|
1
|
Liu J and Duan Y: Saliva: A potential
media for disease diagnostics and monitoring. Oral Oncol.
48:569–577. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Chiappin S, Antonelli G, Gatti R and De
Palo EF: Saliva specimen: A new laboratory tool for diagnostic and
basic investigation. Clin Chim Acta. 383:30–40. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Karnati R, Laurie DE and Laurie GW:
Lacritin and the tear proteome as natural replacement therapy for
dry eye. Exp Eye Res. 117:39–52. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Sitaramamma T, Shivaji S and Rao GN:
Effect of storage on protein concentration of tear samples. Curr
Eye Res. 17:1027–1035. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Wilmarth PA, Riviere MA, Rustvold DL,
Lauten JD, Madden TE and David LL: Two-dimensional liquid
chromatography study of the human whole saliva proteome. J Proteome
Res. 3:1017–1023. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Humphrey SP and Williamson RT: A review of
saliva: Normal composition, flow, and function. J Prosthet Dent.
85:162–169. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Tucker AS: Salivary gland development.
Semin Cell Dev Biol. 18:237–244. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Br H and Mp H: Regulatory mechanisms
driving salivary gland organogenesis. Curr Top Dev Biol.
115:111–130. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Voulgarelis M and Tzioufas AG:
Pathogenetic mechanisms in the initiation and perpetuation of
Sjögren's syndrome. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 6:529–537. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Mavragani CP and Moutsopoulos HM: The
geoepidemiology of Sjögren's syndrome. Autoimmun Rev. 9:A305–A310.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Busamia B, Gonzalez-Moles MA, Ruiz-Avila
I, Brunotto M, Gil-Montoya JA, Bravo M, Gobbi C and Finkelberg A:
Cell apoptosis and proliferation in salivary glands of Sjögren's
syndrome. J Oral Pathol Med. 40:721–725. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Pedersen AM, Dissing S, Fahrenkrug J,
Hannibal J, Reibel J and Nauntofte B: Innervation pattern and
Ca2+ signalling in labial salivary glands of healthy
individuals and patients with primary Sjögren's syndrome (pSS). J
Oral Pathol Med. 29:97–109. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Zoukhri D and Kublin CL: Impaired
neurotransmitter release from lacrimal and salivary gland nerves of
a murine model of Sjögren's syndrome. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.
42:925–932. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dawson LJ, Stanbury J, Venn N, Hasdimir B,
Rogers SN and Smith PM: Antimuscarinic antibodies in primary
Sjögren's syndrome reversibly inhibit the mechanism of fluid
secretion by human submandibular salivary acinar cells. Arthritis
Rheum. 54:1165–1173. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Caulfield VL, Balmer C, Dawson LJ and
Smith PM: A role for nitric oxide-mediated glandular hypofunction
in a non-apoptotic model for Sjogren's syndrome. Rheumatology
(Oxford). 48:727–733. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Dawson LJ, Fox PC and Smith PM: Sjogrens
syndrome-the non-apoptotic model of glandular hypofunction.
Rheumatology (Oxford). 45:792–798. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Soyfoo MS, Vriese CD, Debaix H,
Martin-Martinez MD, Mathieu C, Devuyst O, Steinfeld SD and Delporte
C: Modified aquaporin 5 expression and distribution in
submandibular glands from NOD mice displaying autoimmune
exocrinopathy. Arthritis Rheum. 56:2566–2574. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Aktas O, Prozorovski T, Smorodchenko A,
Savaskan NE, Lauster R, Kloetzel PM, Infante-Duarte C, Brocke S and
Zipp F: Green tea epigallocatechin-3-gallate mediates T cellular
NF-kappa B inhibition and exerts neuroprotection in autoimmune
encephalomyelitis. J Immunol. 173:5794–5800. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Gillespie K, Kodani I, Dickinson DP,
Ogbureke KU, Camba AM, Wu M, Looney S, Chu TC, Qin H, Bisch F, et
al: Effects of oral consumption of the green tea polyphenol EGCG in
a murine model for human Sjogren's syndrome, an autoimmune disease.
Life Sci. 83:581–588. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Dickinson D, Yu H, Ohno S, Thomas C,
Derossi S, Ma YH, Yates N, Hahn E, Bisch F, Yamamoto T and Hsu S:
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate prevents autoimmune-associated down-
regulation of p21 in salivary gland cells through a p53-independent
pathway. Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets. 13:15–24. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Carsons S: A review and update of
Sjögren's syndrome: Manifestations, diagnosis, and treatment. Am J
Manag Care. 7:S433–443. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang NZ, Shi CS, Yao QP, Pan GX, Wang LL,
Wen ZX, Li XC and Dong Y: Prevalence of primary Sjögren's syndrome
in China. J Rheumatol. 22:659–661. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ohno S, Yu H, Dickinson D, Chu TC,
Ogbureke K, Derossi S, Yamamoto T and Hsu S:
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate modulates antioxidant and DNA
repair-related proteins in exocrine glands of a primary Sjogren's
syndrome mouse model prior to disease onset. Autoimmunity.
45:540–546. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Saito K, Mori S, Date F and Ono M:
Epigallocatechin gallate inhibits oxidative stress-induced DNA
damage and apoptosis in MRL-Fas(lpr) mice with autoimmune
sialadenitis via upregulation of heme oxygenase-1 and Bcl-2.
Autoimmunity. 47:13–22. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Hsu S and Dickinson D: A new approach to
managing oral manifestations of Sjogren's syndrome and skin
manifestations of lupus. J Biochem Mol Biol. 39:229–239.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Hsu S, Dickinson DP, Qin H, Lapp C, Lapp
D, Borke J, Walsh DS, Bollag WB, Stöppler H, Yamamoto T, et al:
Inhibition of autoantigen expression by
(-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate (the major constituent of green tea)
in normal human cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 315:805–811.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Hsu SD, Dickinson DP, Qin H, Borke J,
Ogbureke KU, Winger JN, Camba AM, Bollag WB, Stöppler HJ, Sharawy
MM and Schuster GS: Green tea polyphenols reduce autoimmune
symptoms in a murine model for human Sjogren's syndrome and protect
human salivary acinar cells from TNF-alpha-induced cytotoxicity.
Autoimmunity. 40:138–147. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Guo T, Song D, Cheng L and Zhang X:
Interactions of tea catechins with intestinal microbiota and their
implication for human health. Food Sci Biotechnol. 28:1617–1625.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Chiou YS, Wu JC, Huang Q, Shahidi F, Wang
YJ, Ho CT and Pan MH: Metabolic and colonic microbiota
transformation may enhance the bioactivities of dietary
polyphenols. J Funct Foods. 7:3–25. 2014.
|
|
30
|
Pervin M, Unno K, Takagaki A, Isemura M
and Nakamura Y: Function of green tea catechins in the brain:
Epigallocatechin gallate and its metabolites. Int J Mol Sci.
20(3630)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Kim HS, Quon MJ and Kim J: New insights
into the mechanisms of polyphenols beyond antioxidant properties;
lessons from the green tea polyphenol, epigallocatechin 3-gallate.
Redox Biology. 2:187–195. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
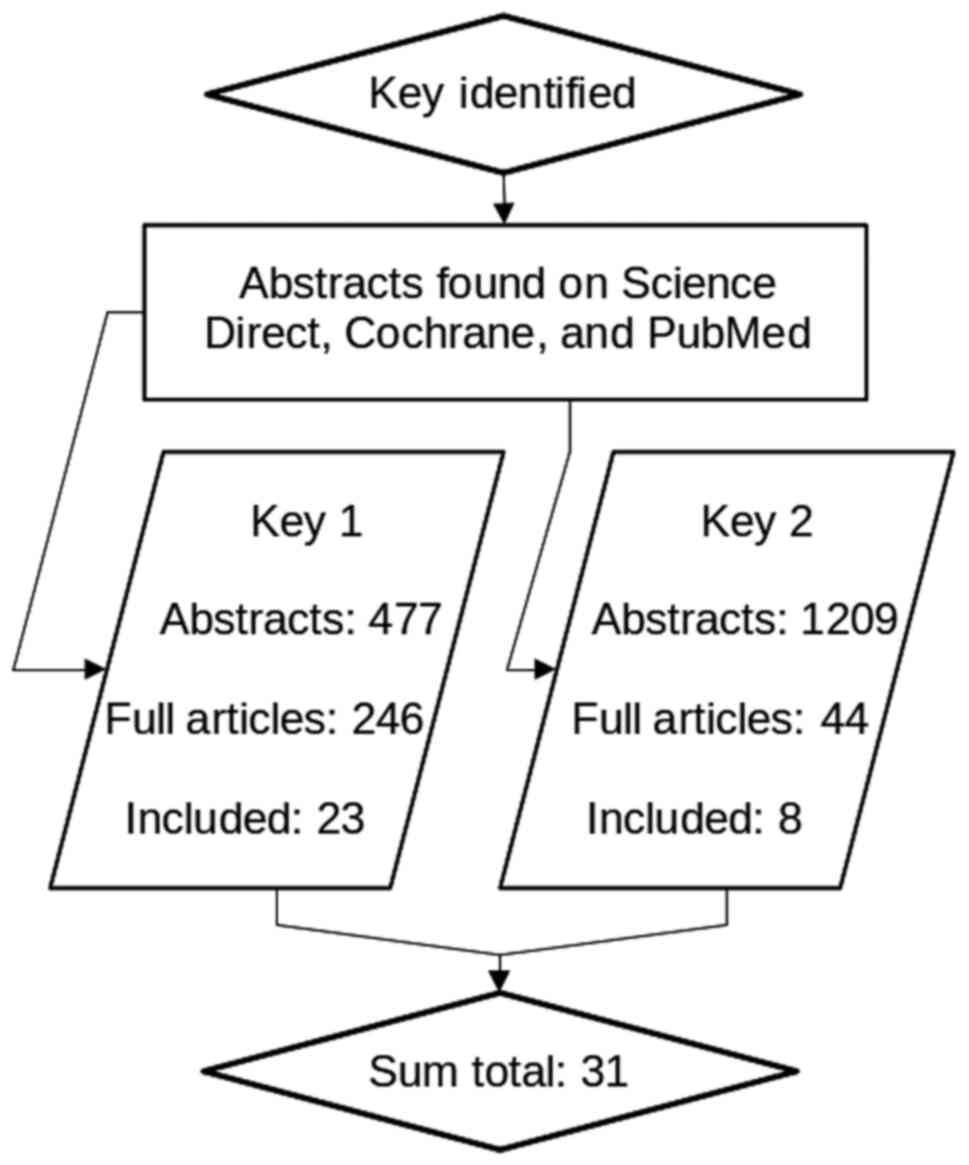
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron
I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, Shamseer L, Tetzlaff JM, Akl EA, Brennan
SE, et al: The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for
reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 372(n71)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Hong W: SNAREs and traffic. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1744:120–144. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Grote E, Hao JC, Bennett MK and Kelly RB:
A targeting signal in VAMP regulating transport to synaptic
vesicles. Cell. 81:581–589. 1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Alberts B, Johnson A, Lewis J, Raff M,
Roberts K and Walter P: Transport from the ER through the Golgi
Apparatus. Molecular Biology of the Cell 4th edition, 2002.
|
|
36
|
Whyte JRC and Munro S: Vesicle tethering
complexes in membrane traffic. J Cell Sci. 115:2627–2637.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chen YA and Scheller RH: SNARE-mediated
membrane fusion. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2:98–106. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Han J, Pluhackova K and Böckmann RA: The
multifaceted role of SNARE proteins in membrane fusion. Front
Physiol. 8(5)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Srivanitchapoom P, Pandey S and Hallett M:
Drooling in Parkinson's Disease: A review. Parkinsonism Relat
Disord. 20:1109–1118. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Yu GY, Zhu ZH, Mao C, Cai ZG, Zou LH, Lu
L, Zhang L, Peng X, Li N and Huang Z: Microvascular autologous
submandibular gland transfer in severe cases of
keratoconjunctivitis sicca. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 33:235–239.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Ewert P, Aguilera S, Alliende C, Kwon YJ,
Albornoz A, Molina C, Urzúa U, Quest AF, Olea N, Pérez P, et al:
Disruption of tight junction structure in salivary glands from
Sjögren's syndrome patients is linked to proinflammatory cytokine
exposure. Arthritis Rheum. 62:1280–1289. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Wong SH, Zhang T, Xu Y, Subramaniam VN,
Griffiths G and Hong W: Endobrevin, a novel synaptobrevin/VAMP-like
protein preferentially associated with the early endosome. Mol Biol
Cell. 9:1549–1563. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Lang T and Jahn R: Core proteins of the
secretory machinery. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 107–127. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Cosen-Binker LI, Binker MG, Wang CC, Hong
W and Gaisano HY: VAMP8 is the v-SNARE that mediates basolateral
exocytosis in a mouse model of alcoholic pancreatitis. J Clin
Invest. 118:2535–2551. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Barrera MJ, Sánchez M, Aguilera S,
Alliende C, Bahamondes V, Molina C, Quest AF, Urzúa U, Castro I,
González S, et al: Aberrant localization of fusion receptors
involved in regulated exocytosis in salivary glands of Sjögren's
syndrome patients is linked to ectopic mucin secretion. J
Autoimmun. 39:83–92. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Wang CC, Shi H, Guo K, Ng CP, Li J, Gan
BQ, Chien Liew H, Leinonen J, Rajaniemi H, et al: VAMP8/endobrevin
as a general vesicular SNARE for regulated exocytosis of the
exocrine system. Mol Biol Cell. 18:1056–1063. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Wang CC, Ng CP, Lu L, Atlashkin V, Zhang
W, Seet LF and Hong W: A role of VAMP8/endobrevin in regulated
exocytosis of pancreatic acinar cells. Dev Cell. 7:359–371.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Takuma T, Arakawa T and Tajima Y:
Interaction of SNARE proteins in rat parotid acinar cells. Arch
Oral Biol. 45:369–375. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Imai A, Nashida T, Yoshie S and Shimomura
H: Intracellular localisation of SNARE proteins in rat parotid
acinar cells: SNARE complexes on the apical plasma membrane. Arch
Oral Biol. 48:597–604. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Stoeckelhuber M, Scherer EQ, Janssen KP,
Slotta-Huspenina J, Loeffelbein DJ, Rohleder NH, Nieberler M,
Hasler R and Kesting MR: The human submandibular gland:
Immunohistochemical analysis of SNAREs and cytoskeletal proteins. J
Histochem Cytochem. 60:110–120. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Goicovich E, Molina C, Pérez P, Aguilera
S, Fernández J, Olea N, Alliende C, Leyton C, Romo R, Leyton L and
González MJ: Enhanced degradation of proteins of the basal lamina
and stroma by matrix metalloproteinases from the salivary glands of
Sjögren's syndrome patients: Correlation with reduced structural
integrity of acini and ducts. Arthritis Rheum. 48:2573–2584.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Coursey TG, Tukler Henriksson J, Barbosa
FL, de Paiva CS and Pflugfelder SC: Interferon-γ-induced unfolded
protein response in conjunctival goblet cells as a cause of mucin
deficiency in Sjögren syndrome. Am J Pathol. 186:1547–1558.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Holt M, Varoqueaux F, Wiederhold K,
Takamori S, Urlaub H, Fasshauer D and Jahn R: Identification of
SNAP-47, a novel Qbc-SNARE with ubiquitous expression. J Biol Chem.
281:17076–17083. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Wang W, Hart PS, Piesco NP, Lu X, Gorry MC
and Hart TC: Aquaporin expression in developing human teeth and
selected orofacial tissues. Calcif Tissue Int. 72:222–227.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Gresz V, Kwon TH, Hurley PT, Varga G,
Zelles T, Nielsen S, Case RM and Steward MC: Identification and
localization of aquaporin water channels in human salivary glands.
Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 281:G247–G254.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Steinfeld S, Cogan E, King LS, Agre P,
Kiss R and Delporte C: Abnormal distribution of aquaporin-5 water
channel protein in salivary glands from Sjögren's syndrome
patients. Lab Invest. 81:143–148. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Krane CM, Melvin JE, Nguyen HV, Richardson
L, Towne JE, Doetschman T and Menon AG: Salivary acinar cells from
aquaporin 5-deficient mice have decreased membrane water
permeability and altered cell volume regulation. J Biol Chem.
276:23413–23420. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Ishikawa Y, Cho G, Yuan Z, Inoue N and
Nakae Y: Aquaporin-5 water channel in lipid rafts of rat parotid
glands. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1758:1053–1060. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Ishikawa Y, Cho G, Yuan Z, Skowronski MT,
Pan Y and Ishida H: Water channels and zymogen granules in salivary
glands. J Pharmacol Sci. 100:495–512. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Ishikawa Y, Eguchi T, Skowronski MT and
Ishida H: Acetylcholine acts on M3 muscarinic receptors and induces
the translocation of aquaporin5 water channel via cytosolic Ca2+
elevation in rat parotid glands. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
245:835–840. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Xiang B, Zhang Y, Li YM, Zhang K, Zhang
YY, Wu LL and Yu GY: Effects of phenylephrine on transplanted
submandibular gland. J Dent Res. 85:1106–1111. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Tsubota K, Hirai S, King LS, Agre P and
Ishida N: Defective cellular trafficking of lacrimal gland
aquaporin-5 in Sjögren's syndrome. Lancet. 357:688–689.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Ma T, Song Y, Gillespie A, Carlson EJ,
Epstein CJ and Verkman AS: Defective secretion of saliva in
transgenic mice lacking aquaporin-5 water channels. J Biol Chem.
274:20071–20074. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Alam J, Koh JH, Kim N, Kwok SK, Park SH,
Song YW, Park K and Choi Y: Detection of autoantibodies against
aquaporin-5 in the sera of patients with primary Sjögren's
syndrome. Immunol Res. 64:848–856. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Alam J, Koh JH, Kwok SK, Park SH, Park K
and Choi Y: Functional Epitopes for Anti-Aquaporin 5 Antibodies in
Sjögren Syndrome. J Dent Res. 96:1414–1421. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Xiao L, Ng TB, Feng YB, Yao T, Wong JH,
Yao RM, Li L, Mo FZ, Xiao Y, Shaw PC, et al: Dendrobium candidum
extract increases the expression of aquaporin-5 in labial glands
from patients with Sjögren's syndrome. Phytomedicine. 18:194–198.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Lin X, Shaw PC, Sze SCW, Tong Y and Zhang
Y: Dendrobium officinale polysaccharides ameliorate the abnormality
of aquaporin 5, pro-inflammatory cytokines and inhibit apoptosis in
the experimental Sjögren's syndrome mice. Int Immunopharmacol.
11:2025–2032. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Sart S, Errachid A, Schneider YJ and
Agathos SN: Modulation of mesenchymal stem cell actin organization
on conventional microcarriers for proliferation and differentiation
in stirred bioreactors. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 7:537–551.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Nashida T, Yoshie S, Imai A and Shimomura
H: Presence of cytoskeleton proteins in parotid glands and their
roles during secretion. Arch Oral Biol. 49:975–982. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Segawa A, Riva A, Loffredo F, Congiu T,
Yamashina S and Testa Riva F: Cytoskeletal regulation of human
salivary secretion studied by high resolution electron microscopy
and confocal laser microscopy. Eur J Morphol. 36 (Suppl):S41–S45.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Perrin D, Möller K, Hanke K and Söling HD:
cAMP and Ca(2+)-mediated secretion in parotid acinar cells is
associated with reversible changes in the organization of the
cytoskeleton. J Cell Biol. 116:127–134. 1992.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Valentijn KM, Gumkowski FD and Jamieson
JD: The subapical actin cytoskeleton regulates secretion and
membrane retrieval in pancreatic acinar cells. J Cell Sci.
112:81–96. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Muallem S, Kwiatkowska K, Xu X and Yin HL:
Actin filament disassembly is a sufficient final trigger for
exocytosis in nonexcitable cells. J Cell Biol. 128:589–598.
1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Busch L, Sterin-Borda L and Borda E:
Differences in the regulatory mechanism of amylase release by rat
parotid and submandibular glands. Arch Oral Biol. 47:717–722.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Birkenfeld J, Kartmann B, Betz H and Roth
D: Cofilin activation during Ca(2+)-triggered secretion from
adrenal chromaffin cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 286:493–498.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Cui L, Elzakra N, Xu S, Xiao GG, Yang Y
and Hu S: Investigation of three potential autoantibodies in
Sjogren's syndrome and associated MALT lymphoma. Oncotarget.
8:30039–30049. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Zhang Y, Hussain M, Yang X, Chen P, Yang
C, Xun Y, Tian Y and Du H: Identification of moesin as a novel
autoantigen in patients with Sjögren's syndrome. Protein Pept Lett.
25:350–355. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Mitic LL, Van Itallie CM and Anderson JM:
Molecular physiology and pathophysiology of tight junctions I.
Tight junction structure and function: Lessons from mutant animals
and proteins. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol.
279:G250–G254. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Beguin P, Errachid A, Larondelle Y and
Schneider YJ: Effect of polyunsaturated fatty acids on tight
junctions in a model of the human intestinal epithelium under
normal and inflammatory conditions. Food Funct. 4:923–931.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Flynn AN, Itani OA, Moninger TO and Welsh
MJ: Acute regulation of tight junction ion selectivity in human
airway epithelia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:3591–3596.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Fox RI, Kang HI, Ando D, Abrams J and Pisa
E: Cytokine mRNA expression in salivary gland biopsies of Sjögren's
syndrome. J Immunol. 152:5532–5539. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Fox PC, Grisius MM, Bermudez DK and Sun D:
Cytokine mRNA expression in labial salivary glands and cytokine
secretion in parotid saliva in Sjögren's syndrome. Adv Exp Med
Biol. 438:909–915. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Baker OJ, Camden JM, Redman RS, Jones JE,
Seye CI, Erb L and Weisman GA: Proinflammatory cytokines tumor
necrosis factor-alpha and interferon-gamma alter tight junction
structure and function in the rat parotid gland Par-C10 cell line.
Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 295:C1191–C1201. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Youakim A and Ahdieh M: Interferon-gamma
decreases barrier function in T84 cells by reducing ZO-1 levels and
disrupting apical actin. Am J Physiol. 276:G1279–G1288.
1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Ma TY, Iwamoto GK, Hoa NT, Akotia V,
Pedram A, Boivin MA and Said HM: TNF-alpha-induced increase in
intestinal epithelial tight junction permeability requires NF-kappa
B activation. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol.
286:G367–376. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Mankertz J, Tavalali S, Schmitz H,
Mankertz A, Riecken EO, Fromm M and Schulzke JD: Expression from
the human occludin promoter is affected by tumor necrosis factor
alpha and interferon gamma. J Cell Sci. 113:2085–2090.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Utech M, Ivanov AI, Samarin SN, Bruewer M,
Turner JR, Mrsny RJ, Parkos CA and Nusrat A: Mechanism of
IFN-gamma-induced endocytosis of tight junction proteins: Myosin
II-dependent vacuolarization of the apical plasma membrane. Mol
Biol Cell. 16:5040–5052. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Manoussakis MN and Kapsogeorgou EK: The
role of epithelial cells in the pathogenesis of Sjögren's syndrome.
Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 32:225–230. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Kawedia JD, Nieman ML, Boivin GP, Melvin
JE, Kikuchi K, Hand AR, Lorenz JN and Menon AG: Interaction between
transcellular and paracellular water transport pathways through
Aquaporin 5 and the tight junction complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
104:3621–3626. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Ichiyama T, Nakatani E, Tatsumi K,
Hideshima K, Urano T, Nariai Y and Sekine J: Expression of
aquaporin 3 and 5 as a potential marker for distinguishing dry
mouth from Sjögren's syndrome. J Oral Sci. 60:212–220.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
91
|
Chow HH, Cai Y, Hakim IA, Crowell JA,
Shahi F, Brooks CA, Dorr RT, Hara Y and Alberts DS:
Pharmacokinetics and safety of green tea polyphenols after
multiple-dose administration of epigallocatechin gallate and
polyphenon E in healthy individuals. Clin Cancer Res. 9:3312–3319.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Fürst R and Zündorf I: Plant-derived
anti-inflammatory compounds: Hopes and disappointments regarding
the translation of preclinical knowledge into clinical progress.
Mediators Inflamm. 2014(146832)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Wyganowska-Świątkowska M,
Matthews-Kozanecka M, Matthews-Brzozowska T, Skrzypczak-Jankun E
and Jankun J: Can EGCG alleviate symptoms of down syndrome by
altering proteolytic activity? Int J Mol Sci.
19(248)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
94
|
Yan X, Li Y, Yu H, Wang W, Wu C, Yang Y,
Hu Y, Shi X and Li J: Epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits
H2O2-induced apoptosis in mouse vascular
smooth muscle cells via 67kD laminin receptor. Sci Rep.
7(7774)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
95
|
Wyganowska-Swiatkowska M, Nohawica M,
Grocholewicz K and Nowak G: Influence of herbal medicines on HMGB1
release, SARS-CoV-2 viral attachment, acute respiratory failure,
and sepsis. A literature review. Int J Mol Sci.
21(4639)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
Soldatenkov VA and Smulson M:
Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase in DNA damage-response pathway:
Implications for radiation oncology. Int J Cancer. 90:59–67.
2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
97
|
Zhang Y, Duan W, Owusu L, Wu D and Xin Y:
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate induces the apoptosis of hepatocellular
carcinoma LM6 cells but not non-cancerous liver cells. Int J Mol
Med. 35:117–124. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
98
|
Harakeh S, Abu-El-Ardat K, Diab-Assaf M,
Niedzwiecki A, El-Sabban M and Rath M: Epigallocatechin-3-gallate
induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in HTLV-1-positive and
-negative leukemia cells. Med Oncol. 25:30–39. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
99
|
Lancaster OM and Baum B: Shaping up to
divide: Coordinating actin and microtubule cytoskeletal remodelling
during mitosis. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 34:109–115. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
100
|
Desouza M, Gunning PW and Stehn JR: The
actin cytoskeleton as a sensor and mediator of apoptosis.
Bioarchitecture. 2:75–87. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
101
|
Mayr C, Wagner A, Neureiter D, Pichler M,
Jakab M, Illig R, Berr F and Kiesslich T: The green tea catechin
epigallocatechin gallate induces cell cycle arrest and shows
potential synergism with cisplatin in biliary tract cancer cells.
BMC Complement Altern Med. 15(194)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
102
|
Yang CS, Lee MJ and Chen L: Human salivary
tea catechin levels and catechin esterase activities: Implication
in human cancer prevention studies. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers
Prev. 8:83–89. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Wheeler DS, Catravas JD, Odoms K,
Denenberg A, Malhotra V and Wong HR: Epigallocatechin-3-gallate, a
green tea-derived polyphenol, inhibits IL-1 beta-dependent
proinflammatory signal transduction in cultured respiratory
epithelial cells. J Nutr. 134:1039–1044. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
104
|
Ahn SC, Kim GY, Kim JH, Baik SW, Han MK,
Lee HJ, Moon DO, Lee CM, Kang JH, Kim BH, et al:
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate, constituent of green tea, suppresses
the LPS-induced phenotypic and functional maturation of murine
dendritic cells through inhibition of mitogen-activated protein
kinases and NF-kappaB. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 313:148–155.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
105
|
Saito K, Mori S, Date F and Hong G:
Epigallocatechin gallate stimulates the neuroreactive salivary
secretomotor system in autoimmune sialadenitis of MRL-Fas(lpr) mice
via activation of cAMP-dependent protein kinase A and inactivation
of nuclear factor κB. Autoimmunity. 48:379–388. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
106
|
Schieven GL: The biology of p38 kinase: A
central role in inflammation. Curr Top Med Chem. 5:921–928.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
107
|
Stillman A, Connors M, Miller M, Qazzaz H
and Dryden G: P-145 oral administration of EGCG, a green tea
polyphenol, both suppresses and rescues mice from DSS-induced
colitis. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 22:S54. 2016.
|
|
108
|
Sakai M, Ohnishi K, Masuda M, Ohminami H,
Yamanaka-Okumura H, Hara T and Taketani Y: Isorhamnetin, a
3'-methoxylated flavonol, enhances the lysosomal proteolysis in
J774.1 murine macrophages in a TFEB-independent manner. Biosci
Biotechnol Biochem. 84:1221–1231. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
109
|
Holczer M, Besze B, Zámbó V, Csala M,
Bánhegyi G and Kapuy O: Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate (EGCG) promotes
autophagy-dependent survival via influencing the balance of
mTOR-AMPK pathways upon endoplasmic reticulum stress. Oxid Med Cell
Longev. 2018(e6721530)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
110
|
Zhang S, Cao M and Fang F: The role of
Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate in autophagy and endoplasmic reticulum
stress (ERS)-induced apoptosis of human diseases. Med Sci Monit.
26(e924558)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
111
|
Zhang L, Wang H, Xu J, Zhu J and Ding K:
Inhibition of cathepsin S induces autophagy and apoptosis in human
glioblastoma cell lines through ROS-mediated PI3K/AKT/mTOR/p70S6K
and JNK signaling pathways. Toxicol Lett. 228:248–259.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
112
|
Hamm-Alvarez SF, Janga SR, Edman MC,
Madrigal S, Shah M, Frousiakis SE, Renduchintala K, Zhu J, Bricel
S, Silka K, et al: Tear cathepsin S as a candidate biomarker for
Sjögren's syndrome. Arthritis Rheumatol. 66:1872–1881.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
113
|
Zhang B, Wang B, Cao S and Wang Y:
Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate (EGCG) attenuates traumatic brain injury
by inhibition of edema formation and oxidative stress. Korean J
Physiol Pharmacol. 19:491–497. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
114
|
Ge R, Zhu Y, Diao Y, Tao L, Yuan W and
Xiong X: Anti-edema effect of epigallocatechin gallate on spinal
cord injury in rats. Brain Res. 1527:40–46. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
115
|
Kim JE, Park H, Jeong MJ and Kang TC:
Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate and PEDF 335 peptide, 67LR activators,
attenuate vasogenic edema, and astroglial degeneration following
status epilepticus. Antioxidants (Basel). 9(854)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
116
|
Nakamura Y, Tsuchiya T, Hara-Chikuma M,
Yasui M and Fukui Y: Identification of compounds in red wine that
effectively upregulate aquaporin-3 as a potential mechanism of
enhancement of skin moisturizing. Biochem Biophys Rep.
24(100864)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
117
|
Wang X, Yang L, Wang J, Zhang Y, Dong R,
Wu X, Yang CS, Zhang Z and Zhang J: A mouse model of subacute liver
failure with ascites induced by step-wise increased doses of
(-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate. Sci Rep. 9(18102)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
118
|
Yan C, Yang J, Shen L and Chen X:
Inhibitory effect of Epigallocatechin gallate on ovarian cancer
cell proliferation associated with aquaporin 5 expression. Arch
Gynecol Obstet. 285:459–467. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
119
|
Tepedelen BE, Soya E and Korkmaz M:
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate reduces the proliferation of benign
prostatic hyperplasia cells via regulation of focal adhesions. Life
Sci. 191:74–81. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
120
|
Fong-Ngern K, Vinaiphat A and
Thongboonkerd V: Microvillar injury in renal tubular epithelial
cells induced by calcium oxalate crystal and the protective role of
epigallocatechin-3-gallate. FASEB J. 31:120–131. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
121
|
Magro F, Fraga S and Soares-da-Silva P:
Interferon-gamma-induced STAT1-mediated membrane retention of NHE1
and associated proteins ezrin, radixin and moesin in HT-29 cells.
Biochem Pharmacol. 70:1312–1319. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
122
|
Meng M, Li YQ, Yan MX, Kou Y and Ren HB:
Effects of epigallocatechin gallate on
diethyldithiocarbamate-induced pancreatic fibrosis in rats. Biol
Pharm Bull. 30:1091–1096. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
123
|
Higashi N, Kohjima M, Fukushima M, Ohta S,
Kotoh K, Enjoji M, Kobayashi N and Nakamuta M:
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate, a green-tea polyphenol, suppresses Rho
signaling in TWNT-4 human hepatic stellate cells. J Lab Clin Med.
145:316–322. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
124
|
Asaumi H, Watanabe S, Taguchi M, Tashiro
M, Nagashio Y, Nomiyama Y, Nakamura H and Otsuki M: Green tea
polyphenol (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits ethanol-induced
activation of pancreatic stellate cells. Eur J Clin Invest.
36:113–122. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
125
|
Cano A, Ettcheto M, Chang JH, Barroso E,
Espina M, Kühne BA, Barenys M, Auladell C, Folch J, Souto EB, et
al: Dual-drug loaded nanoparticles of Epigallocatechin-3-gallate
(EGCG)/Ascorbic acid enhance therapeutic efficacy of EGCG in a
APPswe/PS1dE9 Alzheimer's disease mice model. J Control Release.
301:62–75. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
126
|
Qiu J, Kitamura Y, Miyata Y, Tamaru S,
Tanaka K, Tanaka T and Matsui T: Transepithelial transport of
theasinensins through Caco-2 cell monolayers and their absorption
in Sprague-Dawley rats after oral administration. J Agric Food
Chem. 60:8036–8043. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
127
|
Lagha AB and Grenier D: Tea polyphenols
protect gingival keratinocytes against TNF-α-induced tight junction
barrier dysfunction and attenuate the inflammatory response of
monocytes/macrophages. Cytokine. 115:64–75. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
128
|
Li J, Ye L, Wang X, Liu J, Wang Y, Zhou Y
and Ho W: (-)-Epigallocatechin gallate inhibits endotoxin-induced
expression of inflammatory cytokines in human cerebral
microvascular endothelial cells. J Neuroinflammation.
9(161)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
129
|
Lagha AB, Groeger S, Meyle J and Grenier
D: Green tea polyphenols enhance gingival keratinocyte integrity
and protect against invasion by Porphyromonas gingivalis. Pathog
Dis. 76:2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
130
|
Watson JL, Ansari S, Cameron H, Wang A,
Akhtar M and McKay DM: Green tea polyphenol (-)-epigallocatechin
gallate blocks epithelial barrier dysfunction provoked by IFN-gamma
but not by IL-4. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol.
287:G954–961. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
131
|
Suzuki T and Hara H: Role of flavonoids in
intestinal tight junction regulation. J Nutr Biochem. 22:401–408.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
132
|
Amerongen AV, Bolscher JG and Veerman EC:
Salivary mucins: Protective functions in relation to their
diversity. Glycobiology. 5:733–740. 1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
133
|
Alliende C, Kwon YJ, Brito M, Molina C,
Aguilera S, Pérez P, Leyton L, Quest AF, Mandel U, Veerman E, et
al: Reduced sulfation of muc5b is linked to xerostomia in patients
with Sjögren syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis. 67:1480–1487. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
134
|
Xu H, Shan XF, Cong X, Yang NY, Wu LL, Yu
GY, Zhang Y and Cai ZG: Pre- and post-synaptic effects of botulinum
toxin A on submandibular glands. J Dent Res. 94:1454–1462.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
135
|
Besserer A, Burnotte E, Bienert GP,
Chevalier AS, Errachid A, Grefen C, Blatt MR and Chaumont F:
Selective regulation of maize plasma membrane aquaporin trafficking
and activity by the SNARE SYP121. Plant Cell. 24:3463–3481.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
136
|
Noda Y, Horikawa S, Kanda E, Yamashita M,
Meng H, Eto K, Li Y, Kuwahara M, Hirai K, Pack C, et al: Reciprocal
interaction with G-actin and tropomyosin is essential for
aquaporin-2 trafficking. J Cell Biol. 182:587–601. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
137
|
Beroukas D, Hiscock J, Jonsson R, Waterman
SA and Gordon TP: Subcellular distribution of aquaporin 5 in
salivary glands in primary Sjögren's syndrome. Lancet.
358:1875–1876. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
138
|
Nashida T, Yoshie S, Haga-Tsujimura M,
Imai A and Shimomura H: Atrophy of myoepithelial cells in parotid
glands of diabetic mice; detection using skeletal muscle actin, a
novel marker. FEBS Open Bio. 3:130–134. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
139
|
Mei M, Xiang RL, Cong X, Zhang Y, Li J, Yi
X, Park K, Han JY, Wu LL and Yu GY: Claudin-3 is required for
modulation of paracellular permeability by TNF-α through
ERK1/2/slug signaling axis in submandibular gland. Cell Signal.
27:1915–1927. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
140
|
Cong X, Zhang XM, Zhang Y, Wei T, He QH,
Zhang LW, Hua H, Lee SW, Park K, Yu GY and Wu LL: Disruption of
endothelial barrier function is linked with hyposecretion and
lymphocytic infiltration in salivary glands of Sjögren's syndrome.
Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 1864:3154–3163. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|