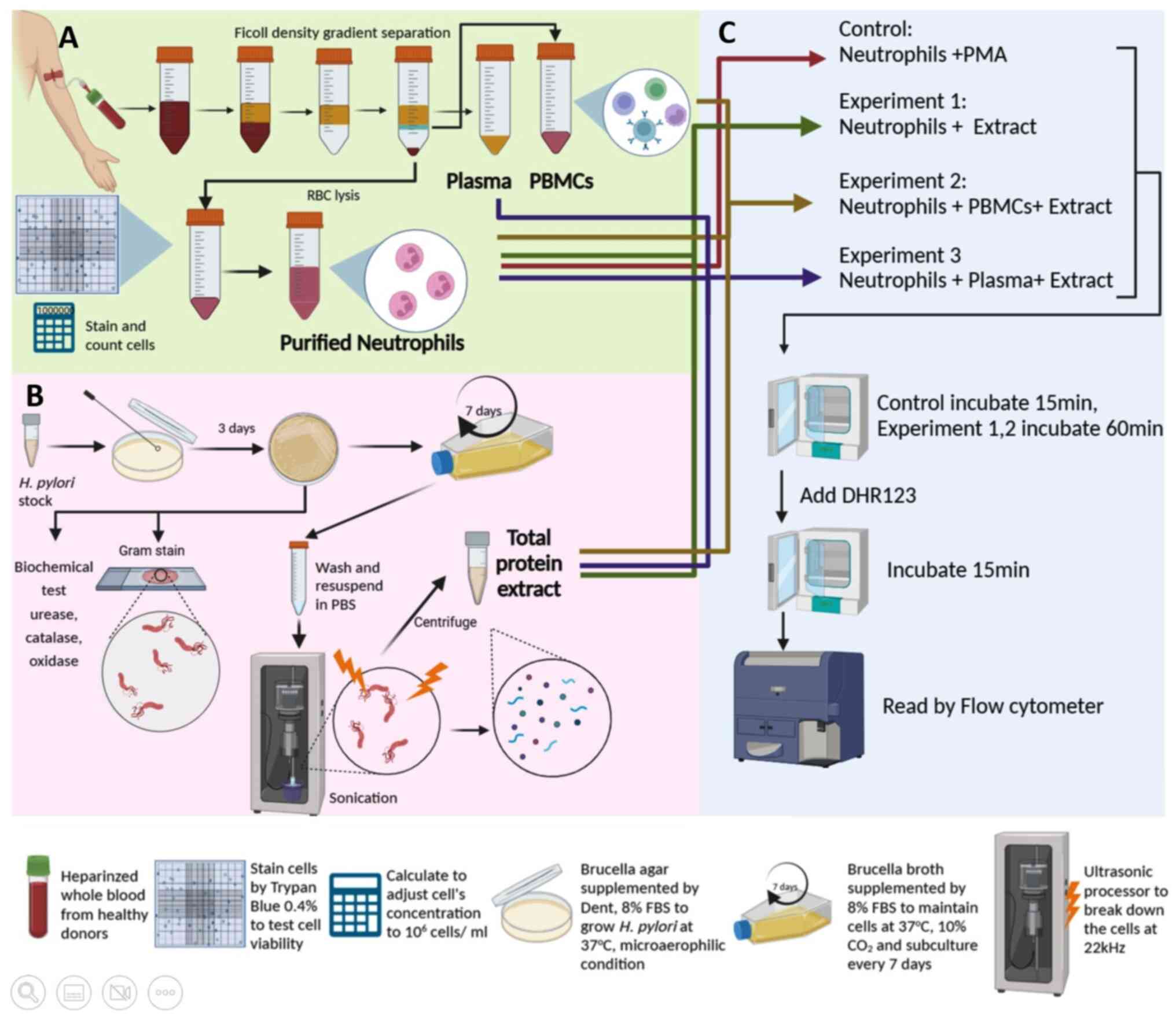
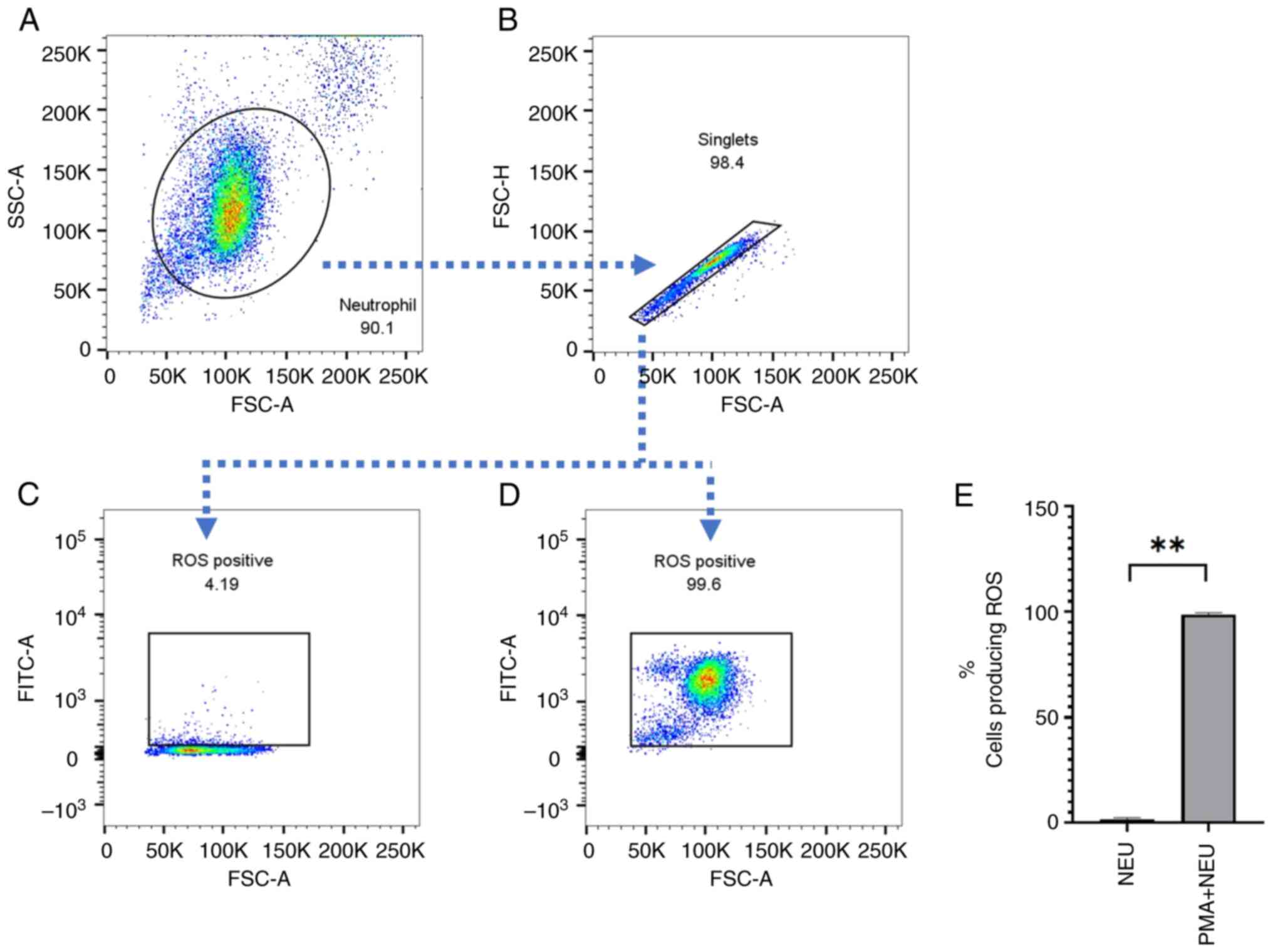
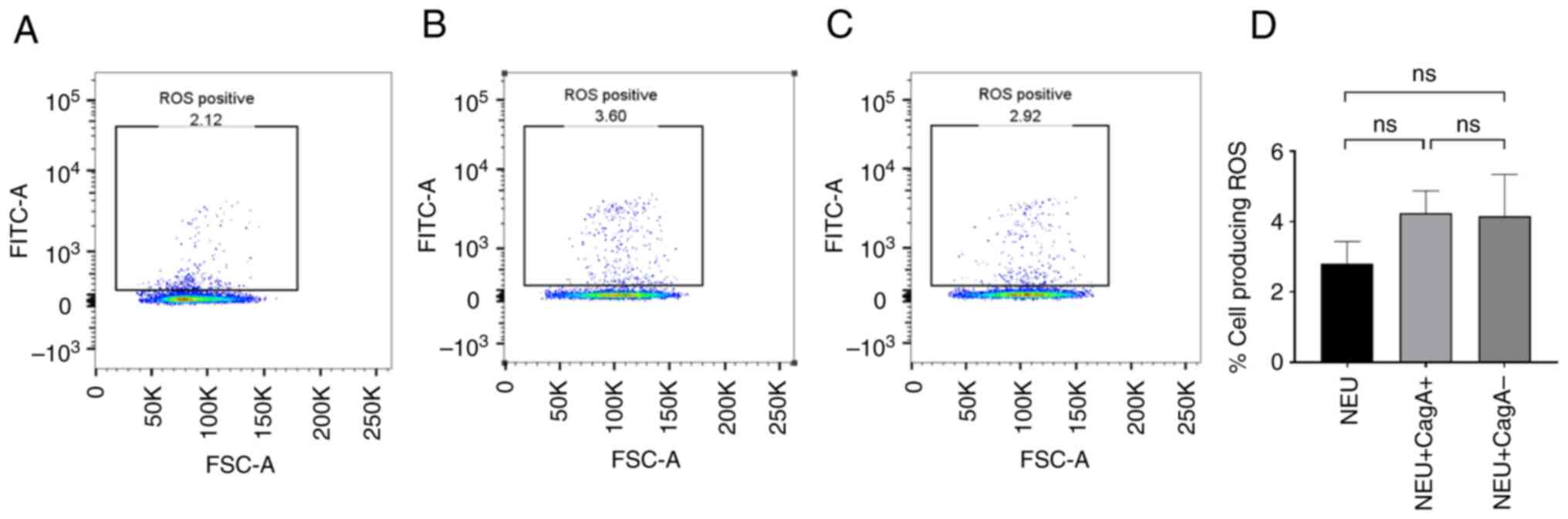
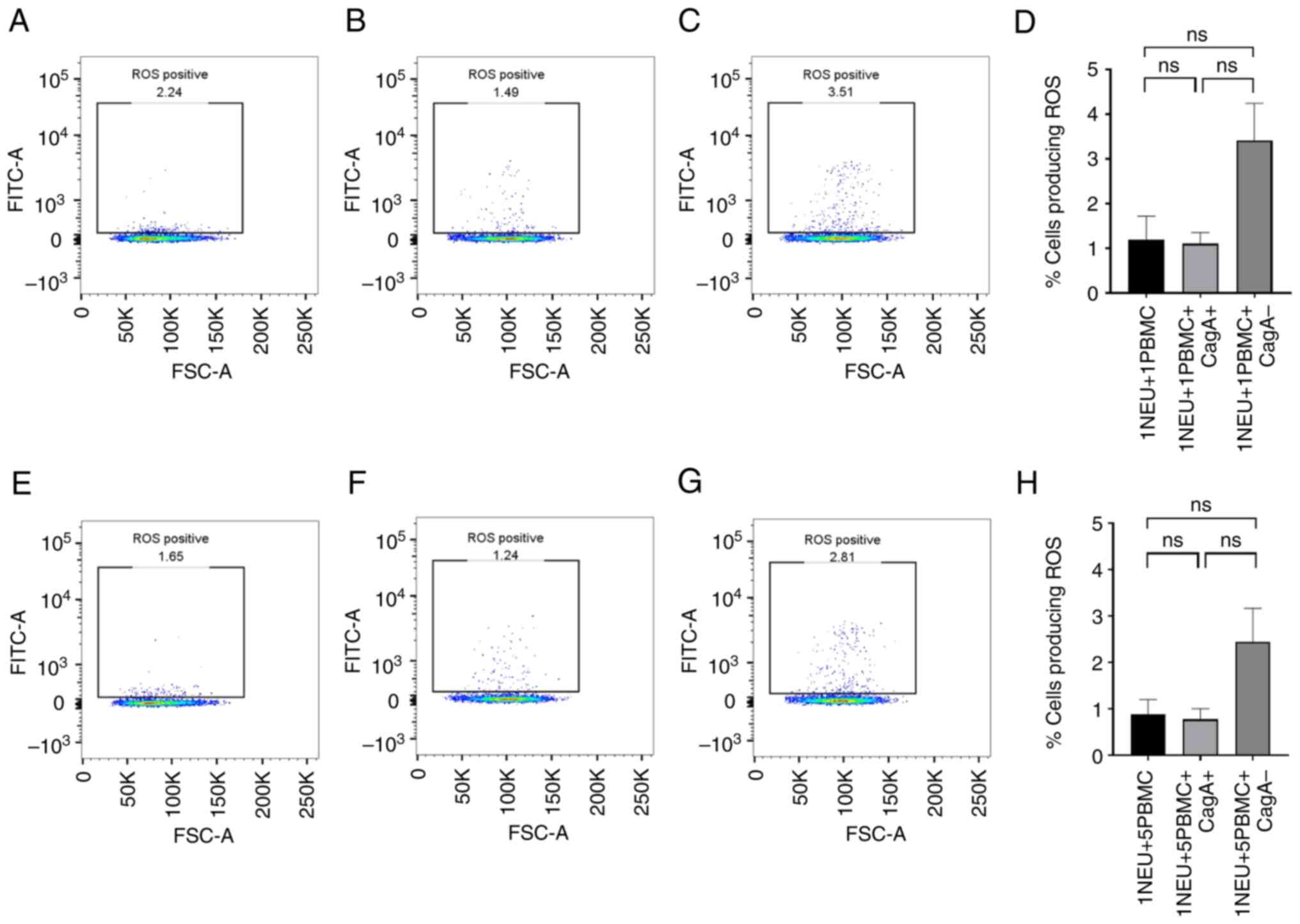
|
1
|
Baj J, Forma A, Sitarz M, Portincasa P,
Garruti G, Krasowska D and Maciejewski R: Helicobacter pylori
virulence factors-mechanisms of bacterial pathogenicity in the
gastric microenvironment. Cells. 10(27)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Noto JM and Peek RM Jr: The helicobacter
pylori cag Pathogenicity Island. Methods Mol Biol. 921:41–50.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Hatakeyama M: Structure and function of
Helicobacter pylori CagA, the first-identified bacterial protein
involved in human cancer. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci.
93:196–219. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Yamaoka Y, Kita M, Kodama T, Sawai N and
Imanishi J: Helicobacter pylori cagA gene and expression of
cytokine messenger RNA in gastric mucosa. Gastroenterology.
110:1744–1752. 1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Crabtree JE, Farmery SM, Lindley IJ,
Figura N, Peichl P and Tompkins DS: CagA/cytotoxic strains of
Helicobacter pylori and interleukin-8 in gastric epithelial cell
lines. J Clin Pathol. 47:945–950. 1994.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Tohidpour A: CagA-mediated pathogenesis of
Helicobacter pylori. Microb Pathog. 93:44–55. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Wright HL, Moots RJ and Edwards SW: The
multifactorial role of neutrophils in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev
Rheumatol. 10:593–601. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Salao K, Spofford EM, Price C, Mairiang E,
Suttiprapa S, Wright HL, Sripa B and Edwards SW: Enhanced
neutrophil functions during Opisthorchis viverrini infections and
correlation with advanced periductal fibrosis. Int J Parasitol.
50:145–152. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Han L, Shu X and Wang J: Helicobacter
pylori-mediated oxidative stress and gastric diseases: A Review.
Front Microbiol. 13(811258)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Psychogios N, Hau DD, Peng J, Guo AC,
Mandal R, Bouatra S, Sinelnikov I, Krishnamurthy R, Eisner R,
Gautam B, et al: The human serum metabolome. PLoS One.
6(e16957)2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Perez-Figueroa E, Torres J, Sanchez-Zauco
N, Contreras-Ramos A, Alvarez-Arellano L and Maldonado-Bernal C:
Activation of NLRP3 inflammasome in human neutrophils by
Helicobacter pylori infection. Innate Immun. 22:103–112.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Faass L, Hauke M, Stein SC and Josenhans
C: Innate immune activation and modulatory factors of Helicobacter
pylori towards phagocytic and nonphagocytic cells. Curr Opin
Immunol. 82(102301)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Pham KT, Weiss E, Jimenez Soto LF,
Breithaupt U, Haas R and Fischer W: CagI is an essential component
of the Helicobacter pylori Cag type IV secretion system and forms a
complex with CagL. PLoS One. 7(e35341)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Almaraz-Arreortua A, Sosa-Luis SA,
Rios-Rios WJ, Romero-Tlalolini MLÁ, Aguilar-Ruiz SR,
Baltiérrez-Hoyos R and Torres Aguilar H: Morphological and
compositional analysis of neutrophil extracellular traps induced by
microbial and chemical stimuli. J Vis Exp. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Parsonnet J, Friedman GD, Orentreich N and
Vogelman H: Risk for gastric cancer in people with CagA positive or
CagA negative Helicobacter pylori infection. Gut. 40:297–301.
1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Seyoum M, Enawgaw B and Melku M: Human
blood platelets and viruses: Defense mechanism and role in the
removal of viral pathogens. Thromb J. 16(16)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Lawton JW, Robinson JP and Till GO: The
effect of intravenous immunoglobulin on the in vitro function of
human neutrophils. Immunopharmacology. 18:97–105. 1989.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Matsuo H, Itoh H, Kitamura N, Kamikubo Y,
Higuchi T, Shiga S, Ichiyama S, Kondo T, Takaori-Kondo A and Adachi
S: Intravenous immunoglobulin enhances the killing activity and
autophagy of neutrophils isolated from immunocompromised patients
against multidrug-resistant bacteria. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
464:94–99. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Halbgebauer R, Schmidt CQ, Karsten CM,
Ignatius A and Huber-Lang M: Janus face of complement-driven
neutrophil activation during sepsis. Semin Immunol. 37:12–20.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
He Y, Wang C, Zhang X, Lu X, Xing J, Lv J,
Guo M, Huo X, Liu X, Lu J, et al: Sustained exposure to
helicobacter pylori lysate inhibits apoptosis and autophagy of
gastric epithelial cells. Front Oncol. 10(581364)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Ki MR, Goo MJ, Park JK, Hong IH, Ji AR,
Han SY, You SY, Lee EM, Kim AY, Park SJ, et al: Helicobacter pylori
accelerates hepatic fibrosis by sensitizing transforming growth
factor-β1-induced inflammatory signaling. Lab Invest. 90:1507–1516.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Skene C, Young A, Every A and Sutton P:
Helicobacter pylori flagella: Antigenic profile and protective
immunity. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 50:249–256. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Whitmore LC, Weems MN and Allen LH:
Cutting Edge: Helicobacter pylori Induces nuclear hypersegmentation
and subtype differentiation of human neutrophils in vitro. J
Immunol. 198:1793–1797. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Gros B, Gomez Perez A, Pleguezuelo M,
Serrano Ruiz FJ, de la Mata M and Rodriguez-Peralvarez M:
Helicobacter species and hepato-biliary tract malignancies: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancers (Basel).
15(595)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Osaki T, Lin Y, Sasahira N, Ueno M,
Yonezawa H, Hojo F, Okuda M, Matsuyama M, Sasaki T, Kobayashi S, et
al: Prevalence estimates of Helicobacter species infection in
pancreatic and biliary tract cancers. Helicobacter.
27(e12866)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Zhou D, Wang JD, Weng MZ, Zhang Y, Wang
XF, Gong W and Quan ZW: Infections of Helicobacter spp. in the
biliary system are associated with biliary tract cancer: A
meta-analysis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 25:447–454.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Aviles-Jimenez F, Guitron A, Segura-Lopez
F, Méndez-Tenorio A, Iwai S, Hernández-Guerrero A and Torres J:
Microbiota studies in the bile duct strongly suggest a role for
Helicobacter pylori in extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Clin
Microbiol Infect. 22:178 e11–178 e22. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Deenonpoe R, Mairiang E, Mairiang P,
Pairojkul C, Chamgramol Y, Rinaldi G, Loukas A, Brindley PJ and
Sripa B: Elevated prevalence of Helicobacter species and virulence
factors in opisthorchiasis and associated hepatobiliary disease.
Sci Rep. 7(42744)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Deenonpoe R, Chomvarin C, Pairojkul C,
Chamgramol Y, Loukas A, Brindley PJ and Sripa B: The carcinogenic
liver fluke Opisthorchis viverrini is a reservoir for species of
Helicobacter. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 16:1751–1758.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Mairiang E, Laha T, Kaewkes S, Loukas A,
Bethony J, Brindley PJ and Sripa B: Hepatobiliary morbidities
detected by ultrasonography in Opisthorchis viverrini-infected
patients before and after praziquantel treatment: A five-year
follow up study. Acta Trop. 217(105853)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Phung HTT, Deenonpoe R, Suttiprapa S,
Mairiang E, Edwards SW and Sripa B: Persistent advanced periductal
fibrosis is associated with cagA-positive Helicobacter pylori
infection in post-praziquantel treatment of opisthorchiasis.
Helicobacter. 27(e12897)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|