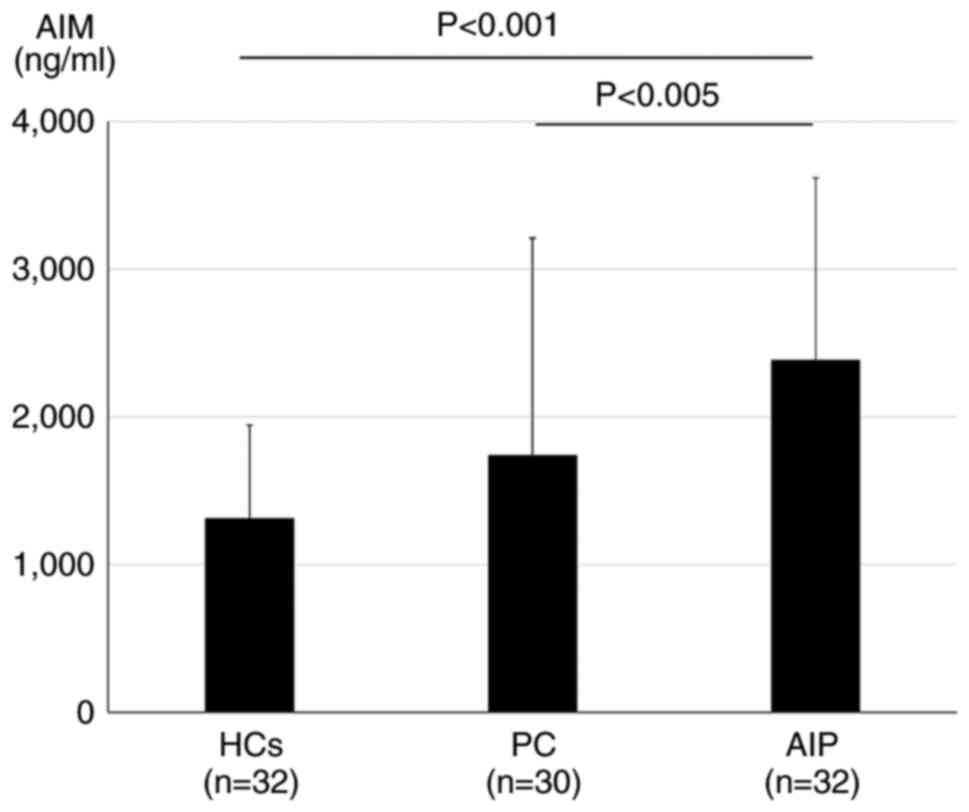
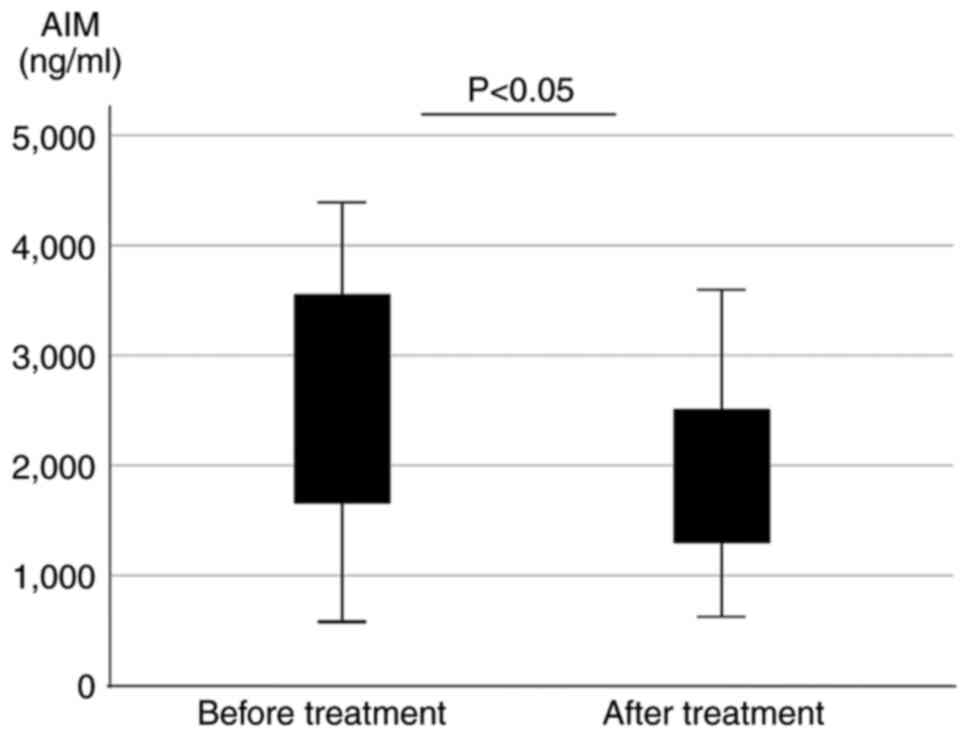
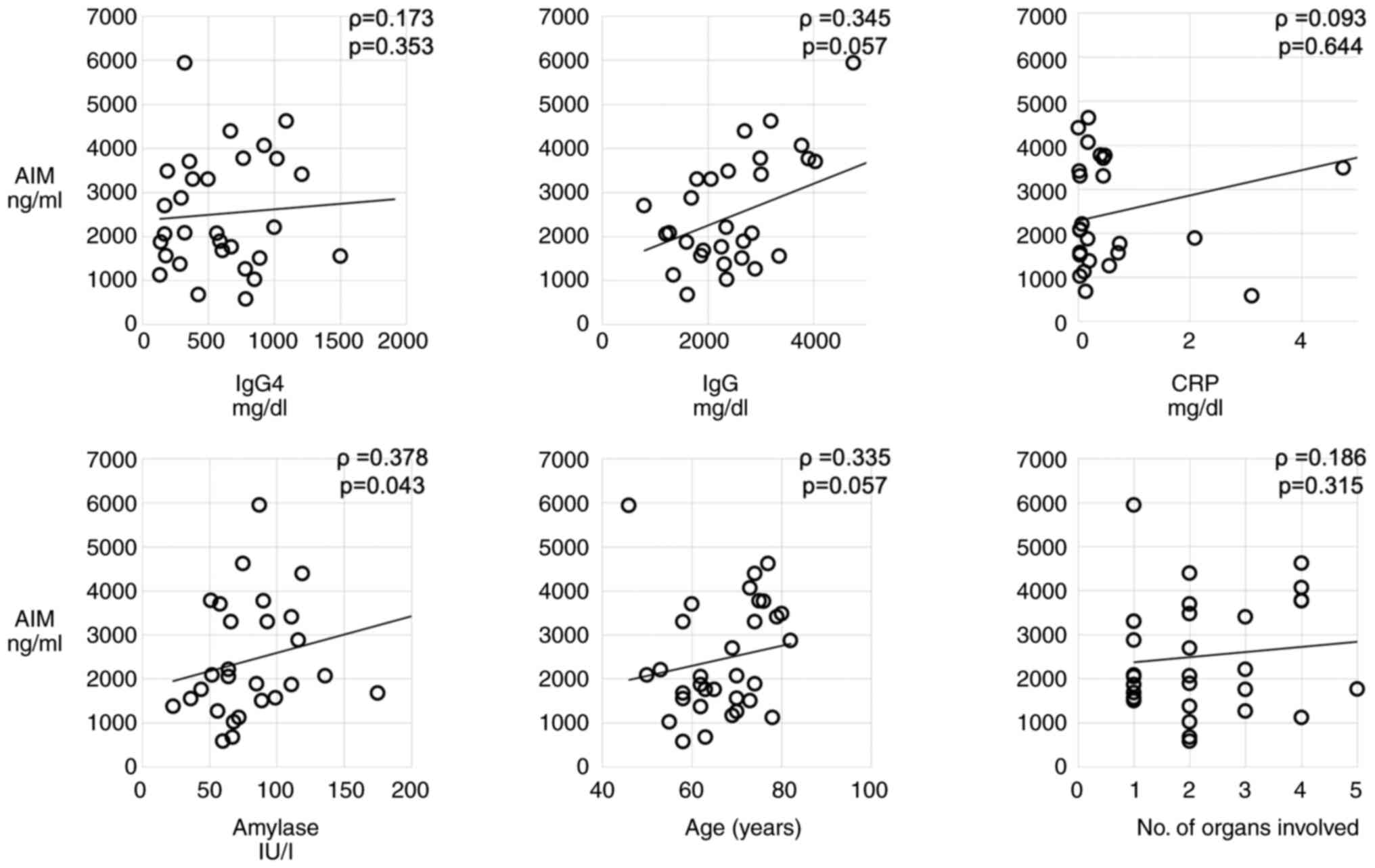
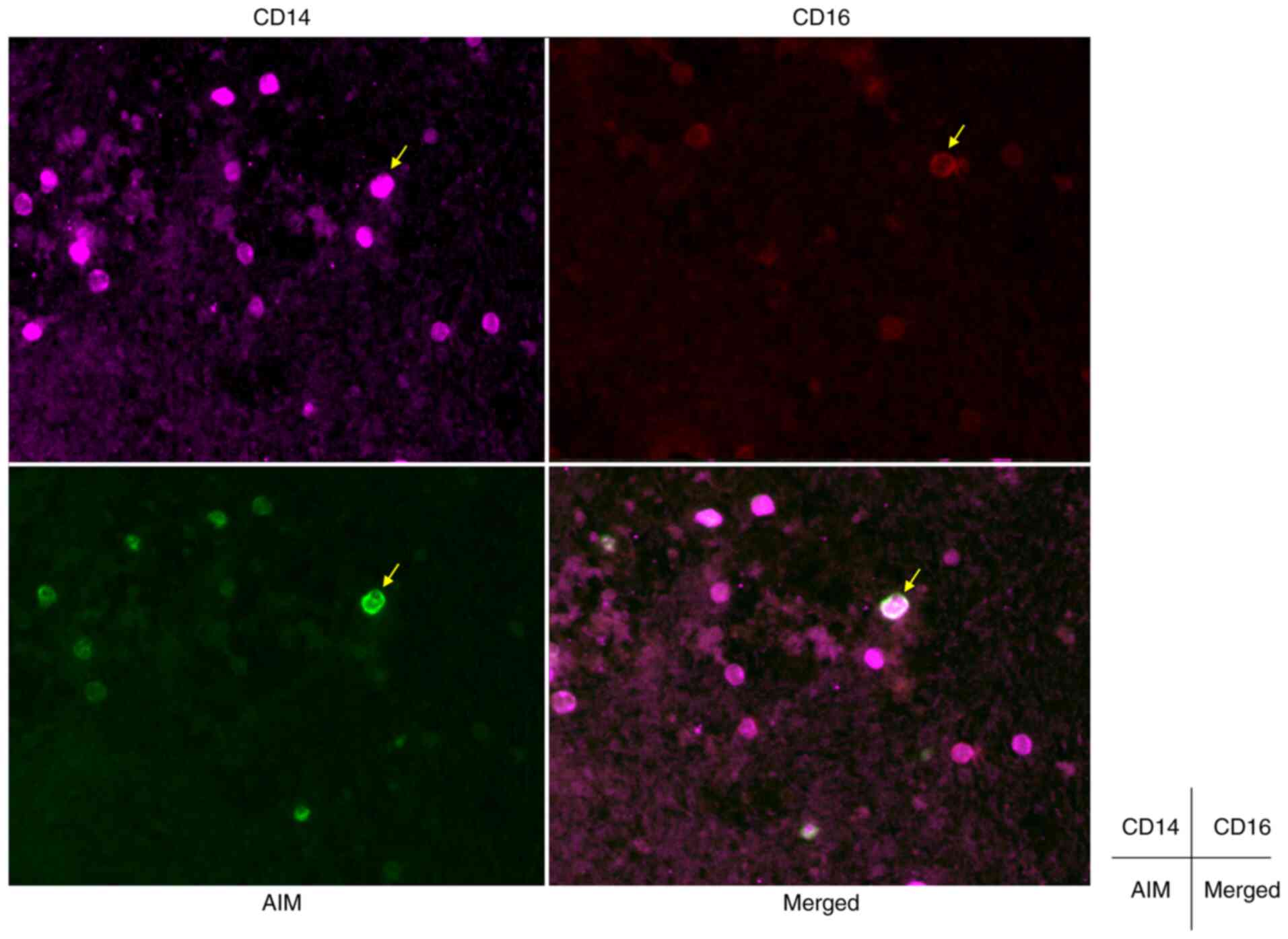
|
1
|
Yoshida K, Toki F, Takeuchi T, Watanabe S,
Shiratori K and Hayashi N: Chronic pancreatitis caused by an
autoimmune abnormality. Proposal of the concept of autoimmune
pancreatitis. Dig Dis Sci. 40:1561–1568. 1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Hamano H, Kawa S, Horiuchi A, Unno H,
Furuya N, Akamatsu T, Fukushima M, Nikaido T, Nakayama K, Usuda N
and Kiyosawa K: High serum IgG4 concentrations in patients with
sclerosing pancreatitis. N Engl J Med. 344:732–738. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Stone JH, Zen Y and Deshpande V:
IgG4-related disease. N Engl J Med. 366:539–551. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Kamisawa T, Zen Y, Pillai S and Stone JH:
IgG4-related disease. Lancet. 385:1460–1471. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Kamisawa T, Funata N, Hayashi Y, Eishi Y,
Koike M, Tsuruta K, Okamoto A, Egawa N and Nakajima H: A new
clinicopathological entity of IgG4-related autoimmune disease. J
Gastroenterol. 38:982–984. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Masamune A, Kikuta K, Hamada S, Tsuji I,
Takeyama Y, Shimosegawa T and Okazaki K: Collaborators. Nationwide
epidemiological survey of autoimmune pancreatitis in Japan in 2016.
J Gastroenterol. 55:462–470. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Miyazaki T, Hirokami Y, Matsuhashi N,
Takatsuka H and Naito M: Increased susceptibility of thymocytes to
apoptosis in mice lacking AIM, a novel murine macrophage-derived
soluble factor belonging to the scavenger receptor cysteine-rich
domain superfamily. J Exp Med. 189:413–422. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Mori M, Kimura H, Iwamura Y, Arai S and
Miyazaki T: Modification of N-glycosylation modulates the secretion
and lipolytic function of apoptosis inhibitor of macrophage (AIM).
FEBS Lett. 586:3569–3574. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Arai S and Miyazaki T: Impacts of the
apoptosis inhibitor of macrophage (AIM) on obesity-associated
inflammatory diseases. Semin Immunopathol. 36:3–12. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Arai S, Shelton JM, Chen M, Bradley MN,
Castrillo A, Bookout AL, Mak PA, Edwards PA, Mangelsdorf DJ,
Tontonoz P, et al: A role for the apoptosis inhibitory factor
AIM/Spα/Api6 in atherosclerosis development. Cell Metab. 1:201–213.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Gangadharan B, Antrobus R, Dwek RA and
Zitzmann N: Novel serum biomarker candidates for liver fibrosis in
hepatitis C patients. Clin Chem. 53:1792–1799. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Mera K, Uto H, Mawatari S, Ido A,
Yoshimine Y, Nosaki T, Oda K, Tabu K, Kumagai K, Tamai T, et al:
Serum levels of apoptosis inhibitor of macrophage are associated
with hepatic fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C. BMC
Gastroenterol. 14(27)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Ono Y, Kanmura S, Morinaga Y, Oda K,
Kawabata K, Arima S, Sasaki F, Nasu Y, Tanoue S, Hashimoto S, et
al: The utility of apoptosis inhibitor of macrophages as a possible
diagnostic marker in patients with Crohn's disease. BMC
Gastroenterol. 17(40)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Okazaki K, Kawa S, Kamisawa T, Naruse S,
Tanaka S, Nishimori I, Ohara H, Ito T, Kiriyama S, Inui K, et al:
Clinical diagnostic criteria of autoimmune pancreatitis: Revised
proposal. J Gastroenterol. 41:626–631. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Shimosegawa T, Okazaki K, Kamisawa T, Kawa
S and Notohara K: International Consensus Diagnostic Criteria for
autoimmune pancreatitis-Guidelines of the International Association
of Pancreatology. Suizo. 26:684–698. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Umehara H, Okazaki K, Masaki Y, Kawano M,
Yamamoto M, Saeki T, Matsui S, Yoshino T, Nakamura S, Kawa S, et
al: Comprehensive diagnostic criteria for IgG4-related disease
(IgG4-RD), 2011. Mod Rheumatol. 22:21–30. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Inoue D, Yoshida K, Yoneda N, Ozaki K,
Matsubara T, Nagai K, Okumura K, Toshima F, Toyama J, Minami T, et
al: IgG4-related disease: Dataset of 235 consecutive patients.
Medicine (Baltimore). 94(e680)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Joseph SB, Bradley MN, Castrillo A, Bruhn
KW, Mak PA, Pei L, Hogenesch J, O'connell RM, Cheng G, Saez E, et
al: LXR-dependent gene expression is important for macrophage
survival and the innate immune response. Cell. 119:299–309.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Valledor AF, Hsu LC, Ogawa S,
Sawka-Verhelle D, Karin M and Glass CK: Activation of liver X
receptors and retinoid X receptors prevents bacterial-induced
macrophage apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:17813–17818.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Wu J, Zhang L, Shi J, He R, Yang W,
Habtezion A, Niu N, Lu P and Xue J: Macrophage phenotypic switch
orchestrates the inflammation and repair/regeneration following
acute pancreatitis injury. EBioMedicine. 58(102920)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Sun GF, Zuo CJ, Shao CW, Wang JH and Zhang
J: Focal autoimmune pancreatitis: Radiological characteristics help
to distinguish from pancreatic cancer. World J Gastroenterol.
19:3634–3641. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Kamisawa T, Takuma K, Tabata T, Inaba Y,
Egawa N, Tsuruta K, Hishima T, Sasaki T and Itoi T: Serum
IgG4-negative autoimmune pancreatitis. J Gastroenterol. 46:108–116.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Ghazale A, Chari ST, Smyrk TC, Levy MJ,
Topazian MD, Takahashi N, Clain JE, Pearson RK, Pelaez-Luna M,
Petersen BT, et al: Value of serum IgG4 in the diagnosis of
autoimmune pancreatitis and in distinguishing it from pancreatic
cancer. Am J Gastroenterol. 102:1646–1653. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Weber SM, Cubukcu-Dimopulo O, Palesty JA,
Suriawinata A, Klimstra D, Brennan MF and Conlon K:
Lymphoplasmacytic sclerosing pancreatitis: Inflammatory mimic of
pancreatic carcinoma. J Gastrointest Surg. 7:129–139.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Hardacre JM, Iacobuzio-Donahue CA, Sohn
TA, Abraham SC, Yeo CJ, Lillemoe KD, Choti MA, Campbell KA,
Schulick RD, Hruban RH, et al: Results of pancreaticoduodenectomy
for lymphoplasmacytic sclerosing pancreatitis. Ann Surg.
237:853–859. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Hart PA, Kamisawa T, Brugge WR, Chung JB,
Culver EL, Czakó L, Frulloni L, Go VL, Gress TM, Kim MH, et al:
Long-term outcomes of autoimmune pancreatitis: A multicentre,
international analysis. Gut. 62:1771–1776. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Okamoto A, Watanabe T, Kamata K, Minaga K
and Kudo M: Recent updates on the relationship between cancer and
autoimmune pancreatitis. Intern Med. 58:1533–1539. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Tang H, Yang H, Zhang P, Wu D, Zhang S,
Zhao J, Peng L, Chen H, Fei Y, Zhang X, et al: Malignancy and
IgG4-related disease: The incidence, related factors and prognosis
from a prospective cohort study in China. Sci Rep. 10:1–7.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Haghbin H, Chuang J, Fatima R,
Zakirkhodjaev N, Lee-Smith W and Aziz M: Correlation of autoimmune
pancreatitis and malignancy: Systematic review and meta-analysis.
Dig Dis Sci. 67:3252–3264. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Yu T, Wu Y, Liu J, Zhuang Y, Jin X and
Wang L: The risk of malignancy in patients with IgG4-related
disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Arthritis Res Ther.
24:1–9. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Yamamoto M, Takahashi H, Tabeya T, Suzuki
C, Naishiro Y, Ishigami K, Yajima H, Shimizu Y, Obara M, Yamamoto
H, et al: Risk of malignancies in IgG4-related disease. Mod
Rheumatol. 22:414–418. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Koyama N, Yamazaki T, Kanetsuki Y, Hirota
J, Asai T, Mitsumoto Y, Mizuno M, Shima T, Kanbara Y, Arai S, et
al: Activation of apoptosis inhibitor of macrophage is a sensitive
diagnostic marker for NASH-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. J
Gastroenterol. 53:770–779. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Furukawa S, Moriyama M, Tanaka A, Maehara
T, Tsuboi H, Iizuka M, Hayashida JN, Ohta M, Saeki T, Notohara K,
et al: Preferential M2 macrophages contribute to fibrosis in
IgG4-related dacryoadenitis and sialoadenitis, so-called Mikulicz's
disease. Clin Immunol. 156:9–18. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|