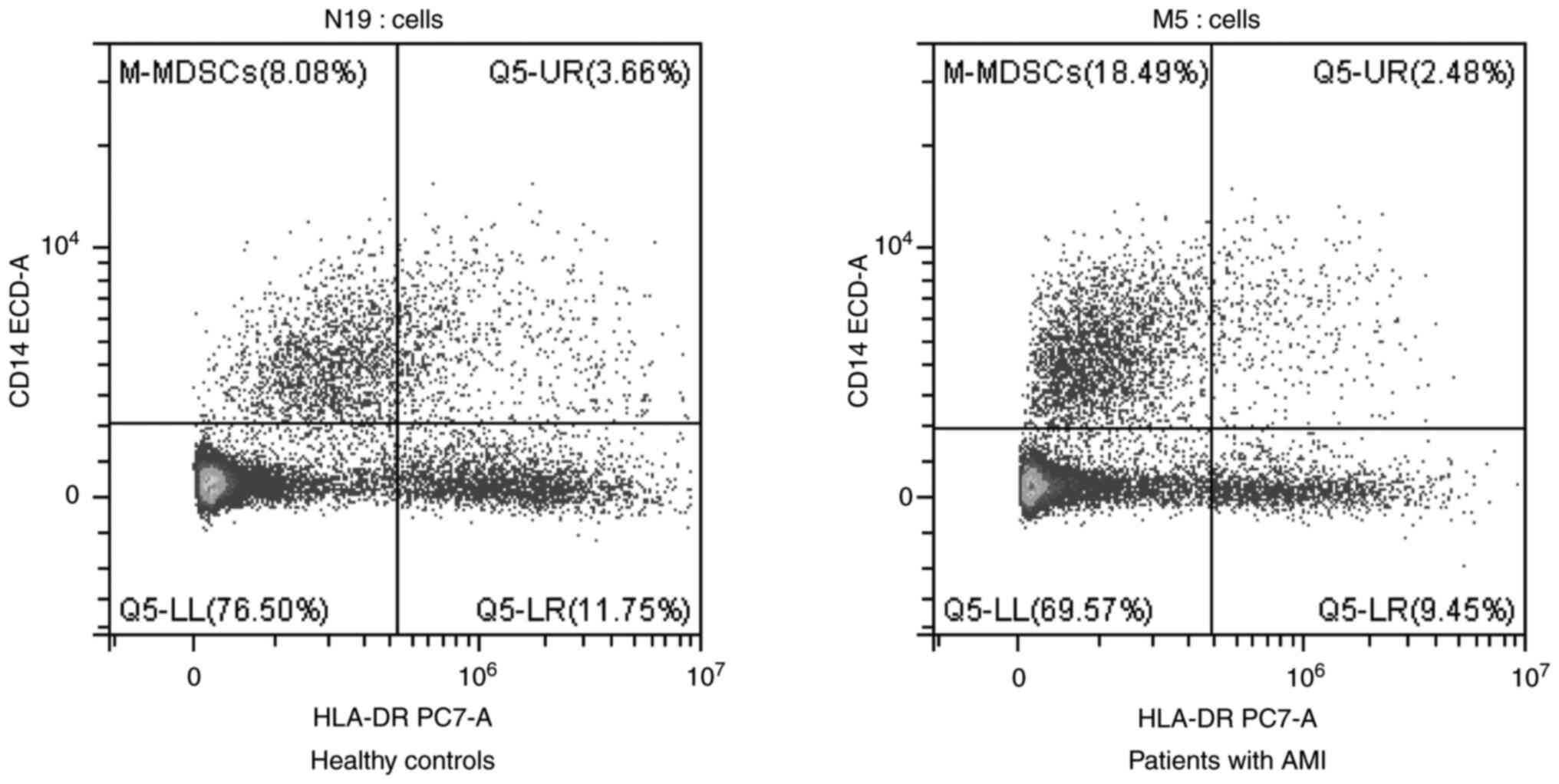
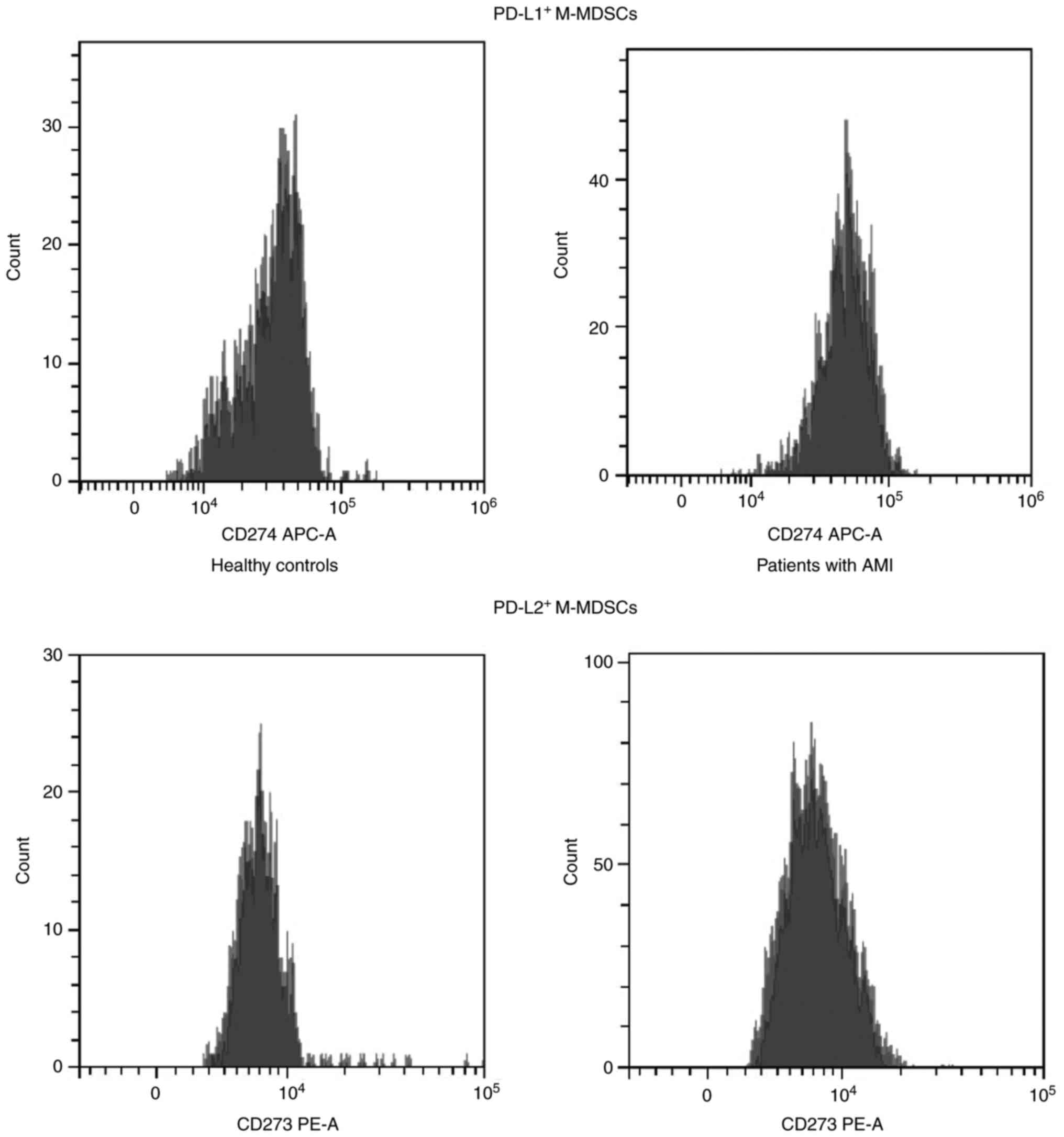
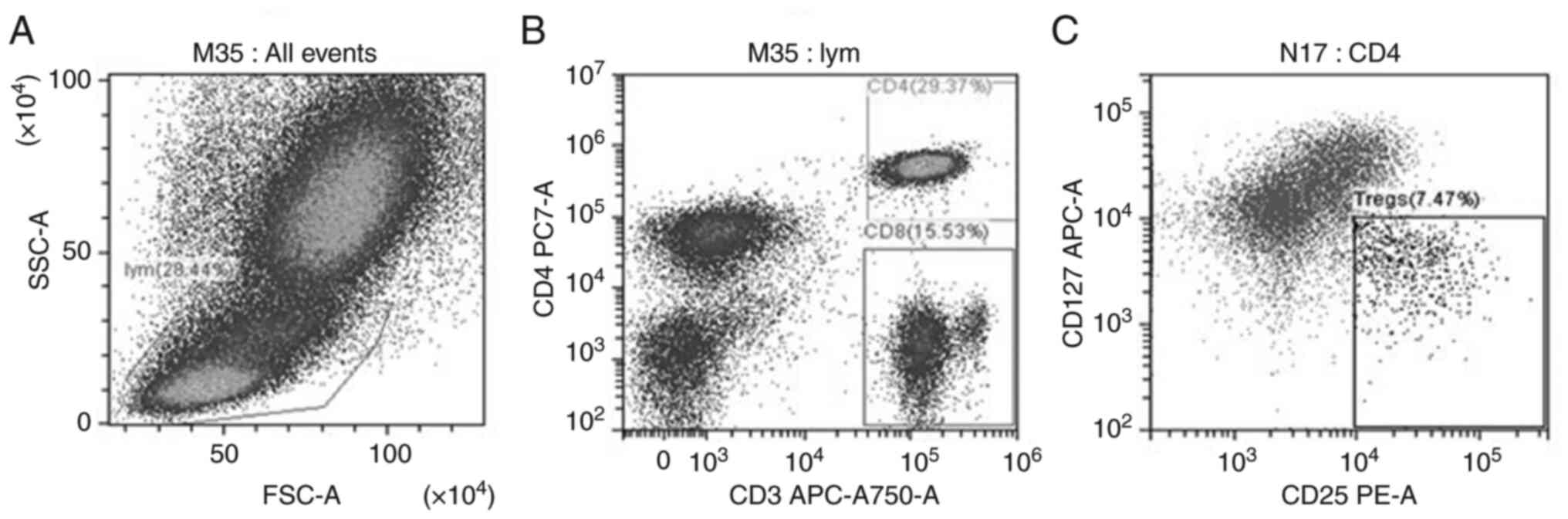
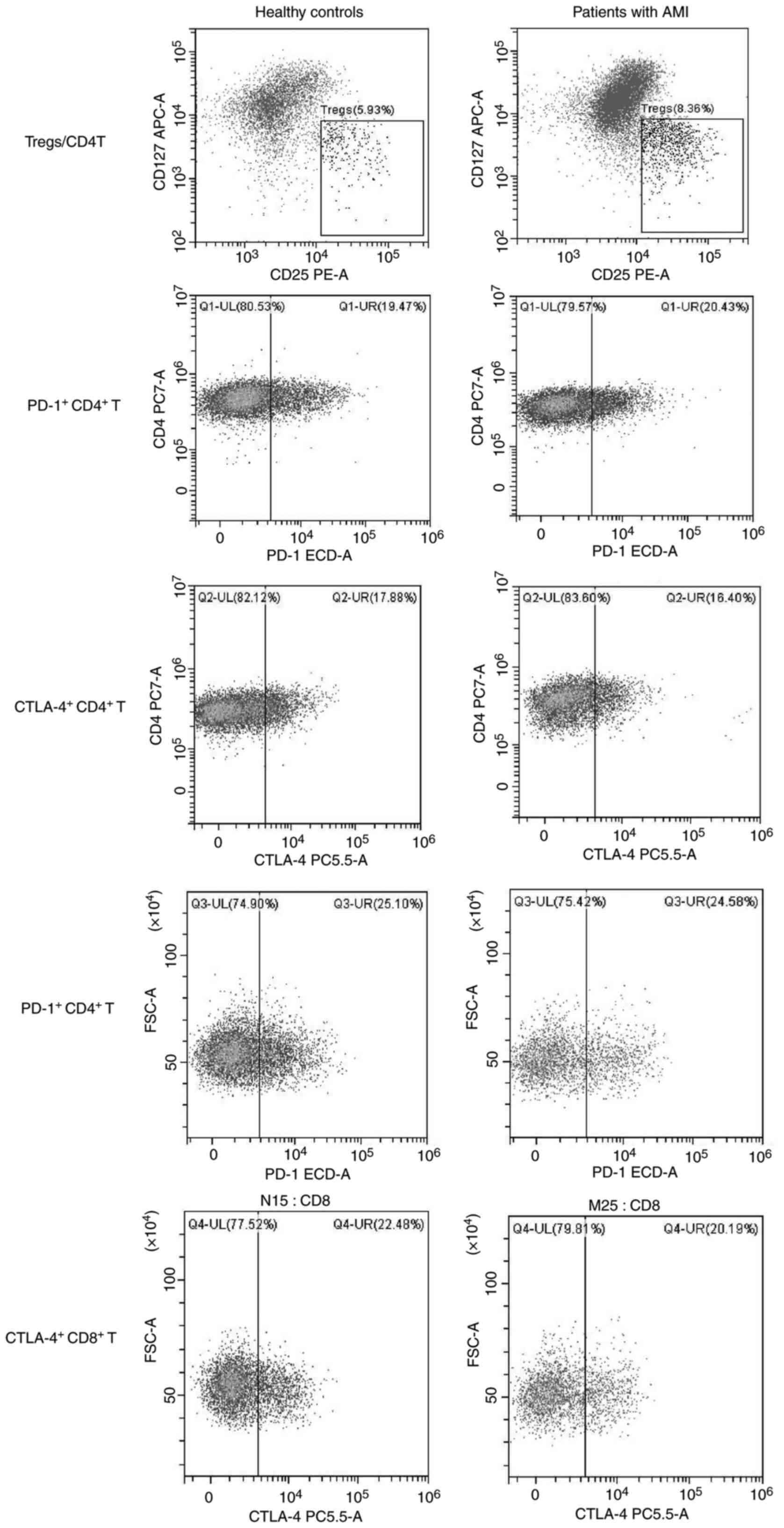
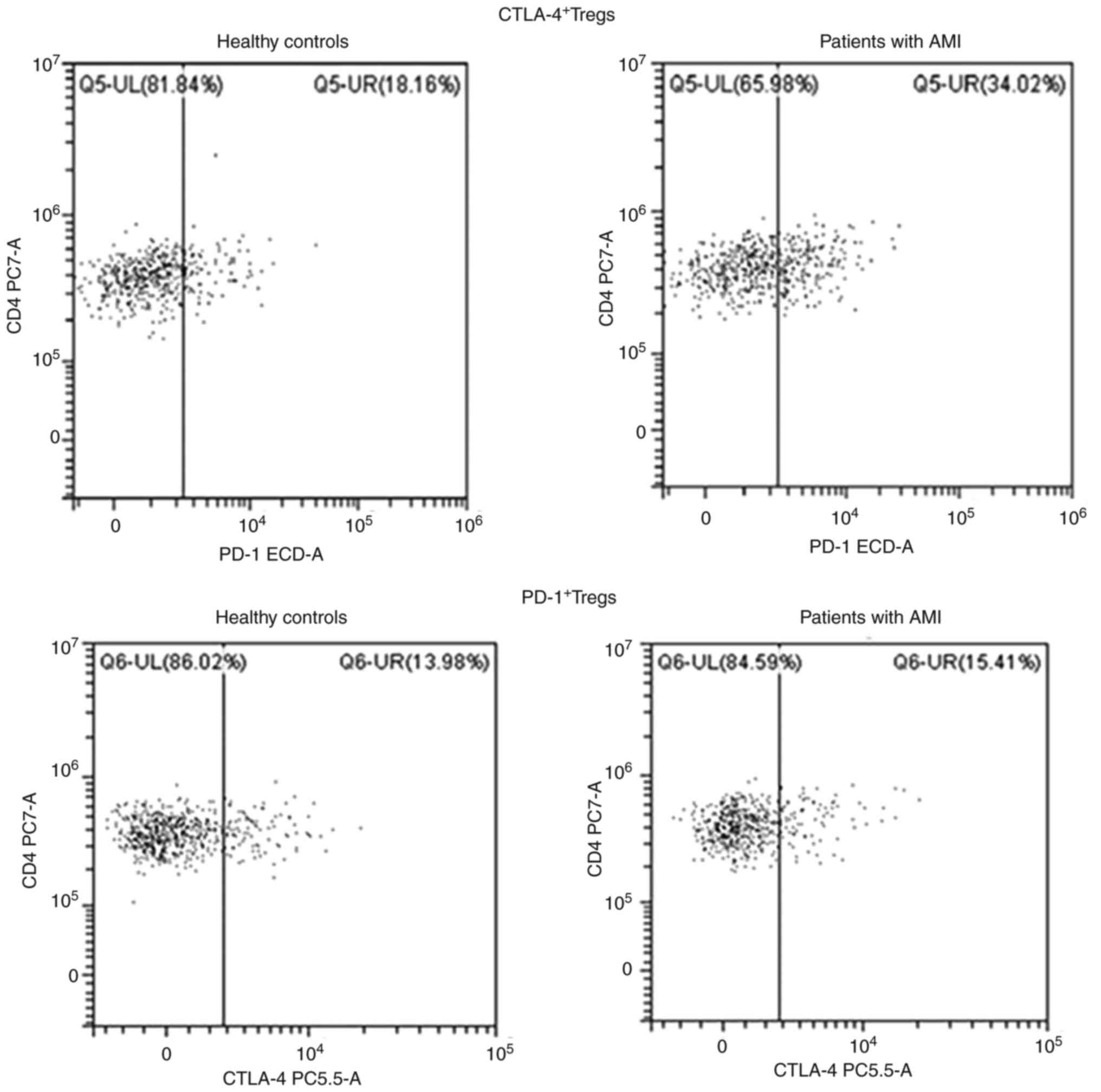
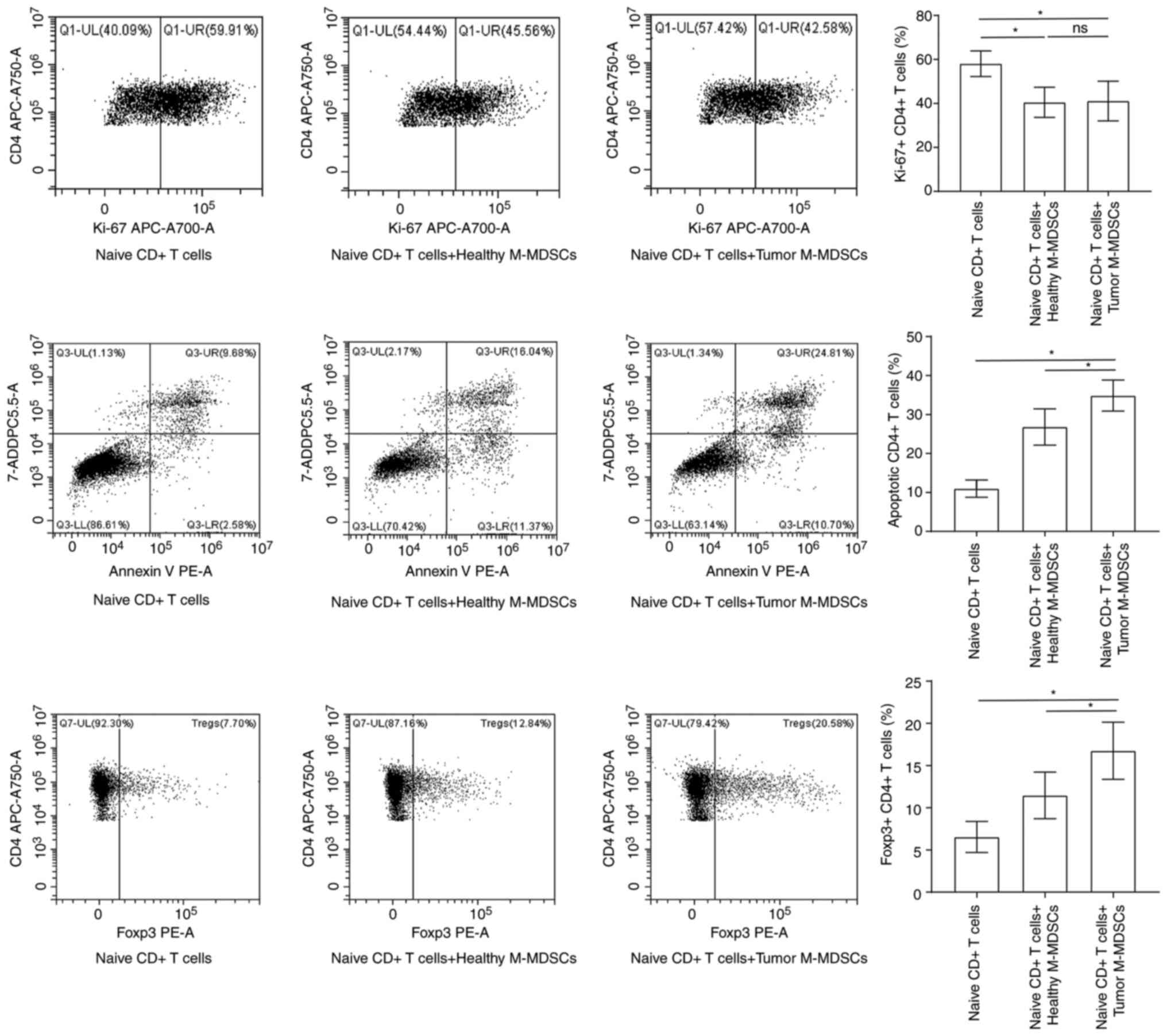
|
1
|
Anderson JL and Morrow DA: Acute
myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 376:2053–2064. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Vogel B, Claessen BE, Arnold SV, Chan D,
Cohen DJ, Giannitsis E, Gibson CM, Goto S, Katus HA, Kerneis M, et
al: ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. Nat Rev Dis
Primers. 5(39)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Alwi I: Targeting inflammation and immune
system in acute myocardial infarction. Acta Med Indones.
51:287–289. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Meng D, Han S, Jeong IS and Kim SW:
Interleukin 10-secreting MSCs via TALEN-mediated gene editing
attenuates left ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction.
Cell Physiol Biochem. 52:728–741. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Luo L, Zeng X, Huang Z, Luo S, Qin L and
Li S: Reduced frequency and functional defects of
CD4+CD25highCD127low/- regulatory
T cells in patients with unexplained recurrent spontaneous
abortion. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 18(62)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Malko D, Elmzzahi T and Beyer M:
Implications of regulatory T cells in non-lymphoid tissue
physiology and pathophysiology. Front Immunol.
13(954798)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Ridker PM, Everett BM, Thuren T, MacFadyen
JG, Chang WH, Ballantyne C, Fonseca F, Nicolau J, Koenig W, Anker
SD, et al: Antiinflammatory therapy with canakinumab for
atherosclerotic disease. N Engl J Med. 377:1119–1131.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Lutgens E, Atzler D, Döring Y, Duchene J,
Steffens S and Weber C: Immunotherapy for cardiovascular disease.
Eur Heart J. 40:3937–3946. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Keskinov AA and Shurin MR: Myeloid
regulatory cells in tumor spreading and metastasis. Immunobiology.
220:236–242. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Gabrilovich DI: Myeloid-derived suppressor
cells. Cancer Immunol Res. 5:3–8. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Groth C, Hu X, Weber R, Fleming V,
Altevogt P, Utikal J and Umansky V: Immunosuppression mediated by
myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) during tumour progression.
Br J Cancer. 120:16–25. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Bronte V, Brandau S, Chen SH, Colombo MP,
Frey AB, Greten TF, Mandruzzato S, Murray PJ, Ochoa A,
Ostrand-Rosenberg S, et al: Recommendations for myeloid-derived
suppressor cell nomenclature and characterization standards. Nat
Commun. 7(12150)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Talmadge JE and Gabrilovich DI: History of
myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Nat Rev Cancer. 13:739–752.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Chang AL, Miska J, Wainwright DA, Dey M,
Rivetta CV, Yu D, Kanojia D, Pituch KC, Qiao J, Pytel P, et al:
CCL2 produced by the glioma microenvironment is essential for the
recruitment of regulatory T cells and myeloid-derived suppressor
cells. Cancer Res. 76:5671–5682. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Lu C, Redd PS, Lee JR, Savage N and Liu K:
The expression profiles and regulation of PD-L1 in tumor-induced
myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Oncoimmunology.
5(e1247135)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Wang JC and Sun L: PD-1/PD-L1, MDSC
pathways, and checkpoint inhibitor therapy in Ph(-)
myeloproliferative neoplasm: A review. Int J Mol Sci.
23(5837)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Bahrami A, Fereidouni M, Pirro M, Bianconi
V and Sahebkar A: Modulation of regulatory T cells by natural
products in cancer. Cancer Lett. 459:72–85. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Park HJ, Park JS, Jeong YH, Son J, Ban YH,
Lee BH, Chen L, Chang J, Chung DH, Choi I and Ha SJ: . PD-1
upregulated on regulatory T cells during chronic virus infection
enhances the suppression of CD8+ T cell immune response
via the interaction with PD-L1 expressed on CD8+ T
cells. J Immunol. 194:5801–5811. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Prima V, Kaliberova LN, Kaliberov S,
Curiel DT and Kusmartsev S: COX2/mPGES1/PGE2 pathway regulates
PD-L1 expression in tumor-associated macrophages and
myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
114:1117–1122. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Noman MZ, Desantis G, Janji B, Hasmim M,
Karray S, Dessen P, Bronte V and Chouaib S: PD-L1 is a novel direct
target of HIF-1α, and its blockade under hypoxia enhanced
MDSC-mediated T cell activation. J Exp Med. 211:781–790.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Teng MW, Ngiow SF, Ribas A and Smyth MJ:
Classifying cancers based on T-cell infiltration and PD-L1. Cancer
Res. 75:2139–2145. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Dolcetti L, Peranzoni E, Ugel S, Marigo I,
Fernandez Gomez A, Mesa C, Geilich M, Winkels G, Traggiai E, Casati
A, et al: Hierarchy of immunosuppressive strength among
myeloid-derived suppressor cell subsets is determined by GM-CSF.
Eur J Immunol. 40:22–35. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Tu S, Bhagat G, Cui G, Takaishi S,
Kurt-Jones EA, Rickman B, Betz KS, Penz-Oesterreicher M, Bjorkdahl
O, Fox JG and Wang TC: Overexpression of interleukin-1beta induces
gastric inflammation and cancer and mobilizes myeloid-derived
suppressor cells in mice. Cancer Cell. 14:408–419. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Bunt SK, Yang L, Sinha P, Clements VK,
Leips J and Ostrand-Rosenberg S: Reduced inflammation in the tumor
microenvironment delays the accumulation of myeloid-derived
suppressor cells and limits tumor progression. Cancer Res.
67:10019–10026. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Rodriguez PC, Hernandez CP, Quiceno D,
Dubinett SM, Zabaleta J, Ochoa JB, Gilbert J and Ochoa AC: Arginase
I in myeloid suppressor cells is induced by COX-2 in lung
carcinoma. J Exp Med. 202:931–939. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Sinha P, Okoro C, Foell D, Freeze HH,
Ostrand-Rosenberg S and Srikrishna G: Proinflammatory S100 proteins
regulate the accumulation of myeloid-derived suppressor cells. J
Immunol. 181:4666–4675. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Zhou L, Miao K, Yin B, Li H, Fan J, Zhu Y,
Ba H, Zhang Z, Chen F, Wang J, et al: Cardioprotective role of
myeloid-derived suppressor cells in heart failure. Circulation.
138:181–197. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Wang S, Tan Q, Hou Y and Dou H: Emerging
roles of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in diabetes. Front
Pharmacol. 12(798320)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Epelman S, Liu PP and Mann DL: Role of
innate and adaptive immune mechanisms in cardiac injury and repair.
Nat Rev Immunol. 15:117–129. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Sun SN, Ni SH, Li Y, Li Y, Liu X, Deng JP,
Chen ZX, Li H, Feng WJ, Huang YS, et al: G-MDSCs promote
aging-related cardiac fibrosis by activating myofibroblasts and
preventing senescence. Cell Death Dis. 12(594)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Oprescu N, Micheu MM, Scafa-Udriste A,
Popa-Fotea NM and Dorobantu M: Inflammatory markers in acute
myocardial infarction and the correlation with the severity of
coronary heart disease. Ann Med. 53:1041–1047. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Karthikeyan T, Raja M, Radha D, Gaur TA,
Geetha J and Sakthivadivel V: Risk factors and inflammatory markers
in acute coronary syndrome-ST elevation myocardial infarction
(STEMI). Horm Mol Biol Clin Investig: Mar 20, 2023 (Epub ahead of
print).
|
|
33
|
Jiang Y, Li X, Xu H, Gu Y, Shi F, Wang F
and Zhang X: Tumour necrosis factor receptor-associated factors:
Interacting protein with forkhead-associated domain inhibition
decreases inflammatory cell infiltration and cardiac remodelling
after acute myocardial infarction. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg.
31:85–92. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Mukherjee S, Ghosh S, Sengupta A, Sarkar
S, Keswani T, Chatterjee R and Bhattacharyya A: IL-6 dependent
expansion of inflammatory MDSCs (CD11b+ Gr-1+) promote Th-17
mediated immune response during experimental cerebral malaria.
Cytokine. 155(155910)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Lou X, Gao D, Yang L, Wang Y and Hou Y:
Endoplasmic reticulum stress mediates the myeloid-derived immune
suppression associated with cancer and infectious disease. J Transl
Med. 21(1)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Xia N, Lu Y, Gu M, Li N, Liu M, Jiao J,
Zhu Z, Li J, Li D, Tang T, et al: A unique population of regulatory
T cells in heart potentiates cardiac protection from myocardial
infarction. Circulation. 142:1956–1973. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Ke D, Fang J, Fan L, Chen Z and Chen L:
Regulatory T cells contribute to rosuvastatin-induced
cardioprotection against ischemia-reperfusion injury. Coron Artery
Dis. 24:334–341. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Weirather J, Hofmann UD, Beyersdorf N,
Ramos GC, Vogel B, Frey A, Ertl G, Kerkau T and Frantz S: Foxp3+
CD4+ T cells improve healing after myocardial infarction by
modulating monocyte/macrophage differentiation. Circ Res.
115:55–67. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Sharir R, Semo J, Shimoni S, Ben-Mordechai
T, Landa-Rouben N, Maysel-Auslender S, Shaish A, Entin-Meer M,
Keren G and George J: Experimental myocardial infarction induces
altered regulatory T cell hemostasis, and adoptive transfer
attenuates subsequent remodeling. PLoS One.
9(e113653)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Feng Q, Li Q, Zhou H, Sun L, Lin C, Jin Y,
Wang D and Guo G: The role of major immune cells in myocardial
infarction. Front Immunol. 13(1084460)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Turnquist HR, Zhao Z, Rosborough BR, Liu
Q, Castellaneta A, Isse K, Wang Z, Lang M, Stolz DB, Zheng XX, et
al: IL-33 expands suppressive CD11b+ Gr-1(int) and regulatory T
cells, including ST2L+ Foxp3+ cells, and mediates regulatory T
cell-dependent promotion of cardiac allograft survival. J Immunol.
187:4598–4610. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Huang B, Pan PY, Li Q, Sato AI, Levy DE,
Bromberg J, Divino CM and Chen SH: Gr-1+CD115+ immature myeloid
suppressor cells mediate the development of tumor-induced T
regulatory cells and T-cell anergy in tumor-bearing host. Cancer
Res. 66:1123–1131. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Yaseen MM, Abuharfeil NM and Darmani H:
Myeloid-derived suppressor cells and the pathogenesis of human
immunodeficiency virus infection. Open Biol.
11(210216)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Guo H, Cao A, Chu S, Wang Y, Zang Y, Mao
X, Wang H, Wang Y, Liu C, Zhang X and Peng W: Astragaloside IV
attenuates podocyte apoptosis mediated by endoplasmic reticulum
stress through upregulating sarco/endoplasmic reticulum
Ca2+-ATPase 2 expression in diabetic nephropathy. Front
Pharmacol. 7(500)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Guo X, Zhang Y, Jiao H and Miao X: The
prognostic significance of PD-L1 expression in patients with
glioblastoma: A meta-analysis. Front Oncol.
12(925560)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Tang L, Bai J, Chung CS, Lomas-Neira J,
Chen Y, Huang X and Ayala A: Programmed cell death receptor ligand
1 modulates the regulatory T cells' capacity to repress
shock/sepsis-induced indirect acute lung injury by recruiting
phosphatase SRC homology region 2 domain-containing phosphatase 1.
Shock. 43:47–54. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Jaworska K, Ratajczak J, Huang L, Whalen
K, Yang M, Stevens BK and Kinsey GR: Both PD-1 ligands protect the
kidney from ischemia reperfusion injury. J Immunol. 194:325–333.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|