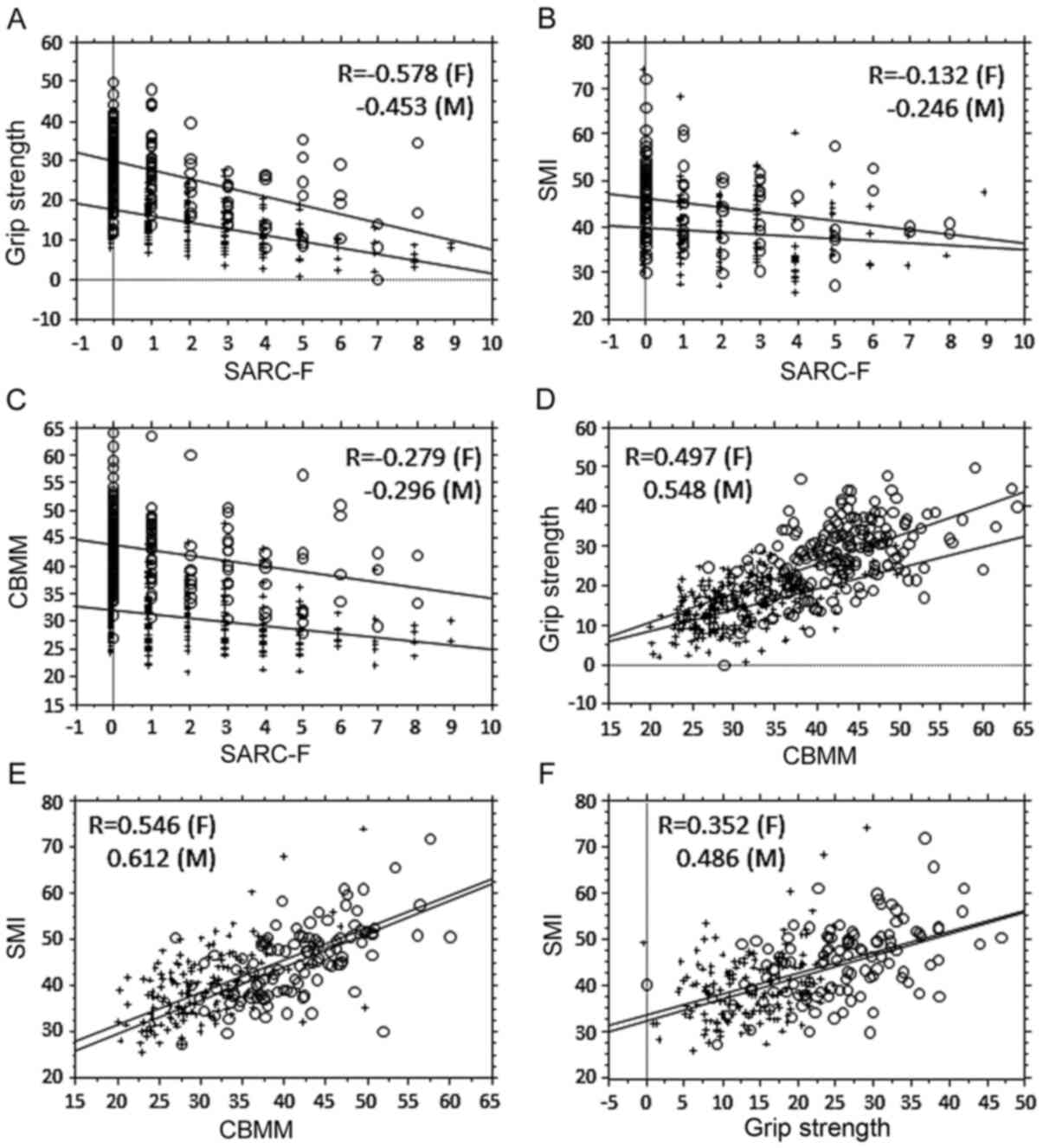
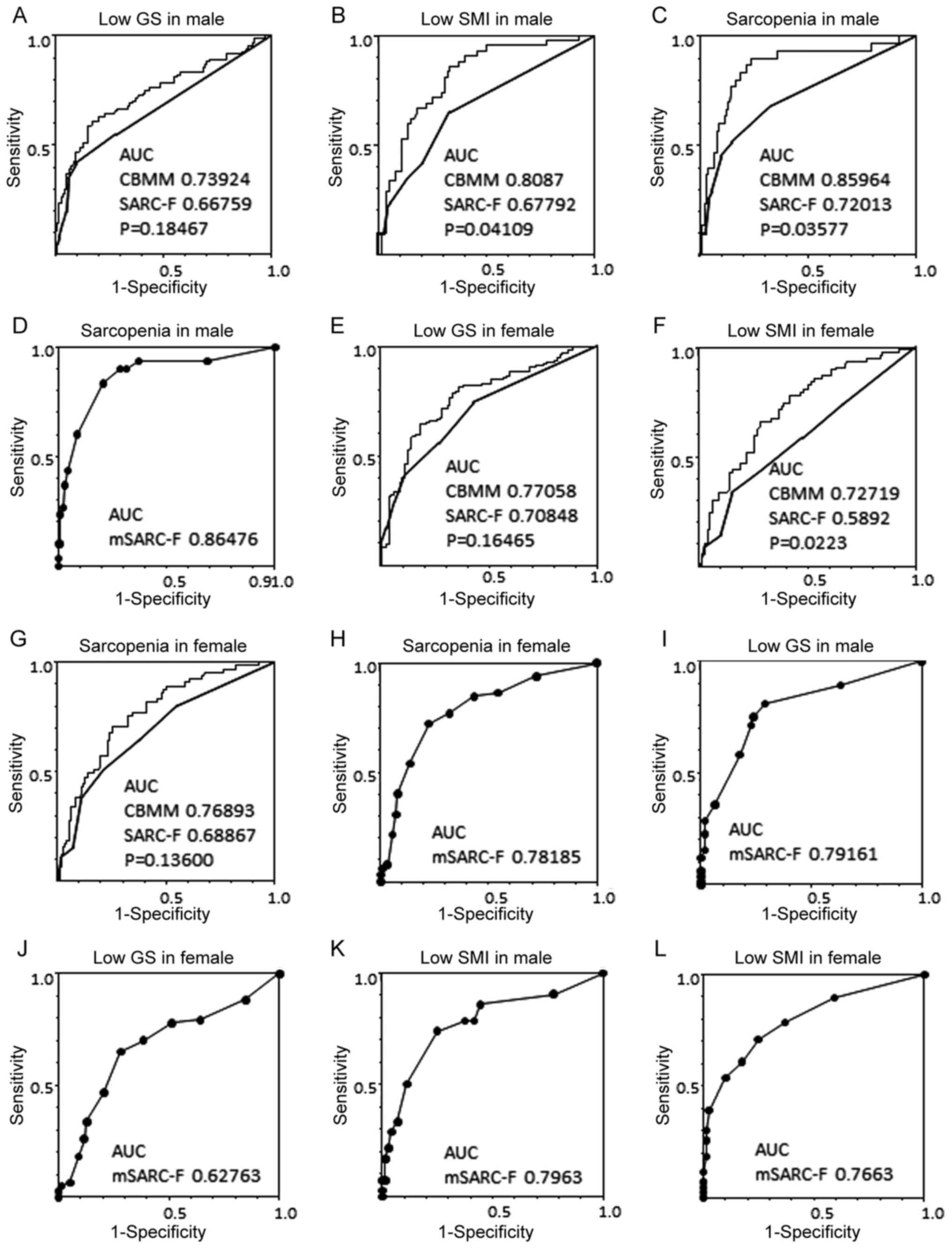
|
1
|
van Vugt JLA, Alferink LJM, Buettner S,
Gaspersz MP, Bot D, Darwish Murad S, Feshtali S, van Ooijen PMA,
Polak WG, Porte RJ, et al: A model including sarcopenia surpasses
the MELD score in predicting waiting list mortality in cirrhotic
liver transplant candidates: A competing risk analysis in a
national cohort. J Hepatol. 68:707–714. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Cruz-Jentoft AJ, Baeyens JP, Bauer JM,
Boirie Y, Cederholm T, Landi F, Martin FC, Michel JP, Rolland Y,
Schneider SM, et al: European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older
People: Sarcopenia: European consensus on definition and diagnosis.
Age Ageing. 39:412–423. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
IWG on Sarcopenia. Sarcopenia: an
undiagnosed condition in older adults. Current consensus
definition: prevalence, etiology, and consequences. International
working group on sarcopenia. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 12:249–256.
2009.
|
|
4
|
Chen LK, Liu LK, Woo J, Assantachai P,
Auyeung TW, Bahyah KS, Chou MY, Chen LY, Hsu PS, Krairit O, et al:
Sarcopenia in Asia: Consensus report of the Asian working group for
sarcopenia. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 15:95–101. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Cruz-Jentoft AJ, Bahat G, Bauer J, Boirie
Y, Bruyère O, Cederholm T, Cooper C, Landi F, Rolland Y, Sayer AA,
et al: Writing Group for the European Working Group on Sarcopenia
in Older People 2 (EWGSOP2), and the Extended Group for EWGSOP2:
Sarcopenia: Revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis.
Age Ageing. 48:16–31. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Malmstrom TK and Morley JE: Sarcopenia:
the target population. J Frailty Aging. 2:55–56. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Chen LK, Woo J, Assantachai P, Auyeung TW,
Chou MY, Iijima K, Jang HC, Kang L, Kim M, Kim S, et al: Asian
Working Group for Sarcopenia: 2019 Consensus Update on Sarcopenia
Diagnosis and Treatment. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 21:300–307.e2.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Ida S, Kojima Y, Hamaoka S, Urawa N, Araki
J, Kaneko R and Murata K: Validity of Japanese version of SARC-F
questionnaire in patients with chronic liver disease. J
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 34:947–953. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Ichikawa T, Miyaaki H, Miuma S, Motoyoshi
Y, Yamashima M, Yamamichi S, Koike M, Honda T, Yajima H, Uehara R,
et al: Calculated body muscle mass as a useful screening marker for
low skeleton muscle mass and sarcopenia in chronic liver disease.
Hepatol Res. 50:704–714. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Kim SW, Jung HW, Kim CH, Kim KI, Chin HJ
and Lee H: A new equation to estimate muscle mass from creatinine
and cystatin C. PLoS One. 11(e0148495)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Nishikawa H, Shiraki M, Hiramatsu A,
Moriya K, Hino K and Nishiguchi S: Japan Society of Hepatology
guidelines for sarcopenia in liver disease (1st edition):
Recommendation from the working group for creation of sarcopenia
assessment criteria. Hepatol Res. 46:951–963. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Hiraoka A, Izumoto H, Ueki H, Yoshino T,
Aibiki T, Okudaira T, Yamago H, Suga Y, Iwasaki R, Tomida H, et al:
Easy surveillance of muscle volume decline in chronic liver disease
patients using finger-circle (yubi-wakka) test. J Cachexia
Sarcopenia Muscle. 10:347–354. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Hirota K, Kawaguchi T, Koya S, Nagamatsu
A, Tomita M, Hashida R, Nakano D, Niizeki T, Matsuse H, Shiba N, et
al: Clinical utility of the Liver Frailty Index for predicting
muscle atrophy in chronic liver disease patients with
hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol Res. 50:330–341. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Child CG and Turcotte JG: Surgery and
portal hypertension. Major Probl Clin Surg. 1:1–85. 1964.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Johnson PJ, Berhane S, Kagebayashi C,
Satomura S, Teng M, Reeves HL, O'Beirne J, Fox R, Skowronska A,
Palmer D, et al: Assessment of liver function in patients with
hepatocellular carcinoma: A new evidence-based approach-the ALBI
grade. J Clin Oncol. 33:550–558. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Kamath PS, Wiesner RH, Malinchoc M, Kremer
W, Therneau TM, Kosberg CL, D'Amico G, Dickson ER and Kim WR: A
model to predict survival in patients with end-stage liver disease.
Hepatology. 33:464–470. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Vallet-Pichard A, Mallet V, Nalpas B,
Verkarre V, Nalpas A, Dhalluin-Venier V, Fontaine H and Pol S:
FIB-4: An inexpensive and accurate marker of fibrosis in HCV
infection. comparison with liver biopsy and fibrotest. Hepatology.
46:32–36. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Matsuo S, Imai E, Horio M, Yasuda Y,
Tomita K, Nitta K, Yamagata K, Tomino Y, Yokoyama H and Hishida A:
Collaborators developing the Japanese equation for estimated GFR.
Revised equations for estimated GFR from serum creatinine in Japan.
Am J Kidney Dis. 53:982–992. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Ichikawa T, Miyaaki H, Miuma S, Motoyoshi
Y, Yamashima M, Yamamichi S, Koike M, Takahashi Y, Honda T, Yajima
H, et al: Indices calculated by serum creatinine and cystatin C as
predictors of liver damage, muscle strength and sarcopenia in liver
disease. Biomed Rep. 12:89–98. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Kashani KB, Frazee EN, Kukrálová L,
Sarvottam K, Herasevich V, Young PM, Kashyap R and Lieske JC:
Evaluating muscle mass by using markers of kidney function:
development of the sarcopenia index. Crit Care Med. 45:e23–e29.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Fujiwara N, Nakagawa H, Kudo Y, Tateishi
R, Taguri M, Watadani T, Nakagomi R, Kondo M, Nakatsuka T, Minami
T, et al: Sarcopenia, intramuscular fat deposition, and visceral
adiposity independently predict the outcomes of hepatocellular
carcinoma. J Hepatol. 63:131–140. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Barbosa-Silva TG, Menezes AMB, Bielemann
RM, Malmstrom TK and Gonzalez MC: Grupo de Estudos em Composição
Corporal e Nutrição (COCONUT): Enhancing SARC-F: Improving
sarcopenia screening in the clinical practice. J Am Med Dir Assoc.
17:1136–1141. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Yang M, Hu X, Xie L, Zhang L, Zhou J, Lin
J, Wang Y, Li Y, Han Z, Zhang D, et al: Screening sarcopenia in
community-dwelling older adults: SARC-F vs SARC-F combined with
calf circumference (SARC-CalF). J Am Med Dir Assoc.
19:277.e1–277.e8. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Ida S, Murata K, Nakadachi D, Ishihara Y,
Imataka K, Uchida A, Monguchi K, Kaneko R, Fujiwara R and Takahashi
H: Development of a Japanese version of the SARC-F for diabetic
patients: An examination of reliability and validity. Aging Clin
Exp Res. 29:935–942. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : Erratum in: Aging
Clin Exp Res 32: 2113, 2020.
|
|
25
|
Hiraoka A, Nagamatsu K, Izumoto H, Yoshino
T, Adachi T, Tsuruta M, Aibiki T, Okudaira T, Yamago H, Suga Y, et
al: SARC-F combined with a simple tool for assessment of muscle
abnormalities in outpatients with chronic liver disease. Hepatol
Res. 50:502–511. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Kera T, Kawai H, Hirano H, Kojima M,
Watanabe Y, Motokawa K, Fujiwara Y, Osuka Y, Kojima N, Kim H, et
al: Limitations of SARC-F in the diagnosis of sarcopenia in
community-dwelling older adults. Arch Gerontol Geriatr.
87(103959)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Malmstrom TK, Miller DK, Simonsick EM,
Ferrucci L and Morley JE: SARC-F: A symptom score to predict
persons with sarcopenia at risk for poor functional outcomes. J
Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 7:28–36. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Yang M, Jiang J, Zeng Y and Tang H:
Sarcopenia for predicting mortality among elderly nursing home
residents: SARC-F versus SARC-CalF. Medicine (Baltimore).
98(e14546)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Papadopoulou SK: Sarcopenia: a
contemporary health problem among older adult populations.
Nutrients. 12(1293)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|