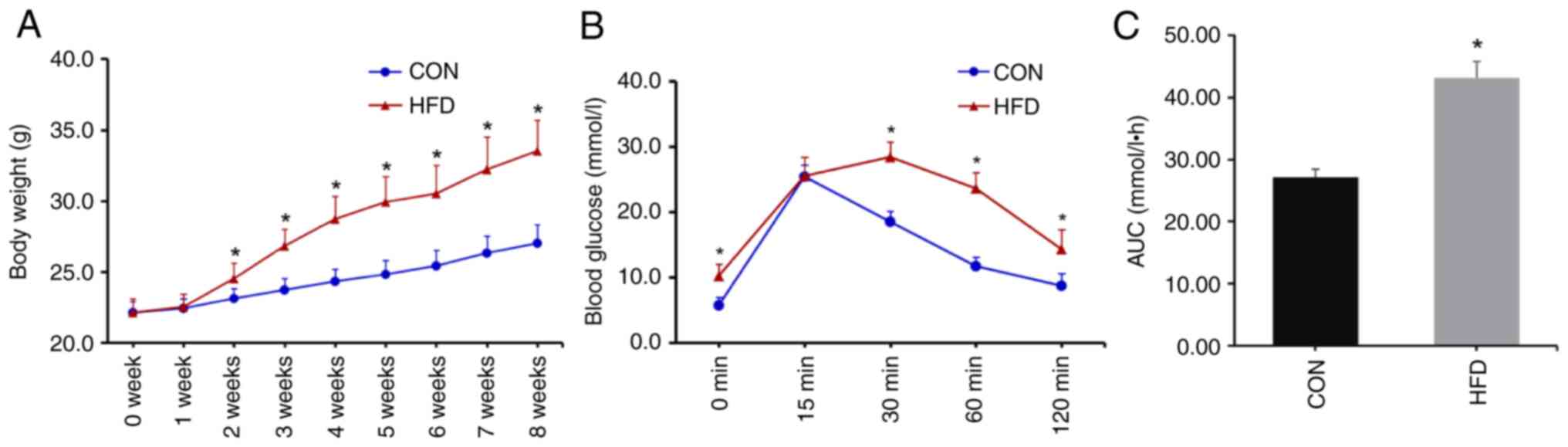
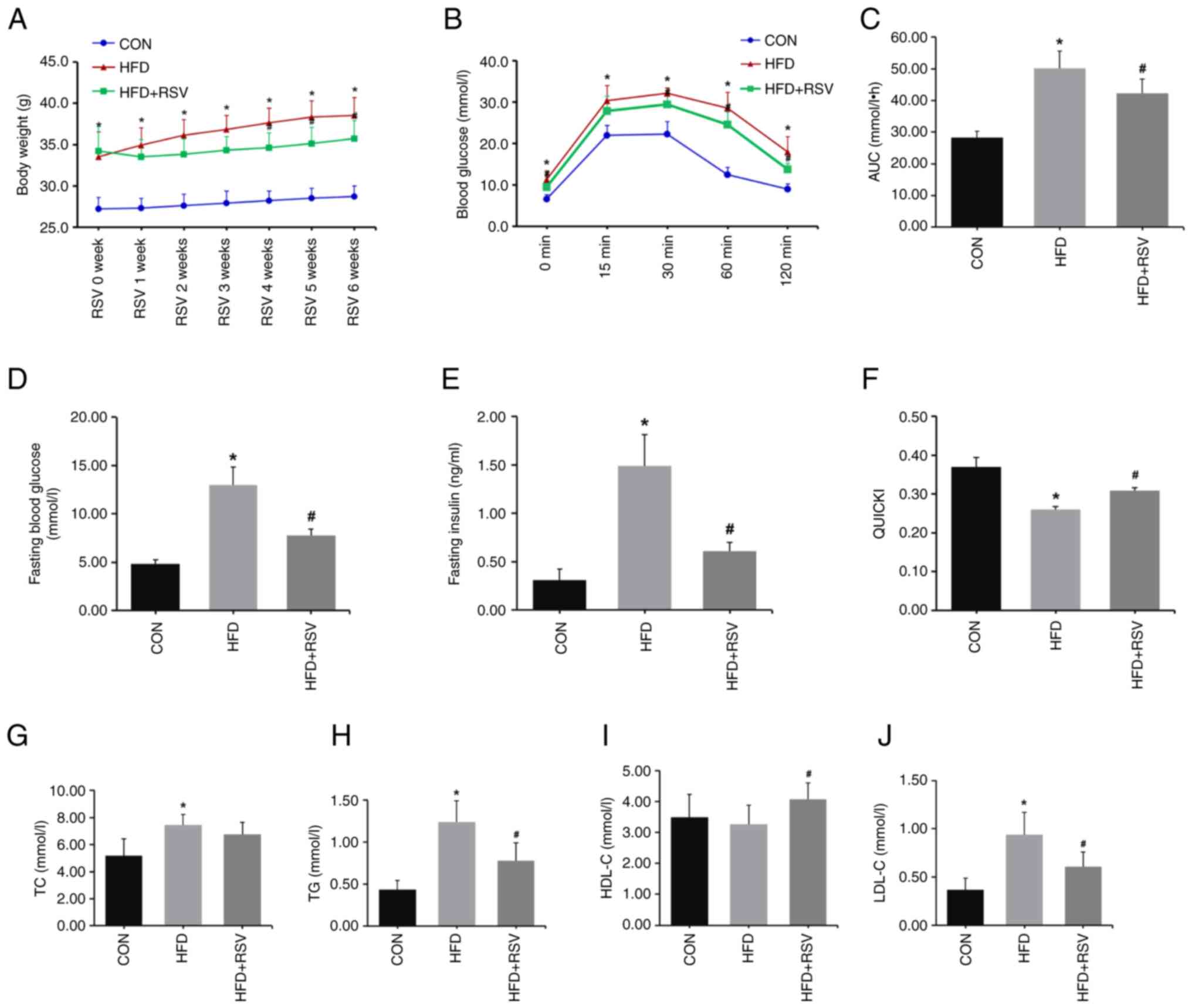
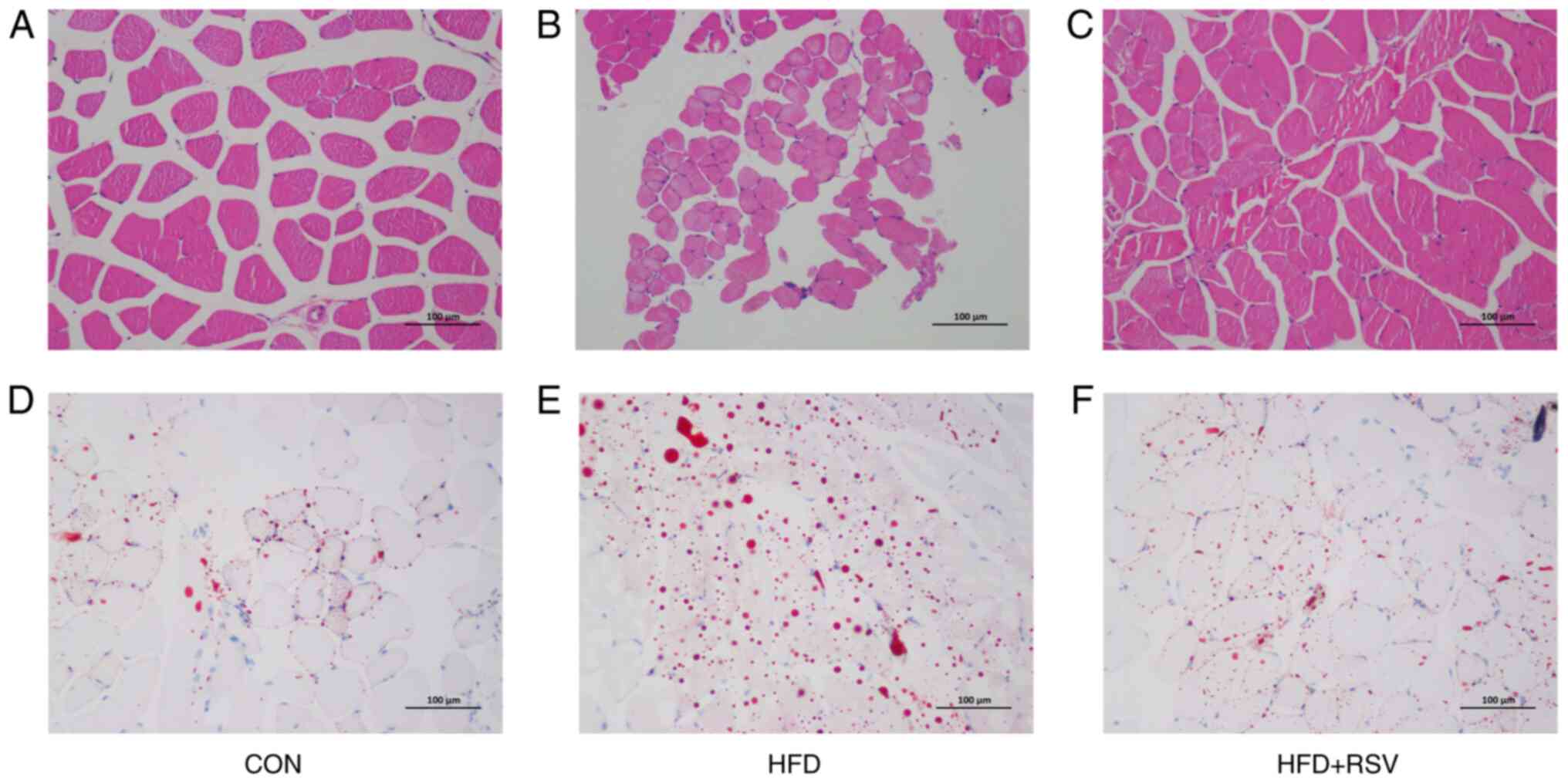
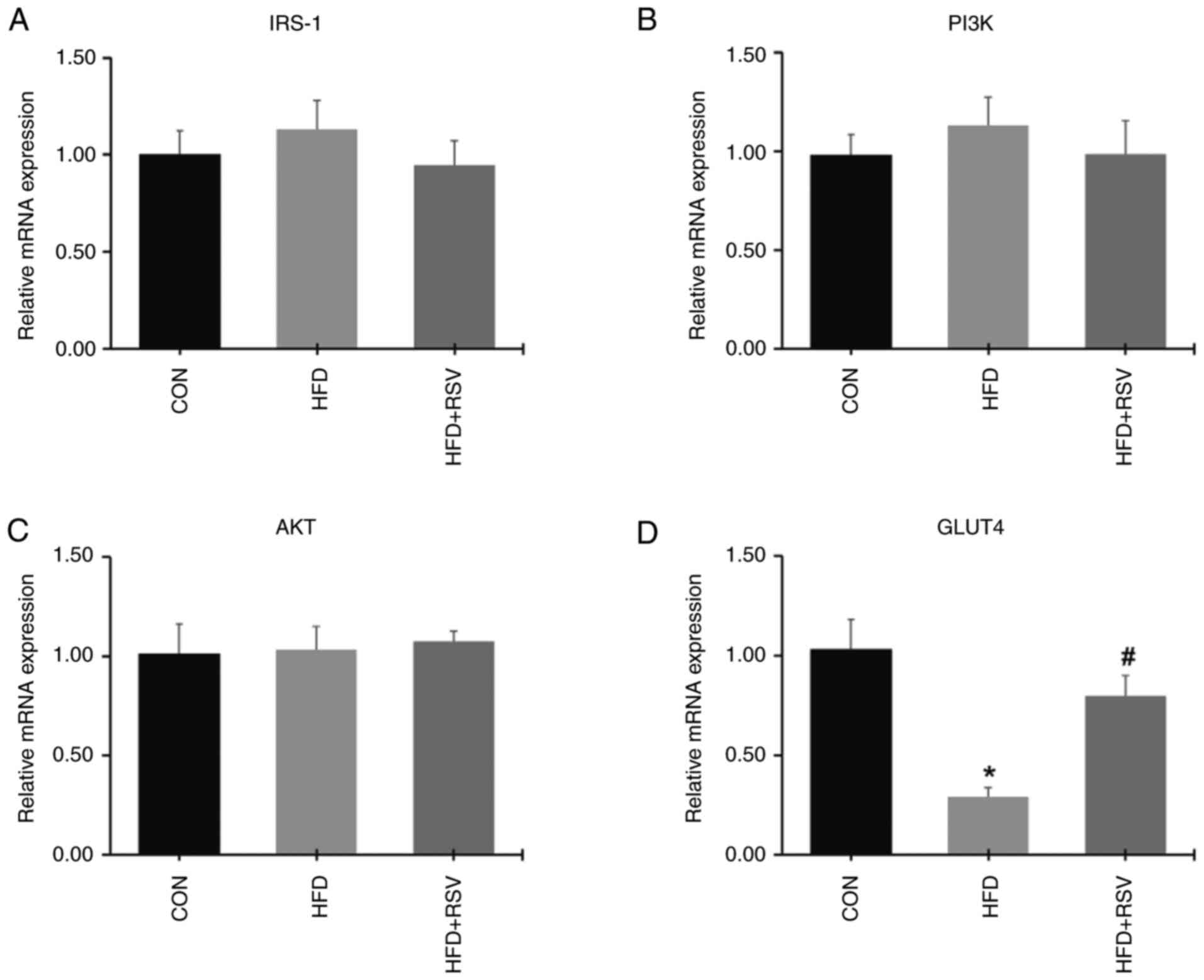
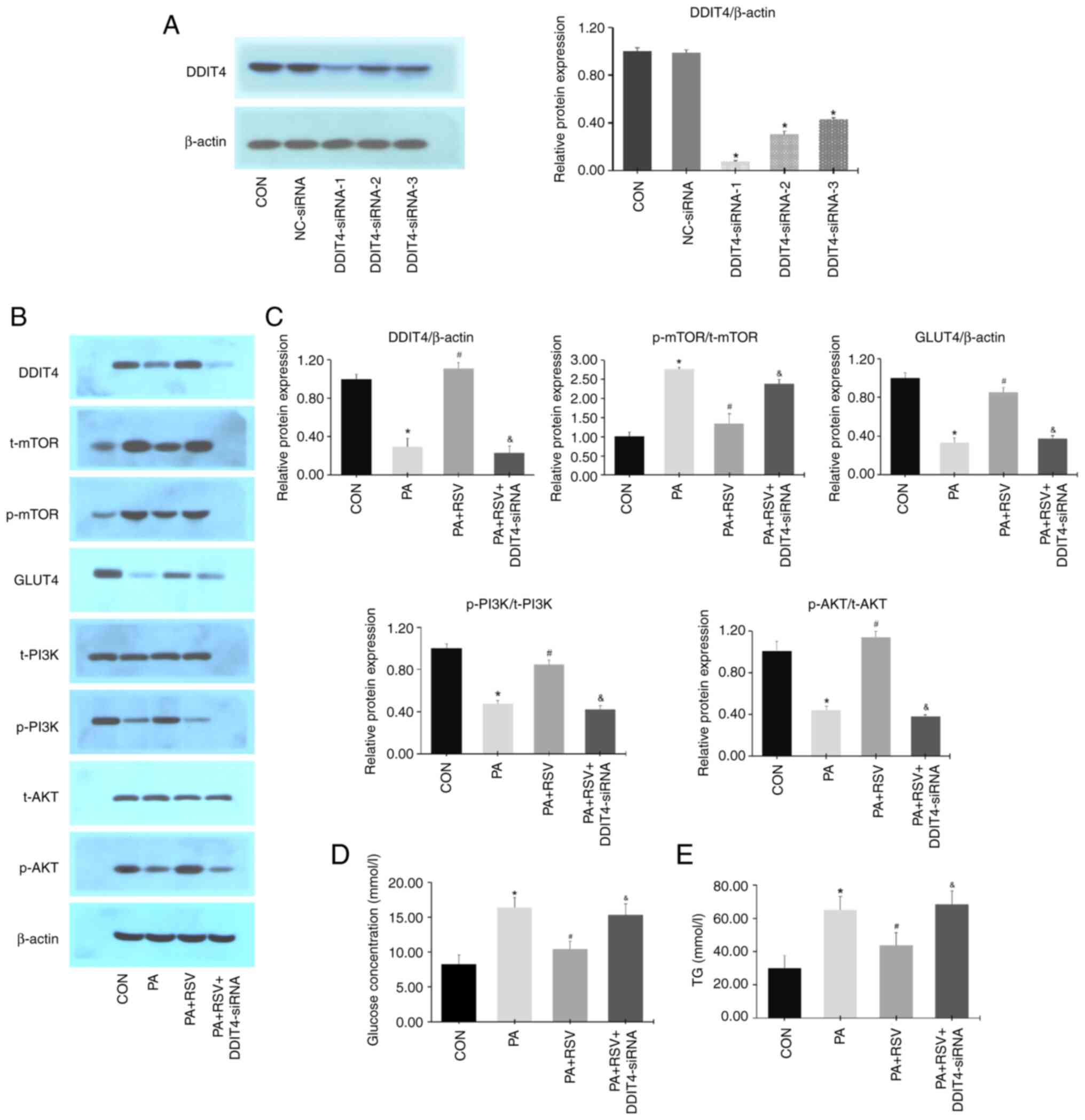
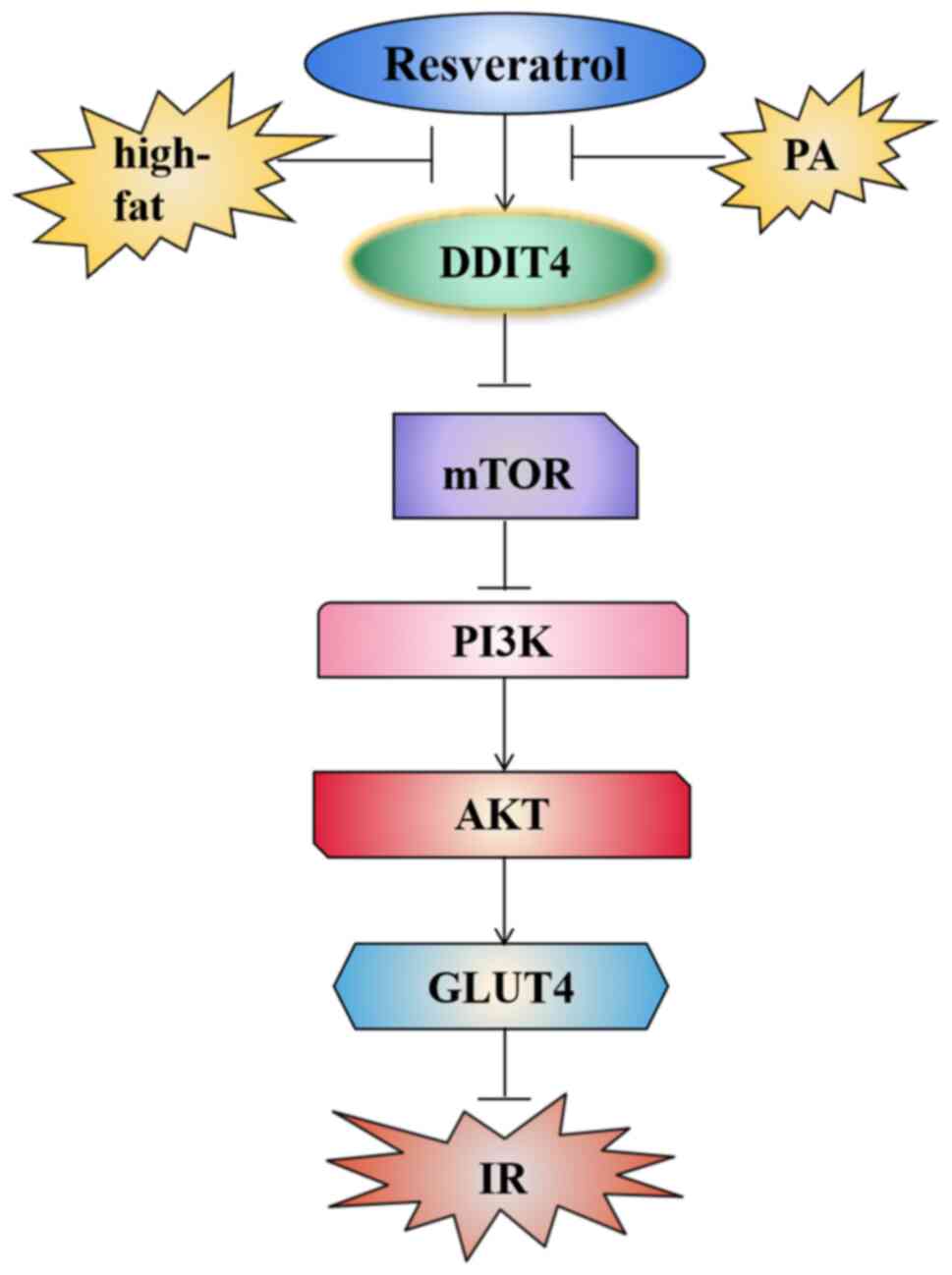
|
1
|
Zhu X, Wu C, Qiu S, Yuan X and Li L:
Effects of resveratrol on glucose control and insulin sensitivity
in subjects with type 2 diabetes: Systematic review and
meta-analysis. Nutr Metab (Lond). 14(60)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Duan TT, Hu XB and Cao ZH: Effect of
resveratrol in treatment of diabetes mellitus. Prog Microbiol
Immunol. 48:99–103. 2020.(In Chinese).
|
|
3
|
Vlavcheski F and Tsiani E: Attenuation of
free fatty acid-induced muscle insulin resistance by rosemary
extract. Nutrients. 10(1623)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Wang L, Gao P, Zhang M, Huang Z, Zhang D,
Deng Q, Li Y, Zhao Z, Qin X, Jin D, et al: Prevalence and ethnic
pattern of diabetes and prediabetes in China in 2013. JAMA.
317:2515–2523. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Khamzina L, Veilleux A, Bergeron S and
Marette A: Increased activation of the mammalian target of
rapamycin pathway in liver and skeletal muscle of obese rats:
Possible involvement in obesity-linked insulin resistance.
Endocrinology. 146:1473–1481. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Tremblay F and Marette A: Amino acid and
insulin signaling via the mTOR/p70 S6 kinase pathway. A negative
feedback mechanism leading to insulin resistance in skeletal muscle
cells. J Biol Chem. 276:38052–38060. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Holz MK, Ballif BA, Gygi SP and Blenis J:
mTOR and S6K1 mediate assembly of the translation preinitiation
complex through dynamic protein interchange and ordered
phosphorylation events. Cell. 123:569–580. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Tinline-Goodfellow CT, Lees MJ and Hodson
N: The skeletal muscle fiber periphery: A nexus of mTOR-related
anabolism. Sports Med Health Sci. 5:10–19. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Ellisen LW, Ramsayer KD, Johannessen CM,
Yang A, Beppu H, Minda K, Oliner JD, McKeon F and Haber DA: REDD1,
a developmentally regulated transcriptional target of p63 and p53,
links p63 to regulation of reactive oxygen species. Mol Cell.
10:995–1005. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Brugarolas J, Lei K, Hurley RL, Manning
BD, Reiling JH, Hafen E, Witters LA, Ellisen LW and Kaelin WG Jr:
Regulation of mTOR function in response to hypoxia by REDD1 and the
TSC1/TSC2 tumor suppressor complex. Genes Dev. 18:2893–2904.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Reiling JH and Hafen E: The
hypoxia-induced paralogs Scylla and Charybdis inhibit growth by
down-regulating S6K activity upstream of TSC in Drosophila. Gene
Dev. 18:2879–2892. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Wang H, Kubica N, Ellisen LW, Jefferson LS
and Kimball SR: Dexamethasone represses signaling through the
mammalian target of rapamycin in muscle cells by enhancing
expression of REDD1. J Biol Chem. 281:39128–39134. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Jin HO, Seo SK, Woo SH, Kim ES, Lee HC,
Yoo DH, An S, Choe TB, Lee SJ, Hong SI, et al: Activating
transcription factor 4 and CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein-beta
negatively regulate the mammalian target of rapamycin via Redd1
expression in response to oxidative and endoplasmic reticulum
stress. Free Radical Bio Med. 46:1158–1167. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Whitney ML, Jefferson LS and Kimball SR:
ATF4 is necessary and sufficient for ER stress-induced upregulation
of REDD1 expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 379:451–455.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
McGhee NK, Jefferson LS and Kimball SR:
Elevated corticosterone associated with food deprivation
upregulates expression in rat skeletal muscle of the mTORC1
repressor, REDD1. J Nutr. 139:828–834. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Dennis MD, Coleman CS, Berg A, Jefferson
LS and Kimball SR: REDD1 enhances protein phosphatase 2A-mediated
dephosphorylation of Akt to repress mTORC1 signaling. Sci Signal.
7(ra68)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Williamson DL, Li Z, Tuder RM, Feinstein
E, Kimball SR and Dungan CM: Altered nutrient response of mTORC1 as
a result of changes in REDD1 expression: Effect of obesity vs REDD1
deficiency. J Appl Physiol (1985). 117:246–256. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Gordon BS, Steiner JL, Williamson DL, Lang
CH and Kimball SR: Emerging role for regulated in development and
DNA damage 1 (REDD1) in the regulation of skeletal muscle
metabolism. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 311:E157–E174.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Zhang ZM, Liu ZH, Nie Q, Zhang XM, Yang
LQ, Wang C, Yang LL and Song GY: Metformin improves high-fat
diet-induced insulin resistance in mice by downregulating the
expression of long noncoding RNA NONMMUT031874.2. Exp Ther Med.
23(332)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Ayala JE, Samuel VT, Morton GJ, Obici S,
Croniger CM, Shulman GI, Wasserman DH and McGuinness OP: NIH Mouse
Metabolic Phenotyping Center Consortium. Standard operating
procedures for describing and performing metabolic tests of glucose
homeostasis in mice. Dis Model Mech. 3:525–534. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Bowe JE, Franklin ZJ, Hauge-Evans AC, King
AJ, Persaud SJ and Jones PM: Metabolic phenotyping guidelines:
Assessing glucose homeostasis in rodent models. J Endocrinol.
222:G13–G25. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Benedé-Ubieto R, Estévez-Vázquez O,
Ramadori P, Cubero FJ and Nevzorova YA: Guidelines and
considerations for metabolic tolerance tests in mice. Diabetes
Metab Syndr Obes. 13:439–450. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Jørgensen MS, Tornqvist KS and Hvid H:
Calculation of glucose dose for intraperitoneal glucose tolerance
tests in lean and obese mice. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci. 56:95–97.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Shu L, Hou G, Zhao H, Huang W, Song G and
Ma H: Resveratrol improves high-fat diet-induced insulin resistance
in mice by downregulating the lncRNA NONMMUT008655.2. Am J Transl
Res. 12:1–18. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Katz A, Nambi SS, Mather K, Baron AD,
Follmann DA, Sullivan G and Quon MJ: Quantitative insulin
sensitivity check index: A simple, accurate method for assessing
insulin sensitivity in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
85:2402–2410. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Jensen TL, Kiersgaard MK, Sørensen DB and
Mikkelsen LF: Fasting of mice: A review. Lab Anim. 47:225–240.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Barber TM, Kabisch S, Randeva HS, Pfeiffer
AFH and Weickert MO: Implications of resveratrol in obesity and
insulin resistance: A state-of-the-art review. Nutrients.
14(2870)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Luo J, Chen S, Wang L, Zhao X and Piao C:
Pharmacological effects of polydatin in the treatment of metabolic
diseases: A review. Phytomedicine. 102(154161)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Ariyanto EF, Danil AS, Rohmawaty E,
Sujatmiko B and Berbudi A: Effect of resveratrol in melinjo seed
(Gnetum gnemon L.) extract on type 2 diabetes mellitus patients and
its possible mechanism: A review. Curr Diabetes Rev.
19(e280222201512)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Shahwan M, Alhumaydhi F, Ashraf GM, Hasan
PMZ and Shamsi A: Role of polyphenols in combating type 2 diabetes
and insulin resistance. Int J Biol Macromol. 206:567–579.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Zhou Q, Wang Y, Han X, Fu S, Zhu C and
Chen Q: Efficacy of resveratrol supplementation on glucose and
lipid metabolism: A meta-analysis and systematic review. Front
Physiol. 13(795980)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Chadt A and Al-Hasani H: Glucose
transporters in adipose tissue, liver, and skeletal muscle in
metabolic health and disease. Pflugers Arch. 472:1273–1298.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Vlavcheski F, Den Hartogh DJ, Giacca A and
Tsiani E: Amelioration of high-insulin-induced skeletal muscle cell
insulin resistance by resveratrol is linked to activation of AMPK
and restoration of GLUT4 translocation. Nutrients.
12(914)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Kang BB and Chiang BH: A novel phenolic
formulation for treating hepatic and peripheral insulin resistance
by regulating GLUT4-mediated glucose uptake. J Tradit Complement
Med. 12:195–205. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Bar-Tana J: Type 2 diabetes-unmet need,
unresolved pathogenesis, mTORC1-centric paradigm. Rev Endocr Metab
Dis. 21:613–629. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Bodur C, Kazyken D, Huang K, Tooley AS,
Cho KW, Barnes TM, Lumeng CN, Myers MG and Fingar DC: TBK1-mTOR
signaling attenuates obesity-linked hyperglycemia and insulin
resistance. Diabetes. 71:2297–2312. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Huang SL, Xie W, Ye YL, Liu J, Qu H, Shen
Y, Xu TF, Zhao ZH, Shi Y, Shen JH and Leng Y: Coronarin A modulated
hepatic glycogen synthesis and gluconeogenesis via inhibiting
mTORC1/S6K1 signaling and ameliorated glucose homeostasis of
diabetic mice. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 44:596–609. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Den Hartogh DJ, Vlavcheski F, Giacca A and
Tsiani E: Attenuation of free fatty acid (FFA)-induced skeletal
muscle cell insulin resistance by resveratrol is linked to
activation of AMPK and inhibition of mTOR and p70S6K. Int J Mol
Sci. 21(4900)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Meng W, Liang X, Chen H, Luo H, Bai J, Li
G, Zhang Q, Xiao T, He S, Zhang Y, et al: Rheb inhibits beiging of
white adipose tissue via PDE4D5-dependent down regulation of the
cAMP-PKA signaling pathway. Diabetes. 66:1198–1213. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Dungan CM and Williamson DL: Regulation of
skeletal muscle insulin-stimulated signaling through the
MEK-REDD1-mTOR axis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 482:1067–1072.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Lee Y, Song MJ, Park JH, Shin MH, Kim MK,
Hwang D, Lee DH and Chung JH: Histone deacetylase 4 reverses
cellular senescence via DDIT4 in dermal fibroblasts. Aging (Albany
NY). 14:4653–4672. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Zhidkova EM, Lylova ES, Grigoreva DD,
Kirsanov KI, Osipova AV, Kulikov EP, Mertsalov SA, Belitsky GA,
Budunova I, Yakubovskaya MG and Lesovaya EA: Nutritional sensor
REDD1 in cancer and inflammation: Friend or foe? Int J Mol Sci.
23(9686)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Murakami T, Hasegawa K and Yoshinaga M:
Rapid induction of REDD1 expression by endurance exercise in rat
skeletal muscle. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 405:615–619.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Regazzetti C, Dumas K, Le Marchand-Brustel
Y, Peraldi P, Tanti JF and Giorgetti-Peraldi S: Regulated in
development and DNA damage responses-1 (REDD1) protein contributes
to insulin signaling pathway in adipocytes. PLoS One.
7(e52154)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Wang H, Wang J, Qu H, Wei H, Ji B, Yang Z,
Wu J, He Q, Luo Y, Liu D, et al: In vitro and in vivo inhibition of
mTOR by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 to improve early diabetic
nephropathy via the DDIT4/TSC2/mTOR pathway. Endocrine. 54:348–359.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Delpino FM and Figueiredo LM: Resveratrol
supplementation and type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 62:4465–4480.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Ma N and Zhang Y: Effects of resveratrol
therapy on glucose metabolism, insulin resistance, inflammation,
and renal function in the elderly patients with type 2 diabetes
mellitus: A randomized controlled clinical trial protocol. Medicine
(Baltimore). 101(e30049)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Karimi M, Abiri B, Guest PC and Vafa M:
Therapeutic effects of resveratrol on nonalcoholic fatty liver
disease through inflammatory, oxidative stress, metabolic, and
epigenetic modifications. Methods Mol Biol. 2343:19–35.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|