|
1
|
Di Pino A, Urbano F, Piro S, Purrello F
and Rabuazzo AM: Update on pre-diabetes: Focus on diagnostic
criteria and cardiovascular risk. World J Diabetes. 7:423–432.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Nathan DM, Davidson MB, DeFronzo RA, Heine
RJ, Henry RR, Pratley R and Zinman B: American Diabetes
Association. Impaired fasting glucose and impaired glucose
tolerance: Implications for care. Diabetes Care. 30:753–759.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Tabák AG, Herder C, Rathmann W, Brunner EJ
and Kivimäki M: Prediabetes: a high-risk state for diabetes
development. Lancet. 379:2279–2290. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
DeFronzo RA and Abdul-Ghani M: Assessment
and treatment of cardiovascular risk in prediabetes: Impaired
glucose tolerance and impaired fasting glucose. Am J Cardiol. 108
(Suppl 3):3B–24B. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Huang Y, Cai X, Mai W, Li M and Hu Y:
Association between prediabetes and risk of cardiovascular disease
and all cause mortality: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ.
355(i5953)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Brannick B, Wynn A and Dagogo-Jack S:
Prediabetes as a toxic environment for the initiation of
microvascular and macrovascular complications. Exp Biol Med
(Maywood). 241:1323–1331. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Abdul-Ghani MA and DeFronzo RA:
Pathophysiology of prediabetes. Curr Diab Rep. 9:193–199.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Bergman M: Pathophysiology of prediabetes
and treatment implications for the prevention of type 2 diabetes
mellitus. Endocrine. 43:504–513. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Fonseca VA: Defining and characterizing
the progression of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 32 Suppl. 2
(Suppl 2):S151–S156. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Tuso P: Prediabetes and lifestyle
modification: Time to prevent a preventable disease. Perm J.
18:88–93. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Portero McLellan KC, Wyne K, Villagomez ET
and Hsueh WA: Therapeutic interventions to reduce the risk of
progression from prediabetes to type 2 diabetes mellitus. Ther Clin
Risk Manag. 10:173–188. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Kloosterman WP and Plasterk RH: The
diverse functions of microRNAs in animal development and disease.
Dev Cell. 11:441–450. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNA: Target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Tang X, Tang G and Ozcan S: Role of
microRNAs in diabetes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1779:697–701.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Deng J and Guo F: MicroRNAs and type 2
diabetes. ExRNA. 1(36)2019.
|
|
17
|
Mitchell PS, Parkin RK, Kroh EM, Fritz BR,
Wyman SK, Pogosova-Agadjanyan EL, Peterson A, Noteboom J, O'Briant
KC, Allen A, et al: Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based
markers for cancer detection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
105:10513–10518. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Chen X, Liang H, Zhang J, Zen K and Zhang
CY: Secreted microRNAs: A new form of intercellular communication.
Trends Cell Biol. 22:125–132. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Vienberg S, Geiger J, Madsen S and
Dalgaard LT: MicroRNAs in metabolism. Acta Physiol (Oxf).
219:346–361. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Jiménez-Lucena R, Camargo A, Alcalá-Diaz
JF, Romero-Baldonado C, Luque RM, van Ommen B, Delgado-Lista J,
Ordovás JM, Pérez-Martínez P, Rangel-Zúñiga OA and López-Miranda J:
A plasma circulating miRNAs profile predicts type 2 diabetes
mellitus and prediabetes: from the CORDIOPREV study. J Exp Mol Med.
50:1–12. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Al-Kafaji G, Al-Mahroos G, Alsayed NA,
Hasan ZA, Nawaz S and Bakhiet M: Peripheral blood microRNA-15a is a
potential biomarker for type 2 diabetes mellitus and pre-diabetes.
Mol Med Rep. 12:7485–7490. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Al-Muhtaresh H and Al-Kafaji G: Evaluation
of two-diabetes related microRNAs suitability as earlier blood
biomarkers for detecting prediabetes and type 2 diabetes mellitus.
J Clin Med. 7(12)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Zhang T, Li L, Shang Q, Lv C, Wang C and
Su B: Circulating miR-126 is a potential biomarker to predict the
onset of type 2 diabetes mellitus in susceptible individuals.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 463:60–63. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
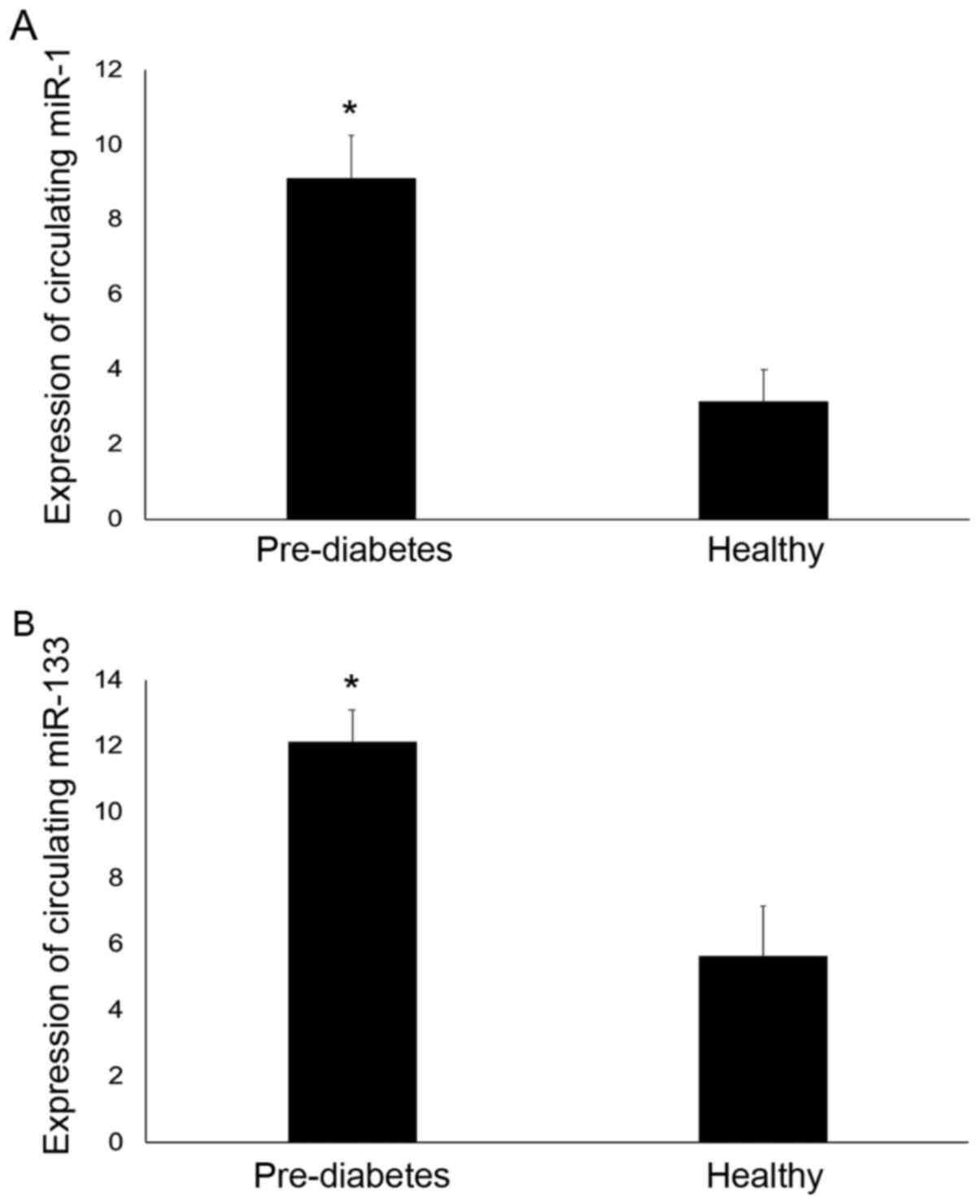
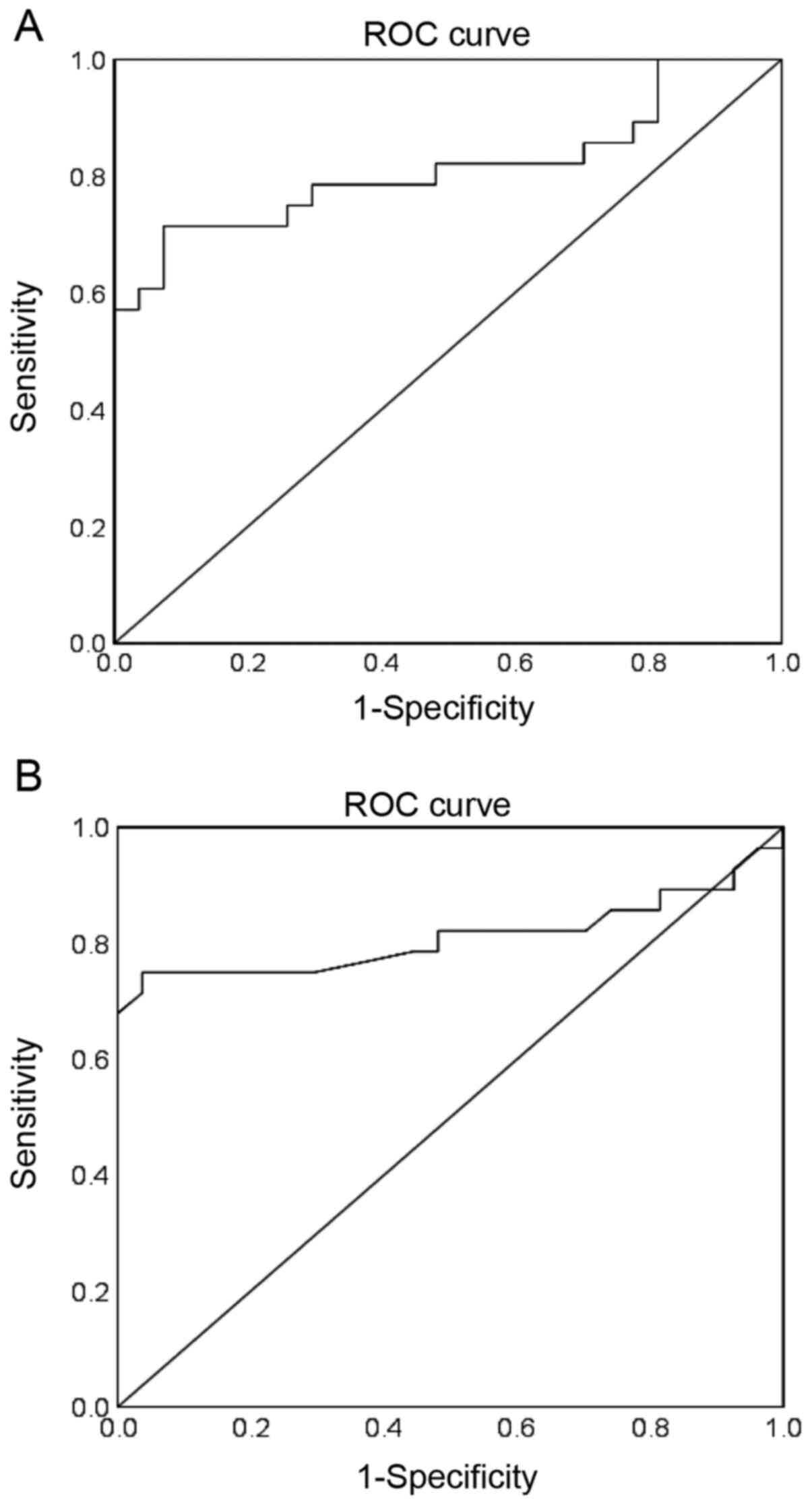
Al-Muhtaresh HA, Salem AH and Al-Kafaji G:
Upregulation of circulating cardiomyocyte-enriched miR-1 and
miR-133 associate with the risk of coronary artery disease in type
2 diabetes patients and serve as potential biomarkers. J Cardiovasc
Transl Res. 12:347–357. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Mitchelson KR and Qin WY: Roles of the
canonical myomiRs miR-1, -133 and -206 in cell development and
disease. World J Biol Chem. 6:162–208. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
DeFronzo RA and Tripathy D: Skeletal
muscle insulin resistance is the primary defect in type 2 diabetes.
Diabetes Care. 32 (Suppl 2):S157–S163. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Granjon A, Gustin MP, Rieusset J, Lefai E,
Meugnier E, Güller I, Cerutti C, Paultre C, Disse E, Rabasa-Lhoret
R, et al: The microRNA signature in response to insulin reveals its
implication in the transcriptional action of insulin in human
skeletal muscle and the role of a sterol regulatory element-binding
protein-1c/myocyte enhancer factor 2C pathway. Diabetes.
58:2555–2564. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
de Gonzalo-Calvo D, van der Meer RW,
Rijzewijk LJ, Smit JW, Revuelta-Lopez E, Nasarre L, Escola-Gil JC,
Lamb HJ and Llorente-Cortes V: Serum microRNA-1 and microRNA-133a
levels reflect myocardial steatosis in uncomplicated type 2
diabetes. Sci Rep. 7(47)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Delic D, Eisele C, Schmid R, Luippold G,
Mayoux E and Grempler R: Characterization of micro-RNA changes
during the progression of type 2 diabetes in zucker diabetic fatty
rats. Int J Mol Sci. 17(665)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
World Health Organization (WHO):
Definition and diagnosis of diabetes mellitus and intermediate
hyperglycaemia: report of a WHO/IDF consultation. WHO, Geneva,
2006. https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/43588?locale%E2%80%91attribute=es&show=full.
Accessed June 16, 2012.
|
|
31
|
American Diabetes Association. Diagnosis
and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 33 (Suppl
1):S62–S69. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS,
Naylor BA, Treacher DF and Turner RC: Homeostasis model assessment:
Insulin resistance and β-cell function from fasting plasma glucose
and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia. 28:412–419.
1985.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Griffiths-Jones S, Grocock RJ, van Dongen
S, Bateman A and Enright AJ: miRBase: microRNA sequences, targets
and gene nomenclature. Nucleic Acids Res. 34:D140–D144.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Horak M, Novak J and Bienertova-Vasku J:
Muscle-specific microRNAs in skeletal muscle development. Dev Biol.
410:1–13. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Colpaert RMW and Calore M: MicroRNAs in
cardiac diseases. Cells. 8(737)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Chen JF, Callis TE and Wang DZ: microRNAs
and muscle disorders. J Cell Sci. 122 (Pt 1):13–20. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Frias Fde T, de Mendonça M, Martins AR,
Gindro AF, Cogliati B, Curi R and Rodrigues AC: MyomiRs as markers
of insulin resistance and decreased myogenesis in skeletal muscle
of diet-induced obese mice. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne).
7(76)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Huang MB, Xu H, Xie SJ, Zhou H and Qu LH:
Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor is regulated by microRNA-133
during skeletal myogenesis. PLoS One. 6(e29173)2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Elia L, Contu R, Quintavalle M, Varrone F,
Chimenti C, Russo MA, Cimino V, De Marinis L, Frustaci A, Catalucci
D and Condorelli G: Reciprocal regulation of microRNA-1 and
insulin-like growth factor-1 signal transduction cascade in cardiac
and skeletal muscle in physiological and pathological conditions.
Circulation. 120:2377–2385. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Clemmons DR: Metabolic actions of
insulin-like growth factor-I in normal physiology and diabetes.
Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 41:425–443, vii-viii.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Rajpathak SN, Gunter MJ, Wylie-Rosett J,
Ho GY, Kaplan RC, Muzumdar R, Rohan TE and Strickler HD: The role
of insulin-like growth factor-I and its binding proteins in glucose
homeostasis and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 25:3–12.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Dunger D, Yuen K and Ong K: Insulin-like
growth factor I and impaired glucose tolerance. Horm Res. 62 (Suppl
1):101–107. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Sandhu MS, Heald AH, Gibson JM,
Cruickshank JK, Dunger DB and Wareham NJ: Circulating
concentrations of insulin-like growth factor-I and development of
glucose intolerance: A prospective observational study. Lancet.
359:1740–1745. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Aguirre GA, De Ita JR, de la Garza RG and
Castilla-Cortazar I: Insulin-like growth factor-1 deficiency and
metabolic syndrome. J Transl Med. 14(3)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Siracusa J, Koulmann N and Banzet S:
Circulating myomiRs: A new class of biomarkers to monitor skeletal
muscle in physiology and medicine. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle.
9:20–27. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Seok H, Lee H, Lee S, Ahn SH, Lee HS, Kim
GD, Peak J, Park J, Cho YK, Jeong Y, et al: Position-specific
oxidation of miR-1 encodes cardiac hypertrophy. Nature.
584:279–285. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Gómez-Ambrosi J, Silva C, Galofré JC,
Escalada J, Santos S, Gil MJ, Valentí V, Rotellar F, Ramírez B,
Salvador J, et al: Body adiposity and type 2 diabetes: Increased
risk with a high body fat percentage even having a normal BMI.
Obesity (Silver Spring). 19:1439–1444. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Khaodhiar L, Cummings S and Apovian CM:
Treating diabetes and prediabetes by focusing on obesity
management. Curr Diab Rep. 9:348–354. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|