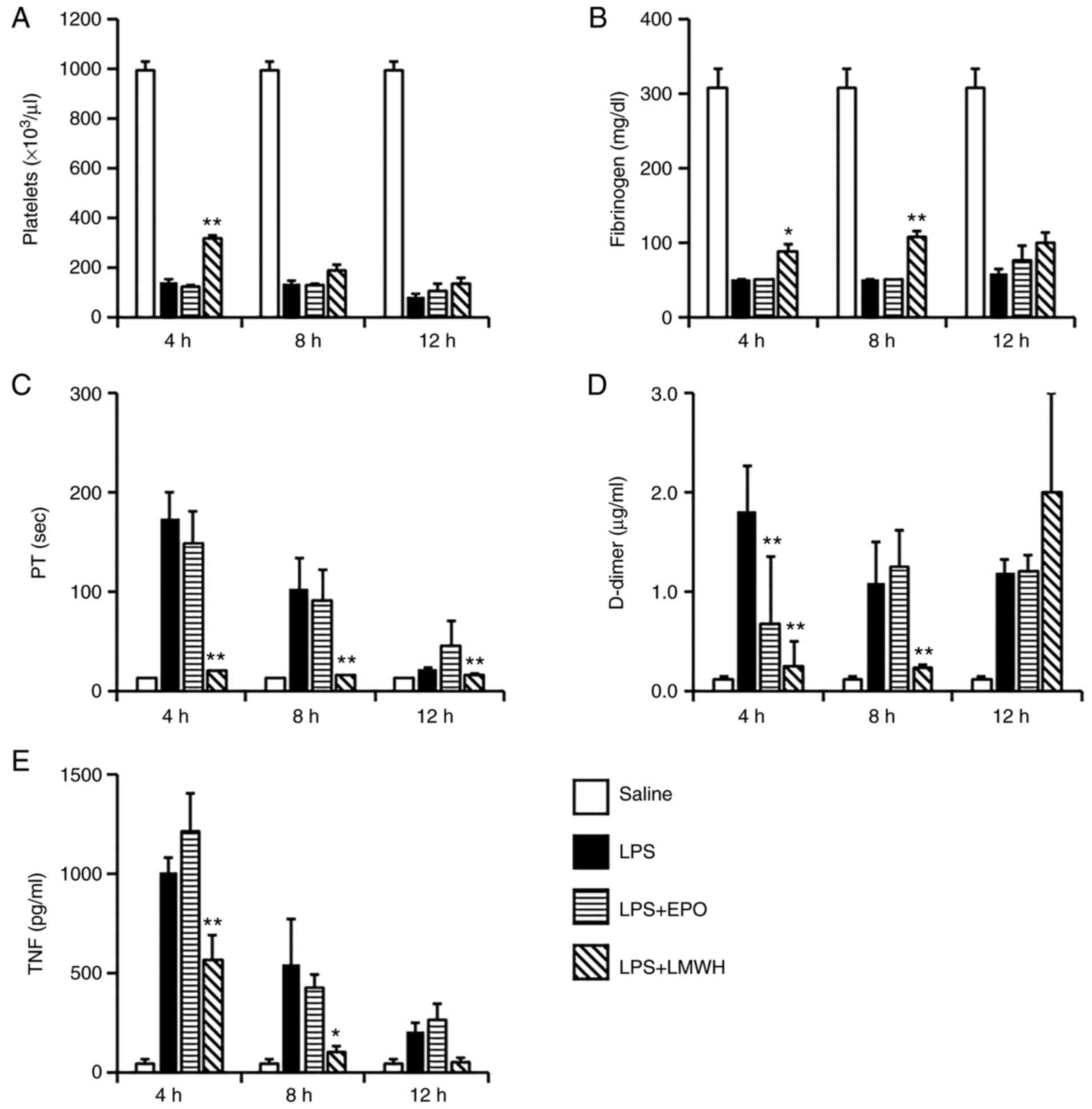
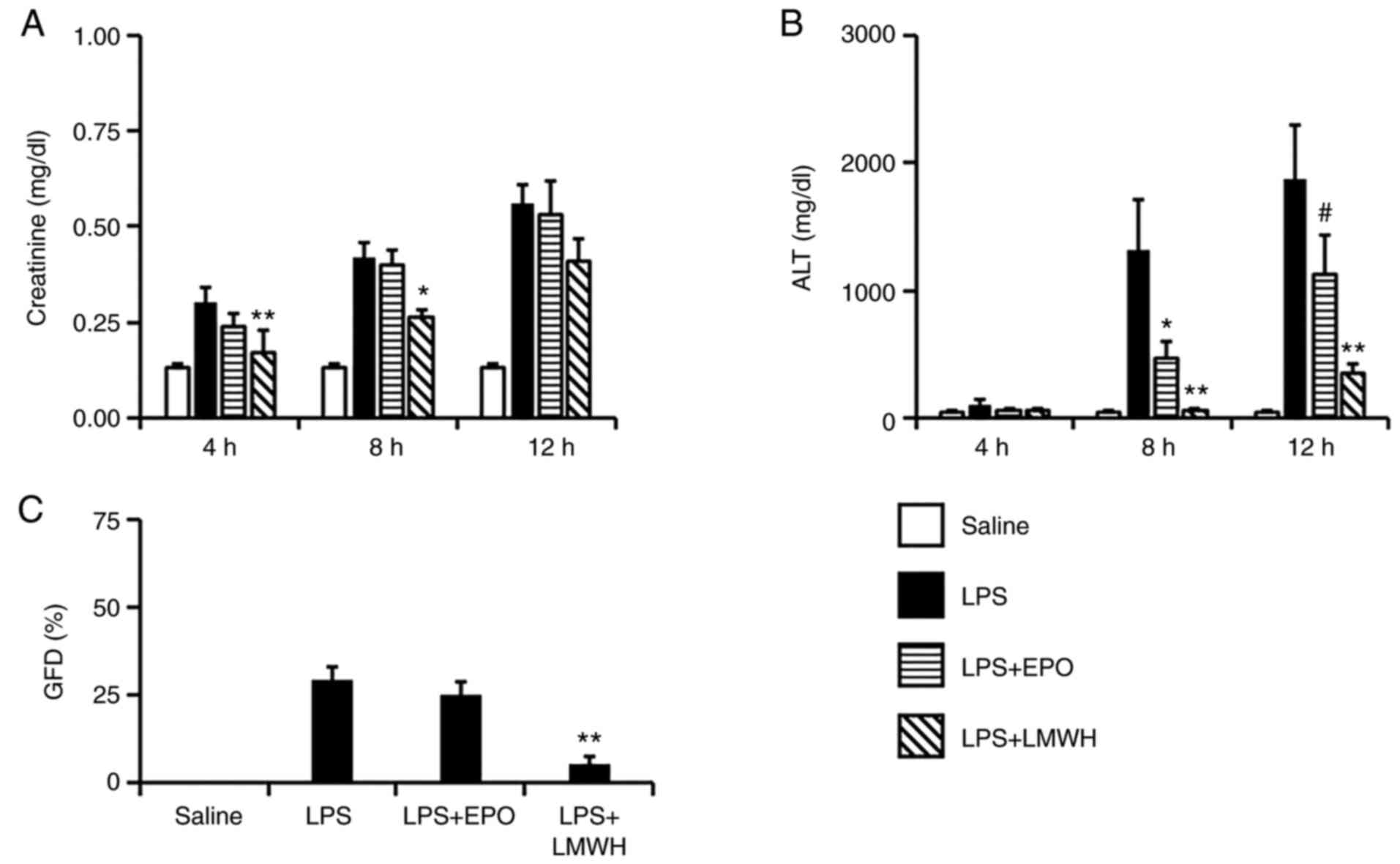
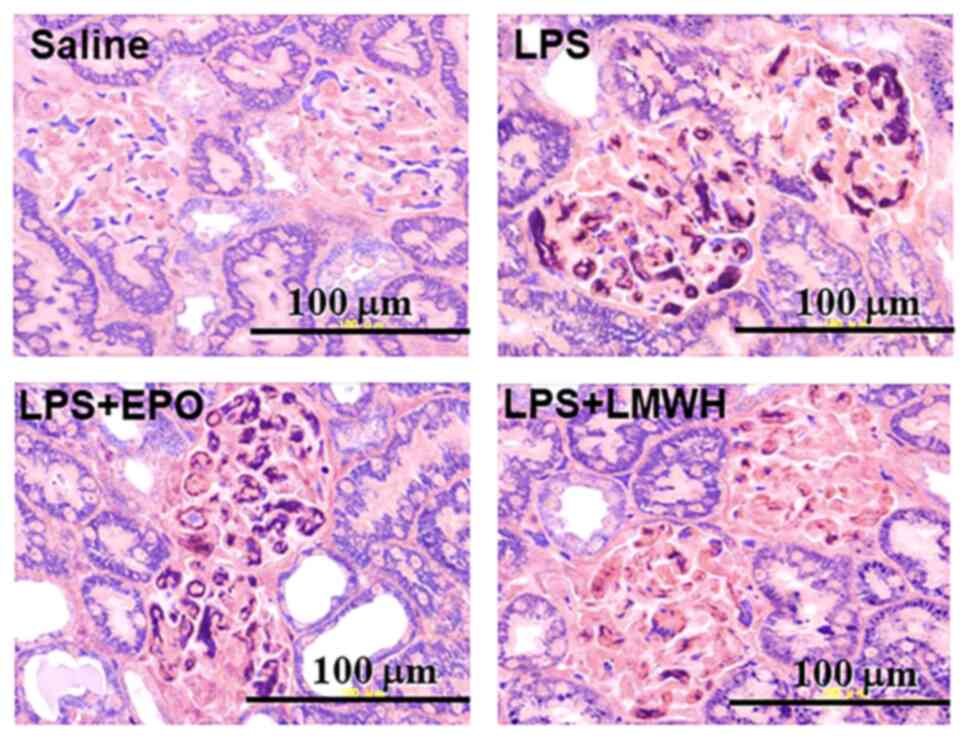
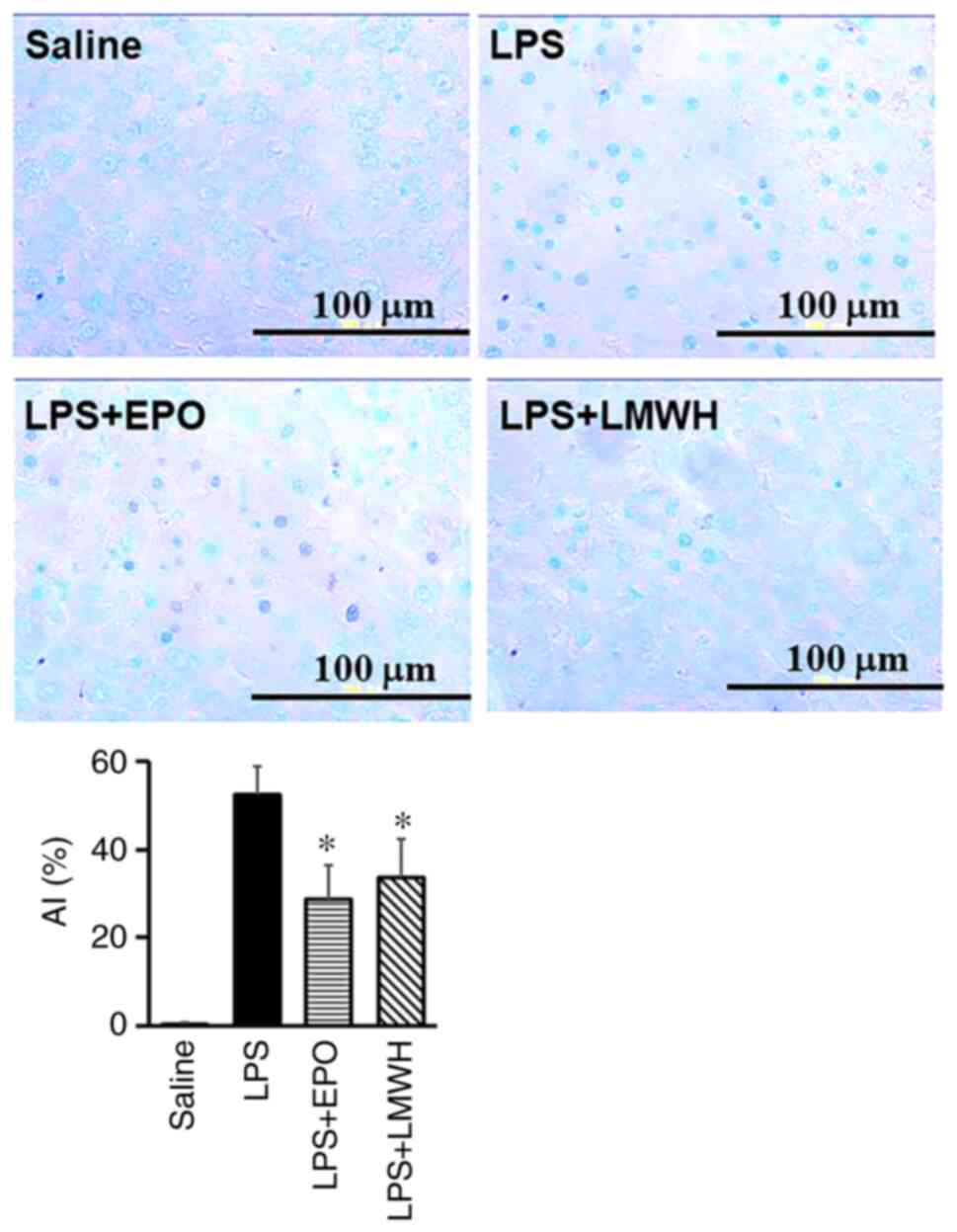
|
1
|
Levi M and Ten Cate H: Disseminated
intravascular coagulation. N Engl J Med. 341:586–592.
1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Adelborg K, Larsen JB and Hvas AM:
Disseminated intravascular coagulation: Epidemiology, biomarkers,
and management. Br J Haematol. 192:803–818. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Asakura H: Classifying types of
disseminated intravascular coagulation: Clinical and animal models.
J Intensive Care. 2(20)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Angus DC and van der Poll T: Severe sepsis
and septic shock. N Engl J Med. 369:840–851. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Brooks MB, Turk JR, Guerrero A, Narayanan
PK, Nolan JP, Besteman EG, Wilson DW, Thomas RA, Fishman CE,
Thompson KL, et al: Non-lethal endotoxin injection: A rat model of
hypercoagulability. PLoS One. 12(e0169976)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Schöchl H, Solomon C, Schulz A, Voelcke W,
Hanke A, Van Griensven M, Redl H and Bahrami S: Thromboelastometry
(TEM) findings in disseminated intravascular coagulation in a pig
model of endotoxinemia. Mol Med. 17:266–272. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Schoergenhofer C, Schwameis M, Gelbenegger
G, Buchtele N, Thaler B, Mussbacher M, Schabbauer G, Wojta J,
Jilma-Stohlawetz P and Jilma B: Inhibition of Protease-activated
receptor (PAR1) reduces activation of the endothelium, coagulation,
fibrinolysis and inflammation during human endotoxemia. Thromb
Haemost. 118:1176–1184. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Levi M and van der Poll T: Coagulation and
sepsis. Thromb Res. 149:38–44. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Suresh S, Rajvanshi PK and Noguchi CT: The
Many Facets of erythropoietin physiologic and metabolic response.
Front Physiol. 10(1534)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Bonomini M, Del Vecchio L, Sirolli V and
Locatelli F: New Treatment approaches for the anemia of CKD. Am J
Kidney Dis. 67:133–142. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Singh AK, Szczech L, Tang KL, Barnhart H,
Sapp S, Wolfson M and Reddan D: CHOIR Investigators. Correction of
anemia with epoetin alfa in chronic kidney disease. N Engl J Med.
355:2085–2098. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Yang J, Zhou J, Wang X, Wang X, Ji L, Wang
S, Chen X and Yang L: Erythropoietin attenuates experimental
contrast-induced nephrology: A role for the janus Kinase 2/Signal
transducer and activator of transcription 3 signaling pathway.
Front Med (Lausanne). 8(634882)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Golmohammadi MG, Banaei S, Nejati K and
Chinifroush-Asl MM: Vitamin D3 and erythropoietin protect against
renal ischemia-reperfusion injury via heat shock protein 70 and
microRNA-21 expression. Sci Rep. 10(20906)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Thiemermann C: Beneficial effects of
erythropoietin in preclinical models of shock and organ failure.
Crit Care. 11(132)2007.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Silva I, Alipio C, Pinto R and Mateus V:
Potential anti-inflammatory effect of erythropoietin in
non-clinical studies in vivo: A systematic review. Biomed
Pharmacother. 139(111558)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Li K, Liu TX, Li JF, Ma YR, Liu ML, Wang
YQ, Wu R, Li B, Shi LZ and Chen C: rhEPO inhibited cell apoptosis
to alleviate acute kidney injury in sepsis by AMPK/SIRT1 activated
autophagy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 517:557–565. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Tu Q, Zhu Y, Yuan Y, Guo L, Liu L, Yao L,
Zou Y, Li J and Chen F: Gypenosides inhibit inflammatory response
and apoptosis of endothelial and epithelial cells in LPS-Induced
ALI: A study based on bioinformatic analysis and in vivo/vitro
experiments. Drug Des Devel Ther. 15:289–303. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Duan H, Zhang Q, Liu J, Li R, Wang D, Peng
W and Wu C: Suppression of apoptosis in vascular endothelial cell,
the promising way for natural medicines to treat atherosclerosis.
Pharmacol Res. 168(105599)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Bombeli T, Karsan A, Tait JF and Harlan
JM: Apoptotic vascular endothelial cells become procoagulant.
Blood. 89:2429–2442. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Toltl LJ, Swystun LL, Pepler L and Liaw
PC: Protective effects of activated protein C in sepsis. Thromb
Haemost. 100:582–592. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Woo S, Krzyzanski W and Jusko WJ:
Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic modeling of recombinant human
erythropoietin after intravenous and subcutaneous administration in
rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 319:1297–1306. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Asakura H, Sano Y, Yoshida T, Omote M,
Ontachi Y, Mizutani T, Yamazaki M, Morishita E, Takami A, Miyamoto
K and Nakao S: Beneficial effect of low-molecular-weight heparin
against lipopolysaccharide-induced disseminated intravascular
coagulation in rats is abolished by coadministration of tranexamic
acid. Intensive Care Med. 30:1950–1955. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Asakura H, Sano Y, Omote M, Yoshida T,
Ontachi Y, Mizutani T, Kaneda M, Yamazaki M, Morishita E, Takami A,
et al: Significance of decreased plasma D-dimer levels following
lipopolysaccharide-induced disseminated intravascular coagulation
in rats. Int J Hematol. 79:394–399. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Koroglu TF, Yilmaz O, Ozer E, Baskin H,
Gokmen N, Kumral A, Duman M and Ozkan H: Erythropoietin attenuates
lipopolysaccharide-induced splenic and thymic apoptosis in rats.
Physiol Res. 55:309–316. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhou HB, Chen JM, Cai JT, Du Q and Wu CN:
Anticancer activity of genistein on implanted tumor of human SG7901
cells in nude mice. World J Gastroenterol. 14:627–631.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Colantuoni A, Martini R, Caprari P,
Ballestri M, Capecchi PL, Gnasso A, Lo Presti R, Marcoccia A, Rossi
M and Caimi G: COVID-19 Sepsis and microcirculation dysfunction.
Front Physiol. 11(747)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Okajima K: Regulation of inflammatory
responses by natural anticoagulants. Immunol Rev. 184:258–274.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Suga Y, Kubo A, Katsura H, Staub Y,
Tashiro K, Yamada S, Morishita E and Asakura H: Detailed
exploration of pathophysiology involving inflammatory status and
bleeding symptoms between lipopolysaccharide- and tissue
factor-induced disseminated intravascular coagulation in rats. Int
J Hematol. 114:172–178. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Stoyanoff TR, Todaro JS, Aguirre MV,
Zimmermann MC and Brandan NC: Amelioration of
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute kidney injury by erythropoietin:
Involvement of mitochondria-regulated apoptosis. Toxicology.
318:13–21. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Le Minh K, Klemm K, Abshagen K, Eipel C,
Menger MD and Vollmar B: Attenuation of inflammation and apoptosis
by pre- and posttreatment of darbepoetin-alpha in acute liver
failure of mice. Am J Pathol. 170:1954–1963. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Deepa PR and Varalakshmi P: Influence of a
low-molecular-weight heparin derivative on the nitric oxide levels
and apoptotic DNA damage in adriamycin-induced cardiac and renal
toxicity. Toxicology. 217:176–183. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Zhang W, Tian Y, Gao Q, Li X, Li Y, Zhang
J, Yao C, Wang Y, Wang H, Zhao Y, et al: Inhibition of apoptosis
reduces diploidization of haploid mouse embryonic stem cells during
differentiation. Stem Cell Reports. 15:185–197. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Wang H, Zhang W, Gao Q, Cao X, Li Y, Li X,
Min Z, Yu Y, Guo Y and Shuai L: Extractive from Hypericum ascyron L
promotes serotonergic neuronal differentiation in vitro. Stem Cell
Res. 31:42–50. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|