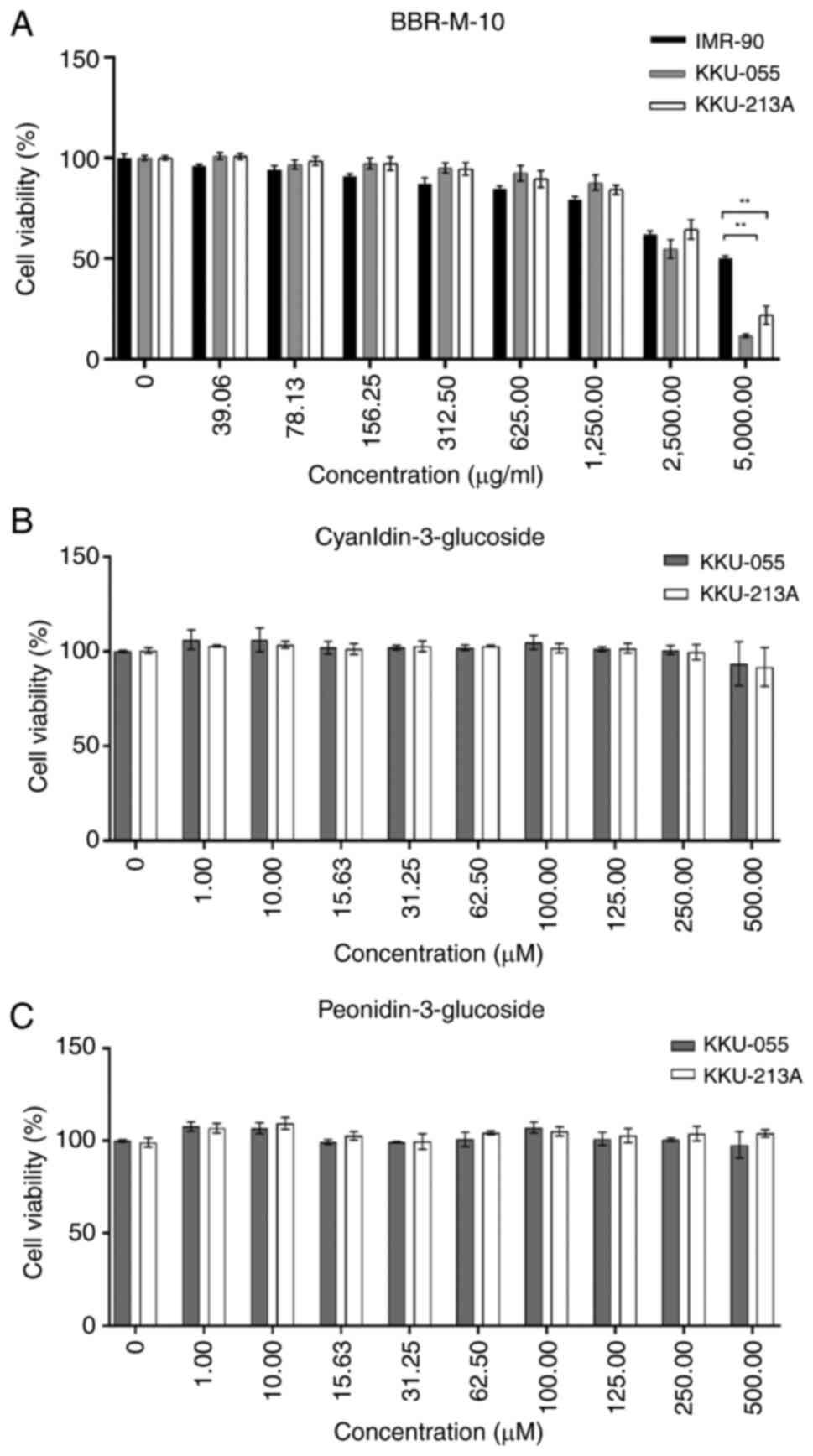
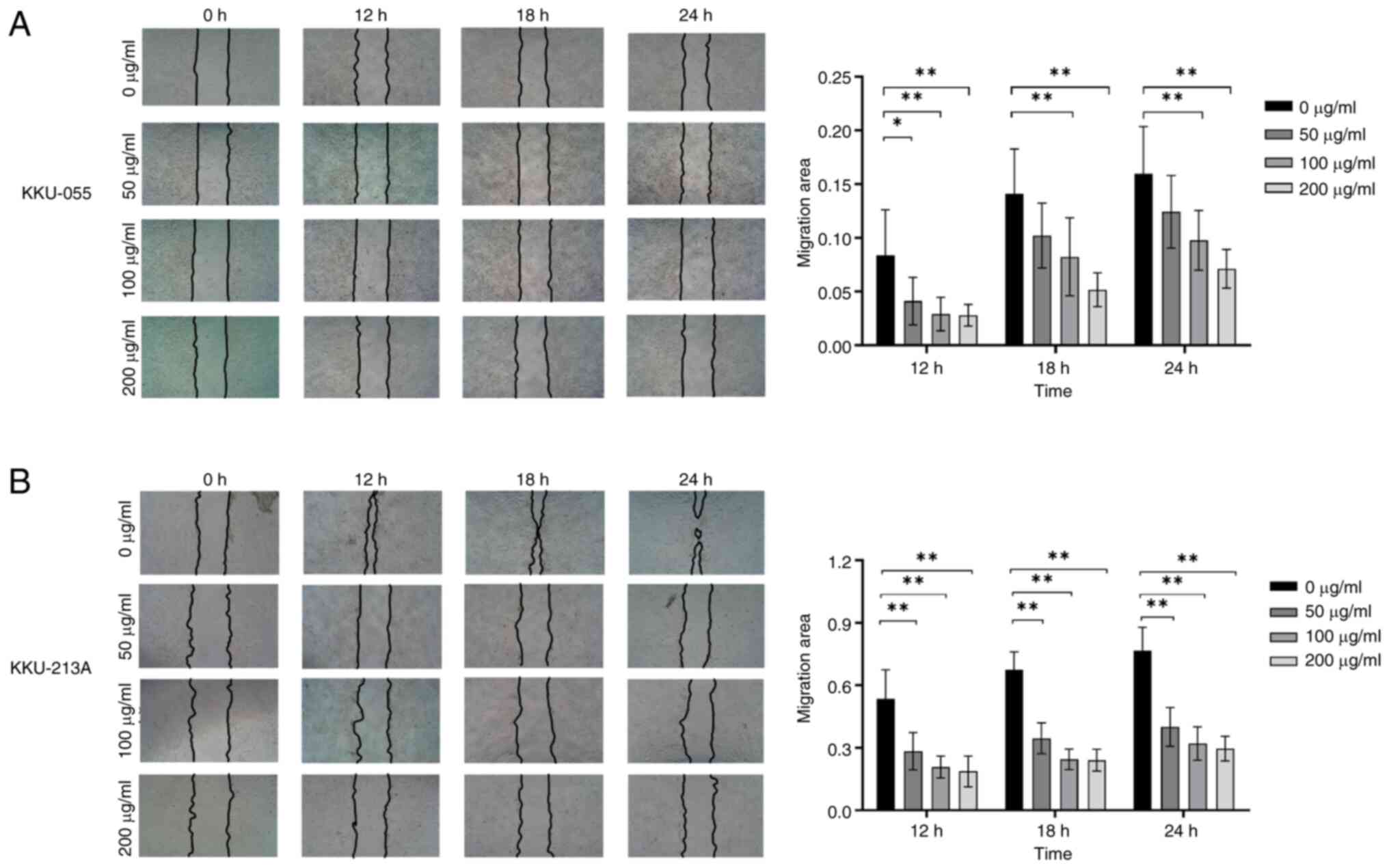
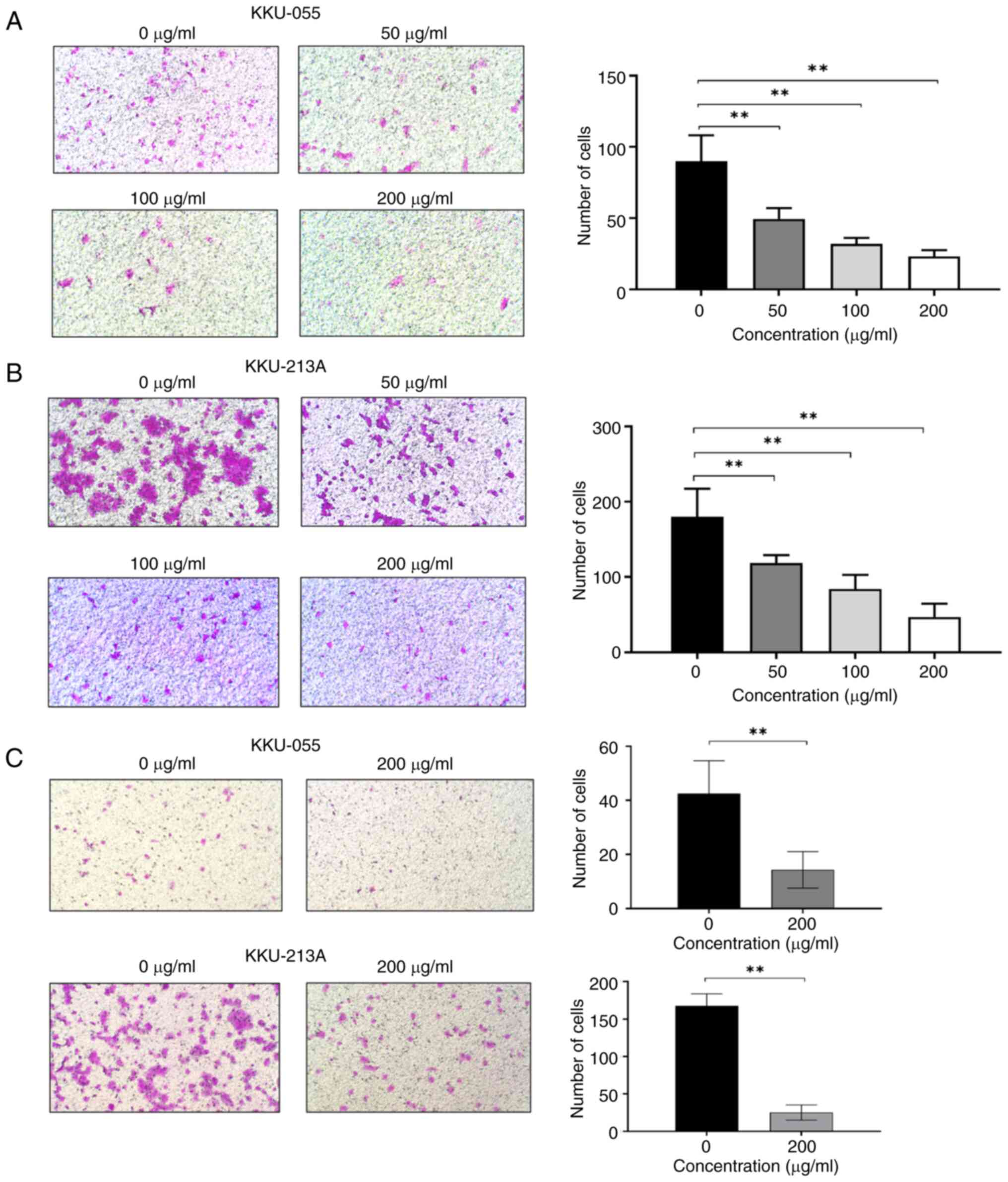
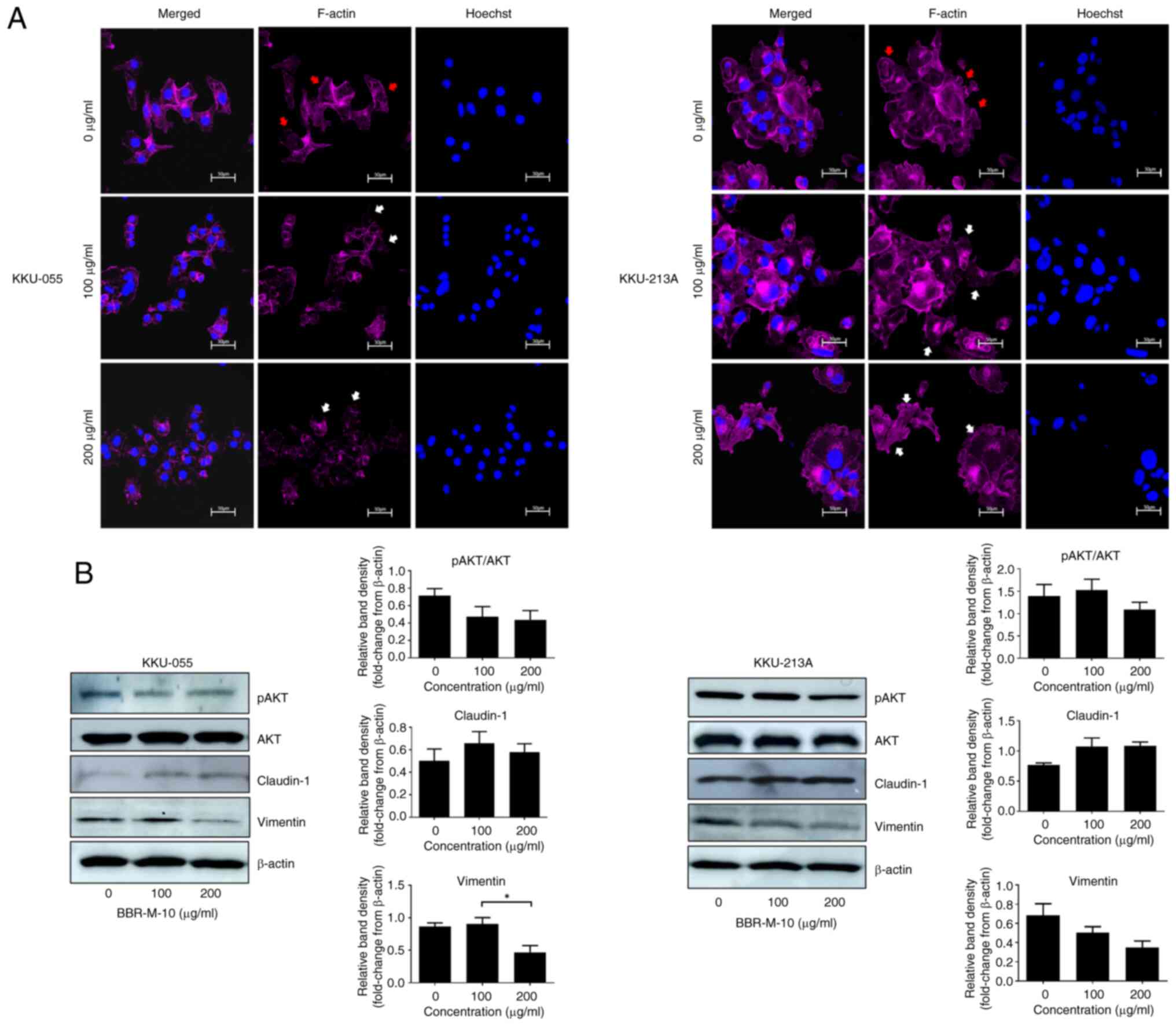
|
1
|
Tan BL, Norhaizan ME and Chan LC: Rice
bran: From waste to nutritious food ingredients. Nutrients.
15(2503)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Wisetkomolmat J, Arjin C, Satsook A,
Seel-Audom M, Ruksiriwanich W, Prom UTC and Sringarm K: Comparative
analysis of nutritional components and phytochemical attributes of
selected Thai rice bran. Front Nutr. 9(833730)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Manzoor A, Kumar Pandey V, Dar AH, Fayaz
U, Dash KK, Shams R, Ahmad S, Bashir I, Fayaz J, Singh P, et al:
Rice bran: Nutritional, phytochemical, and pharmacological profile
and its contribution to human health promotion. Food Chem Adv.
2(100296)2023.
|
|
4
|
Gonçalves AC, Nunes AR, Falcão A, Alves G
and Silva LR: Dietary effects of anthocyanins in human health: a
comprehensive review. Pharmaceuticals (Basel).
14(690)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Khoo HE, Azlan A, Tang ST and Lim SM:
Anthocyanidins and anthocyanins: Colored pigments as food,
pharmaceutical ingredients, and the potential health benefits. Food
Nutr Res. 61(1361779)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
de Sousa Moraes LF, Sun X, Peluzio MDCG
and Zhu MJ: Anthocyanins/anthocyanidins and colorectal cancer: What
is behind the scenes? Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 59:59–71.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Khophai S, Chokchaisiri S, Talabnin K,
Ketudat Cairns JR and Talabnin C: Black rice bran-derived
anthocyanins prevent H2O2-induced oxidative stress and DNA damage
in cholangiocytes through activation of the Nrf2-NQO1 axis.
ScienceAsia (In press).
|
|
8
|
Joshua M, Okere C, Sylvester O, Yahaya M,
Precious O, Dluya T, Um JY, Neksumi M, Boyd J, Vincent-Tyndall J,
et al: Disruption of angiogenesis by anthocyanin-rich extracts of
Hibiscus sabdariffa. Int J Sci Eng Res. 8:299–307. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Wang L, Zhou P, Feng R, Luo Z, Li X and
Gao L: Anti-proliferation activities of Oryza sativa L.
anthocyanins-Hohenbuehelia serotina polysaccharides complex after
in vitro gastrointestinal digestion. Food Chem Toxicol.
135(111012)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Chen PN, Kuo WH, Chiang CL, Chiou HL,
Hsieh YS and Chu SC: Black rice anthocyanins inhibit cancer cells
invasion via repressions of MMPs and u-PA expression. Chem Biol
Interact. 163:218–229. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Sun W, Zhang ND, Zhang T, Li YN, Xue H,
Cao JL, Hou WS, Liu J, Wang Y and Jin CH: Cyanidin-3-O-glucoside
induces the apoptosis of human gastric cancer MKN-45 cells through
ROS-mediated signaling pathways. Molecules. 28(652)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Lee J, Shin A, Oh JH and Kim J: Colors of
vegetables and fruits and the risks of colorectal cancer. World J
Gastroenterol. 23:2527–2538. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Xu C, Zeng XT, Liu TZ, Zhang C, Yang ZH,
Li S and Chen XY: Fruits and vegetables intake and risk of bladder
cancer: A PRISMA-compliant systematic review and dose-response
meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Medicine (Baltimore).
94(e759)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Larsson SC, Bergkvist L and Wolk A: Fruit
and vegetable consumption and incidence of gastric cancer: A
prospective study. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 15:1998–2001.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Srivatanakul P, Sriplung H and Deerasamee
S: Epidemiology of liver cancer: An overview. Asian Pac J Cancer
Prev. 5:118–125. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sripa B and Pairojkul C:
Cholangiocarcinoma: Lessons from Thailand. Curr Opin Gastroenterol.
24:349–356. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Sarcognato S, Sacchi D, Fassan M, Fabris
L, Cadamuro M, Zanus G, Cataldo I, Capelli P, Baciorri F,
Cacciatore M and Guido M: Cholangiocarcinoma. Pathologica.
113:158–169. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
van Tienderen GS, van Beek MEA, Schurink
IJ, Rosmark O, Roest HP, Tieleman J, Demmers J, Muntz I, Conboy J,
Westergren-Thorsson G, et al: Modelling metastatic colonization of
cholangiocarcinoma organoids in decellularized lung and lymph
nodes. Front Oncol. 12(1101901)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Intuyod K, Priprem A, Limphirat W,
Charoensuk L, Pinlaor P, Pairojkul C, Lertrat K and Pinlaor S:
Anti-inflammatory and anti-periductal fibrosis effects of an
anthocyanin complex in Opisthorchis viverrini-infected
hamsters. Food Chem Toxicol. 74:206–215. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Intuyod K, Priprem A, Pairojkul C,
Hahnvajanawong C, Vaeteewoottacharn K, Pinlaor P and Pinlaor S:
Anthocyanin complex exerts anti-cholangiocarcinoma activities and
improves the efficacy of drug treatment in a gemcitabine-resistant
cell line. Int J Oncol. 52:1715–1726. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Sripa B, Seubwai W, Vaeteewoottacharn K,
Sawanyawisuth K, Silsirivanit A, Kaewkong W, Muisuk K, Dana P,
Phoomak C, Lert-Itthiporn W, et al: Functional and genetic
characterization of three cell lines derived from a single tumor of
an Opisthorchis viverrini-associated cholangiocarcinoma
patient. Hum Cell. 33:695–708. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Pangestu NS, Chueakwon P, Talabnin K,
Khiaowichit J and Talabnin C: RNF43 overexpression attenuates the
Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway to suppress tumour progression in
cholangiocarcinoma. Oncol Lett. 22(846)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Talabnin C, Trasaktaweesakul T,
Jaturutthaweechot P, Asavaritikrai P, Kongnawakun D, Silsirivanit
A, Araki N and Talabnin K: Altered O-linked glycosylation in benign
and malignant meningiomas. PeerJ. 12(e16785)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Nichols WW, Cristofalo VJ, Toji LH, Greene
AE, Aronson MM, Dwight S, Charpentier R and Hoffman E:
Characterization of a new human diploid cell line-IMR-91. In Vitro.
19:797–804. 1983.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Izdebska M, Zielińska W, Grzanka D and
Gagat M: The role of actin dynamics and actin-binding proteins
expression in epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and its
association with cancer progression and evaluation of possible
therapeutic targets. Biomed Res Int. 2018(4578373)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Karimi Roshan M, Soltani A, Soleimani A,
Rezaie Kahkhaie K, Afshari AR and Soukhtanloo M: Role of AKT and
mTOR signaling pathways in the induction of epithelial-mesenchymal
transition (EMT) process. Biochimie. 165:229–234. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Lucena MC, Carvalho-Cruz P, Donadio JL,
Oliveira IA, de Queiroz RM, Marinho-Carvalho MM, Sola-Penna M, de
Paula IF, Gondim KC, McComb ME, et al: Epithelial mesenchymal
transition induces aberrant glycosylation through hexosamine
biosynthetic pathway activation. J Biol Chem. 291:12917–12929.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Brown JS, Amend SR, Austin RH, Gatenby RA,
Hammarlund EU and Pienta KJ: Updating the definition of cancer. Mol
Cancer Res. 21:1142–1147. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Anderson RL, Balasas T, Callaghan J,
Coombes RC, Evans J, Hall JA, Kinrade S, Jones D, Jones PS, Jones
R, et al: A framework for the development of effective
anti-metastatic agents. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 16:185–204.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Chansitthichok S, Chamnan P, Sarkhampee P,
Lertsawatvicha N, Voravisutthikul P and Wattanarath P: Survival of
patients with cholangiocarcinoma receiving surgical treatment in an
O. viverrini endemic area in Thailand: A retrospective
cohort study. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 21:903–909. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Sarkhampee P, Ouransatien W,
Lertsawatvicha N, Chansitthichok S and Wattanarath P: Survival
outcome of 736 cholangiocarcinoma patient receiving surgical
treatment in Thailand. HPB. 25 (Suppl 2):S265–S266. 2023.
|
|
33
|
Zhou J, Zhu YF, Chen XY, Han B, Li F, Chen
JY, Peng XL, Luo LP, Chen W and Yu XP: Black rice-derived
anthocyanins inhibit HER-2-positive breast cancer
epithelial-mesenchymal transition-mediated metastasis in
vitro by suppressing FAK signaling. Int J Mol Med.
40:1649–1656. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Jongsomchai K, Leardkamolkarn V and
Mahatheeranont S: A rice bran phytochemical, cyanidin 3-glucoside,
inhibits the progression of PC3 prostate cancer cell. Anat Cell
Biol. 53:481–492. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Maruyama M, Kobayashi N, Westerman KA,
Sakaguchi M, Allain JE, Totsugawa T, Okitsu T, Fukazawa T, Weber A,
Stolz DB, et al: Establishment of a highly differentiated
immortalized human cholangiocyte cell line with SV40T and hTERT.
Transplantation. 77:446–451. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Prakobwong S, Gupta SC, Kim JH, Sung B,
Pinlaor P, Hiraku Y, Wongkham S, Sripa B, Pinlaor S and Aggarwal
BB: Curcumin suppresses proliferation and induces apoptosis in
human biliary cancer cells through modulation of multiple cell
signaling pathways. Carcinogenesis. 32:1372–1380. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Wu A, Zhu Y, Han B, Peng J, Deng X, Chen
W, Du J, Ou Y, Peng X and Yu X: Delphinidin induces cell cycle
arrest and apoptosis in HER-2 positive breast cancer cell lines by
regulating the NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways. Oncol Lett.
22(832)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Huang Y, Hong W and Wei X: The molecular
mechanisms and therapeutic strategies of EMT in tumor progression
and metastasis. J Hematol Oncol. 15(129)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Lai X, Li Q, Wu F, Lin J, Chen J, Zheng H
and Guo L: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metabolic
switching in cancer: Lessons from somatic cell reprogramming. Front
Cell Dev Biol. 8(760)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Lamouille S, Xu J and Derynck R: Molecular
mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 15:178–196. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Lorente G, Syriani E and Morales M: Actin
filaments at the leading edge of cancer cells are characterized by
a high mobile fraction and turnover regulation by profilin I. PLoS
One. 9(e85817)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Chen M, Zhu W, Liang Z, Yao S, Zhang X and
Zheng Y: Effect of f-actin organization in lamellipodium on
viscoelasticity and migration of Huh-7 cells under pH
microenvironments using AM-FM atomic force microscopy. Front Phys.
9(674958)2021.
|
|
43
|
Chung WL, Eibauer M, Li W,
Boujemaa-Paterski R, Geiger B and Medalia O: A network of mixed
actin polarity in the leading edge of spreading cells. Commun Biol.
5(1338)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Olson MF and Sahai E: The actin
cytoskeleton in cancer cell motility. Clin Exp Metastasis.
26:273–287. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Lee EJ, Kang MK, Kim YH, Kim DY, Oh H, Kim
SI, Oh SY and Kang YH: Dietary chrysin suppresses formation of
actin cytoskeleton and focal adhesion in AGE-exposed mesangial
cells and diabetic kidney: Role of autophagy. Nutrients.
11(127)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Berr AL, Wiese K, Dos Santos G, Koch CM,
Anekalla KR, Kidd M, Davis JM, Cheng Y, Hu YS and Ridge KM:
Vimentin is required for tumor progression and metastasis in a
mouse model of non-small cell lung cancer. Oncogene. 42:2074–2087.
2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Usman S, Waseem NH, Nguyen TKN, Mohsin S,
Jamal A, Teh MT and Waseem A: Vimentin is at the heart of
epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT) mediated metastasis.
Cancers (Basel). 13(4985)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Rao RK and Samak G: Bile duct epithelial
tight junctions and barrier function. Tissue Barriers.
1(e25718)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Bhat AA, Syed N, Therachiyil L, Nisar S,
Hashem S, Macha MA, Yadav SK, Krishnankutty R, Muralitharan S,
Al-Naemi H, et al: Claudin-1, A double-edged sword in cancer. Int J
Mol Sci. 21(569)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Maharati A and Moghbeli M: PI3K/AKT
signaling pathway as a critical regulator of epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in colorectal tumor cells. Cell Commun Signal.
21(201)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Yothaisong S, Dokduang H, Techasen A,
Namwat N, Yongvanit P, Bhudhisawasdi V, Puapairoj A, Riggins GJ and
Loilome W: Increased activation of PI3K/AKT signaling pathway is
associated with cholangiocarcinoma metastasis and PI3K/mTOR
inhibition presents a possible therapeutic strategy. Tumour Biol.
34:3637–3648. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Vaquero J, Guedj N, Clapéron A, Nguyen
Ho-Bouldoires TH, Paradis V and Fouassier L: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in cholangiocarcinoma: From clinical evidence to
regulatory networks. J Hepatol. 66:424–441. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Suman S, Kurisetty V, Das TP, Vadodkar A,
Ramos G, Lakshmanaswamy R and Damodaran C: Activation of AKT
signaling promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and tumor
growth in colorectal cancer cells. Mol Carcinog. 53 (Suppl
1):E151–E160. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Moghbeli M: PI3K/AKT pathway as a pivotal
regulator of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in lung tumor cells.
Cancer Cell Int. 24(165)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Chen W, Wu S, Zhang G, Wang W and Shi Y:
Effect of AKT inhibition on epithelial-mesenchymal transition and
ZEB1-potentiated radiotherapy in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oncol
Lett. 6:1234–1240. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Lee S, Choi EJ, Cho EJ, Lee YB, Lee JH, Yu
SJ, Yoon JH and Kim YJ: Inhibition of PI3K/Akt signaling suppresses
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma
through the Snail/GSK-3/beta-catenin pathway. Clin Mol Hepatol.
26:529–539. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Layosa MAA, Lage NN, Chew BP, Atienza L,
Mertens-Talcott S, Talcott S and Noratto GD: Dark sweet cherry
(Prunus avium) phenolics enriched in anthocyanins induced apoptosis
in MDA-MB-453 breast cancer cells through MAPK-dependent signaling
and reduced invasion via Akt and PLCγ-1 downregulation. Nutr
Cancer. 73:1985–1997. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Zhong W, Tong Y, Li Y, Yuan J, Hu S, Hu T
and Song G: Mesenchymal stem cells in inflammatory microenvironment
potently promote metastatic growth of cholangiocarcinoma via
activating Akt/NF-κB signaling by paracrine CCL5. Oncotarget.
8:73693–73704. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Chen XY, Zhou J, Luo LP, Han B, Li F, Chen
JY, Zhu YF, Chen W and Yu XP: Black rice anthocyanins suppress
metastasis of breast cancer cells by targeting RAS/RAF/MAPK
pathway. Biomed Res Int. 2015(414250)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Gabius HJ: The sugar code: Why glycans are
so important. Biosystems. 164:102–111. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Pucci M, Malagolini N and Dall'Olio F:
Glycobiology of the epithelial to mesenchymal transition.
Biomedicines. 9(770)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Park DD, Xu G, Park SS, Haigh NE, Phoomak
C, Wongkham S, Maverakis E and Lebrilla CB: Combined analysis of
secreted proteins and glycosylation identifies prognostic features
in cholangiocarcinoma. J Cell Physiol. 239(e31147)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Lu J, Isaji T, Im S, Fukuda T, Hashii N,
Takakura D, Kawasaki N and Gu J: β-Galactoside
α2,6-sialyltranferase 1 promotes transforming growth
factor-β-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Biol Chem.
289:34627–34641. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|