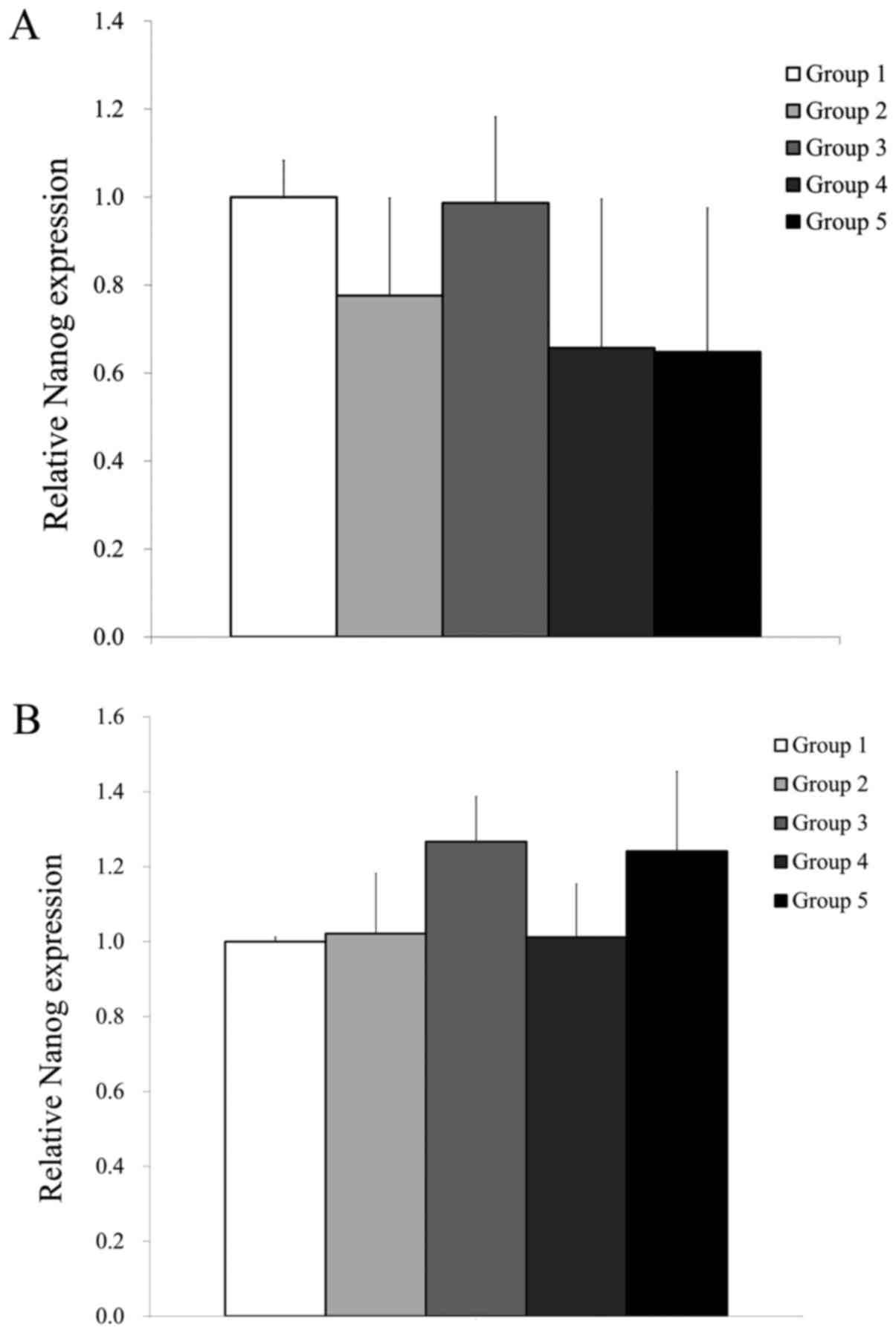
|
1
|
Pasca SP: The rise of three-dimensional
human brain cultures. Nature. 553:437–445. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Mazza G, Al-Akkad W, Rombouts K and
Pinzani M: Liver tissue engineering: From implantable tissue to
whole organ engineering. Hepatol Commun. 2:131–141. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Ong SM, Zhang C, Toh YC, Kim SH, Foo HL,
Tan CH, van Noort D, Park S and Yu H: A gel-free 3D microfluidic
cell culture system. Biomaterials. 29:3237–3244. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Pamies D, Block K, Lau P, Gribaldo L,
Pardo CA, Barreras P, Smirnova L, Wiersma D, Zhao L, Harris G, et
al: Rotenone exerts developmental neurotoxicity in a human brain
spheroid model. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 354:101–114.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Lee GH, Suh Y and Park JY: A paired bead
and magnet array for molding microwells with variable concave
geometries. J Vis Exp. 28(55548)2018.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Bauman E, Feijao T, Carvalho DTO, Granja
PL and Barrias CC: Xeno-free pre-vascularized spheroids for
therapeutic applications. Sci Rep. 8(230)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Redondo-Castro E, Cunningham CJ, Miller J,
Brown H, Allan SM and Pinteaux E: Changes in the secretome of
tri-dimensional spheroid-cultured human mesenchymal stem cells in
vitro by interleukin-1 priming. Stem Cell Res Ther.
9(11)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Lee SI, Yeo SI, Kim BB, Ko Y and Park JB:
Formation of size-controllable spheroids using gingiva-derived stem
cells and concave microwells: Morphology and viability tests.
Biomed Rep. 4:97–101. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Cen LP, Ng TK, Liang JJ, Zhuang X, Yao X,
Yam GHF, Chen H, Cheung HS, Zhang M and Pang CP: Human periodontal
ligament-derived stem cells promote retinal ganglion cell survival
and axon regeneration after optic nerve injury. Stem Cells.
36:844–856. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Taniguchi D, Matsumoto K, Tsuchiya T,
Machino R, Takeoka Y, Elgalad A, Gunge K, Takagi K, Taura Y,
Hatachi G, et al: Scaffold-free trachea regeneration by tissue
engineering with bio-3D printing. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg.
26:745–752. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Oberringer M, Bubel M, Jennewein M,
Guthörl S, Morsch T, Bachmann S, Metzger W and Pohlemann T: The
role of adipose-derived stem cells in a self-organizing 3D model
with regard to human soft tissue healing. Mol Cell Biochem.
445:195–210. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Tae JY, Lee SI, Ko Y and Park JB: Enhanced
osteogenic differentiation potential of stem-cell spheroids created
from a coculture of stem cells and endothelial cells. Implant Dent.
26:922–928. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Tae JY, Lee H, Lee H, Ko Y and Park JB:
Osteogenic potential of cell spheroids composed of varying ratios
of gingiva-derived and bone marrow stem cells using concave
microwells. Exp Ther Med. 16:2287–2294. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Jin SH, Lee JE, Yun JH, Kim I, Ko Y and
Park JB: Isolation and characterization of human mesenchymal stem
cells from gingival connective tissue. J Periodontal Res.
50:461–467. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Jeong CH, Kim SM, Lim JY, Ryu CH, Jun JA
and Jeun SS: Mesenchymal stem cells expressing brain-derived
neurotrophic factor enhance endogenous neurogenesis in an ischemic
stroke model. Biomed Res Int. 2014(129145)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
World Medical Association. World medical
association declaration of helsinki: Ethical principles for medical
research involving human subjects. JAMA. 310:2191–2194.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Kang SH, Park JB, Kim I, Lee W and Kim H:
Assessment of stem cell viability in the initial healing period in
rabbits with a cranial bone defect according to the type and form
of scaffold. J Periodontal Implant Sci. 49:258–267. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Tae JY, Ko Y and Park JB: Evaluation of
fibroblast growth factor-2 on the proliferation of osteogenic
potential and protein expression of stem cell spheroids composed of
stem cells derived from bone marrow. Exp Ther Med. 18:326–331.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Lee H, Min SK, Song Y, Park YH and Park
JB: Bone morphogenetic protein-7 upregulates genes associated with
osteoblast differentiation, including collagen I, Sp7 and IBSP in
gingiva-derived stem cells. Exp Ther Med. 18:2867–2876.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Kook YM, Kim H, Kim S, Heo CY, Park MH,
Lee K and Koh WG: Promotion of vascular morphogenesis of
endothelial cells co-cultured with human adipose-derived
mesenchymal stem cells using polycaprolactone/gelatin nanofibrous
scaffolds. Nanomaterials (Basel). 8(117)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Oliveira MN, Pillat MM, Motaln H, Ulrich H
and Lah TT: Kinin-B1 receptor stimulation promotes invasion and is
involved in cell-cell interaction of co-cultured glioblastoma and
mesenchymal stem cells. Sci Rep. 8(1299)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Lee SI, Ko Y and Park JB: Evaluation of
the maintenance of stemness, viability, and differentiation
potential of gingiva-derived stem-cell spheroids. Exp Ther Med.
13:1757–1764. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Ha DH, Pathak S, Yong CS, Kim JO, Jeong JH
and Park JB: Potential differentiation ability of gingiva
originated human mesenchymal stem cell in the presence of
tacrolimus. Sci Rep. 6(34910)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Takahashi K, Tanabe K, Ohnuki M, Narita M,
Ichisaka T, Tomoda K and Yamanaka S: Induction of pluripotent stem
cells from adult human fibroblasts by defined factors. Cell.
131:861–872. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Zhou X, Zhou YP, Huang GR, Gong BL, Yang
B, Zhang DX, Hu P and Xu SR: Expression of the stem cell marker,
Nanog, in human endometrial adenocarcinoma. Int J Gynecol Pathol.
30:262–270. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Lee H, Min SK and Park JB: Effects of
demographic factors on adipogenic and chondrogenic differentiation
in bone marrow-derived stem cells. Exp Ther Med. 17:3548–3554.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Khoshlahni N, Sagha M, Mirzapour T, Zarif
MN and Mohammadzadeh-Vardin M: Iron depletion with deferoxamine
protects bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells against
oxidative stress-induced apoptosis. Cell Stress Chaperones.
25:1059–1069. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Dustin ML: Visualization of cell-cell
interaction contacts: Synapses and kinapses. Self Nonself. 2:85–97.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|