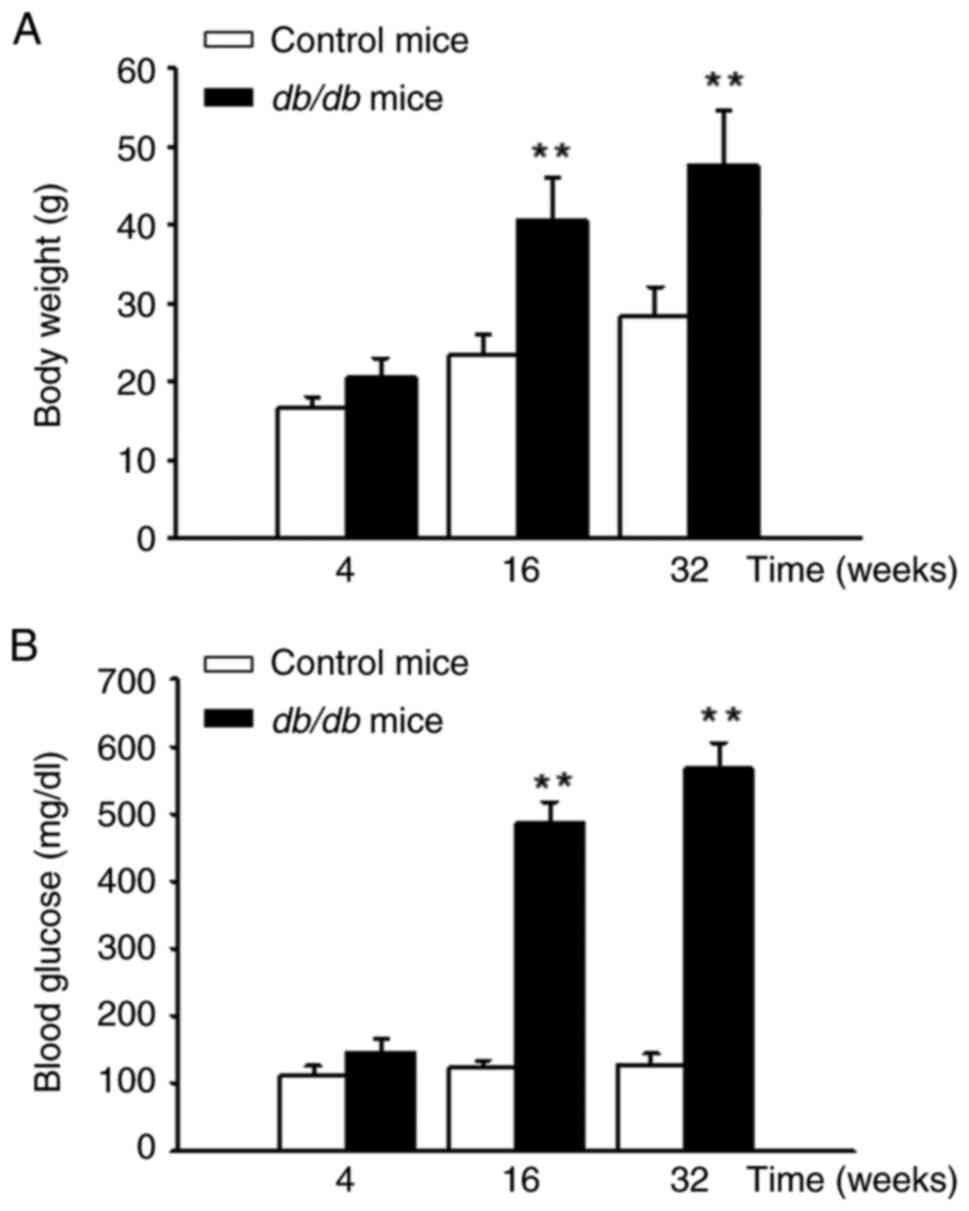
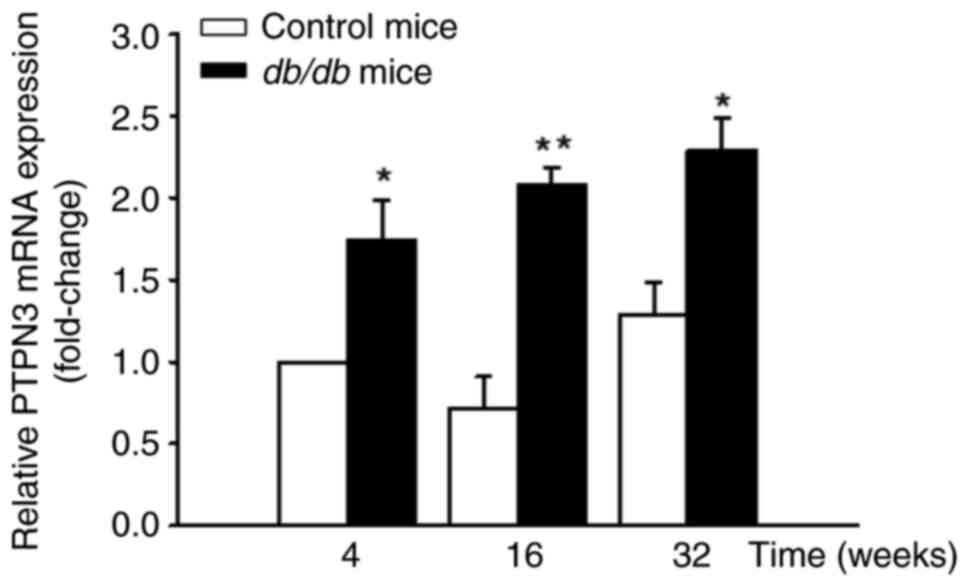
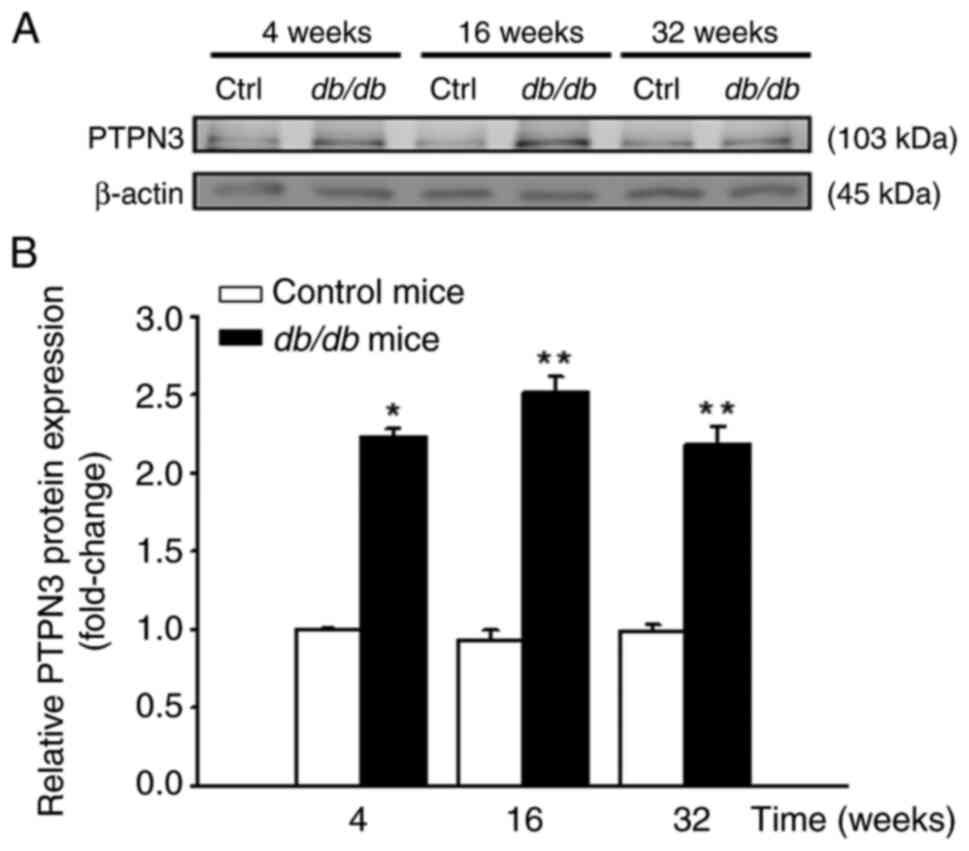
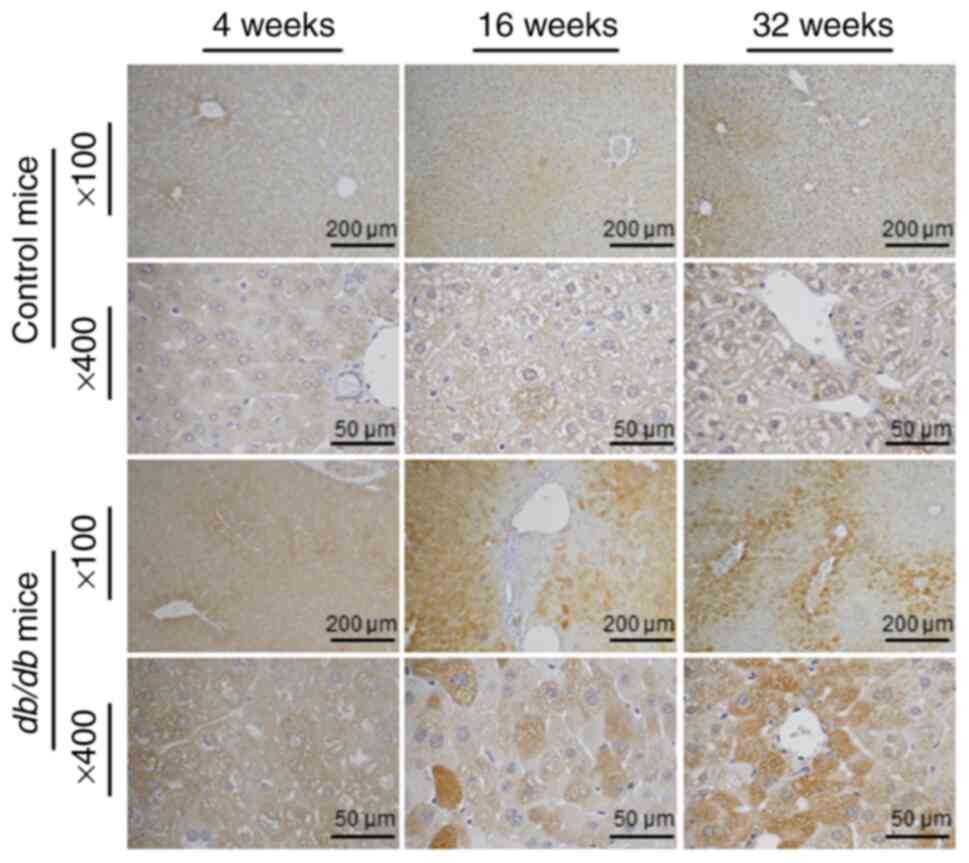
|
1
|
Gray SP and Jandeleit-Dahm K: The
pathobiology of diabetic vascular complications-cardiovascular and
kidney disease. J Mol Med (Berl). 92:441–452. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Faselis C, Katsimardou A, Imprialos K,
Deligkaris P, Kallistratos M and Dimitriadis K: Microvascular
complications of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Curr Vasc Pharmacol.
18:117–124. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Ryu TY, Park J and Scherer PE:
Hyperglycemia as a risk factor for cancer progression. Diabetes
Metab J. 38:330–336. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Wojciechowska J, Krajewski W, Bolanowski
M, Kręcicki T and Zatoński T: Diabetes and cancer: A review of
current knowledge. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 124:263–275.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Sladek R, Rocheleau G, Rung J, Dina C,
Shen L, Serre D, Boutin P, Vincent D, Belisle A, Hadjadj S, et al:
A genome-wide association study identifies novel risk loci for type
2 diabetes. Nature. 445:881–885. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Vincent EE and Yaghootkar H: Using
genetics to decipher the link between type 2 diabetes and cancer:
Shared aetiology or downstream consequence? Diabetologia.
63:1706–1717. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Han S, Williams S and Mustelin T:
Cytoskeletal protein tyrosine phosphatase PTPH1 reduces T cell
antigen receptor signaling. Eur J Immunol. 30:1318–1325.
2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Young JA, Becker AM, Medeiros JJ, Shapiro
VS, Wang A, Farrar JD, Quill TA, van Huijsduijnen RH and van Oers
NSC: The protein tyrosine phosphatase PTPN4/PTP-MEG1, an enzyme
capable of dephosphorylating the TCR ITAMs and regulating
NF-kappaB, is dispensable for T cell development and/or T cell
effector functions. Mol Immunol. 45:3756–3766. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Pilecka I, Patrignani C, Pescini R,
Curchod ML, Perrin D, Xue Y, Yasenchak J, Clark A, Magnone MC,
Zaratin P, et al: Protein-tyrosine phosphatase H1 controls growth
hormone receptor signaling and systemic growth. J Biol Chem.
282:35405–35415. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Wu CW, Chen JH, Kao HL, Li AFY, Lai CH,
Chi C and Lin WC: PTPN3 and PTPN4 tyrosine phosphatase expression
in human gastric adenocarcinoma. Anticancer Res. 26:1643–1649.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gao Q, Zhao YJ, Wang XY, Guo WJ, Gao S,
Wei L, Shi JY, Shi GM, Wang ZC, Zhang YN, et al: Activating
mutations in PTPN3 promote cholangiocarcinoma cell proliferation
and migration and are associated with tumor recurrence in patients.
Gastroenterology. 146:1397–1407. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Elbein SC, Kern PA, Rasouli N,
Yao-Borengasser A, Sharma NK and Das SK: Global gene expression
profiles of subcutaneous adipose and muscle from glucose-tolerant,
insulin-sensitive, and insulin-resistant individuals matched for
BMI. Diabetes. 60:1019–1029. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Hochberg I, Tran QT, Barkan AL, Saltiel
AR, Chandler WF and Bridges D: Gene expression signature in adipose
tissue of acromegaly patients. PLoS One.
10(e0129359)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Ohno T, Shimizu M, Shirakami Y, Baba A,
Kochi T, Kubota M, Tsurumi H, Tanaka T and Moriwaki H: Metformin
suppresses diethylnitrosamine-induced liver tumorigenesis in obese
and diabetic C57BL/KsJ-+Leprdb/+Leprdb mice. PLoS One.
10(e0124081)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Guest PC and Rahmoune H: Characterization
of the db/db mouse model of type 2 diabetes. Methods Mol Biol.
1916:195–201. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Chen H, Charlat O and Tartaglia LA:
Genetics of leptin and obesity: db/db mice as a model for human
obesity. Nat Rev Genet. 13:145–155. 2012.
|
|
17
|
Chua SC, White DW and Wu-Peng XS:
Phenotype of fatty liver and diabetes in leptin receptor-deficient
db/db mice. J Clin Invest. 97:1258–1264. 1996.
|
|
18
|
King AJ: The use of animal models in
diabetes research. Br J Pharmacol. 166:877–894. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Sharma K and Ziyadeh FN: Hyperglycemia and
diabetic complications: The role of TGF-β in the pathogenesis of
diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int. 48 (Suppl 52):S7–S10. 1995.
|
|
20
|
American Diabetes Association. Diagnosis
and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 33 (Suppl
1):S62–S69. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Tang YH, Wang YH, Chen CC, Chan CJ, Tsai
FJ and Chen SY: Genetic and functional effects of adiponectin in
type 2 diabetes mellitus development. Int J Mol Sci.
23(13544)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Huang TH, Chen CC, Liu HM, Lee TZ and
Shieh SH: Resveratrol pretreatment attenuates concanavalin
A-induced hepatitis through reverse of aberration in the immune
response and regenerative capacity in aged mice. Sci Rep.
7(2705)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Giovannucci E, Harlan DM, Archer MC,
Bergenstal RM, Gapstur SM, Habel LA, Pollak M, Regensteiner JG and
Yee D: Diabetes and cancer: A consensus report. CA Cancer J Clin.
60:207–221. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Bonagiri PR and Shubrook JH: Review of
associations between type 2 diabetes and cancer. Clin Diabetes.
38:256–265. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Bogdanov P, Corraliza L, Villena JA,
Carvalho AR, Garcia-Arumí J, Ramos D, Ruberte J, Simó R and
Hernández C: The db/db mouse: A useful model for the study of
diabetic retinal neurodegeneration. PLoS One.
9(e97302)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Tonks NK and Neel BG: Combinatorial
control of the specificity of protein tyrosine phosphatases. Curr
Opin Cell Biol. 13:182–195. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Nishad R, Mukhi D, Menon RK and Pasupulati
AK: Growth hormone and metabolic homeostasis. EMJ Diabet. 6:78–87.
2018.
|
|
28
|
Iwamoto N, Onishi H, Masuda S, Imaizumi A,
Sakanashi K, Morisaki S, Nagao S, Koga S, Ozono K, Umebayashi M, et
al: PTPN3 inhibition contributes to the activation of the dendritic
cell function to be a promising new immunotherapy target. J Cancer
Res Clin Oncol. 149:14619–14630. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Stentz FB, Umpierrez GE, Cuervo R and
Kitabchi AE: Proinflammatory cytokines, markers of cardiovascular
risks, oxidative stress, and lipid peroxidation in patients with
hyperglycemic crises. Diabetes. 53:2079–2086. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Lee H, Kim MJ, Lee IK, Hong CW and Jeon
JH: Impact of hyperglycemia on immune cell function: A
comprehensive review. Diabetol Int. 15:745–760. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Pickup JC: Inflammation and activated
innate immunity in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes
Care. 27:813–823. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Chang SC and Yang WCV: Hyperglycemia,
tumorigenesis, and chronic inflammation. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol.
108:146–153. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Yin N, Lepp A, Ji Y, Mortensen M, Hou S,
Qi XM, Myers CR and Chen G: The K-Ras effector p38γ MAPK confers
intrinsic resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors by stimulating
EGFR transcription and EGFR dephosphorylation. J Biol Chem.
292:15070–15079. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Zhou Z, Lin Z, Wang M, Wang L, Ji Y, Yang
J, Yang Y, Zhu G and Liu T: Identification and verification of
PTPN3 as a novel biomarker in predicting cancer prognosis,
immunity, and immunotherapeutic efficacy. Eur J Med Res.
29(12)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|