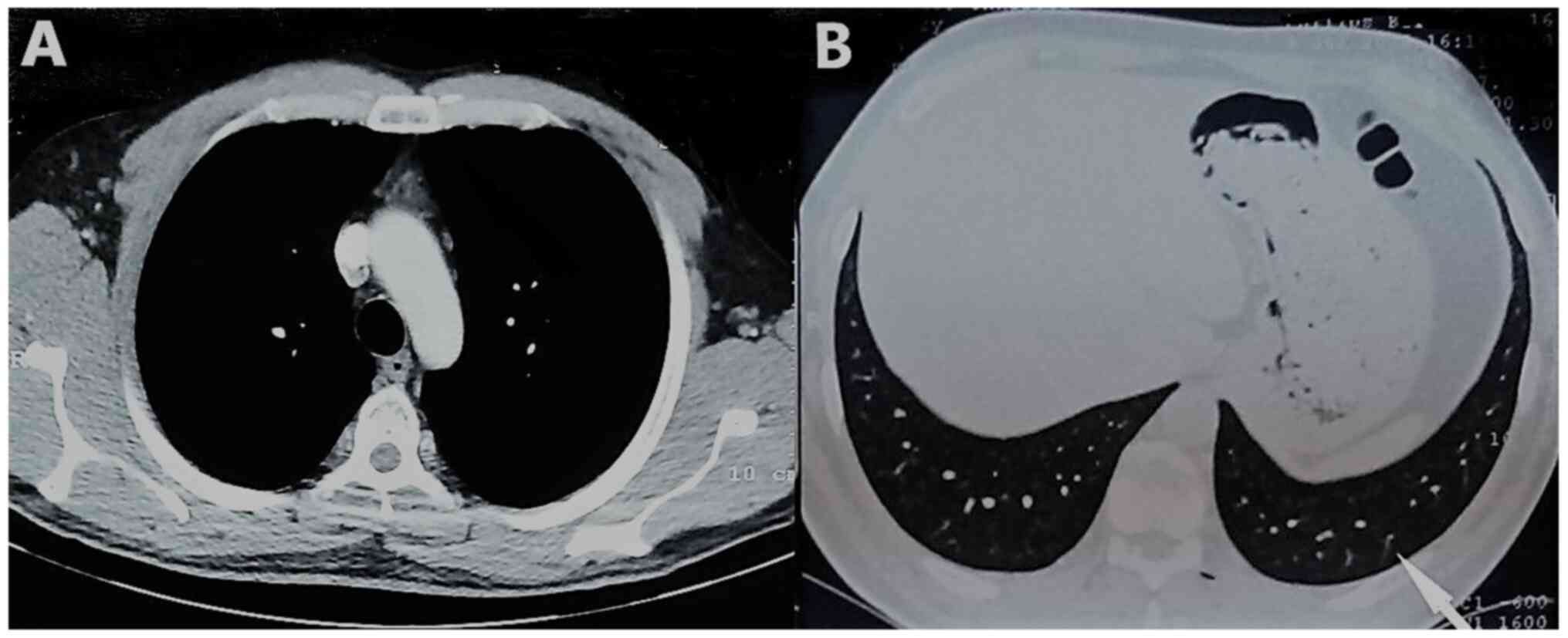
Spandidos Publications style
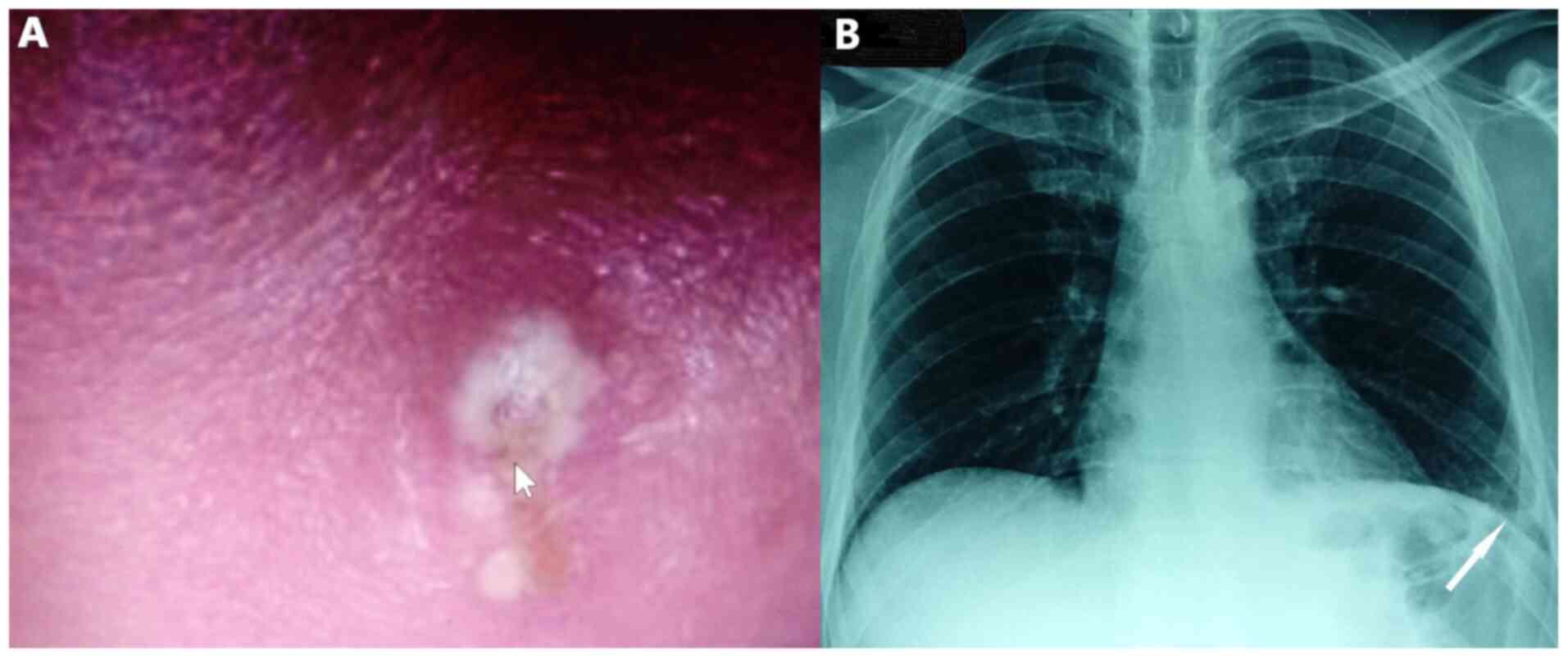
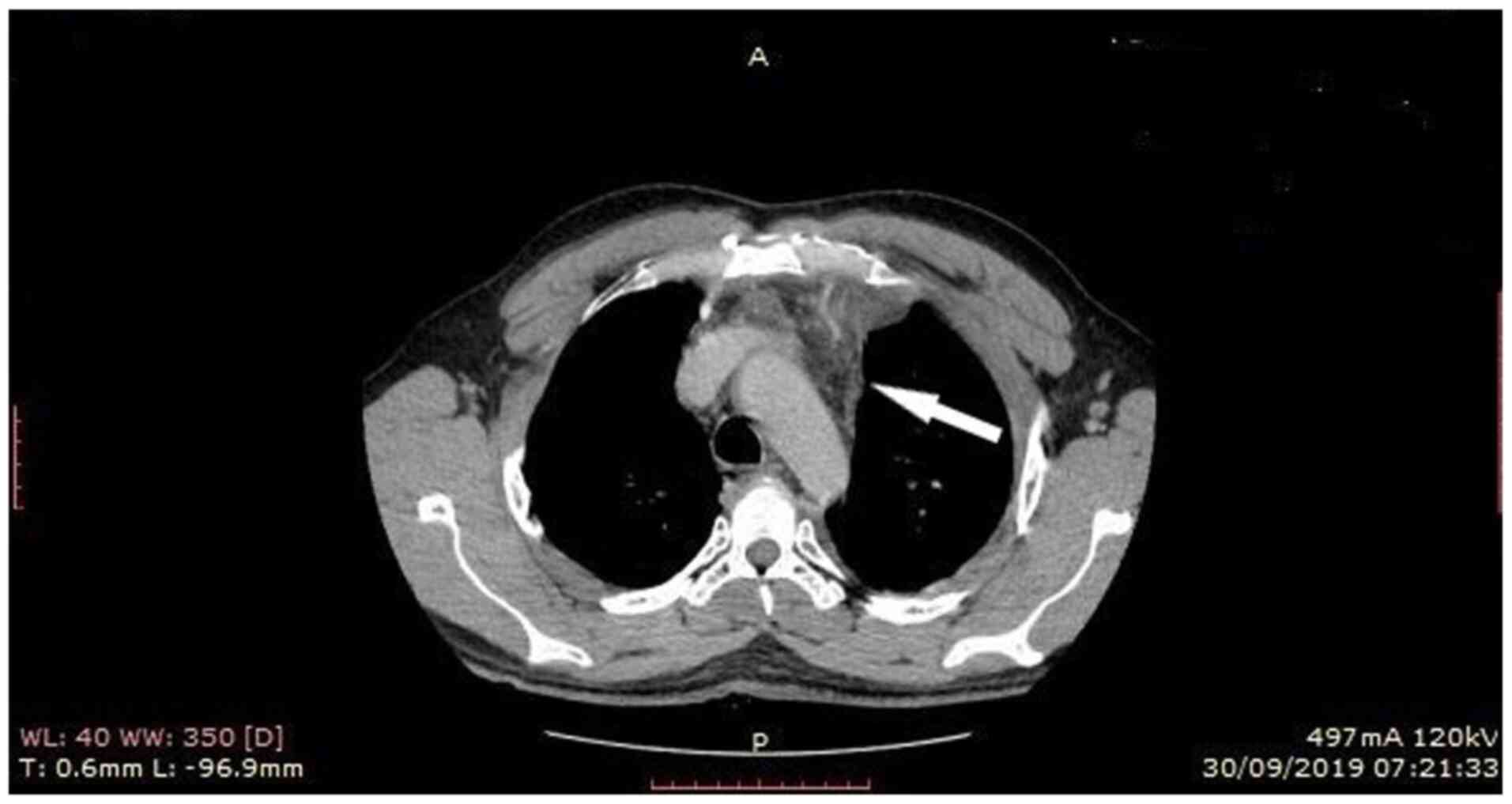
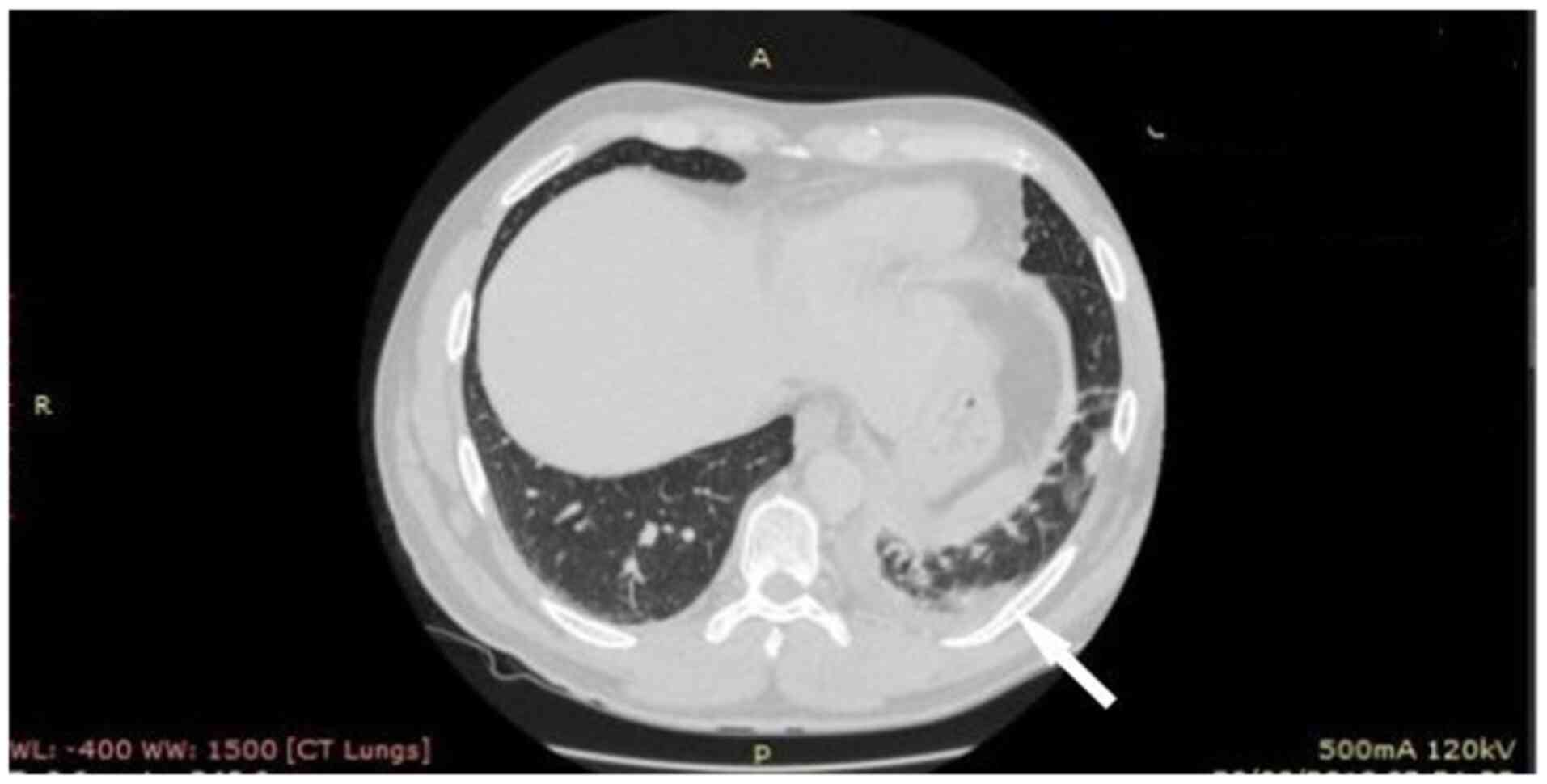
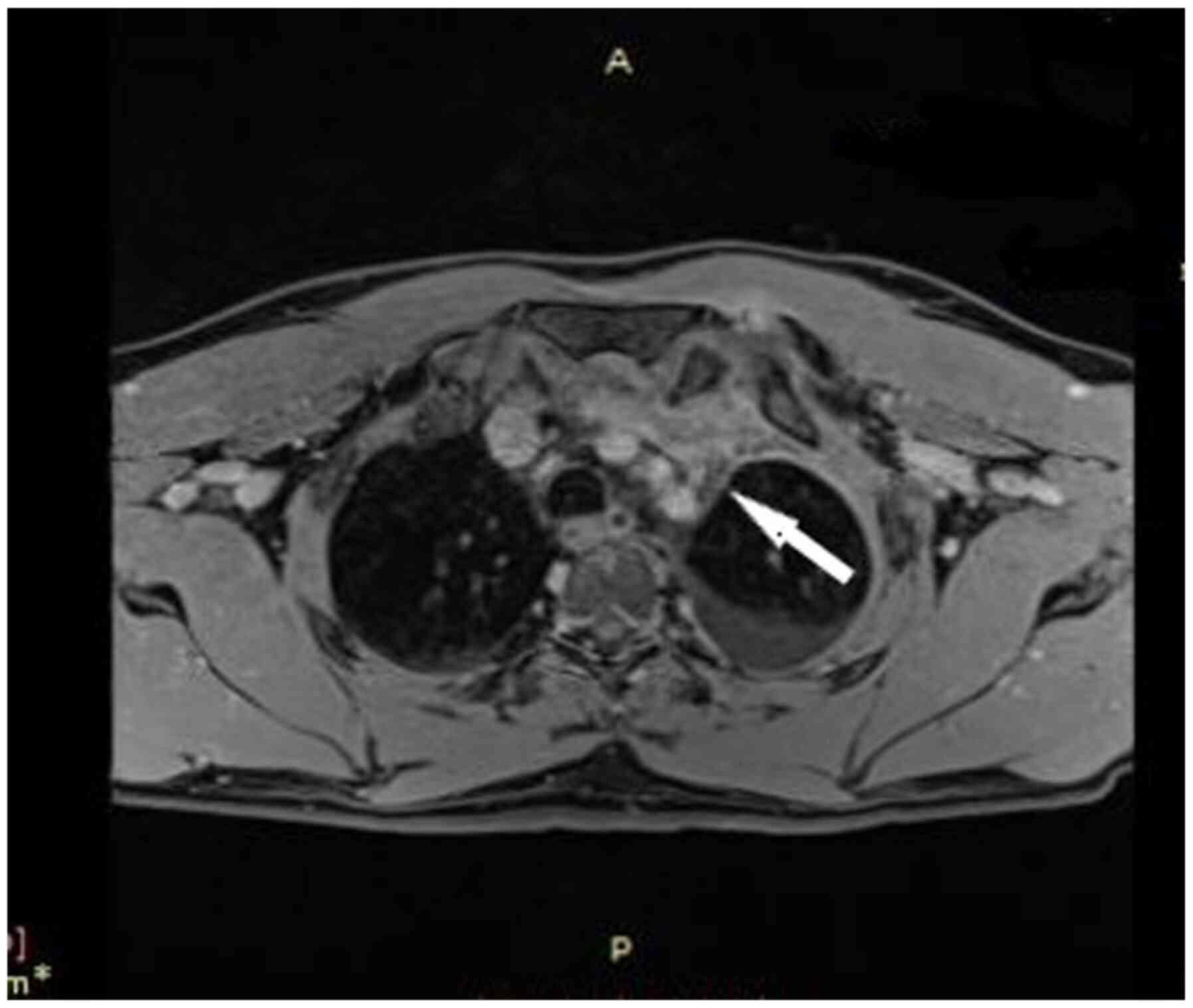
Mantzouranis K, Georgakopoulou VE, Mermigkis D, Damaskos C, Garmpis N, Papalexis P, Gkoufa A, Drossos P, Chlapoutakis S, Garmpi A, Garmpi A, et al: <em>Staphylococcus aureus</em> mediastinitis following a skin infection in a non‑immunocompromised patient: A case report. Biomed Rep 15: 104, 2021.
APA
Mantzouranis, K., Georgakopoulou, V.E., Mermigkis, D., Damaskos, C., Garmpis, N., Papalexis, P. ... Tsiafaki, X. (2021). <em>Staphylococcus aureus</em> mediastinitis following a skin infection in a non‑immunocompromised patient: A case report. Biomedical Reports, 15, 104. https://doi.org/10.3892/br.2021.1480
MLA
Mantzouranis, K., Georgakopoulou, V. E., Mermigkis, D., Damaskos, C., Garmpis, N., Papalexis, P., Gkoufa, A., Drossos, P., Chlapoutakis, S., Garmpi, A., Sklapani, P., Trakas, N., Tsiafaki, X."<em>Staphylococcus aureus</em> mediastinitis following a skin infection in a non‑immunocompromised patient: A case report". Biomedical Reports 15.6 (2021): 104.
Chicago
Mantzouranis, K., Georgakopoulou, V. E., Mermigkis, D., Damaskos, C., Garmpis, N., Papalexis, P., Gkoufa, A., Drossos, P., Chlapoutakis, S., Garmpi, A., Sklapani, P., Trakas, N., Tsiafaki, X."<em>Staphylococcus aureus</em> mediastinitis following a skin infection in a non‑immunocompromised patient: A case report". Biomedical Reports 15, no. 6 (2021): 104. https://doi.org/10.3892/br.2021.1480