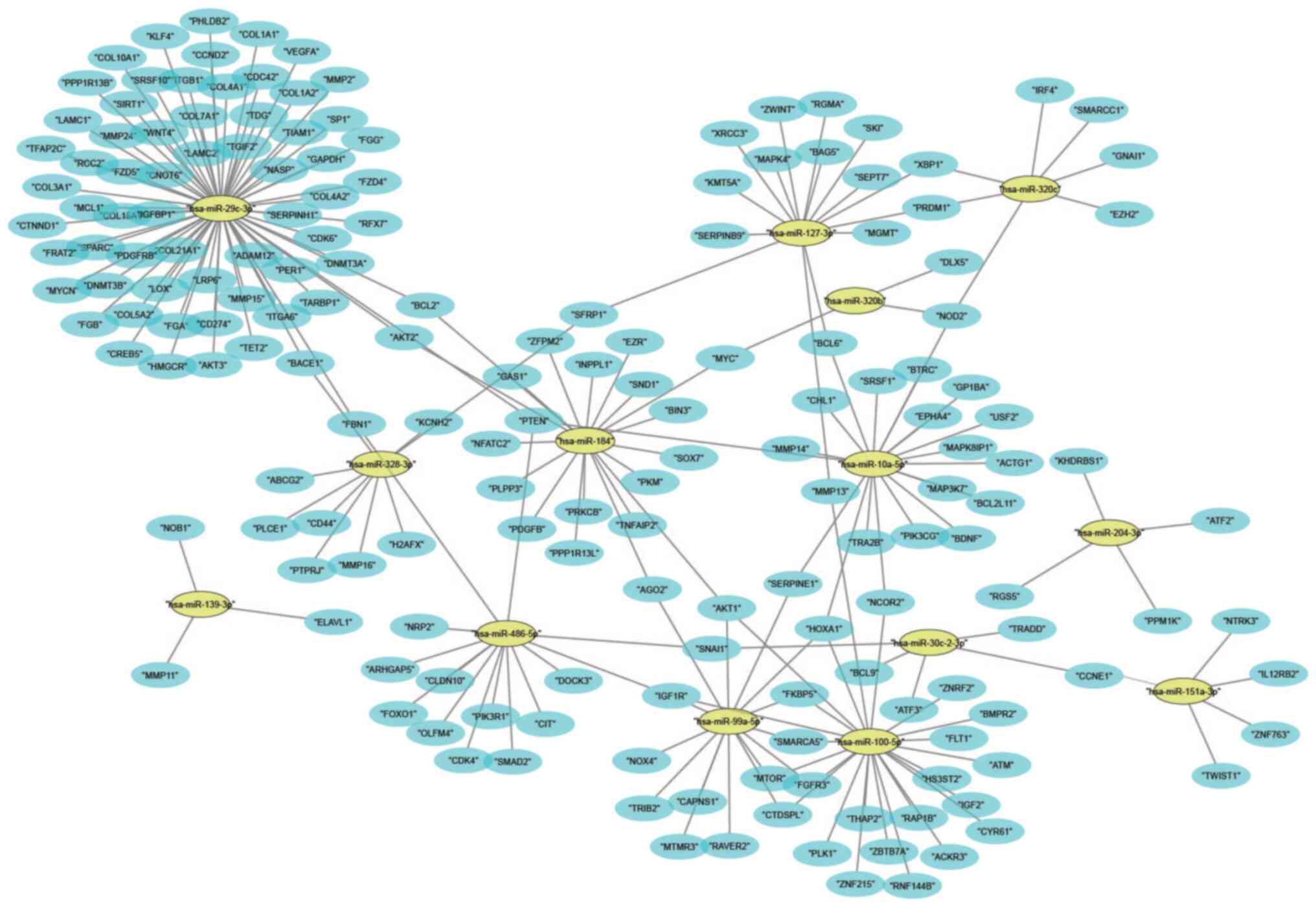
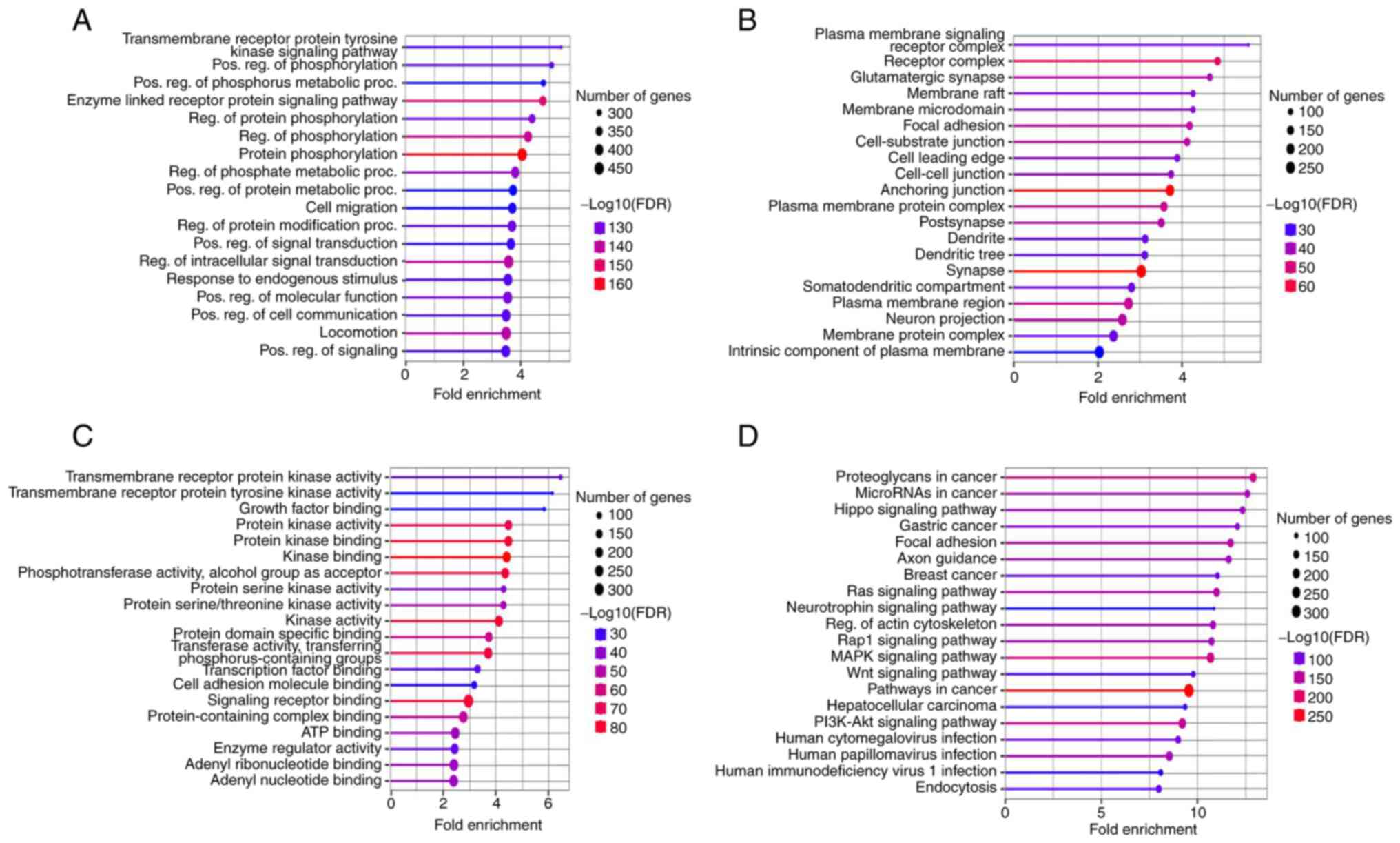
|
1
|
Pawluczyk I, Nicholson M, Barbour S, Er L,
Selvaskandan H, Bhachu JS and Barratt J: A pilot study to predict
risk of IgA nephropathy progression based on miR-204 expression.
Kidney Int Rep. 6:2179–2188. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Das U, Dakshinamurty KV, Prayaga A and
Uppin M: Spectrum of IgA nephropathy in a single center. Saudi J
Kidney Dis Transpl. 26:1057–1063. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Selvaskandan H, Pawluczyk I and Barratt J:
MicroRNAs: A new avenue to understand, investigate and treat
immunoglobulin A nephropathy? Clin Kidney J. 11:29–37.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Molyneux K, Wimbury D, Pawluczyk I, Muto
M, Bhachu J, Mertens PR, Feehally J and Barratt J:
β1,4-galactosyltransferase 1 is a novel receptor for IgA in human
mesangial cells. Kidney Int. 92:1458–1468. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Currie EG, Coburn B, Porfilio EA, Lam P,
Rojas OL, Novak J, Yang S, Chowdhury RB, Ward LA, Wang PW, et al:
Immunoglobulin A nephropathy is characterized by anticommensal
humoral immune responses. JCI Insight. 7(e141289)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Suzuki H, Kiryluk K, Novak J, Moldoveanu
Z, Herr AB, Renfrow MB, Wyatt RJ, Scolari F, Mestecky J, Gharavi AG
and Julian BA: The pathophysiology of IgA nephropathy. J Am Soc
Nephrol. 22:1795–1803. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Lv J, Wong MG, Hladunewich MA, Jha V, Hooi
LS, Monaghan H, Zhao M, Barbour S, Jardine MJ, Reich HN, et al:
Effect of oral methylprednisolone on decline in kidney function or
kidney failure in patients with IgA nephropathy: The TESTING
randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 327:1888–1898. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Lai KN, Tang SC, Schena FP, Novak J,
Tomino Y, Fogo AB and Glassock RJ: IgA nephropathy. Nat Rev Dis
Primers. 2(16001)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Chuammitri P, Vannamahaxay S, Sornpet B,
Pringproa K and Patchanee P: Detection and characterization of
microRNA expression profiling and its target genes in response to
canine parvovirus in crandell reese feline kidney cells. PeerJ.
8(e8522)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Yanaihara N, Caplen N, Bowman E, Seike M,
Kumamoto K, Yi M, Stephens RM, Okamoto A, Yokota J, Tanaka T, et
al: Unique microRNA molecular profiles in lung cancer diagnosis and
prognosis. Cancer Cell. 9:189–198. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Huang YS, Dai Y, Yu XF, Bao SY, Yin YB,
Tang M and Hu CX: Microarray analysis of microRNA expression in
hepatocellular carcinoma and non-tumorous tissues without viral
hepatitis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 23:87–94. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Iorio MV, Ferracin M, Liu CG, Veronese A,
Spizzo R, Sabbioni S, Magri E, Pedriali M, Fabbri M, Campiglio M,
et al: MicroRNA gene expression deregulation in human breast
cancer. Cancer Res. 65:7065–7070. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Schetter AJ, Leung SY, Sohn JJ, Zanetti
KA, Bowman ED, Yanaihara N, Yuen ST, Chan TL, Kwong DL, Au GK, et
al: MicroRNA expression profiles associated with prognosis and
therapeutic outcome in colon adenocarcinoma. JAMA. 299:425–236.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Bloomston M, Frankel WL, Petrocca F,
Volinia S, Alder H, Hagan JP, Liu CG, Bhatt D, Taccioli C and Croce
CM: MicroRNA expression patterns to differentiate pancreatic
adenocarcinoma from normal pancreas and chronic pancreatitis. JAMA.
297:1901–1908. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Schultz NA, Werner J, Willenbrock H,
Roslind A, Giese N, Horn T, Wøjdemann M and Johansen JS: MicroRNA
expression profiles associated with pancreatic adenocarcinoma and
ampullary adenocarcinoma. Mod Pathol. 25:1609–1622. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Rozenblum E, Schutte M, Goggins M, Hahn
SA, Panzer S, Zahurak M, Goodman SN, Sohn TA, Hruban RH, Yeo CJ and
Kern SE: Tumor-suppressive pathways in pancreatic carcinoma. Cancer
Res. 57:1731–1734. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Jansson MD and Lund AH: MicroRNAs and
cancer. Mol Oncol. 6:590–610. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Vegter EL, van der Meer, de Windt LJ,
Pinto MY and Voors AA: MicroRNAs in kidney physiology and disease.
Eur J Heart Fail. 18:457–468. 2016.
|
|
19
|
Trionfini P, Benigni A and Remuzzi G:
MicroRNAs in kidney physiology and disease. Nat Rev Nephrol.
11:23–33. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Liu L, Duan A, Guo Q, Sun G, Cui W, Lu X,
Yu H and Luo P: Detection of microRNA-33a-5p in serum, urine and
renal tissue of patients with IgA nephropathy. Exp Ther Med.
21(205)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Wang G, Kwan BC, Lai FM, Choi PC, Chow KM,
Li PK and Szeto CC: Intrarenal expression of microRNAs in patients
with IgA nephropathy. Lab Invest. 90:98–103. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Wang G, Kwan BC, Lai FM, Chow KM, Li PK
and Szeto CC: Elevated levels of miR-146a and miR-155 in kidney
biopsy and urine from patients with IgA nephropathy. Dis Markers.
30:171–179. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Qin W, Chung AC, Huang XR, Meng XM, Hui
DS, Yu CM, Sung JJ and Lan HY: TGF-β/Smad3 signaling promotes renal
fibrosis by inhibiting miR-29. J Am Soc Nephrol. 22:1462–1474.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Politano G, Orso F, Raimo M, Benso A,
Savino A, Taverna D and Di Carlo S: CyTRANSFINDER: A Cytoscape 3.3
plugin for three-component (TF, gene, miRNA) signal transduction
pathway construction. BMC Bioinformatics. 17(157)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Scionti K, Molyneux K, Selvaskandan H,
Barratt J and Cheung CK: New insights into the pathogenesis and
treatment strategies in IgA nephropathy. Glomerular Dis. 2:15–29.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Wang G, Kwan BC, Lai FM, Chow KM, Kam-Tao
Li P and Szeto CC: Expression of microRNAs in the urinary sediment
of patients with IgA nephropathy. Dis Markers. 28:79–86.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Serino G, Sallustio F, Cox SN, Pesce F and
Schena FP: Abnormal miR-148b expression promotes aberrant
glycosylation of IgA1 in IgA nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol.
23:814–824. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Yao X, Zhai Y, An H, Gao J, Chen Y, Zhang
W and Zhao Z: MicroRNAs in IgA nephropathy. Ren Fail. 43:1298–1310.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Liang H, Gong F, Zhang S, Zhang CY, Zen K
and Chen X: The origin, function, and diagnostic potential of
extracellular microRNAs in human body fluids. Wiley Interdiscip Rev
RNA. 5:285–300. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Wang J, Chen J and Sen S: MicroRNA as
biomarkers and diagnostics. J Cell Physiol. 231:25–30.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Xu BY, Meng SJ, Shi SF, Liu LJ, Lv JC, Zhu
L and Zhang H: MicroRNA-21-5p participates in IgA nephropathy by
driving T helper cell polarization. J Nephrol. 33:551–560.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Rodriguez A, Vigorito E, Clare S, Warren
MV, Couttet P, Soond DR, van Dongen S, Grocock RJ, Das PP, Miska
EA, et al: Requirement of bic/microRNA-155 for normal immune
function. Science. 316:608–611. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Fan Q, Lu R, Zhu M, Yan Y, Guo X, Qian Y,
Zhang L, Dai H, Ni Z and Gu L: Serum miR-192 is related to
tubulointerstitial lesion and short-term disease progression in IgA
nephropathy. Nephron. 142:195–207. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Ichii O, Otsuka S, Sasaki N, Namiki Y,
Hashimoto Y and Kon Y: Altered expression of microRNA miR-146a
correlates with the development of chronic renal inflammation.
Kidney Int. 81:280–292. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Lin TJ, Yang SS, Hua KF, Tsai YL, Lin SH
and Ka SM: SPAK plays a pathogenic role in IgA nephropathy through
the activation of NF-κB/MAPKs signaling pathway. Free Radic Biol
Med. 99:214–224. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Wang Z, Liao Y, Wang L, Lin Y, Ye Z, Zeng
X, Liu X, Wei F and Yang N: Small RNA deep sequencing reveals novel
miRNAs in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with IgA
nephropathy. Mol Med Rep. 22:3378–3386. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Hu M, Zhu S, Xiong S, Xue X and Zhou X:
MicroRNAs and the PTEN/PI3K/Akt pathway in gastric cancer (review).
Oncol Rep. 41:1439–1454. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Zhang BG, Li JF, Yu BQ, Zhu ZG, Liu BY and
Yan M: microRNA-21 promotes tumor proliferation and invasion in
gastric cancer by targeting PTEN. Oncol Rep. 27:1019–1026.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Zhu S, Zhang L, Zhao Z, Fu W, Fu K, Liu G
and Jia W: MicroRNA-92a-3p inhibits the cell proliferation,
migration and invasion of Wilms tumor by targeting NOTCH1. Oncol
Rep. 40:571–578. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Zhang C, Yu S, Zheng B, Liu D, Wan F, Ma
Y, Wang J, Gao Z and Shan Z: miR-30c-5p reduces renal
ischemia-reperfusion involving macrophage. Med Sci Monit.
25:4362–4369. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Schneider C, Setty M, Holmes AB, Maute RL,
Leslie CS, Mussolin L, Rosolen A, Dalla-Favera R and Basso K:
MicroRNA 28 controls cell proliferation and is down-regulated in
B-cell lymphomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 111:8185–8190.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Feng Z, Zhang C, Wu R and Hu W: Tumor
suppressor p53 meets microRNAs. J Mol Cell Biol. 3:44–50.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Wu L, Han X, Jiang X, Ding H, Qi C, Yin Z,
Xiao J, Xiong L, Guo Q, Ye Z, et al: Downregulation of renal
Hsa-miR-127-3p contributes to the overactivation of type I
interferon signaling pathway in the kidney of lupus nephritis.
Front Immunol. 12(747616)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Saito Y, Liang G, Egger G, Friedman JM,
Chuang JC, Coetzee GA and Jones PA: Specific activation of
microRNA-127 with downregulation of the proto-oncogene BCL6 by
chromatin-modifying drugs in human cancer cells. Cancer Cell.
9:435–443. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Craft JE: Follicular helper T cells in
immunity and systemic autoimmunity. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 8:337–347.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Lv W, Fan F, Wang Y, Gonzalez-Fernandez E,
Wang C, Yang L, Booz GW and Roman RJ: Therapeutic potential of
microRNAs for the treatment of renal fibrosis and CKD. Physiol
Genomics. 50:20–34. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Li JY, Yong TY, Michael MZ and Gleadle JM:
Review: The role of microRNAs in kidney disease. Nephrology
(Carlton). 15:599–608. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Miguel V: The extracellular miRNA
fingerprint of kidney disease: A narrative review. ExRNA.
4(12)2022.
|