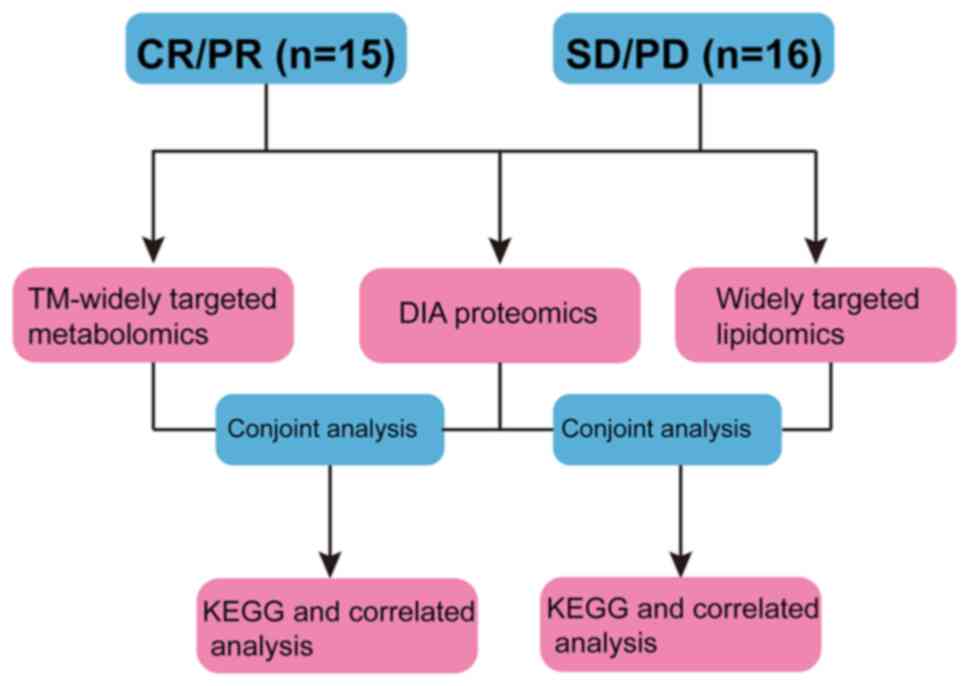
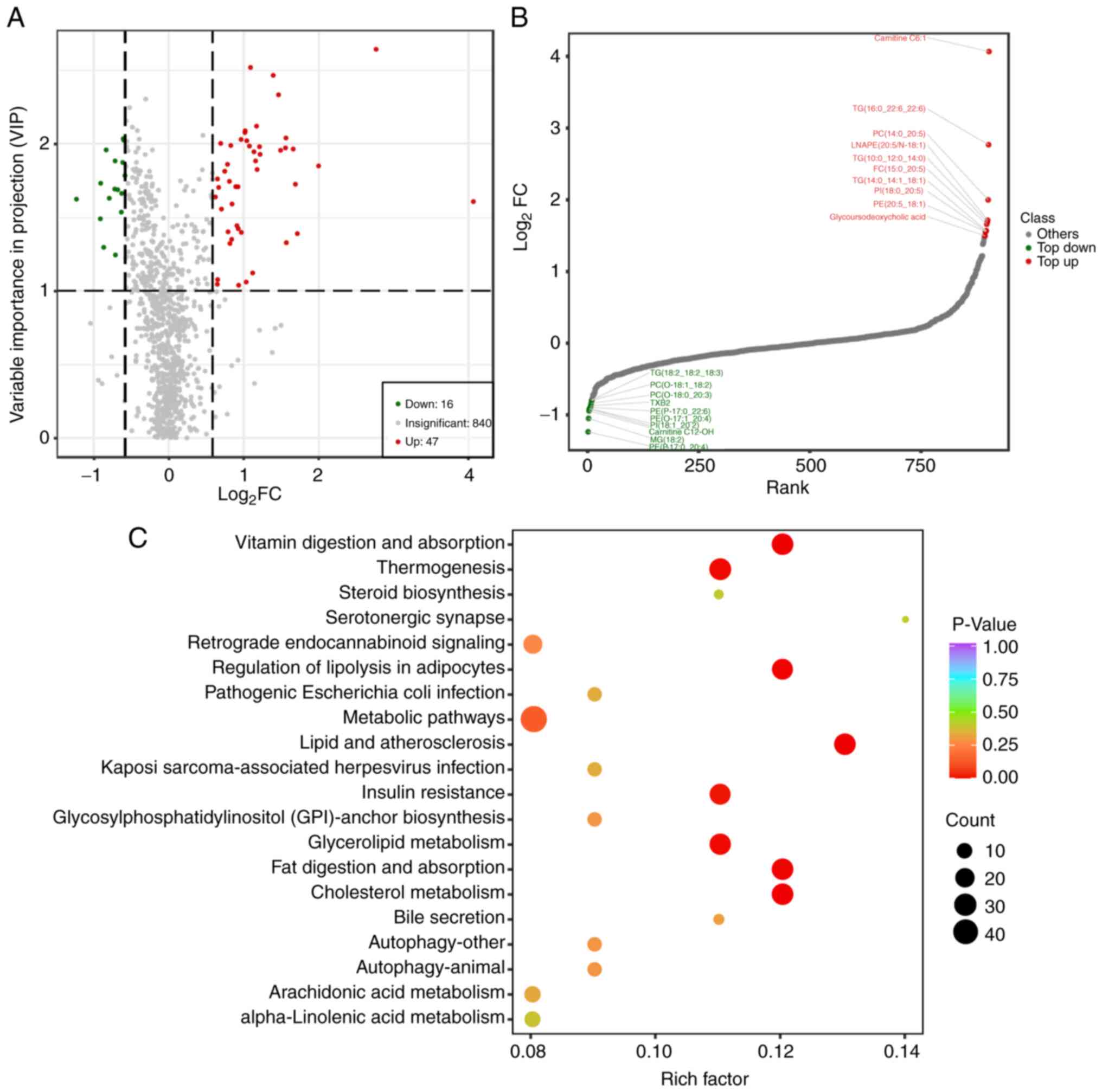
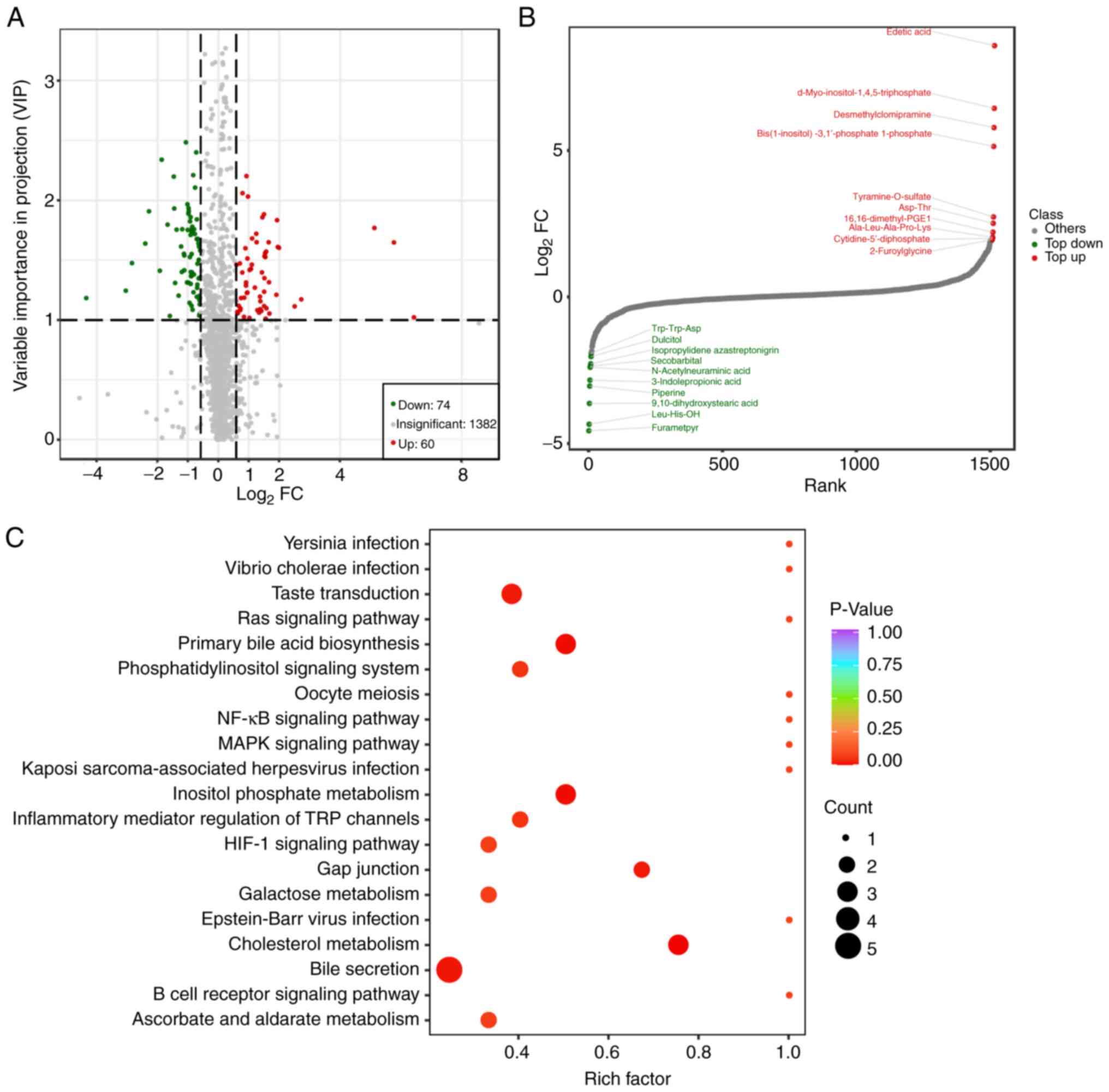
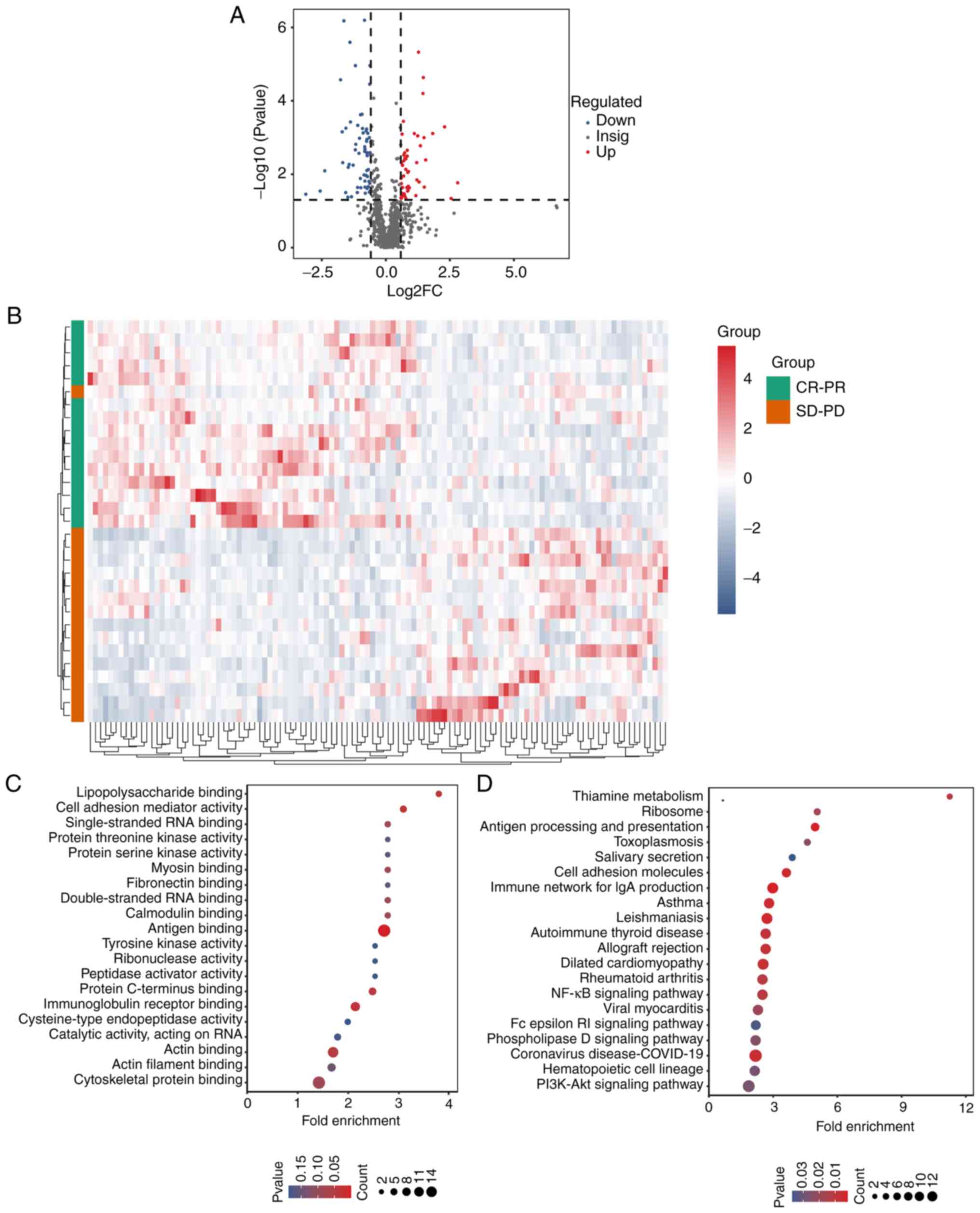
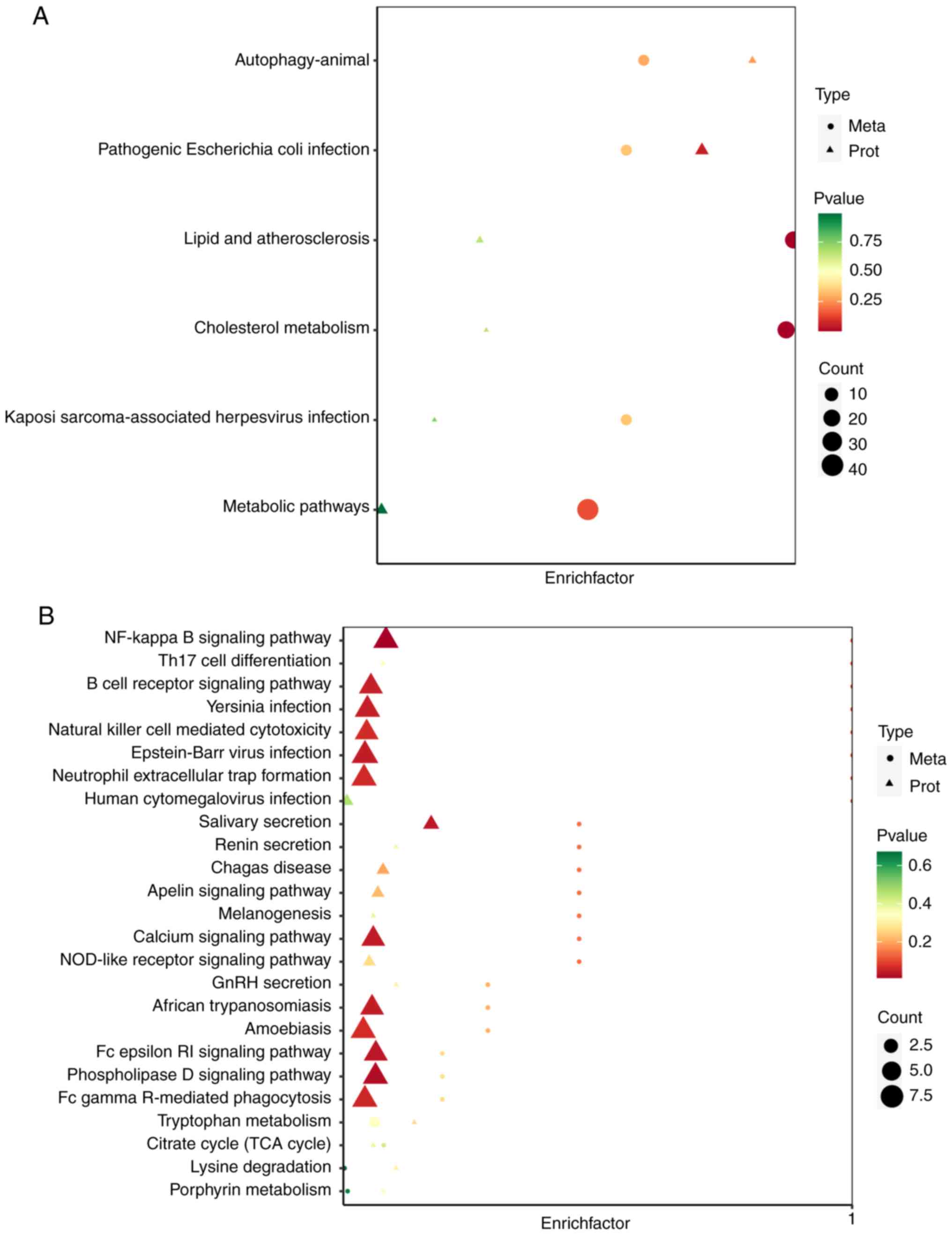
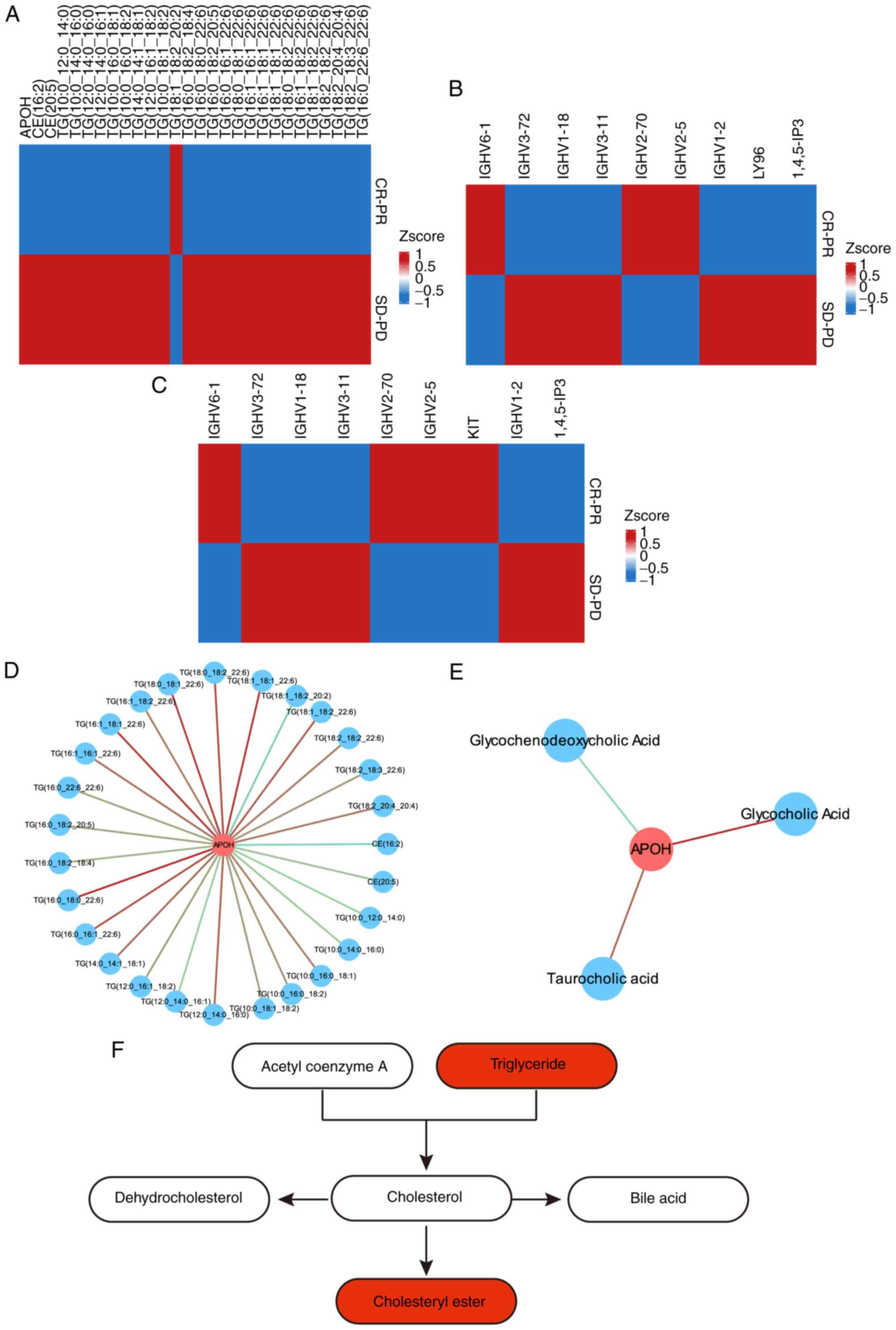
|
1
|
Bagchi S, Yuan R and Engleman EG: Immune
checkpoint inhibitors for the treatment of cancer: Clinical impact
and mechanisms of response and resistance. Annu Rev Pathol.
16:223–249. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Carlino MS, Larkin J and Long GV: Immune
checkpoint inhibitors in melanoma. Lancet. 398:1002–1014.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Li F, Chen Y, Pang M, Yang P and Jing H:
Immune checkpoint inhibitors and cellular treatment for lymphoma
immunotherapy. Clin Exp Immunol. 205:1–11. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Kojima T, Shah MA, Muro K, Francois E,
Adenis A, Hsu CH, Doi T, Moriwaki T, Kim SB, Lee SH, et al:
Randomized phase III KEYNOTE-181 study of pembrolizumab versus
chemotherapy in advanced esophageal cancer. J Clin Oncol.
38:4138–4148. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Kato K, Cho BC, Takahashi M, Okada M, Lin
CY, Chin K, Kadowaki S, Ahn MJ, Hamamoto Y, Doki Y, et al:
Nivolumab versus chemotherapy in patients with advanced oesophageal
squamous cell carcinoma refractory or intolerant to previous
chemotherapy (ATTRACTION-3): A multicentre, randomised, open-label,
phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 20:1506–1517. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Huang J, Xu J, Chen Y, Zhuang W, Zhang Y,
Chen Z, Chen J, Zhang H, Niu Z, Fan Q, et al: Camrelizumab versus
investigator's choice of chemotherapy as second-line therapy for
advanced or metastatic oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma
(ESCORT): A multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase 3 study.
Lancet Oncol. 21:832–842. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Sun JM, Shen L, Shah MA, Enzinger P,
Adenis A, Doi T, Kojima T, Metges JP, Li Z, Kim SB, et al:
Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for
first-line treatment of advanced oesophageal cancer (KEYNOTE-590):
A randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 study. Lancet.
398:759–771. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Luo H, Lu J, Bai Y, Mao T, Wang J, Fan Q,
Zhang Y, Zhao K, Chen Z, Gao S, et al: Effect of camrelizumab vs
placebo added to chemotherapy on survival and progression-free
survival in patients with advanced or metastatic esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma: The ESCORT-1st randomized clinical trial.
JAMA. 326:916–925. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Rinschen MM, Ivanisevic J, Giera M and
Siuzdak G: Identification of bioactive metabolites using activity
metabolomics. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 20:353–367. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Muthubharathi BC, Gowripriya T and
Balamurugan K: Metabolomics: Small molecules that matter more. Mol
Omics. 17:210–229. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Chen PH, Cai L, Huffman K, Yang C, Kim J,
Faubert B, Boroughs L, Ko B, Sudderth J, McMillan EA, et al:
Metabolic diversity in human non-small cell lung cancer cells. Mol
Cell. 76:838–851.e5. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Shen Y, Sun M, Zhu J, Wei M, Li H, Zhao P,
Wang J, Li R, Tian L, Tao Y, et al: Tissue metabolic profiling
reveals major metabolic alteration in colorectal cancer. Mol Omics.
17:464–471. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Li L and Ma J: Molecular characterization
of metabolic subtypes of gastric cancer based on metabolism-related
lncRNA. Sci Rep. 11(21491)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Chen CJ, Lee DY, Yu J, Lin YN and Lin TM:
Recent advances in LC-MS-based metabolomics for clinical biomarker
discovery. Mass Spectrom Rev. (e21785)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (Epub ahead of
print).
|
|
15
|
Seger C and Salzmann L: After another
decade: LC-MS/MS became routine in clinical diagnostics. Clin
Biochem. 82:2–11. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Beccaria M and Cabooter D: Current
developments in LC-MS for pharmaceutical analysis. Analyst.
145:1129–1157. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Zhang S, Wang H and Zhu MJ: A sensitive
GC/MS detection method for analyzing microbial metabolites short
chain fatty acids in fecal and serum samples. Talanta. 196:249–254.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Beale DJ, Pinu FR, Kouremenos KA, Poojary
MM, Narayana VK, Boughton BA, Kanojia K, Dayalan S, Jones OAH and
Dias DA: Review of recent developments in GC-MS approaches to
metabolomics-based research. Metabolomics. 14(152)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Hu R, Li T, Yang Y, Tian Y and Zhang L:
NMR-based metabolomics in cancer research. Adv Exp Med Biol.
1280:201–218. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Bichmann L, Gupta S, Rosenberger G,
Kuchenbecker L, Sachsenberg T, Ewels P, Alka O, Pfeuffer J,
Kohlbacher O and Röst H: DIAproteomics: A multifunctional data
analysis pipeline for data-independent acquisition proteomics and
peptidomics. J Proteome Res. 20:3758–3766. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Ma L, Muscat JE, Sinha R, Sun D and Xiu G:
Proteomics of exhaled breath condensate in lung cancer and controls
using data-independent acquisition (DIA): A pilot study. J Breath
Res. 15(026002)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Krasny L and Huang PH: Data-independent
acquisition mass spectrometry (DIA-MS) for proteomic applications
in oncology. Mol Omics. 17:29–42. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Zheng X, Xu K, Zhou B, Chen T, Huang Y, Li
Q, Wen F, Ge W, Wang J, Yu S, et al: A circulating extracellular
vesicles-based novel screening tool for colorectal cancer revealed
by shotgun and data-independent acquisition mass spectrometry. J
Extracell Vesicles. 9(1750202)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Rao J, Wan X, Tou F, He Q, Xiong A, Chen
X, Cui W and Zheng Z: Molecular characterization of advanced
colorectal cancer using serum proteomics and metabolomics. Front
Mol Biosci. 8(687229)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Zhang Q, Zhang Y, Sun S, Wang K, Qian J,
Cui Z, Tao T and Zhou J: ACOX2 is a prognostic marker and impedes
the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma via PPARα pathway. Cell
Death Dis. 12(15)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Kong R, Qian X and Ying W: Pancreatic
cancer cells spectral library by DIA-MS and the phenotype analysis
of gemcitabine sensitivity. Sci Data. 9(283)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Keam SP, Gulati T, Gamell C, Caramia F,
Huang C, Schittenhelm RB, Kleifeld O, Neeson PJ, Haupt Y and
Williams SG: Exploring the oncoproteomic response of human prostate
cancer to therapeutic radiation using data-independent acquisition
(DIA) mass spectrometry. Prostate. 78:563–575. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Sun Y, Li L, Zhou Y, Ge W, Wang H, Wu R,
Liu W, Chen H, Xiao Q, Cai X, et al: Stratification of follicular
thyroid tumours using data-independent acquisition proteomics and a
comprehensive thyroid tissue spectral library. Mol Oncol.
16:1611–1624. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Oken MM, Creech RH, Tormey DC, Horton J,
Davis TE, McFadden ET and Carbone PP: Toxicity and response
criteria of the Eastern cooperative oncology group. Am J Clin
Oncol. 5:649–655. 1982.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Schwartz LH, Litière S, de Vries E, Ford
R, Gwyther S, Mandrekar S, Shankar L, Bogaerts J, Chen A, Dancey J,
et al: RECIST 1.1-update and clarification: From the RECIST
committee. Eur J Cancer. 62:132–137. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Greene FL, Page DL, Fleming ID, Fritz AG,
Balch CM, Haller DG and Morrow M (eds): AJCC cancer staging manual.
6th edition. American Joint Committe on Cancer, Chicago, IL,
pp91-99, 2002.
|
|
32
|
Demichev V, Messner CB, Vernardis SI,
Lilley KS and Ralser M: DIA-NN: Neural networks and interference
correction enable deep proteome coverage in high throughput. Nat
Methods. 17:41–44. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Yu G, Wang LG, Han Y and He QY:
clusterProfiler: An R package for comparing biological themes among
gene clusters. OMICS. 16:284–287. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Yang T, Hui R, Nouws J, Sauler M, Zeng T
and Wu Q: Untargeted metabolomics analysis of esophageal squamous
cell cancer progression. J Transl Med. 20(127)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
White L, Ma J, Liang S, Sanchez-Espiridion
B and Liang D: LC-MS/MS determination of d-mannose in human serum
as a potential cancer biomarker. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 137:54–59.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Mir SA, Rajagopalan P, Jain AP, Khan AA,
Datta KK, Mohan SV, Lateef SS, Sahasrabuddhe N, Somani BL, Keshava
Prasad TS, et al: LC-MS-based serum metabolomic analysis reveals
dysregulation of phosphatidylcholines in esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. J Proteomics. 127:96–102. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Zhang J, Bowers J, Liu L, Wei S, Gowda GA,
Hammoud Z and Raftery D: Esophageal cancer metabolite biomarkers
detected by LC-MS and NMR methods. PLoS One.
7(e30181)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Liang S, Sanchez-Espiridion B, Xie H, Ma
J, Wu X and Liang D: Determination of proline in human serum by a
robust LC-MS/MS method: Application to identification of human
metabolites as candidate biomarkers for esophageal cancer early
detection and risk stratification. Biomed Chromatogr. 29:570–577.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Song E, Zhu R, Hammoud ZT and Mechref Y:
LC-MS/MS quantitation of esophagus disease blood serum
glycoproteins by enrichment with hydrazide chemistry and lectin
affinity chromatography. J Proteome Res. 13:4808–4820.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Zhang H, Wang L, Hou Z, Ma H, Mamtimin B,
Hasim A and Sheyhidin I: Metabolomic profiling reveals potential
biomarkers in esophageal cancer progression using liquid
chromatography-mass spectrometry platform. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 491:119–125. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Guo JH, Xing GL, Fang XH, Wu HF, Zhang B,
Yu JZ, Fan ZM and Wang LD: Proteomic profiling of fetal esophageal
epithelium, esophageal cancer, and tumor-adjacent esophageal
epithelium and immunohistochemical characterization of a
representative differential protein, PRX6. World J Gastroenterol.
23:1434–1442. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Yazdian-Robati R, Ahmadi H, Riahi MM, Lari
P, Aledavood SA, Rashedinia M, Abnous K and Ramezani M: Comparative
proteome analysis of human esophageal cancer and adjacent normal
tissues. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 20:265–271. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
O'Neill JR, Pak HS, Pairo-Castineira E,
Save V, Paterson-Brown S, Nenutil R, Vojtěšek B, Overton I, Scherl
A and Hupp TR: Quantitative shotgun proteomics unveils candidate
novel esophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC)-specific proteins. Mol Cell
Proteomics. 16:1138–1150. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Schwacke J, Millar TP, Hammond CE, Saha A,
Hoffman BJ, Romagnuolo J, Hill EG and Smolka AJ: Discrimination of
normal and esophageal cancer plasma proteomes by MALDI-TOF mass
spectrometry. Dig Dis Sci. 60:1645–1654. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Wang D, Chen J, Han J, Wang K, Fang W, Jin
J and Xue S: iTRAQ and two-dimensional-LC-MS/MS reveal NAA10 is a
potential biomarker in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Proteomics Clin Appl. 16(e2100081)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Singh S, Bano A, Saraya A, Das P and
Sharma R: iTRAQ-based analysis for the identification of MARCH8
targets in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Proteomics.
236(104125)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Wang X, Peng Y, Xie M, Gao Z, Yin L, Pu Y
and Liu R: Identification of extracellular matrix protein 1 as a
potential plasma biomarker of ESCC by proteomic analysis using
iTRAQ and 2D-LC-MS/MS. Proteomics Clin Appl.
11(1600163)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Deng F, Zhou K, Li Q, Liu D, Li M, Wang H,
Zhang W and Ma Y: iTRAQ-based quantitative proteomic analysis of
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 37:1909–1918.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Liu W, Xie L, He YH, Wu ZY, Liu LX, Bai
XF, Deng DX, Xu XE, Liao LD, Lin W, et al: Large-scale and
high-resolution mass spectrometry-based proteomics profiling
defines molecular subtypes of esophageal cancer for therapeutic
targeting. Nat Commun. 12(4961)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Li Y, Yang B, Ma Y, Peng X, Wang Z, Sheng
B, Wei Z, Cui Y and Liu Z: Phosphoproteomics reveals therapeutic
targets of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Signal Transduct
Target Ther. 6(381)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Joyce D, Albanese C, Steer J, Fu M,
Bouzahzah B and Pestell RG: NF-kappaB and cell-cycle regulation:
the cyclin connection. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 12:73–90.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Grivennikov SI and Karin M: Dangerous
liaisons: STAT3 and NF-kappaB collaboration and crosstalk in
cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 21:11–19. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Vanden Berghe T, Linkermann A,
Jouan-Lanhouet S, Walczak H and Vandenabeele P: Regulated necrosis:
The expanding network of non-apoptotic cell death pathways. Nat Rev
Mol Cell Biol. 15:135–147. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Taniguchi K, Wu LW, Grivennikov SI, de
Jong PR, Lian I, Yu FX, Wang K, Ho SB, Boland BS, Chang JT, et al:
A gp130-Src-YAP module links inflammation to epithelial
regeneration. Nature. 519:57–62. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Johnson RF and Perkins ND: Nuclear
factor-κB, p53, and mitochondria: Regulation of cellular metabolism
and the Warburg effect. Trends Biochem Sci. 37:317–324.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Xia Y, Shen S and Verma IM: NF-κB, an
active player in human cancers. Cancer Immunol Res. 2:823–830.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Wu Y and Zhou BP: Inflammation: A driving
force speeds cancer metastasis. Cell Cycle. 8:3267–3273.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Amato CM, Hintzsche JD, Wells K, Applegate
A, Gorden NT, Vorwald VM, Tobin RP, Nassar K, Shellman YG, Kim J,
et al: Pre-treatment mutational and transcriptomic landscape of
responding metastatic melanoma patients to anti-PD1 immunotherapy.
Cancers (Basel). 12(1943)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Roh W, Chen PL, Reuben A, Spencer CN,
Prieto PA, Miller JP, Gopalakrishnan V, Wang F, Cooper ZA, Reddy
SM, et al: Integrated molecular analysis of tumor biopsies on
sequential CTLA-4 and PD-1 blockade reveals markers of response and
resistance. Sci Transl Med. 9(eaah3560)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Shi LZ, Fu T, Guan B, Chen J, Blando JM,
Allison JP, Xiong L, Subudhi SK, Gao J and Sharma P: Interdependent
IL-7 and IFN-γ signalling in T-cell controls tumour eradication by
combined α-CTLA-4+α-PD-1 therapy. Nat Commun.
7(12335)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Dong MB, Wang G, Chow RD, Ye L, Zhu L, Dai
X, Park JJ, Kim HR, Errami Y, Guzman CD, et al: Systematic
immunotherapy target discovery using genome-scale in vivo CRISPR
screens in CD8 T cells. Cell. 178:1189–1204.e23. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Li G, Boucher JC, Kotani H, Park K, Zhang
Y, Shrestha B, Wang X, Guan L, Beatty N, Abate-Daga D and Davila
ML: 4-1BB enhancement of CAR T function requires NF-κB and TRAFs.
JCI Insight. 3(e121322)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Philipson BI, O'Connor RS, May MJ, June
CH, Albelda SM and Milone MC: 4-1BB costimulation promotes CAR T
cell survival through noncanonical NF-κB signaling. Sci Signal.
13(eaay8248)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Schumacher LY, Vo DD, Garban HJ,
Comin-Anduix B, Owens SK, Dissette VB, Glaspy JA, McBride WH,
Bonavida B, Economou JS and Ribas A: Immunosensitization of tumor
cells to dendritic cell-activated immune responses with the
proteasome inhibitor bortezomib (PS-341, Velcade). J Immunol.
176:4757–4765. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Enzler T, Sano Y, Choo MK, Cottam HB,
Karin M, Tsao H and Park JM: Cell-selective inhibition of NF-κB
signaling improves therapeutic index in a melanoma chemotherapy
model. Cancer Discov. 1:496–507. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Xiao Z, Su Z, Han S, Huang J, Lin L and
Shuai X: Dual pH-sensitive nanodrug blocks PD-1 immune checkpoint
and uses T cells to deliver NF-κB inhibitor for antitumor
immunotherapy. Sci Adv. 6(eaay7785)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Cai M, He J, Xiong J, Tay LW, Wang Z, Rog
C, Wang J, Xie Y, Wang G, Banno Y, et al: Phospholipase
D1-regulated autophagy supplies free fatty acids to counter
nutrient stress in cancer cells. Cell Death Dis.
7(e2448)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Palikaras K, Lionaki E and Tavernarakis N:
Mechanisms of mitophagy in cellular homeostasis, physiology and
pathology. Nat Cell Biol. 20:1013–1022. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Ganesan R, Mallets E and Gomez-Cambronero
J: The transcription factors Slug (SNAI2) and Snail (SNAI1)
regulate phospholipase D (PLD) promoter in opposite ways towards
cancer cell invasion. Mol Oncol. 10:663–676. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Ho HY, Lin CW, Chien MH, Reiter RJ, Su SC,
Hsieh YH and Yang SF: Melatonin suppresses TPA-induced metastasis
by downregulating matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression through
JNK/SP-1 signaling in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Pineal Res.
61:479–492. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Issuree PD, Pushparaj PN, Pervaiz S and
Melendez AJ: Resveratrol attenuates C5a-induced inflammatory
responses in vitro and in vivo by inhibiting phospholipase D and
sphingosine kinase activities. FASEB J. 23:2412–2424.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Park MH and Min do S: Quercetin-induced
downregulation of phospholipase D1 inhibits proliferation and
invasion in U87 glioma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
412:710–715. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Garcia A, Zheng Y, Zhao C, Toschi A, Fan
J, Shraibman N, Brown HA, Bar-Sagi D, Foster DA and Arbiser JL:
Honokiol suppresses survival signals mediated by Ras-dependent
phospholipase D activity in human cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res.
14:4267–4274. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Huang B, Song BL and Xu C: Cholesterol
metabolism in cancer: Mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. Nat
Metab. 2:132–141. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Voisin M, de Medina P, Mallinger A, Dalenc
F, Huc-Claustre E, Leignadier J, Serhan N, Soules R, Ségala G,
Mougel A, et al: Identification of a tumor-promoter cholesterol
metabolite in human breast cancers acting through the
glucocorticoid receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 114:E9346–E9355.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Chimento A, Casaburi I, Avena P, Trotta F,
De Luca A, Rago V, Pezzi V and Sirianni R: Cholesterol and its
metabolites in tumor growth: Therapeutic potential of statins in
cancer treatment. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne).
9(807)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Ding X, Zhang W, Li S and Yang H: The role
of cholesterol metabolism in cancer. Am J Cancer Res. 9:219–227.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Wang Y, Liu C and Hu L: Cholesterol
regulates cell proliferation and apoptosis of colorectal cancer by
modulating miR-33a-PIM3 pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
511:685–692. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Liu Z, Liu X, Liu S and Cao Q: Cholesterol
promotes the migration and invasion of renal carcinoma cells by
regulating the KLF5/miR-27a/FBXW7 pathway. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 502:69–75. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Raccosta L, Fontana R, Maggioni D,
Lanterna C, Villablanca EJ, Paniccia A, Musumeci A, Chiricozzi E,
Trincavelli ML, Daniele S, et al: The oxysterol-CXCR2 axis plays a
key role in the recruitment of tumor-promoting neutrophils. J Exp
Med. 210:1711–1728. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Condamine T, Dominguez GA, Youn JI,
Kossenkov AV, Mony S, Alicea-Torres K, Tcyganov E, Hashimoto A,
Nefedova Y, Lin C, et al: Lectin-type oxidized LDL receptor-1
distinguishes population of human polymorphonuclear myeloid-derived
suppressor cells in cancer patients. Sci Immunol.
1(aaf8943)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Goossens P, Rodriguez-Vita J, Etzerodt A,
Masse M, Rastoin O, Gouirand V, Ulas T, Papantonopoulou O, Van Eck
M, Auphan-Anezin N, et al: Membrane cholesterol efflux drives
tumor-associated macrophage reprogramming and tumor progression.
Cell Metab. 29:1376–1389.e4. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Kidani Y, Elsaesser H, Hock MB, Vergnes L,
Williams KJ, Argus JP, Marbois BN, Komisopoulou E, Wilson EB,
Osborne TF, et al: Sterol regulatory element-binding proteins are
essential for the metabolic programming of effector T cells and
adaptive immunity. Nat Immunol. 14:489–499. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Larsen SB, Dehlendorff C, Skriver C,
Dalton SO, Jespersen CG, Borre M, Brasso K, Nørgaard M, Johansen C,
Sørensen HT, et al: Postdiagnosis statin use and mortality in
danish patients with prostate cancer. J Clin Oncol. 35:3290–3297.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Xia Y, Xie Y, Yu Z, Xiao H, Jiang G, Zhou
X, Yang Y, Li X, Zhao M, Li L, et al: The mevalonate pathway is a
druggable target for vaccine adjuvant discovery. Cell.
175:1059–1073.e21. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Maione F, Oliaro-Bosso S, Meda C, Di
Nicolantonio F, Bussolino F, Balliano G, Viola F and Giraudo E: The
cholesterol biosynthesis enzyme oxidosqualene cyclase is a new
target to impair tumour angiogenesis and metastasis dissemination.
Sci Rep. 5(9054)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Lanterna C, Musumeci A, Raccosta L, Corna
G, Moresco M, Maggioni D, Fontana R, Doglioni C, Bordignon C,
Traversari C and Russo V: The administration of drugs inhibiting
cholesterol/oxysterol synthesis is safe and increases the efficacy
of immunotherapeutic regimens in tumor-bearing mice. Cancer Immunol
Immunother. 65:1303–1315. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Lu Y, Wang Y, Qiu Y and Xuan W: Analysis
of the relationship between the expression level of TTR and APOH
and prognosis in patients with colorectal cancer metastasis based
on bioinformatics. Contrast Media Mol Imaging.
2022(1121312)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Li X, Wang L, Wang L, Feng Z and Peng C:
Single-cell sequencing of hepatocellular carcinoma reveals cell
interactions and cell heterogeneity in the microenvironment. Int J
Gen Med. 14:10141–10153. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Mandili G, Notarpietro A, Khadjavi A,
Allasia M, Battaglia A, Lucatello B, Frea B, Turrini F, Novelli F,
Giribaldi G and Destefanis P: Beta-2-glycoprotein-1 and
alpha-1-antitrypsin as urinary markers of renal cancer in von
Hippel-Lindau patients. Biomarkers. 23:123–130. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
91
|
Fan T, Lu Z, Liu Y, Wang L, Tian H, Zheng
Y, Zheng B, Xue L, Tan F, Xue Q, et al: A novel immune-related
seventeen-gene signature for predicting early stage lung squamous
cell carcinoma prognosis. Front Immunol. 12(665407)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Qiu XT, Song YC, Liu J, Wang ZM, Niu X and
He J: Identification of an immune-related gene-based signature to
predict prognosis of patients with gastric cancer. World J
Gastrointest Oncol. 12:857–876. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|