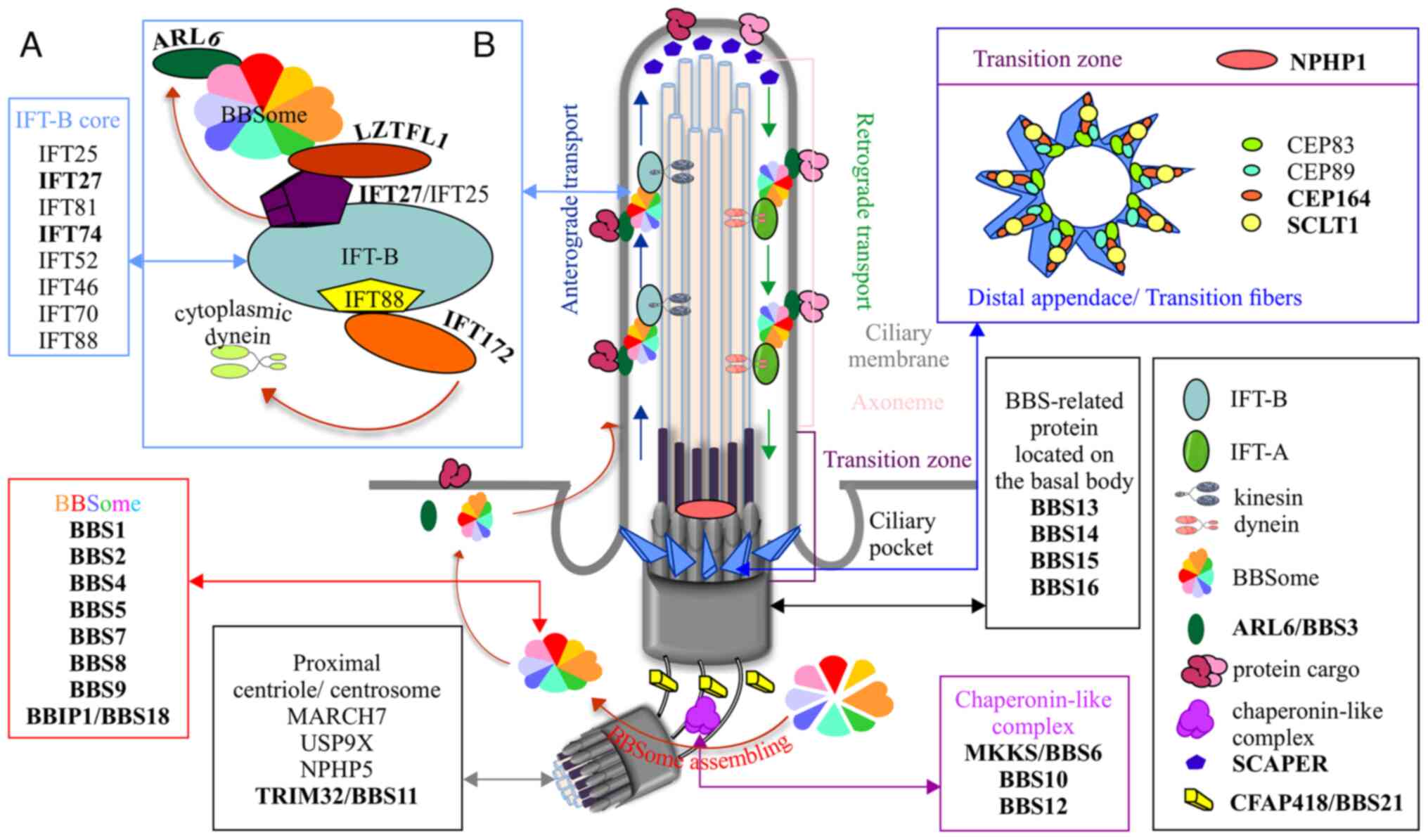
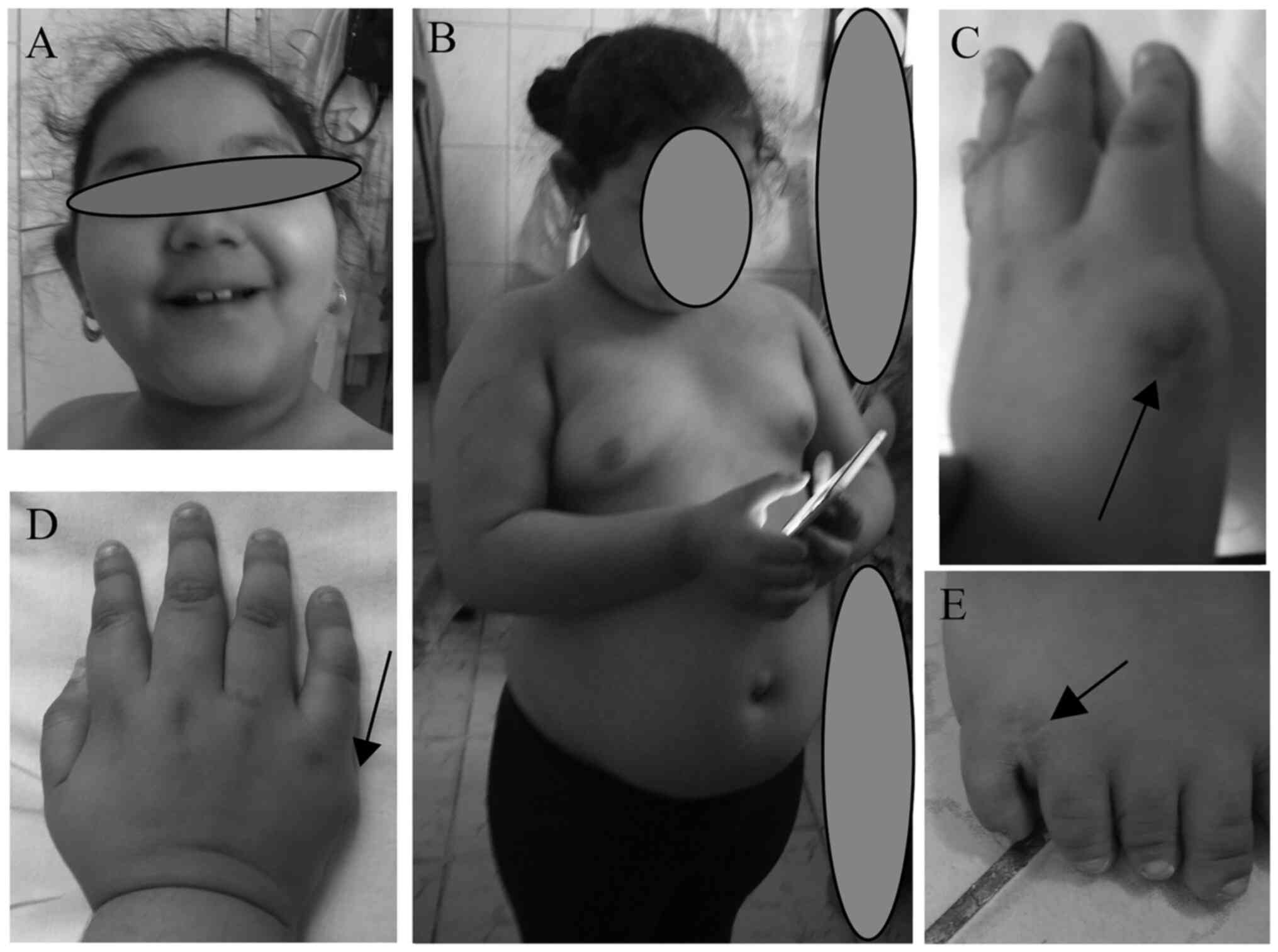
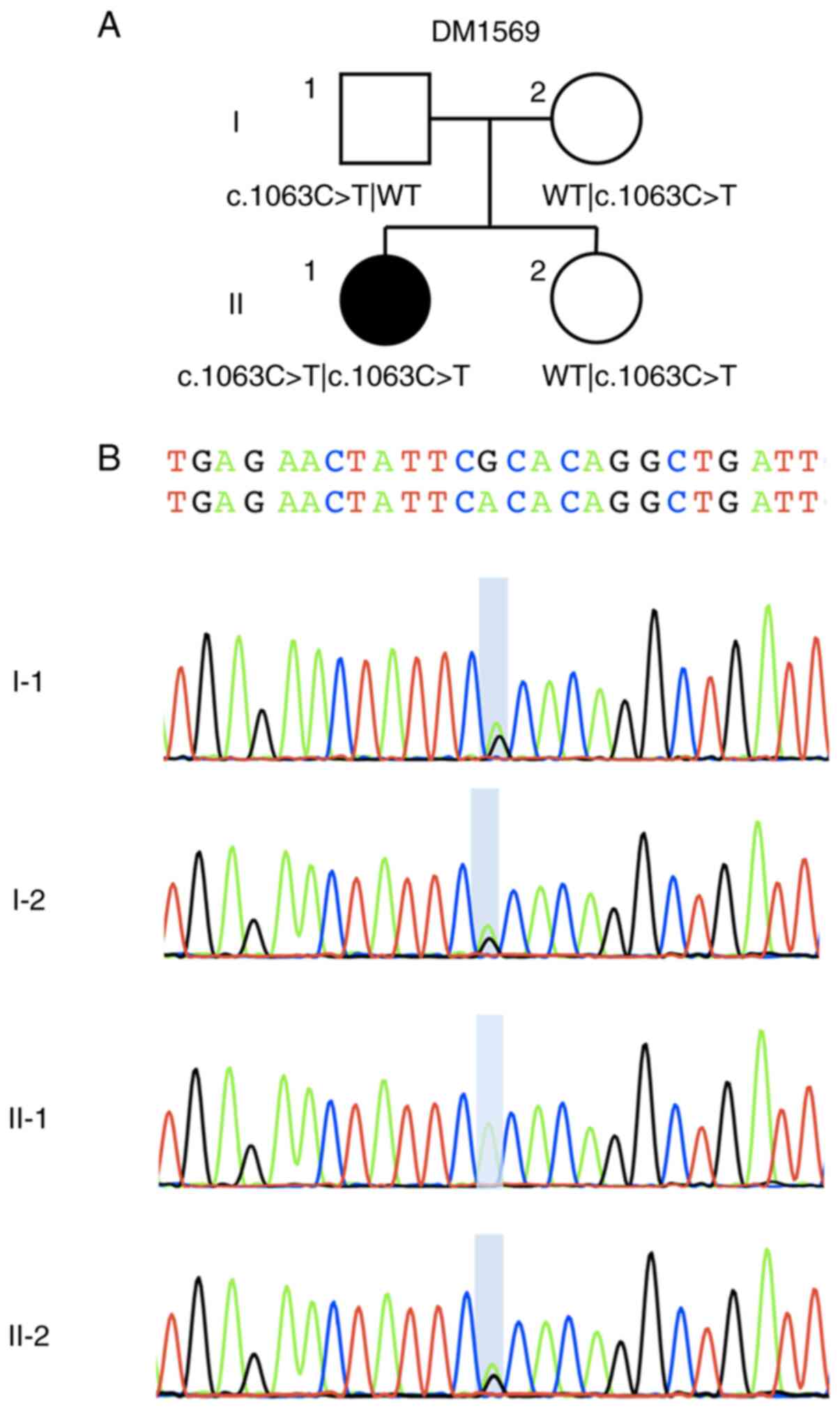
|
1
|
Zaghloul NA and Katsanis N: Mechanistic
insights into Bardet-Biedl syndrome, a model ciliopathy. J Clin
Invest. 119:428–437. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Kousi M, Soylemez O, Ozanturk A, Mourtzi
N, Akle S, Jungreis I, Muller J, Cassa CA, Brand H, Mokry JA, et
al: Evidence for secondary-variant genetic burden and non-random
distribution across biological modules in a recessive ciliopathy.
Nat Genet. 52:1145–1150. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Focșa IO, Budișteanu M and Bălgrădean M:
Clinical and genetic heterogeneity of primary ciliopathies
(Review). Int J Mol Med. 48(176)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Forsythe E and Beales PL: Bardet-Biedl
syndrome. Eur J Hum Genet. 21:8–13. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Beales PL, Elcioglu N, Woolf AS, Parker D
and Flinter FA: New criteria for improved diagnosis of Bardet-Biedl
syndrome: Results of a population survey. J Med Genet. 36:437–446.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Weihbrecht K, Goar WA, Pak T, Garrison JE,
DeLuca AP, Stone EM, Scheetz TE and Sheffield VC: Keeping an eye on
bardet-biedl syndrome: A Comprehensive review of the role of
bardet-biedl syndrome genes in the eye. Med Res Arch.
5(10.18103/mra.v5i9.1526)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Forsythe E, Kenny J, Bacchelli C and
Beales PL: Managing bardet-biedl syndrome-now and in the future.
Front Pediatr. 6(23)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Imhoff O, Marion V, Stoetzel C, Durand M,
Holder M, Sigaudy S, Sarda P, Hamel CP, Brandt C, Dollfus H and
Moulin B: Bardet-Biedl syndrome: A study of the renal and
cardiovascular phenotypes in a French cohort. Clin J Am Soc
Nephrol. 6:22–29. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Mujahid S, Hunt KF, Cheah YS, Forsythe E,
Hazlehurst JM, Sparks K, Mohammed S, Tomlinson JW, Amiel SA,
Carroll PV, et al: The endocrine and metabolic characteristics of a
large bardet-biedl syndrome clinic population. J Clin Endocrinol
Metab. 103:1834–1841. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Kerr EN, Bhan A and Heon E: Exploration of
the cognitive, adaptive and behavioral functioning of patients
affected with Bardet-Biedl syndrome. Clin Genet. 89:426–433.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Forsyth RL and Gunay-Aygun M: Bardet-biedl
syndrome overview. In: GeneReviews® [Internet]. Adam MP,
Ardinger HH, Pagon RA, et al (eds). University of
Washington, Seattle, WA, 1993.
|
|
12
|
Forsythe E, Sparks K, Best S, Borrows S,
Hoskins B, Sabir A, Barrett T, Williams D, Mohammed S, Goldsmith D,
et al: Risk factors for severe renal disease in bardet-biedl
syndrome. J Am Soc Nephrol. 28:963–970. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Putoux A, Attie-Bitach T, Martinovic J and
Gubler MC: Phenotypic variability of Bardet-Biedl syndrome:
Focusing on the kidney. Pediatr Nephrol. 27:7–15. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Marchese E, Ruoppolo M, Perna A, Capasso G
and Zacchia M: Exploring key challenges of understanding the
pathogenesis of kidney disease in bardet-biedl syndrome. Kidney Int
Rep. 5:1403–1415. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Moore SJ, Green JS, Fan Y, Bhogal AK,
Dicks E, Fernandez BA, Stefanelli M, Murphy C, Cramer BC, Dean JC,
et al: Clinical and genetic epidemiology of Bardet-Biedl syndrome
in Newfoundland: A 22-year prospective, population-based, cohort
study. Am J Med Genet A. 132A:352–360. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Elbedour K, Zucker N, Zalzstein E, Barki Y
and Carmi R: Cardiac abnormalities in the Bardet-Biedl syndrome:
Echocardiographic studies of 22 patients. Am J Med Genet.
52:164–169. 1994.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Branfield Day L, Quammie C, Héon E, Bhan
A, Batmanabane V, Dai T and Kamath BM: Liver anomalies as a
phenotype parameter of Bardet-Biedl syndrome. Clin Genet.
89:507–509. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Olson AJ, Krentz AD, Finta KM, Okorie UC
and Haws RM: Thoraco-abdominal abnormalities in bardet-biedl
syndrome: Situs inversus and heterotaxy. J Pediatr. 204:31–37.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Jin H, White SR, Shida T, Schulz S, Aguiar
M, Gygi SP, Bazan JF and Nachury MV: The conserved Bardet-Biedl
syndrome proteins assemble a coat that traffics membrane proteins
to cilia. Cell. 141:1208–1219. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Nachury MV, Loktev AV, Zhang Q, Westlake
CJ, Peränen J, Merdes A, Slusarski DC, Scheller RH, Bazan JF,
Sheffield VC and Jackson PK: A core complex of BBS proteins
cooperates with the GTPase Rab8 to promote ciliary membrane
biogenesis. Cell. 129:1201–1213. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Lechtreck KF: IFT-cargo interactions and
protein transport in cilia. Trends Biochem Sci. 40:765–778.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Bhogaraju S, Engel BD and Lorentzen E:
Intraflagellar transport complex structure and cargo interactions.
Cilia. 2(10)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Liew GM, Ye F, Nager AR, Murphy JP, Lee
JS, Aguiar M, Breslow DK, Gygi SP and Nachury MV: The
intraflagellar transport protein IFT27 promotes BBSome exit from
cilia through the GTPase ARL6/BBS3. Dev Cell. 31:265–278.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Eguether T, San Agustin JT, Keady BT,
Jonassen JA, Liang Y, Francis R, Tobita K, Johnson CA, Abdelhamed
ZA, Lo CW and Pazour GJ: IFT27 links the BBSome to IFT for
maintenance of the ciliary signaling compartment. Dev Cell.
31:279–290. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Brown JM, Cochran DA, Craige B, Kubo T and
Witman GB: Assembly of IFT trains at the ciliary base depends on
IFT74. Curr Biol. 25:1583–1593. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Bujakowska KM, Zhang Q, Siemiatkowska AM,
Liu Q, Place E, Falk MJ, Consugar M, Lancelot ME, Antonio A, Lonjou
C, et al: Mutations in IFT172 cause isolated retinal degeneration
and Bardet-Biedl syndrome. Hum Mol Genet. 24:230–242.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Seo S, Baye LM, Schulz NP, Beck JS, Zhang
Q, Slusarski DC and Sheffield VC: BBS6, BBS10, and BBS12 form a
complex with CCT/TRiC family chaperonins and mediate BBSome
assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:1488–1493. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Alvarez-Satta M, Castro-Sanchez S and
Valverde D: Bardet-biedl syndrome as a chaperonopathy: Dissecting
the major role of chaperonin-like BBS proteins (BBS6-BBS10-BBS12).
Front Mol Biosci. 4(55)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Dawe HR, Smith UM, Cullinane AR, Gerrelli
D, Cox P, Badano JL, Blair-Reid S, Sriram N, Katsanis N,
Attie-Bitach T, et al: The Meckel-gruber syndrome proteins MKS1 and
meckelin interact and are required for primary cilium formation.
Hum Mol Genet. 16:173–186. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Barbelanne M, Hossain D, Chan DP, Peranen
J and Tsang WY: Nephrocystin proteins NPHP5 and Cep290 regulate
BBSome integrity, ciliary trafficking and cargo delivery. Hum Mol
Genet. 24:2185–2200. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Williams CL, Li C, Kida K, Inglis PN,
Mohan S, Semenec L, Bialas NJ, Stupay RM, Chen N, Blacque OE, et
al: MKS and NPHP modules cooperate to establish basal
body/transition zone membrane associations and ciliary gate
function during ciliogenesis. J Cell Biol. 192:1023–1041.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Marion V, Stutzmann F, Gerard M, De Melo
C, Schaefer E, Claussmann A, Hellé S, Delague V, Souied E, Barrey
C, et al: Exome sequencing identifies mutations in LZTFL1, a BBSome
and smoothened trafficking regulator, in a family with Bardet-Biedl
syndrome with situs inversus and insertional polydactyly. J Med
Genet. 49:317–321. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Seo S, Zhang Q, Bugge K, Breslow DK,
Searby CC, Nachury MV and Sheffield VC: A novel protein LZTFL1
regulates ciliary trafficking of the BBSome and Smoothened. PLoS
Genet. 7(e1002358)2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Das A, Qian J and Tsang WY: USP9X
counteracts differential ubiquitination of NPHP5 by MARCH7 and
BBS11 to regulate ciliogenesis. PLoS Genet.
13(e1006791)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Heon E, Kim G, Qin S, Garrison JE, Tavares
E, Vincent A, Nuangchamnong N, Scott CA, Slusarski DC and Sheffield
VC: Mutations in C8ORF37 cause Bardet Biedl syndrome (BBS21). Hum
Mol Genet. 25:2283–2294. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Lindstrand A, Davis EE, Carvalho CM,
Pehlivan D, Willer JR, Tsai IC, Ramanathan S, Zuppan C, Sabo A,
Muzny D, et al: Recurrent CNVs and SNVs at the NPHP1 locus
contribute pathogenic alleles to Bardet-Biedl syndrome. Am J Hum
Genet. 94:745–754. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Morisada N, Hamada R, Miura K, Ye MJ, Nozu
K, Hattori M and Iijima K: Bardet-Biedl syndrome in two unrelated
patients with identical compound heterozygous SCLT1 mutations. CEN
Case Rep. 9:260–265. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Shamseldin HE, Shaheen R, Ewida N,
Bubshait DK, Alkuraya H, Almardawi E, Howaidi A, Sabr Y, Abdalla
EM, Alfaifi AY, et al: The morbid genome of ciliopathies: An
update. Genet Med. 22:1051–1060. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Yang TT, Chong WM, Wang WJ, Mazo G, Tanos
B, Chen Z, Tran TMN, Chen YD, Weng RR, Huang CE, et al:
Super-resolution architecture of mammalian centriole distal
appendages reveals distinct blade and matrix functional components.
Nat Commun. 9(2023)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Wormser O, Gradstein L, Yogev Y, Perez Y,
Kadir R, Goliand I, Sadka Y, El Riati S, Flusser H, Nachmias D, et
al: SCAPER localizes to primary cilia and its mutation affects
cilia length, causing Bardet-Biedl syndrome. Eur J Hum Genet.
27:928–940. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Khan SA, Muhammad N, Khan MA, Kamal A,
Rehman ZU and Khan S: Genetics of human Bardet-Biedl syndrome, an
updates. Clin Genet. 90:3–15. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Niederlova V, Modrak M, Tsyklauri O,
Huranova M and Stepanek O: Meta-analysis of genotype-phenotype
associations in Bardet-Biedl syndrome uncovers differences among
causative genes. Hum mutat. 40:2068–2087. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
M'Hamdi O, Ouertani I, Maazoul F and
Chaabouni-Bouhamed H: Prevalence of bardet-biedl syndrome in
tunisia. J Community Genet. 2:97–99. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Farag TI and Teebi AS: High incidence of
Bardet Biedl syndrome among the Bedouin. Clin Genet. 36:463–464.
1989.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Farag TI and Teebi AS: Bardet-Biedl and
laurence-moon syndromes in a mixed arab population. Clin Genet.
33:78–82. 1988.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Abu Safieh L, Aldahmesh MA, Shamseldin H,
Hashem M, Shaheen R, Alkuraya H, Al Hazzaa SA, Al-Rajhi A and
Alkuraya FS: Clinical and molecular characterisation of
Bardet-Biedl syndrome in consanguineous populations: The power of
homozygosity mapping. J Med Genet. 47:236–241. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Sathya Priya C, Sen P, Umashankar V, Gupta
N, Kabra M, Kumaramanickavel G, Stoetzel C, Dollfus H and Sripriya
S: Mutation spectrum in BBS genes guided by homozygosity mapping in
an Indian cohort. Clin Genet. 87:161–166. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Katsanis N, Eichers ER, Ansley SJ, Lewis
RA, Kayserili H, Hoskins BE, Scambler PJ, Beales PL and Lupski JR:
BBS4 is a minor contributor to Bardet-Biedl syndrome and may also
participate in triallelic inheritance. Am J Hum Genet. 71:22–29.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Katsanis N: The oligogenic properties of
Bardet-Biedl syndrome. Hum Mol Genet. 13:R65–R71. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Katsanis N, Ansley SJ, Badano JL, Eichers
ER, Lewis RA, Hoskins BE, Scambler PJ, Davidson WS, Beales PL and
Lupski JR: Triallelic inheritance in Bardet-Biedl syndrome, a
Mendelian recessive disorder. Science. 293:2256–2259.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Davis EE, Zhang Q, Liu Q, Diplas BH, Davey
LM, Hartley J, Stoetzel C, Szymanska K, Ramaswami G, Logan CV, et
al: TTC21B contributes both causal and modifying alleles across the
ciliopathy spectrum. Nat Genet. 43:189–196. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Badano JL, Leitch CC, Ansley SJ,
May-Simera H, Lawson S, Lewis RA, Beales PL, Dietz HC, Fisher S and
Katsanis N: Dissection of epistasis in oligogenic Bardet-Biedl
syndrome. Nature. 439:326–330. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Lindstrand A, Frangakis S, Carvalho CM,
Richardson EB, McFadden KA, Willer JR, Pehlivan D, Liu P,
Pediaditakis IL, Sabo A, et al: Copy-number variation contributes
to the mutational load of bardet-biedl syndrome. Am J Hum Genet.
99:318–336. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Delvallée C, Nicaise S, Antin M, Leuvrey
AS, Nourisson E, Leitch CC, Kellaris G, Stoetzel C, Geoffroy V,
Scheidecker S, et al: A BBS1 SVA F retrotransposon insertion is a
frequent cause of Bardet-Biedl syndrome. Clin Genet. 99:318–324.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Shaheen R, Szymanska K, Basu B, Patel N,
Ewida N, Faqeih E, Al Hashem A, Derar N, Alsharif H, Aldahmesh MA,
et al: Characterizing the morbid genome of ciliopathies. Genome
Biol. 17(242)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
World Medical Association Declaration of
Helsinki. Ethical principles for medical research involving human
subjects. JAMA. 310:2191–2194. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Li H and Durbin R: Fast and accurate short
read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics.
25:1754–1760. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Poplin R, Ruano-Rubio V, DePristo M,
Fennell TJ, Carneiro MO, Van der Auwera GA, Kling DE, Gauthier LD,
Levy-Moonshine A, Roazen D, et al: Scaling accurate genetic variant
discovery to tens of thousands of samples. bioRxiv: doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/201178.
|
|
59
|
DePristo MA, Banks E, Poplin R, Garimella
KV, Maguire JR, Hartl C, Philippakis AA, del Angel G, Rivas MA,
Hanna M, et al: A framework for variation discovery and genotyping
using next-generation DNA sequencing data. Nat Genet. 43:491–498.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
McKenna A, Hanna M, Banks E, Sivachenko A,
Cibulskis K, Kernytsky A, Garimella K, Altshuler D, Gabriel S, Daly
M and DePristo MA: The Genome Analysis Toolkit: A MapReduce
framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome
Res. 20:1297–1303. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Cingolani P, Platts A, Wang le L, Coon M,
Nguyen T, Wang L, Land SJ, Lu X and Ruden DM: A program for
annotating and predicting the effects of single nucleotide
polymorphisms, SnpEff: SNPs in the genome of Drosophila
melanogaster strain w1118; iso-2; iso-3. Fly (Austin). 6:80–92.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Robinson JT, Thorvaldsdóttir H, Winckler
W, Guttman M, Lander ES, Getz G and Mesirov JP: Integrative
genomics viewer. Nat Biotechnol. 29:24–26. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Richards S, Aziz N, Bale S, Bick D, Das S,
Gastier-Foster J, Grody WW, Hegde M, Lyon E, Spector E, et al:
Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence
variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American College
of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular
Pathology. Genet Med. 17:405–424. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Stoetzel C, Muller J, Laurier V, Davis EE,
Zaghloul NA, Vicaire S, Jacquelin C, Plewniak F, Leitch CC, Sarda
P, et al: Identification of a novel BBS gene (BBS12) highlights the
major role of a vertebrate-specific branch of chaperonin-related
proteins in Bardet-Biedl syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 80:1–11.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Katsanis N, Beales PL, Woods MO, Lewis RA,
Green JS, Parfrey PS, Ansley SJ, Davidson WS and Lupski JR:
Mutations in MKKS cause obesity, retinal dystrophy and renal
malformations associated with Bardet-Biedl syndrome. Nat Genet.
26:67–70. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Stoetzel C, Laurier V, Davis EE, Muller J,
Rix S, Badano JL, Leitch CC, Salem N, Chouery E, Corbani S, et al:
BBS10 encodes a vertebrate-specific chaperonin-like protein and is
a major BBS locus. Nat Genet. 38:521–524. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Mukherjee K and Brocchieri L: Ancient
origin of chaperonin gene paralogs involved in ciliopathies. J
Phylogenetics Evol Biol. 1(107)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Billingsley G, Bin J, Fieggen KJ, Duncan
JL, Gerth C, Ogata K, Wodak SS, Traboulsi EI, Fishman GA, Paterson
A, et al: Mutations in chaperonin-like BBS genes are a major
contributor to disease development in a multiethnic Bardet-Biedl
syndrome patient population. J Med Genet. 47:453–463.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Castro-Sánchez S, Álvarez-Satta M, Cortón
M, Guillén E, Ayuso C and Valverde D: Exploring genotype-phenotype
relationships in Bardet-Biedl syndrome families. J Med Genet.
52:503–513. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Iurian SI, Arts H, Brunner H and Fintina
D: Bardet-biedl Syndrome-case presentation. Romanian J Pediatrics.
64:289–292. 2015.
|
|
71
|
Manara E, Paolacci S, D'Esposito F, Abeshi
A, Ziccardi L, Falsini B, Colombo L, Iarossi G, Pilotta A, Boccone
L, et al: Mutation profile of BBS genes in patients with
Bardet-Biedl syndrome: An Italian study. Ital J Pediatr.
45(72)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|