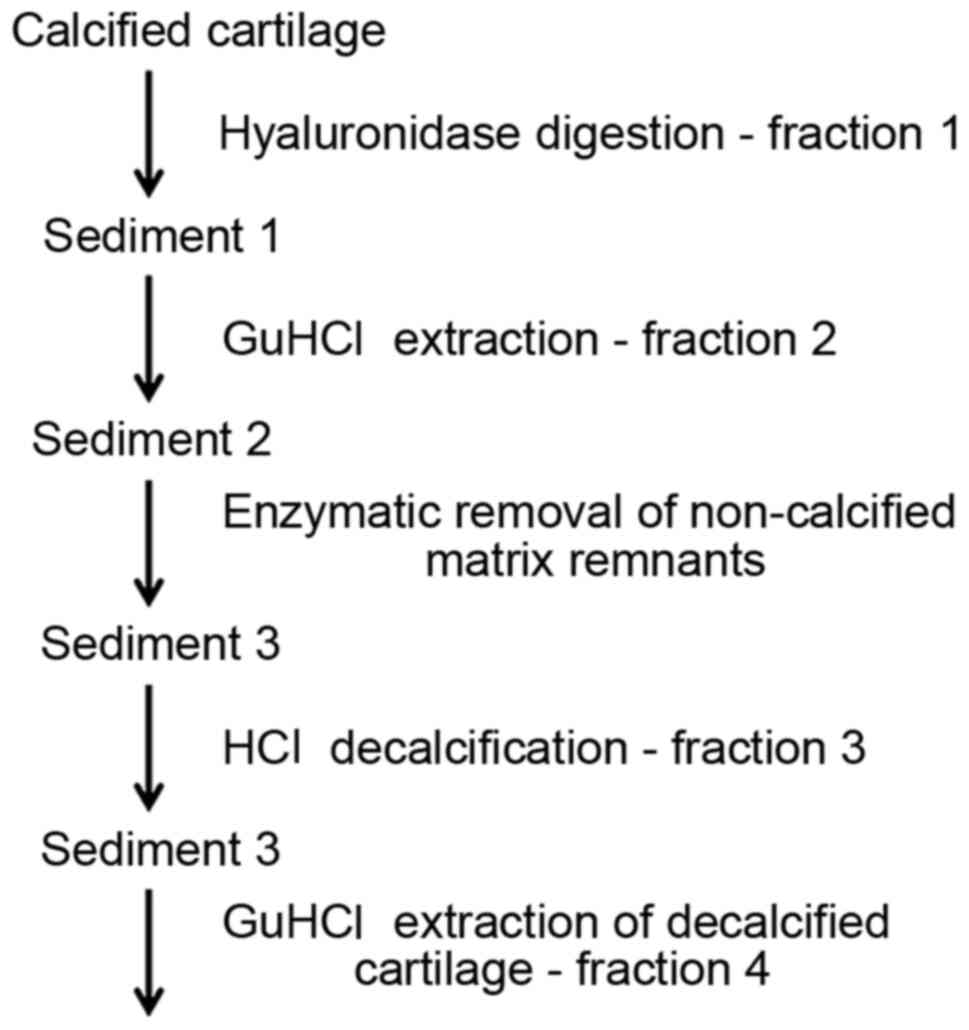
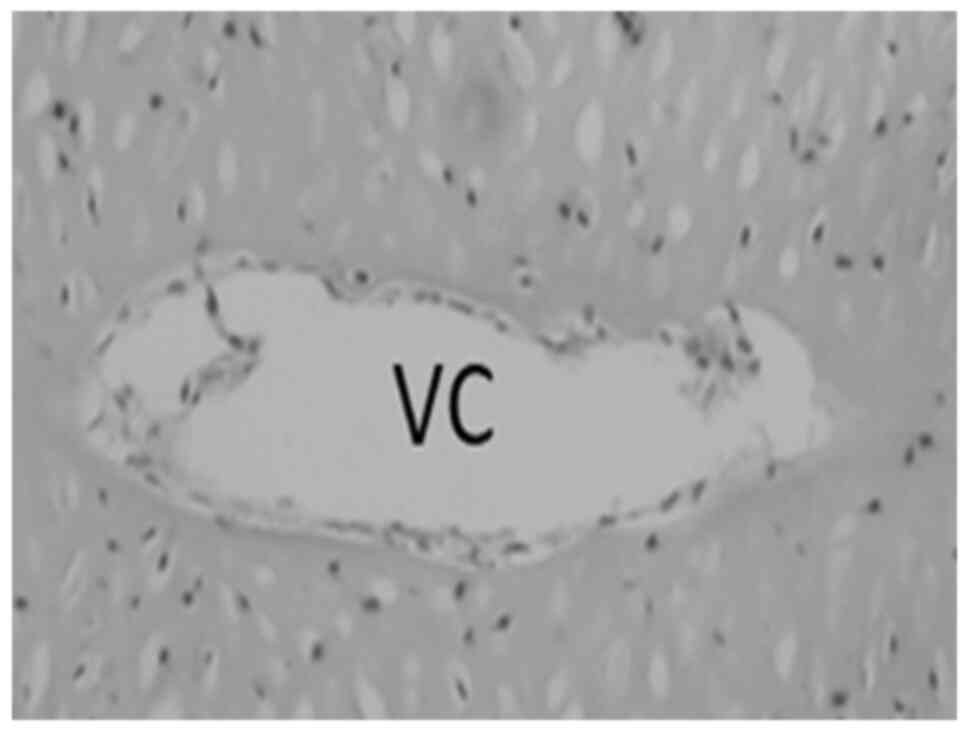
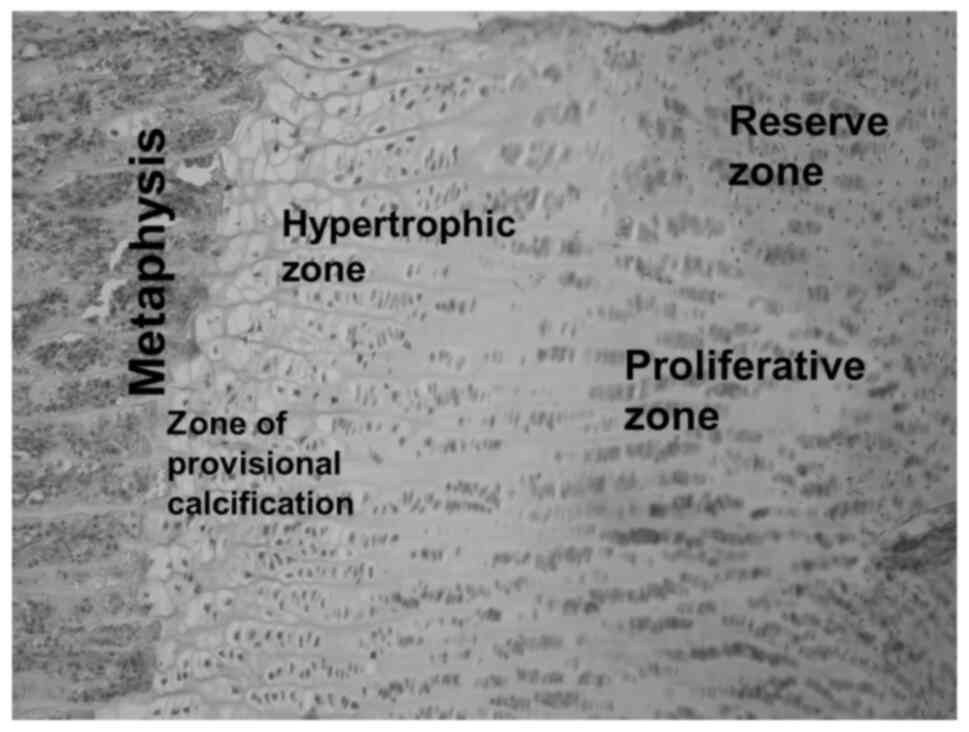
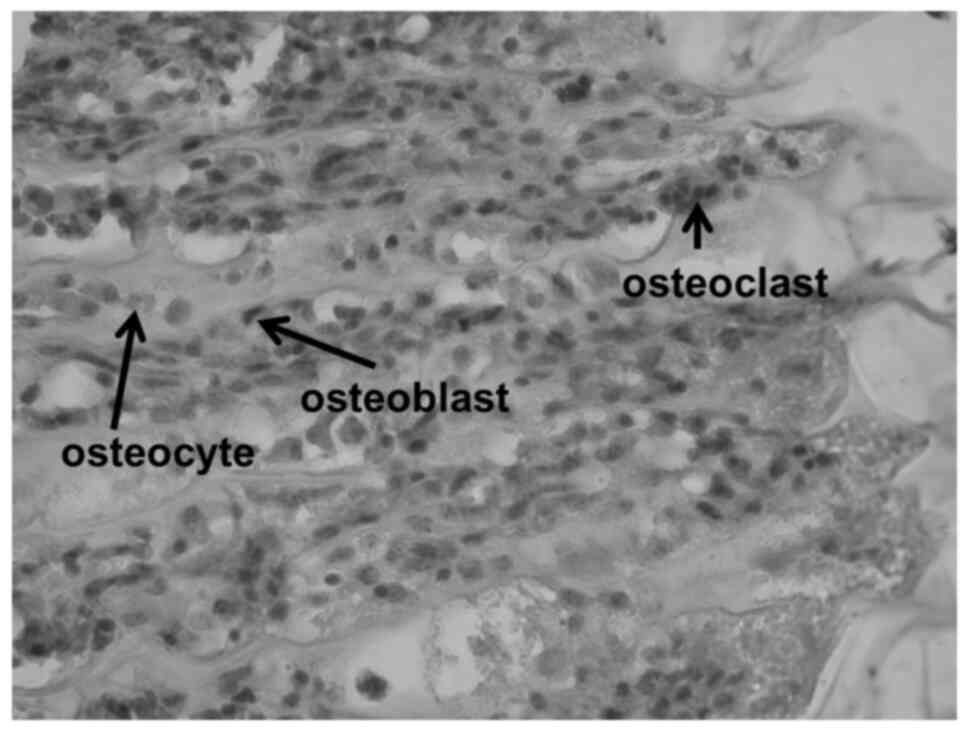
|
1
|
Wozney JM: Overview of bone morphogenetic
proteins. Spine. 27 (Suppl 1):S2–S8. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Tsumaki N and Yoshikawa H: The role of
bone morphogenetic proteins in endochondral bone formation.
Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 16:279–285. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Brighton CT: Structure and function of the
growth plate. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 136:22–32. 1978.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Brochhausen C, Lehmann M, Halstenberg S,
Meurer A, Klaus G and Kirkpatrick CJ: Signalling molecules and
growth factors for tissue engineering of cartilage-what can we
learn from the growth plate? J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 3:416–429.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Schenk RK, Spiro D and Wiener J: Cartilage
resorption in the tibial epiphyseal plate of growing rats. J Cell
Biol. 34:275–291. 1967.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Mackie EJ, Tatarczuch L and Mirams M: The
skeleton: a multi-functional complex organ: the growth plate
chondrocyte and endochondral ossification. J Endocrinol.
211:109–121. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Arsenault AL and Hunziker EB: Electron
microscopic analysis of mineral deposits in the calcifying
epiphyseal growth plate. Calcif Tissue Int. 42:119–126.
1988.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Bonucci E: Fine structure of early
cartilage calcification. J Ultrastruct Res. 20:33–50.
1967.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Anderson HC: Vesicles associated with
calcification in the matrix of epiphyseal cartilage. J Cell Biol.
41:59–72. 1969.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Ali SY, Sajdera SW and Anderson HC:
Isolation and characterization of calcifying matrix vesicles from
epiphyseal cartilage. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 67:1513–1520.
1970.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Wuthier RE and Lipscomb GF: Matrix
vesicles: Structure, composition, formation and function in
calcification. Front Biosci. 16:2812–2902. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Cui L, Houston DA, Farquharson C and
MacRae VE: Characterisation of matrix vesicles in skeletal and soft
tissue mineralisation. Bone. 87:147–158. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Nahar NN, Missana LR, Garimella R, Tague
SE and Anderson HC: Matrix vesicles are carriers of bone
morphogenetic proteins (BMPs), vascular endothelial growth factor
(VEGF), and noncollagenous matrix proteins. J Bone Miner Metab.
26:514–519. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Anderson HC, Hodges PT, Aguilera XM,
Missana L and Moylan PE: Bone morphogenetic protein (BMP)
localization in developing human and rat growth plate, metaphysis,
epiphysis, and articular cartilage. J Histochem Cytochem.
48:1493–1502. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Chang SC, Hoang B, Thomas JT, Vukicevic S,
Luyten FP, Ryba NJ, Kozak CA, Reddi AH and Moos M Jr:
Cartilage-derived morphogenetic proteins. New members of the
transforming growth factor-beta superfamily predominantly expressed
in long bones during human embryonic development. J Biol Chem.
269:28227–28234. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Reddi AH: Cartilage morphogenetic
proteins: Role in joint development, homoeostasis, and
regeneration. Ann Rheum Dis. 62 (Suppl 2):ii73–ii78.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Hyc A, Moskalewski S and Osiecka-Iwan A:
Influence of cartilage interstitial fluid on the mRNA levels of
matrix proteins, cytokines, metalloproteases and their inhibitors
in synovial membrane. Int J Mol Med. 38:937–942. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Zhang X, Zara J, Siu RK, Ting K and Soo C:
The role of NELL-1, a growth factor associated with
craniosynostosis, in promoting bone regeneration. J Dent Res.
89:865–878. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Sheikh Z, Javaid MA, Hamdan N and Hashmi
R: Bone regeneration using bone morphogenetic oroteins and various
biomaterial carriers. Materials (Basel). 8:1778–1816.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Cao X and Chen D: The BMP signaling and in
vivo bone formation. Gene. 357:1–8. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Kishigami S and Mishina Y: BMP signaling
and early embryonic patterning. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev.
16:265–278. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Wozney JM: The bone morphogenetic protein
family and osteogenesis. Mol Reprod Dev. 32:160–167.
1992.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Gerber HP, Vu TH, Ryan AM, Kowalski J,
Werb Z and Ferrara N: VEGF couples hypertrophic cartilage
remodeling, ossification and angiogenesis during endochondral bone
formation. Nat Med. 5:623–628. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Wu M, Chen G and Li YP: TGF-β and BMP
signaling in osteoblast, skeletal development, and bone formation,
homeostasis and disease. Bone Res. 4(16009)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
James AW, Shen J, Tsuei R, Nguyen A,
Khadarian K, Meyers CA, Pan HC, Li W, Kwak JH, Asatrian G, et al:
NELL-1 induces Sca-1+ mesenchymal progenitor cell
expansion in models of bone maintenance and repair. JCI Insight.
2(2)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Brighton CT, Sugioka Y and Hunt RM:
Cytoplasmic structures of epiphyseal plate chondrocytes.
Quantitative evaluation using electron micrographs of rat
costochondral junctions with special reference to the fate of
hypertrophic cells. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 55:771–784.
1973.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Byard RW, Foster BK and Byers S:
Immunohistochemical characterisation of the costochondral junction
in SIDS. J Clin Pathol. 46:108–112. 1993.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Clark CC, Tolin BS and Brighton CT: The
effect of oxygen tension on proteoglycan synthesis and aggregation
in mammalian growth plate chondrocytes. J Orthop Res. 9:477–484.
1991.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Poland TPotRo: Dziennik Ustaw SCG. Law
Gazette SCG, pp1-7, 2003.
|
|
30
|
Brem G and Nowshari MA: Nuclear transfer
in cattle. Methods Mol Biol. 254:213–226. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Perez-Riverol Y, Csordas A, Bai J,
Bernal-Llinares M, Hewapathirana S, Kundu DJ, Inuganti A, Griss J,
Mayer G, Eisenacher M, et al: The PRIDE database and related tools
and resources in 2019: Improving support for quantification data.
Nucleic Acids Res. 47:D442–D450. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Gabner S, Häusler G and Böck P: Vascular
canals in permanent hyaline cartilage: Development, corrosion of
nonmineralized cartilage matrix, and removal of matrix degradation
products. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 300:1067–1082. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Schenk RK, Wiener J and Spiro D: Fine
structural aspects of vascular invasion of the tibial epiphyseal
plate of growing rats. Acta Anat (Basel). 69:1–17. 1968.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Deckers MM, Van Beek ER, Van Der Pluijm G,
Wetterwald A, Wee-Pals LV, Cecchini MG, Papapoulos SE and Löwik CW:
Dissociation of angiogenesis and osteoclastogenesis during
endochondral bone formation in neonatal mice. J Bone Miner Res.
17:998–1007. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Lee ER, Lamplugh L, Shepard NL and Mort
JS: The septoclast, a cathepsin B-rich cell involved in the
resorption of growth plate cartilage. J Histochem Cytochem.
43:525–536. 1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Gartland A, Mason-Savas A, Yang M, MacKay
CA, Birnbaum MJ and Odgren PR: Septoclast deficiency accompanies
postnatal growth plate chondrodysplasia in the toothless (tl)
osteopetrotic, colony-stimulating factor-1 (CSF-1)-deficient rat
and is partially responsive to CSF-1 injections. Am J Pathol.
175:2668–2675. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Anderson CE and Parker J: Invasion and
resorption in enchondral ossification. An electron microscopic
study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 48:899–914. 1966.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Włodarski KH, Brodzikowska A and Kuzaka B:
Are chondroclasts and osteoclasts identical? Folia Biol (Krakow).
62:143–147. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Lewinson D and Silbermann M: Chondroclasts
and endothelial cells collaborate in the process of cartilage
resorption. Anat Rec. 233:504–514. 1992.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Shibata S, Suzuki S and Yamashita Y: An
ultrastructural study of cartilage resorption at the site of
initial endochondral bone formation in the fetal mouse mandibular
condyle. J Anat. 191:65–76. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Baron R: Molecular mechanisms of bone
resorption by the osteoclast. Anat Rec. 224:317–324.
1989.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Gupta A, Edwards JC and Hruska KA:
Cellular distribution and regulation of NHE-1 isoform of the NA-H
exchanger in the avian osteoclast. Bone. 18:87–95. 1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Stenbeck G and Horton MA: Endocytic
trafficking in actively resorbing osteoclasts. J Cell Sci.
117:827–836. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Nesbitt SA and Horton MA: Trafficking of
matrix collagens through bone-resorbing osteoclasts. Science.
276:266–269. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Cappariello A, Maurizi A, Veeriah V and
Teti A: The great beauty of the osteoclast. Arch Biochem Biophys.
558:70–78. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Takito J, Inoue S and Nakamura M: The
sealing zone in osteoclasts: A self-organized structure on the
bone. Int J Mol Sci. 19(19)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Salo J, Lehenkari P, Mulari M, Metsikkö K
and Väänänen HK: Removal of osteoclast bone resorption products by
transcytosis. Science. 276:270–273. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Reddy S, Devlin R, Menaa C, Nishimura R,
Choi SJ, Dallas M, Yoneda T and Roodman GD: Isolation and
characterization of a cDNA clone encoding a novel peptide (OSF)
that enhances osteoclast formation and bone resorption. J Cell
Physiol. 177:636–645. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Loeser RF, Chubinskaya S, Pacione C and Im
HJ: Basic fibroblast growth factor inhibits the anabolic activity
of insulin-like growth factor 1 and osteogenic protein 1 in adult
human articular chondrocytes. Arthritis Rheum. 52:3910–3917.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Tanjaya J, Zhang Y, Lee S, Shi J, Chen E,
Ang P, Zhang X, Tetradis S, Ting K, Wu B, et al: Efficacy of
intraperitoneal administration of PEGylated NELL-1 for bone
formation. Biores Open Access. 5:159–170. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Sampath TK, Maliakal JC, Hauschka PV,
Jones WK, Sasak H, Tucker RF, White KH, Coughlin JE, Tucker MM and
Pang RH: Recombinant human osteogenic protein-1 (hOP-1) induces new
bone formation in vivo with a specific activity comparable with
natural bovine osteogenic protein and stimulates osteoblast
proliferation and differentiation in vitro. J Biol Chem.
267:20352–20362. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Wutzl A, Rauner M, Seemann R, Millesi W,
Krepler P, Pietschmann P and Ewers R: Bone morphogenetic proteins
2, 5, and 6 in combination stimulate osteoblasts but not
osteoclasts in vitro. J Orthop Res. 28:1431–1439. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Gao X, Usas A, Lu A, Tang Y, Wang B, Chen
CW, Li H, Tebbets JC, Cummins JH and Huard J: BMP2 is superior to
BMP4 for promoting human muscle-derived stem cell-mediated bone
regeneration in a critical-sized calvarial defect model. Cell
Transplant. 22:2393–2408. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Bahamonde ME and Lyons KM: BMP3: To be or
not to be a BMP. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 83-A (Suppl 1):S56–S62.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Storm EE, Huynh TV, Copeland NG, Jenkins
NA, Kingsley DM and Lee SJ: Limb alterations in brachypodism mice
due to mutations in a new member of the TGF beta-superfamily.
Nature. 368:639–643. 1994.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Polinkovsky A, Robin NH, Thomas JT, Irons
M, Lynn A, Goodman FR, Reardon W, Kant SG, Brunner HG, van der
Burgt I, et al: Mutations in CDMP1 cause autosomal dominant
brachydactyly type C. Nat Genet. 17:18–19. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Klammert U, Mueller TD, Hellmann TV,
Wuerzler KK, Kotzsch A, Schliermann A, Schmitz W, Kuebler AC,
Sebald W and Nickel J: GDF-5 can act as a context-dependent BMP-2
antagonist. BMC Biol. 13(77)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Yamashita H, Shimizu A, Kato M, Nishitoh
H, Ichijo H, Hanyu A, Morita I, Kimura M, Makishima F and Miyazono
K: Growth/differentiation factor-5 induces angiogenesis in vivo.
Exp Cell Res. 235:218–226. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Celeste AJ, Iannazzi JA, Taylor RC, Hewick
RM, Rosen V, Wang EA and Wozney JM: Identification of transforming
growth factor beta family members present in bone-inductive protein
purified from bovine bone. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 87:9843–9847.
1990.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Friedman MS, Long MW and Hankenson KD:
Osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells is
regulated by bone morphogenetic protein-6. J Cell Biochem.
98:538–554. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Kingsley DM: The TGF-beta superfamily: New
members, new receptors, and new genetic tests of function in
different organisms. Genes Dev. 8:133–146. 1994.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Longobardi L, Li T, Myers TJ, O'Rear L,
Ozkan H, Li Y, Contaldo C and Spagnoli A: TGF-β type II
receptor/MCP-5 axis: At the crossroad between joint and growth
plate development. Dev Cell. 23:71–81. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Chen G, Deng C and Li YP: TGF-β and BMP
signaling in osteoblast differentiation and bone formation. Int J
Biol Sci. 8:272–288. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Derynck R and Akhurst RJ: Differentiation
plasticity regulated by TGF-beta family proteins in development and
disease. Nat Cell Biol. 9:1000–1004. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Centrella M, McCarthy TL and Canalis E:
Skeletal tissue and transforming growth factor beta. FASEB J.
2:3066–3073. 1988.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Dallas SL, Rosser JL, Mundy GR and
Bonewald LF: Proteolysis of latent transforming growth factor-beta
(TGF-beta)-binding protein-1 by osteoclasts. A cellular mechanism
for release of TGF-beta from bone matrix. J Biol Chem.
277:21352–21360. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Nagao M, Hamilton JL, Kc R, Berendsen AD,
Duan X, Cheong CW, Li X, Im HJ and Olsen BR: Vascular endothelial
growth factor in cartilage development and osteoarthritis. Sci Rep.
7(13027)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Patil AS, Sable RB and Kothari RM:
Occurrence, biochemical profile of vascular endothelial growth
factor (VEGF) isoforms and their functions in endochondral
ossification. J Cell Physiol. 227:1298–1308. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Bluteau G, Julien M, Magne D,
Mallein-Gerin F, Weiss P, Daculsi G and Guicheux J: VEGF and VEGF
receptors are differentially expressed in chondrocytes. Bone.
40:568–576. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Zelzer E and Olsen BR: Multiple roles of
vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in skeletal development,
growth, and repair. Curr Top Dev Biol. 65:169–187. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Hu K and Olsen BR: Osteoblast-derived VEGF
regulates osteoblast differentiation and bone formation during bone
repair. J Clin Invest. 126:509–526. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Liu Y and Olsen BR: Distinct VEGF
functions during bone development and homeostasis. Arch Immunol
Ther Exp (Warsz). 62:363–368. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Liu Y, Berendsen AD, Jia S, Lotinun S,
Baron R, Ferrara N and Olsen BR: Intracellular VEGF regulates the
balance between osteoblast and adipocyte differentiation. J Clin
Invest. 122:3101–3113. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Li B, Wang H, Qiu G, Su X and Wu Z:
Synergistic effects of vascular endothelial growth factor on bone
morphogenetic proteins induced bone formation in vivo: Influencing
factors and future research directions. BioMed Res Int.
2016(2869572)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Kakudo N, Kusumoto K, Wang YB, Iguchi Y
and Ogawa Y: Immunolocalization of vascular endothelial growth
factor on intramuscular ectopic osteoinduction by bone
morphogenetic protein-2. Life Sci. 79:1847–1855. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Dilling CF, Wada AM, Lazard ZW, Salisbury
EA, Gannon FH, Vadakkan TJ, Gao L, Hirschi K, Dickinson ME, Davis
AR, et al: Vessel formation is induced prior to the appearance of
cartilage in BMP-2-mediated heterotopic ossification. J Bone Miner
Res. 25:1147–1156. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Hogan BL: Bone morphogenetic proteins in
development. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 6:432–438. 1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Nagai H, Tsukuda R and Mayahara H: Effects
of basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) on bone formation in
growing rats. Bone. 16:367–373. 1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Du M, Zhu T, Duan X, Ge S, Li N, Sun Q and
Yang P: Acellular dermal matrix loading with bFGF achieves similar
acceleration of bone regeneration to BMP-2 via differential effects
on recruitment, proliferation and sustained osteodifferentiation of
mesenchymal stem cells. Mater Sci Eng C. 70:62–70. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Arnott JA, Lambi AG, Mundy C, Hendesi H,
Pixley RA, Owen TA, Safadi FF and Popoff SN: The role of connective
tissue growth factor (CTGF/CCN2) in skeletogenesis. Crit Rev
Eukaryot Gene Expr. 21:43–69. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Bell PA, Dennis EP, Hartley CL, Jackson
RM, Porter A, Boot-Handford RP, Pirog KA and Briggs MD:
Mesencephalic astrocyte-derived neurotropic factor is an important
factor in chondrocyte ER homeostasis. Cell Stress Chaperones.
24:159–173. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Termaat MF, Den Boer FC, Bakker FC, Patka
P and Haarman HJ: Bone morphogenetic proteins. Development and
clinical efficacy in the treatment of fractures and bone defects. J
Bone Joint Surg Am. 87:1367–1378. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Vukicevic S, Oppermann H, Verbanac D,
Jankolija M, Popek I, Curak J, Brkljacic J, Pauk M, Erjavec I,
Francetic I, et al: The clinical use of bone morphogenetic proteins
revisited: A novel biocompatible carrier device OSTEOGROW for bone
healing. Int Orthop. 38:635–647. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
James AW, LaChaud G, Shen J, Asatrian G,
Nguyen V, Zhang X, Ting K and Soo C: A Review of the Clinical Side
Effects of Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2. Tissue Eng Part B Rev.
22:284–297. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Epstein NE: Basic science and spine
literature document bone morphogenetic protein increases cancer
risk. Surg Neurol Int. 5 (Suppl 15):S552–S560. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|