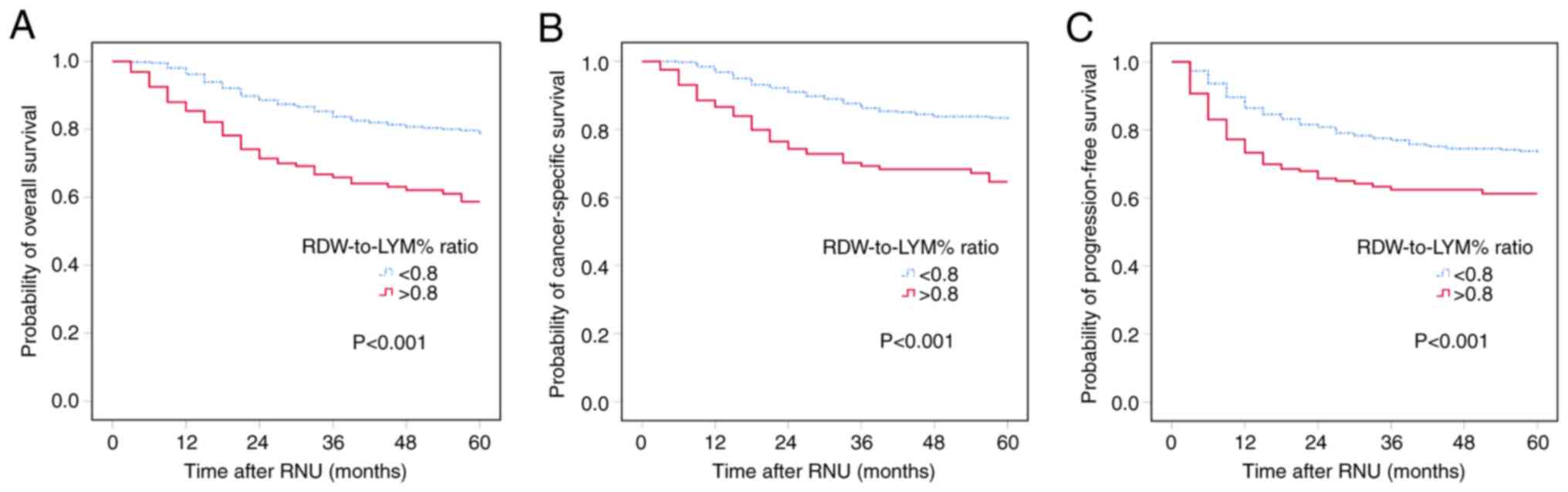
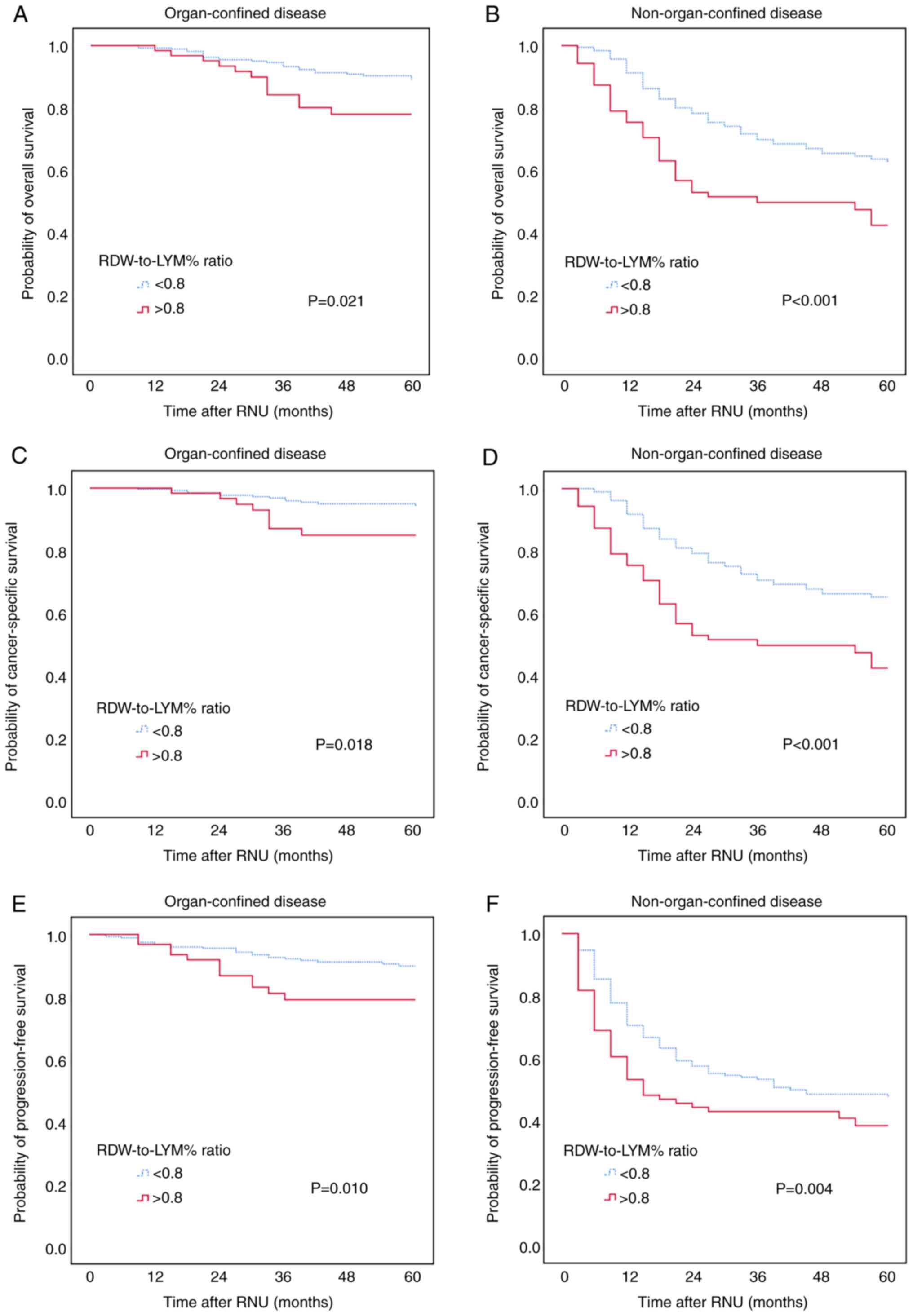
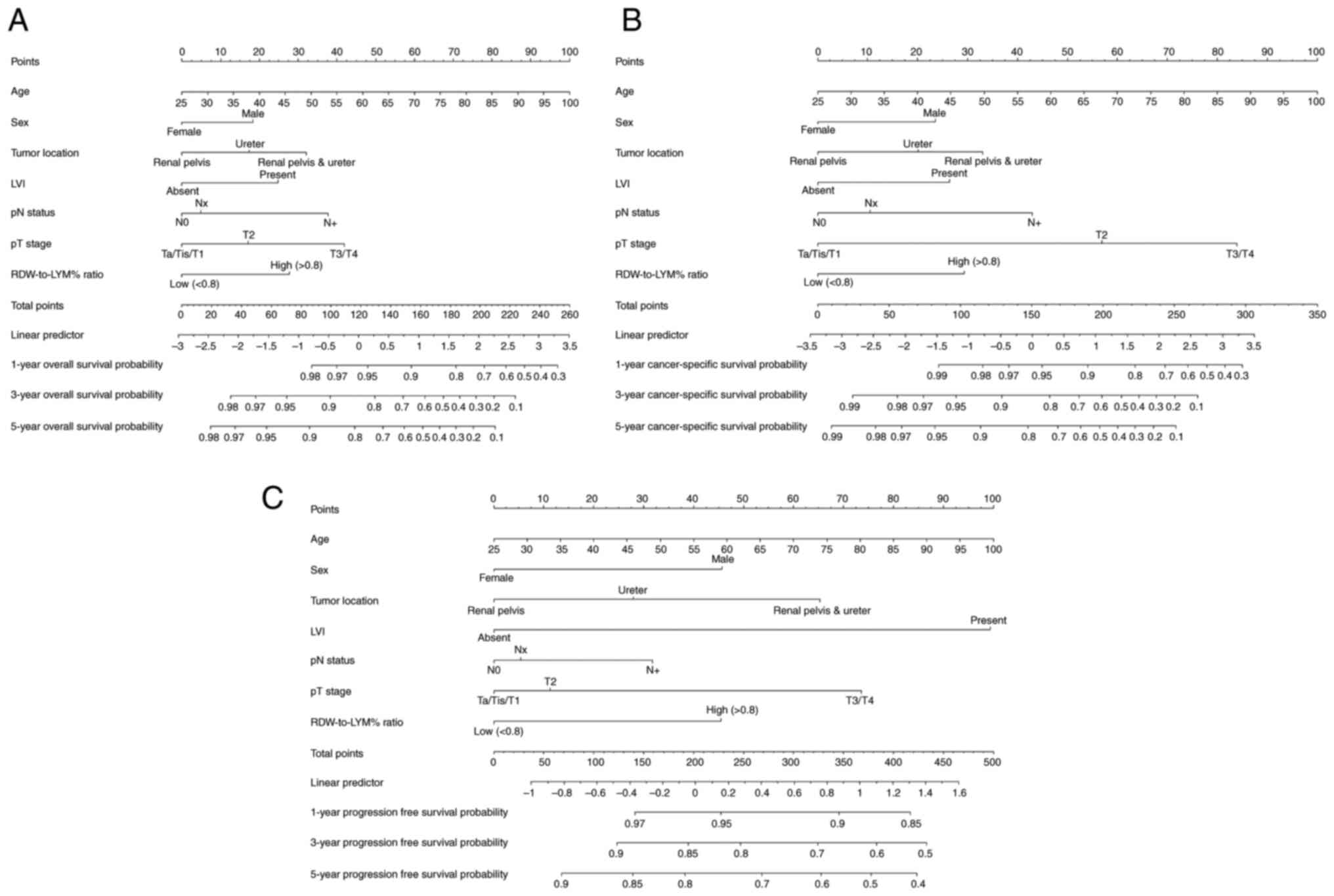
|
1
|
Rouprêt M, Babjuk M, Burger M, Capoun O,
Cohen D, Compérat EM, Cowan NC, Dominguez-Escrig JL, Gontero P,
Hugh Mostafid A, et al: European association of urology guidelines
on upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma: 2020 Update. Eur Urol.
79:62–79. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: . Cancer
statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin. 69:7–34. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Chang YH, Hsu WL, Lee YK, Chiang CJ, Yang
YW, You SL, Chen YC and Lai TS: Trends and sex-specific incidence
of upper urinary tract cancer in Taiwan: A birth cohort study.
Cancer Med. 12:15350–15357. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Margulis V, Shariat SF, Matin SF, Kamat
AM, Zigeuner R, Kikuchi E, Lotan Y, Weizer A, Raman JD and Wood CG:
Upper Tract Urothelial Carcinoma CollaborationThe Upper Tract
Urothelial Carcinoma Collaboration. Outcomes of radical
nephroureterectomy: A series from the upper tract urothelial
carcinoma collaboration. Cancer. 115:1224–1233. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Birtle A, Johnson M, Chester J, Jones R,
Dolling D, Bryan RT, Harris C, Winterbottom A, Blacker A, Catto
JWF, et al: Adjuvant chemotherapy in upper tract urothelial
carcinoma (the POUT trial): A phase 3, open-label, randomised
controlled trial. Lancet. 395:1268–1277. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Leow JJ, Chong YL, Chang SL, Valderrama
BP, Powles T and Bellmunt J: Neoadjuvant and adjuvant chemotherapy
for upper tract urothelial carcinoma: A 2020 systematic review and
meta-analysis, and future perspectives on systemic therapy. Eur
Urol. 79:635–654. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Vartolomei MD, Kimura S, Ferro M,
Vartolomei L, Foerster B, Abufaraj M and Shariat SF: Is
neutrophil-to-lymphocytes ratio a clinical relevant preoperative
biomarker in upper tract urothelial carcinoma? A meta-analysis of
4385 patients. World J Urol. 36:1019–1029. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Duan J, Pan L and Yang M: Preoperative
elevated neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and derived NLR are
associated with poor prognosis in patients with breast cancer: A
meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 97(e13340)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Dalpiaz O, Krieger D, Ehrlich GC, Pohlmann
K, Stojakovic T, Pummer K, Zigeuner R, Pichler M and Hutterer GC:
Validation of the preoperative platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio as a
prognostic factor in a European cohort of patients with upper tract
urothelial carcinoma. Urol Int. 98:320–327. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Feng JF, Huang Y and Chen QX: Preoperative
platelet lymphocyte ratio (PLR) is superior to neutrophil
lymphocyte ratio (NLR) as a predictive factor in patients with
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. World J Surg Oncol.
12(58)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Jan HC, Hu CY, Yang WH and Ou CH:
Combination of platelet-lymphocyte ratio and monocyte-lymphocyte
ratio as a new promising prognostic factor in upper tract
urothelial carcinoma with large tumor sizes >3 cm. Clin
Genitourin Cancer. 18:e484–e500. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Li T, Xu H, Yang L, Tan P and Wei Q:
Predictive value of preoperative lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio for
patients with upper tract urothelial carcinoma. Clin Chim Acta.
492:50–56. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Cananzi FCM, Minerva EM, Samà L, Ruspi L,
Sicoli F, Conti L, Fumagalli Romario U and Quagliuolo VL:
Preoperative monocyte-to-lymphocyte ratio predicts recurrence in
gastrointestinal stromal tumors. J Surg Oncol. 119:12–20.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Jan HC, Yang WH and Ou CH: Combination of
the preoperative systemic immune-inflammation index and
monocyte-lymphocyte ratio as a novel prognostic factor in patients
with upper-tract urothelial carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 26:669–684.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Aziz MH, Sideras K, Aziz NA, Mauff K, Haen
R, Roos D, Saida L, Suker M, van der Harst E, Mieog JS, et al: The
systemic-immune-inflammation index independently predicts survival
and recurrence in resectable pancreatic cancer and its prognostic
value depends on bilirubin levels: A retrospective multicenter
cohort study. Ann Surg. 270:139–146. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Ma W, Mao S, Bao M, Wu Y, Guo Y, Liu J,
Wang R, Li C, Zhang J, Zhang W and Yao X: Prognostic significance
of red cell distribution width in bladder cancer. Transl Androl
Urol. 9:295–302. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Huang TB, Zhu LY, Zhou GC and Ding XF:
Pre-treatment red blood cell distribution width as a predictor of
clinically significant prostate cancer. Int Urol Nephrol.
53:1765–1771. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Huang H, Li L, Luo W, Yang Y, Ni Y, Song
T, Zhu Y, Yang Y and Zhang L: Lymphocyte percentage as a valuable
predictor of prognosis in lung cancer. J Cell Mol Med.
26:1918–1931. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Levey AS, Bosch JP, Lewis JB, Greene T,
Rogers N and Roth D: A more accurate method to estimate glomerular
filtration rate from serum creatinine: A new prediction equation.
Modification of diet in renal disease study group. Ann Intern Med.
130:461–470. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Edge SB and Compton CC: The American joint
committee on cancer: The 7th edition of the AJCC cancer staging
manual and the future of TNM. Ann Surg Oncol. 17:1471–1474.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Eble JN, Sauter G, Epstein JI and
Sesterhenn IA (eds): Pathology and genetics of tumours of the
urinary system and male genital organs. WHO Classification of
Tumours. IARC Press, Lyon, 2004.
|
|
22
|
Coussens LM and Werb Z: Inflammation and
cancer. Nature. 420:860–867. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Dolan RD, Lim J, McSorley ST, Horgan PG
and McMillan DC: The role of the systemic inflammatory response in
predicting outcomes in patients with operable cancer: Systematic
review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep. 7(16717)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Price JM, Mistry HB, Betts G, Cheadle EJ,
Dixon L, Garcez K, Illidge T, Iyizoba-Ebozue Z, Lee LW, McPartlin
A, et al: Pretreatment lymphocyte count predicts benefit from
concurrent chemotherapy with radiotherapy in oropharyngeal cancer.
J Clin Oncol. 40:2203–2212. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Thiangphak E, Pruegsanusak K and Buhachat
R: Pretreatment lymphocyte count as independent prognostic factor
in patients with locally advanced cervical cancer treated with
concurrent chemoradiotherapy. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 159:672–678.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Kobayashi N, Usui S, Kikuchi S, Goto Y,
Sakai M, Onizuka M and Sato Y: Preoperative lymphocyte count is an
independent prognostic factor in node-negative non-small cell lung
cancer. Lung Cancer. 75:223–227. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Jimbo H, Horimoto Y, Ishizuka Y, Nogami N,
Shikanai A, Saito M and Watanabe J: Absolute lymphocyte count
decreases with disease progression and is a potential prognostic
marker for metastatic breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
196:291–298. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Fukuokaya W, Kimura T, Miki J, Kimura S,
Watanabe H, Bo F, Okada D, Aikawa K, Ochi A, Suzuki K, et al: Red
cell distribution width predicts time to recurrence in patients
with primary non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer and improves the
accuracy of the EORTC scoring system. Urol Oncol.
38:638.e15–638.e23. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Thurner EM, Krenn-Pilko S, Langsenlehner
U, Stojakovic T, Pichler M, Gerger A, Kapp KS and Langsenlehner T:
The elevated C-reactive protein level is associated with poor
prognosis in prostate cancer patients treated with radiotherapy.
Eur J Cancer. 51:610–619. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Szkandera J, Stotz M, Absenger G,
Stojakovic T, Samonigg H, Kornprat P, Schaberl-Moser R, Alzoughbi
W, Lackner C, Ress AL, et al: Validation of C-reactive protein
levels as a prognostic indicator for survival in a large cohort of
pancreatic cancer patients. Br J Cancer. 110:183–188.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Iivanainen S, Ahvonen J, Knuuttila A,
Tiainen S and Koivunen JP: Elevated CRP levels indicate poor
progression-free and overall survival on cancer patients treated
with PD-1 inhibitors. ESMO Open. 4(e000531)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Salvagno GL, Sanchis-Gomar F, Picanza A
and Lippi G: Red blood cell distribution width: A simple parameter
with multiple clinical applications. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci.
52:86–105. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
de Gonzalo-Calvo D, de Luxán-Delgado B,
Rodríguez-González S, García-Macia M, Suárez FM, Solano JJ,
Rodríguez-Colunga MJ and Coto-Montes A: Interleukin 6, soluble
tumor necrosis factor receptor I and red blood cell distribution
width as biological markers of functional dependence in an elderly
population: A translational approach. Cytokine. 58:193–198.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Lippi G, Targher G, Montagnana M, Salvagno
GL, Zoppini G and Guidi GC: Relation between red blood cell
distribution width and inflammatory biomarkers in a large cohort of
unselected outpatients. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 133:628–632.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|