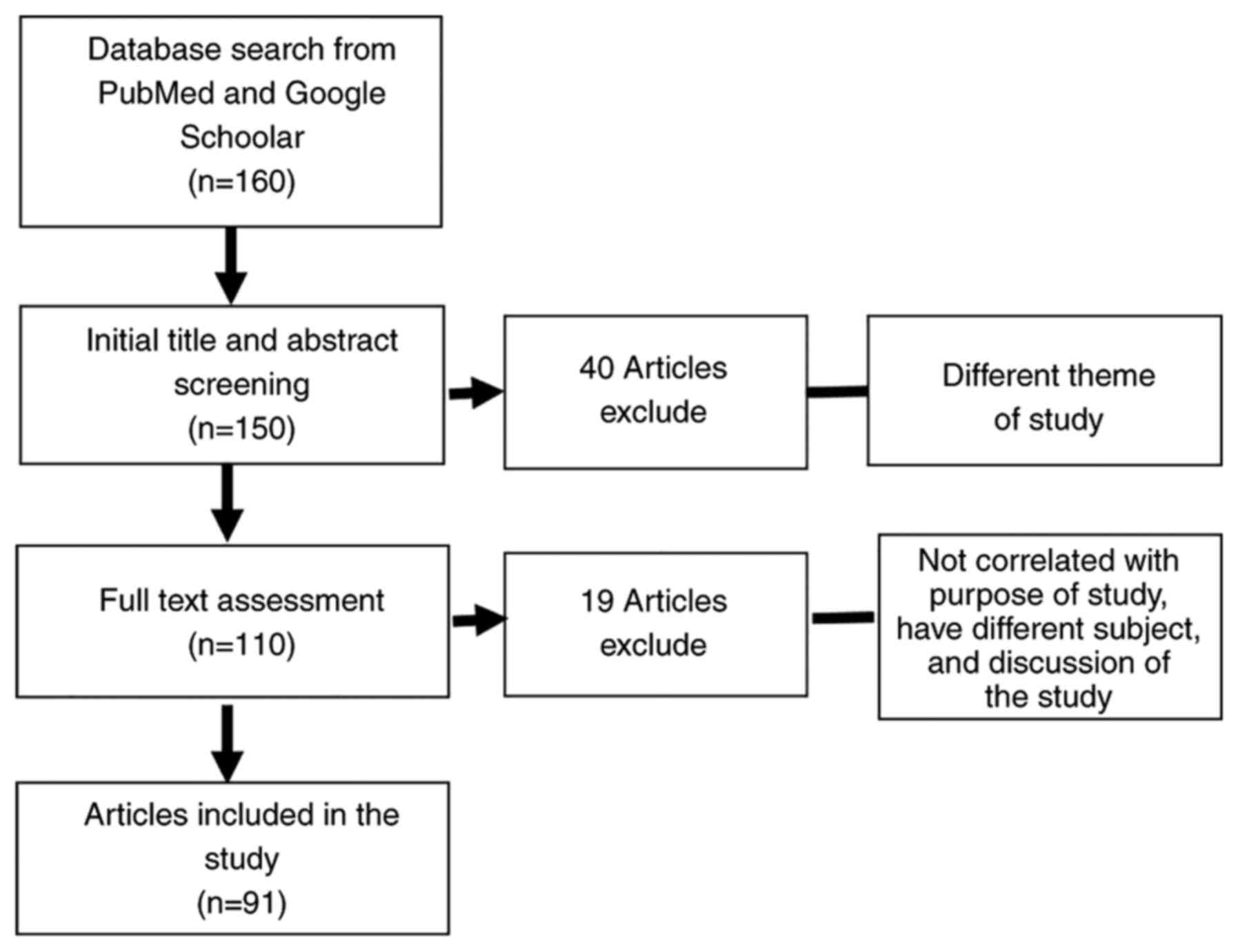
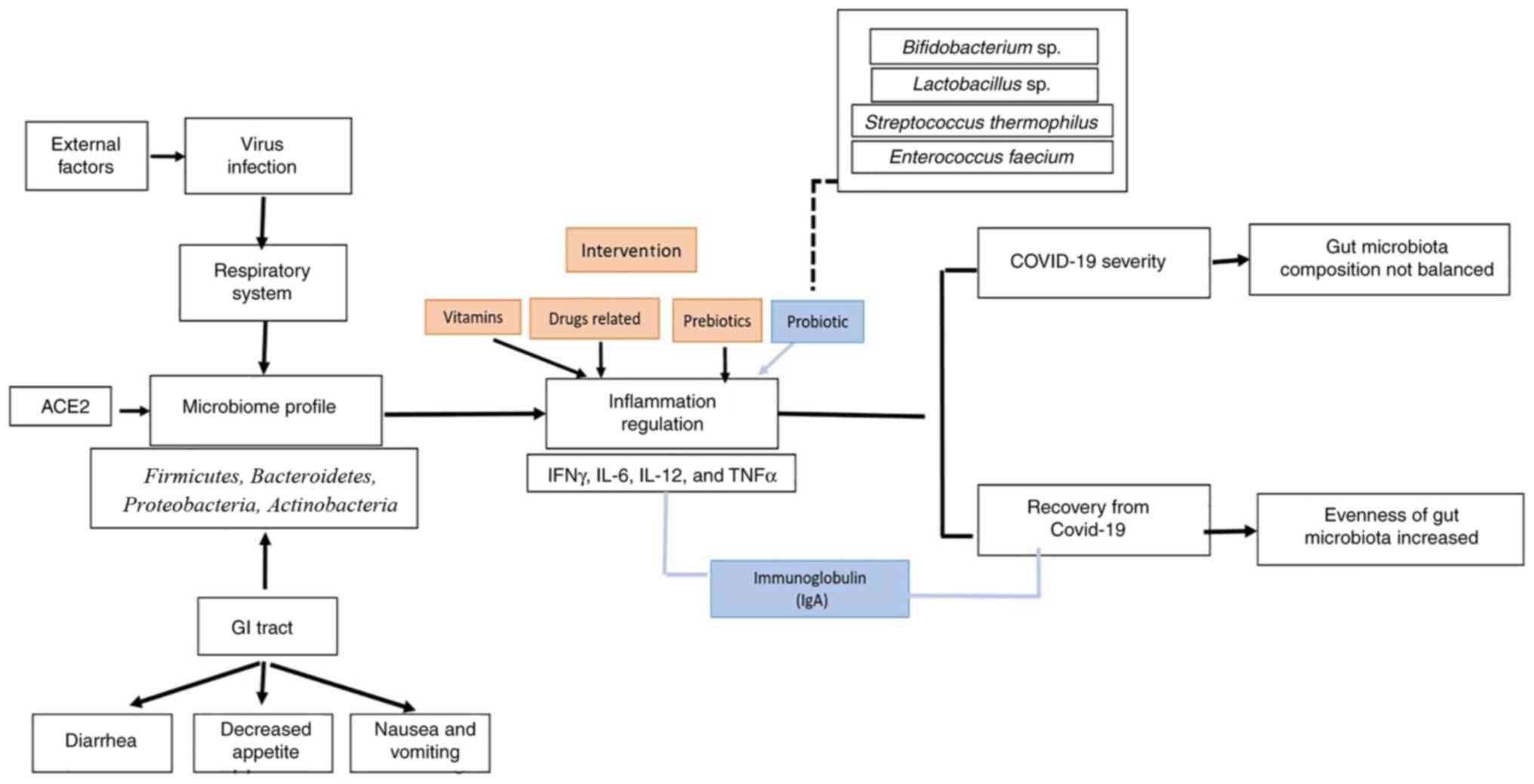
|
1
|
Chan JFW, Yuan S, Kok KH, To KK, Chu H,
Yang J, Xing F, Liu J, Yip CC, Poon RW, et al: A familial cluster
of pneumonia associated with the 2019 novel coronavirus indicating
person-to-person transmission: A study of a family cluster. Lancet.
395:514–523. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Kang MK, Kim KO, Kim MC, Cho JH, Kim SB,
Park JG, Kim KH, Lee SH, Jang BI and Kim TN: Clinical
characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 patients with diarrhea
in Daegu. Korean J Intern Med. 35:1261–1269. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Tariq R, Saha S, Furqan F, Hassett L,
Pardi D and Khanna S: Prevalence and Mortality of COVID-19 patients
with gastrointestinal symptoms: A systematic review and
Meta-analysis. Mayo Clin Proc. 95:1632–1648. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Graham MS, Sudre CH, May A, Antonelli M,
Murray B, Varsavsky T, Kläser K, Canas LS, Molteni E, Modat M, et
al: Changes in symptomatology, reinfection, and transmissibility
associated with the SARS-CoV-2 variant B.1.1.7: An ecological
study. Lancet Public Heal. 6:e335–e345. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Cascella M, Rajnik M, Cuomo A, Dulebohn SC
and Di Napoli R: Features, evaluation and treatment coronavirus
(COVID-19. Review from StatPearls Publishing, Treasure Island (FL),
10 Mar, 2020.
|
|
6
|
Pan L, Mu M, Yang P, Sun Y, Wang R, Yan J,
Li P, Hu B, Wang J, Hu C, et al: Clinical characteristics of
COVID-19 patients with digestive symptoms in Hubei, China: A
descriptive, cross-sectional, multicenter study. Am J
Gastroenterol. 115:766–773. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Nogueira-de-Almeida CA, Del Ciampo LA,
Ferraz IS, Del Ciampo IRL, Contini AA and Ued FDV: COVID-19 and
obesity in childhood and adolescence: A clinical review. J Pediatr
(Rio J). 95:546–558. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Yang J, Hu J and Zhu C: Obesity aggravates
COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Med Virol.
93:257–261. 2021.
|
|
9
|
Gao F, Zheng KI, Wang XB, Sun QF, Pan KH,
Wang TY, Chen YP, Targher G, Byrne CD, George J and Zheng MH:
Obesity is a risk factor for greater COVID-19 severity. Diabetes
Care. 43:e72–e74. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Al-Salameh A, Lanoix JP, Bennis Y,
Andrejak C, Brochot E, Deschasse G, Dupont H, Goeb V, Jaureguy M,
Lion S, et al: Characteristics and outcomes of COVID-19 in
hospitalized patients with and without diabetes. Diabetes Metab Res
Rev. 37(e3388)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Wang F, Yang Y, Dong K, Yan Y, Zhang S,
Ren H, Yu X and Shi X: Clinical characteristics of 28 patients with
Diabetes and COVID-19 in Wuhan, China. Endocr Pract. 26:668–674.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Li J, Wang X, Chen J, Zuo X, Zhang H and
Deng A: COVID-19 infection may cause ketosis and ketoacidosis.
Diabetes Obes Metab. 22:1935–1941. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Khan M, Mathew BJ, Gupta P, Garg G,
Khadanga S, Vyas AK and Singh AK: Gut dysbiosis and il-21 response
in patients with severe covid-19. Microorganisms.
9(1292)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Zuo T, Zhang F, Lui GCY, Yeoh YK, Li AYL,
Zhan H, Wan Y, Chung ACK, Cheung CP, Chen N, et al: Alterations in
gut microbiota of patients with COVID-19 during time of
hospitalization. Gastroenterology. 159:944–955.e8. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Kim HN, Joo EJ, Lee CW, Ahn KS, Kim HL,
Park Dong-II and Park SK: Reversion of gut microbiota during the
recovery Phase in patients with asymptomatic or mild Covid-19:
Longitudinal study. Microorganisms. 9(1237)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Moreira-Rosário A, Marques C, Pinheiro H,
Araújo JR, Ribeiro P, Rocha R, Mota I, Pestana D, Ribeiro R,
Pereira A, et al: Gut microbiota diversity and C-reactive protein
are predictors of disease severity in COVID-19 patients. Front
Microbiol. 12(705020)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Ren Z, Wang H, Cui G, Lu H, Wang L, Luo H,
Chen X, Ren H, Sun R, Liu W, et al: Alterations in the human oral
and gut microbiomes and lipidomics in COVID-19. Gut. 70:1253–1265.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Groves HT, Higham SL, Moffatt MF, Cox MJ
and Tregoning JS: Respiratory viral infection alters the gut
microbiota by inducing Inappetence. MBio. 11:e03236–19.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Aljabr W, Alruwaili M, Penrice-Randal R,
Alrezaihi A, Harrison AJ, Ryan Y, Bentley E, Jones B, Alhatlani BY,
AlShahrani D, et al: Amplicon and Metagenomic Analysis of Middle
East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS) Coronavirus and the Microbiome in
Patients with Severe MERS. mSphere. 6(e0021921)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Raman R, Patel KJ and Ranjan K: COVID-19:
Unmasking emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants, vaccines and therapeutic
strategies. Biomolecules. 11(993)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Trypsteen W, Van Cleemput J, Snippenberg
WV, Gerlo S and Vandekerckhove L: On the whereabouts of SARS-CoV-2
in the human body: A systematic review. PLoS Pathog.
16(e1009037)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Holshue ML, DeBolt C, Lindquist S, Lofy
KH, Wiesman J, Bruce H, Spitters C, Ericson K, Wilkerson S, Tural
A, et al: First Case of 2019 novel coronavirus in the united
states. N Engl J Med. 382:929–936. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Guan WJ, Ni ZY, Hu Y, Liang WH, Ou CQ, He
JX, Liu L, Shan H, Lei CL, Hui DSC, et al: Clinical characteristics
of coronavirus disease 2019 in china. N Engl J Med. 382:1708–1720.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Sultan S, Altayar O, Siddique SM, Davitkov
P, Feuerstein JD, Lim JK, Falck-Ytter Y and El-Serag HB: AGA
Institute. Electronic address: simpleewilson@gastro.org. AGA
institute rapid review of the gastrointestinal and liver
manifestations of COVID-19, Meta-analysis of international data,
and recommendations for the consultative management of patients
with COVID-19. Gastroenterology. 159:320–334.e27. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Zhang J, Garrett S and Sun J:
Gastrointestinal symptoms, pathophysiology, and treatment in
COVID-19. Genes Dis. 8:385–400. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Xiao F, Tang M, Zheng X, Liu Y, Li X and
Shan H: Evidence for gastrointestinal infection of SARS-CoV-2.
Gastroenterology. 158:1831–1833.e3. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Clemente-Suárez VJ, Ramos-Campo DJ,
Mielgo-Ayuso J, Dalamitros AA, Nikolaidis PA, Hormeño-Holgado A and
Tornero-Aguilera JF: Nutrition in the actual covid-19 pandemic. A
narrative review. Nutrients. 13(1924)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Liang X, Zhou R, Li Y, Yang L, Su M and
Lai KP: Clinical characterization and therapeutic targets of
vitamin A in patients with hepatocholangiocarcinoma and coronavirus
disease. Aging (Albany NY). 13:15785–15800. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Rajpal A, Rahimi L and Ismail-Beigi F:
Factors leading to high morbidity and mortality of COVID-19 in
patients with type 2 diabetes. J Diabetes. 12:895–908.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Penninger JM, Grant MB and Sung JJY: The
role of angiotensin converting enzyme 2 in modulating gut
microbiota, intestinal inflammation, and coronavirus infection.
Gastroenterology. 160:39–46. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Hashimoto T, Perlot T, Rehman A,
Trichereau J, Ishiguro H, Paolino M, Sigl V, Hanada T, Hanada R,
Lipinski S, et al: ACE2 links amino acid malnutrition to microbial
ecology and intestinal inflammation. Nature. 487:477–481.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Yang T, Chakraborty S, Saha P, Mell B,
Cheng X, Yeo JY, Mei X, Zhou G, Mandal J, Golonka R, et al:
Gnotobiotic rats reveal that gut microbiota regulates colonic mRNA
of Ace2, the receptor for SARS-CoV-2 Infectivity. Hypertension.
76:e1–e3. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Sánchez B, Delgado S, Blanco-Míguez A,
Lourenço A, Gueimonde M and Margolles A: Probiotics, gut
microbiota, and their influence on host health and disease. Mol
Nutr Food Res. 61(1600240)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Putignani L, Del Chierico F, Petrucca A,
Vernocchi P and Dallapiccola B: The human gut microbiota: A dynamic
interplay with the host from birth to senescence settled during
childhood. Pediatr Res. 76:2–10. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Hills RD Jr, Pontefract BA, Mishcon HR,
Black CA, Sutton SC and Theberge CR: Gut Microbiome: Profound
implications for diet and disease. Nutrients.
11(1613)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Villapol S: Gastrointestinal symptoms
associated with COVID-19: Impact on the gut microbiome. Transl Res.
226:57–69. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Lv Y, Qin X, Jia H, Chen S, Sun W and Wang
X: The association between gut microbiota composition and BMI in
Chinese male college students, as analysed by next-generation
sequencing. Br J Nutr. 122:986–995. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Wiertsema SP, van Bergenhenegouwen J,
Garssen J and Knippels LMJ: The interplay between the gut
microbiome and the immune system in the context of infectious
diseases throughout life and the role of nutrition in optimizing
treatment strategies. Nutrients. 13(886)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Mullish BH, Marchesi JR, McDonald JAK,
Pass DA, Masetti G, Michael DR, Plummer S, Jack AA, Davies TS,
Hughes TR and Wang D: Probiotics reduce self-reported symptoms of
upper respiratory tract infection in overweight and obese adults:
Should we be considering probiotics during viral pandemics? Gut
Microbes. 13:1–9. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Aktas B and Aslim B: Gut-lung axis and
dysbiosis in COVID-19. Turk J Biol. 44:265–272. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Dang AT and Marsland BJ: Microbes,
metabolites, and the gut-lung axis. Mucosal Immunol. 12:843–850.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Taco-Masias AA, Fernandez-Aristi AR,
Cornejo-Tapia A, Aguilar-Luis MA, del Valle LJ, Silva-Caso W,
Zavaleta-Gavidia V, Weilg P, Cornejo-Pacherres H, Bazán-Mayra J, et
al: Gut microbiota in hospitalized children with acute infective
gastroenteritis caused by virus or bacteria in a regional Peruvian
hospital. PeerJ. 8(e9964)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Liu B, Li M, Zhou Z, Guan X and Xiang Y:
Can we use interleukin-6 (IL-6) blockade for coronavirus disease
2019 (COVID-19)-induced cytokine release syndrome (CRS)? J
Autoimmun. 111(102452)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Zhang X, Shi L, Sun T and Guo K: Dysbiosis
of gut microbiota and its correlation with dysregulation of
cytokines in psoriasis patients. BMC Microbiol.
21(78)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Blanco-Melo D, Nilsson-Payant BE, Liu WC,
Uhl S, Hoagland D, Møller R, Jordan TX, Oishi K, Panis M, Sachs D,
et al: Imbalanced host response to SARS-CoV-2 drives development of
COVID-19. Cell. 181:1036–1045.e9. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Lin CH, Chen CC, Chiang HL, Liou JM, Chang
CM, Lu TP, Chuang EY, Tai YC, Cheng C, Lin HY and Wu MS: Altered
gut microbiota and inflammatory cytokine responses in patients with
Parkinson's disease. J Neuroinflammation. 16(129)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
He Y, Wang J, Li F and Shi Y: Main
clinical features of COVID-19 and potential prognostic and
therapeutic value of the microbiota in SARS-CoV-2 infections. Front
Microbiol. 11(1302)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Brancaccio M, Mennitti C, Gentile A,
Correale L, Buzzachera CF, Ferraris C, Montomoli C, Frisso G,
Borrelli P and Scudiero O: Effects of the covid-19 pandemic on job
activity, dietary Behaviours and physical activity habits of
university population of Naples, federico II-Italy. Int J Environ
Res Public Health. 18(1502)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Quiroga R, Nistal E, Estébanez B, Porras
D, Juárez-Fernández M, Martínez-Flórez S, García-Mediavilla MV, de
Paz JA, González-Gallego J, Sánchez-Campos S and Cuevas MJ:
Exercise training modulates the gut microbiota profile and impairs
inflammatory signaling pathways in obese children. Exp Mol Med.
52:1048–1061. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Campbell SC, Wisniewski PJ, Noji M,
McGuinness LR, Häggblom MM, Lightfoot SA, Joseph LB and Kerkhof LJ:
The effect of diet and exercise on intestinal integrity and
microbial diversity in mice. PLoS One. 11(e0150502)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Clarke SF, Murphy EF, O'Sullivan O, Lucey
AJ, Humphreys M, Hogan A, Hayes P, O'Reilly M, Jeffery IB,
Wood-Martin R, et al: Exercise and associated dietary extremes
impact on gut microbial diversity. Gut. 63:1913–1920.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Metsios GS, Moe RH and Kitas GD: Exercise
and inflammation. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol.
34(101504)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
da Silveira MP, da Silva Fagundes KK,
Bizuti MR, Starck É, Rossi RC and de Resende E Silva DT: Physical
exercise as a tool to help the immune system against COVID-19: An
integrative review of the current literature. Clin Exp Med.
21:15–28. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Singh K and Rao A: Probiotics: A potential
immunomodulator in COVID-19 infection management. Nutr Res.
87:1–12. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Lehtoranta L, Pitkäranta A and Korpela R:
Probiotics in respiratory virus infections. Eur J Clin Microbiol
Infect Dis. 33:1289–1302. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Celiberto LS, Pinto RA, Rossi EA, Vallance
BA and Cavallini DCU: Isolation and characterization of potentially
probiotic bacterial strains from mice: Proof of concept for
personalized probiotics. Nutrients. 10(1684)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Tenorio-Jiménez C, Martínez-Ramírez MJ,
Del Castillo-Codes I, Arraiza-Irigoyen C, Tercero-Lozano M, Camacho
J, Chueca N, García F, Olza J, Plaza-Díaz J, et al:
Lactobacillus reuteri V3401 reduces inflammatory biomarkers
and modifies the gastrointestinal microbiome in adults with
metabolic syndrome: The PROSIR study. Nutrients.
11(1761)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Walton GE, Gibson GR and Hunter KA:
Mechanisms linking the human gut microbiome to prophylactic and
treatment strategies for COVID-19. Br J Nutr. 126:219–227.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
McNulty NP, Yatsunenko T, Hsiao A, Faith
JJ, Muegge BD, Goodman AL, Henrissat B, Oozeer R, Cools-Portier S,
Gobert G, et al: The impact of a consortium of fermented milk
strains on the gut microbiome of gnotobiotic mice and monozygotic
twins. Sci Transl Med. 3(106ra106)2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Redondo-Useros N, Gheorghe A, Díaz-Prieto
LE, Villavisencio B, Marcos A and Nova E: Associations of probiotic
fermented milk (PFM) and yogurt consumption with
Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus components of the
gut microbiota in healthy adults. Nutrients. 11(651)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Holscher HD: Dietary fiber and prebiotics
and the gastrointestinal microbiota. Gut Microbes. 8:172–184.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Sanders ME, Merenstein DJ, Reid G, Gibson
GR and Rastall RA: Probiotics and prebiotics in intestinal health
and disease: From biology to the clinic. Nat Rev Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 16:605–616. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Frei R, Akdis M and O'Mahony L:
Prebiotics, probiotics, synbiotics, and the immune system:
Experimental data and clinical evidence. Curr Opin Gastroenterol.
31:153–158. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Costabile A, Deaville ER, Morales AM and
Gibson GR: Prebiotic potential of a maize-based soluble fibre and
impact of dose on the human gut microbiota. PLoS One.
11(e0144457)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Antunes AEC, Vinderola G, Xavier-Santos D
and Sivieri K: Food research international. Food Res Int.
37:195–197. 2004.
|
|
66
|
Oristrell J, Oliva JC, Casado E, Subirana
I, Domínguez D, Toloba A, Balado A and Grau M: Vitamin D
supplementation and COVID-19 risk: A population-based, cohort
study. J Endocrinol Invest: Jul 17, 2021 (Epub ahead of print).
|
|
67
|
Robles-Vera I, Callejo M, Ramos R, Duarte
J and Perez-Vizcaino F: Impact of Vitamin D deficit on the rat gut
microbiome. Nutrients. 11(2564)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Thomas RL, Jiang L, Adams JS, Xu ZZ, Shen
J, Janssen S, Ackermann G, Vanderschueren D, Pauwels S, Knight R,
et al: Vitamin D metabolites and the gut microbiome in older men.
Nat Commun. 11(5997)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Wenban C, Heer RS, Baktash V, Kandiah P,
Katsanouli T, Pandey A, Goindoo R, Ajaz A, Van den Abbeele K,
Mandal AKJ and Missouris CG: Dexamethasone treatment may mitigate
adverse effects of vitamin D deficiency in hospitalized Covid-19
patients. J Med Virol. 93:6605–6610. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Li R, Wu K, Li Y, Liang X, Tse WKF, Yang L
and Lai KP: Revealing the targets and mechanisms of vitamin A in
the treatment of COVID-19. Aging (Albany NY). 12:15784–15796.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Huda MN, Ahmad SM, Kalanetra KM, Taft DH,
Alam MJ, Khanam A, Raqib R, Underwood MA, Mills DA and Stephensen
CB: Neonatal Vitamin A supplementation and Vitamin A status are
associated with gut microbiome composition in Bangladeshi infants
in early infancy and at 2 years of age. J Nutr. 149:1075–1088.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Murni IK, Prawirohartono EP and Triasih R:
Potential role of vitamins and Zinc on acute respiratory infections
including Covid-19. Glob Pediatr Heal. 8:1–8. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Iyer M, Jayaramayya K, Subramaniam MD, Lee
SB, Dayem AA, Cho SG and Vellingiri B: COVID-19 : An update on
diagnostic and therapeutic approaches. BMB Rep. 53:191–205.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Brusselaers N: Prescribed drugs and the
microbiome. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 48:331–342.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Zeppa SD, Agostini D, Piccoli G and
Stocchi V: Gut microbiota status in COVID-19 : An unrecognized
player? Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 10(576551)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Xu R, Lu R, Zhang T, Wu Q, Cai W, Han X,
Wan Z, Jin X, Zhang Z and Zhang C: Temporal association between
human upper respiratory and gut bacterial microbiomes during the
course of COVID-19 in adults. Commun Biol. 4(24)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Weersma RK, Zhernakova A and Fu J:
Interaction between drugs and the gut microbiome. Gut.
69:1510–1519. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Dormont F, Brusini R, Cailleau C, Reynaud
F, Peramo A, Gendron A, Mougin J, Gaudin F, Varna M and Couvreur P:
Squalene-based multidrug nanoparticles for improved mitigation of
uncontrolled inflammation in rodents. Sci Adv.
6(eaaz5466)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Liu L, Zheng Y, Yang J, Lv J and Fan C:
Clinical observation on 13 novel coronavirus pneumonia cases
treated with integrated traditional Chinese and Western Medicine.
Zhejiang J Integr Tradit West Med. 30:349–351. 2020.
|
|
80
|
Dai T, Wang M, Wang P, Dai L, Dai R and
Meng Q: Inhibition effects of eight anti-coronavirus drugs on
glycosides metabolism and glycosidases in human gut microflora.
Pharmazie. 76:195–201. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Pan ZY, Chang YX, Han N, Hou FY, Lee BJY,
Zhi FC, Yang RF and Bi YJ: Short-term high-dose gavage of
hydroxychloroquine changes gut microbiota but not the intestinal
integrity and immunological responses in mice. Life Sci.
264(118450)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Million M, Lagier J, Gautret P, Colson P,
Fournier PE, Amrane S, Hocquart M, Mailhe M, Esteves-Vieira V,
Doudier B, et al: Early treatment of COVID-19 patients with
hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin: A retrospective analysis of
1061 cases in Marseille France. Travel Med Infect Dis.
35(101738)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Parker EPK, Praharaj I, John J, Kaliappan
SP, Kampmann B, Kang G and Grassly NC: Changes in the intestinal
microbiota following the administration of azithromycin in a
randomised placebo-controlled trial among infants in south India.
Sci Rep. 7(9168)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Li R, Wang H, Shi Q, Wang N, Zhang Z,
Xiong C, Liu J, Chen Y, Jiang L and Jiang Q: Effects of oral
florfenicol and azithromycin on gut microbiota and adipogenesis in
mice. PLoS One. 12(e0181690)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Ried K, Travica N, Dorairaj R and Sali A:
Herbal formula improves upper and lower gastrointestinal symptoms
and gut health in Australian adults with digestive disorders. Nutr
Res. 76:37–51. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Li Y, Liu X, Guo L, Li J, Zhong D, Zhang
Y, Clarke M and Jin R: Traditional Chinese medicine for treating
novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) pneumonia: Protocol for a systematic
review and meta-analysis. Syst Rev. 9(75)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
de Munter J, Pavlov D, Gorlova A, Sicker
M, Proshin A, Kalueff AV, Svistunov A, Kiselev D, Nedorubov A,
Morozov S, et al: Increased oxidative stress in the prefrontal
cortex as a shared feature of depressive- and PTSD-like syndromes:
Effects of a standardized herbal antioxidant. Front Nutr.
8(661455)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Lyu M, Wang YF, Fan GW, Wang XY, Xu SY and
Zhu Y: Balancing herbal medicine and functional food for prevention
and treatment of cardiometabolic diseases through modulating gut
microbiota. Front Microbiol. 8(2146)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Peterson CT, Sharma V, Uchitel S,
Denniston K, Chopra D, Mills PJ and Peterson SN: Prebiotic
potential of herbal medicines used in digestive health and disease.
J Altern Complement Med. 24:656–665. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Ma J, Zhou Q and Li H: Gut microbiota and
nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Insights on mechanisms and
therapy. Nutrients. 9(1124)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
91
|
Chen Z, Lv Y, Xu H and Deng L: Herbal
medicine, gut microbiota, and COVID-19. Front Pharmacol.
12(646560)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|