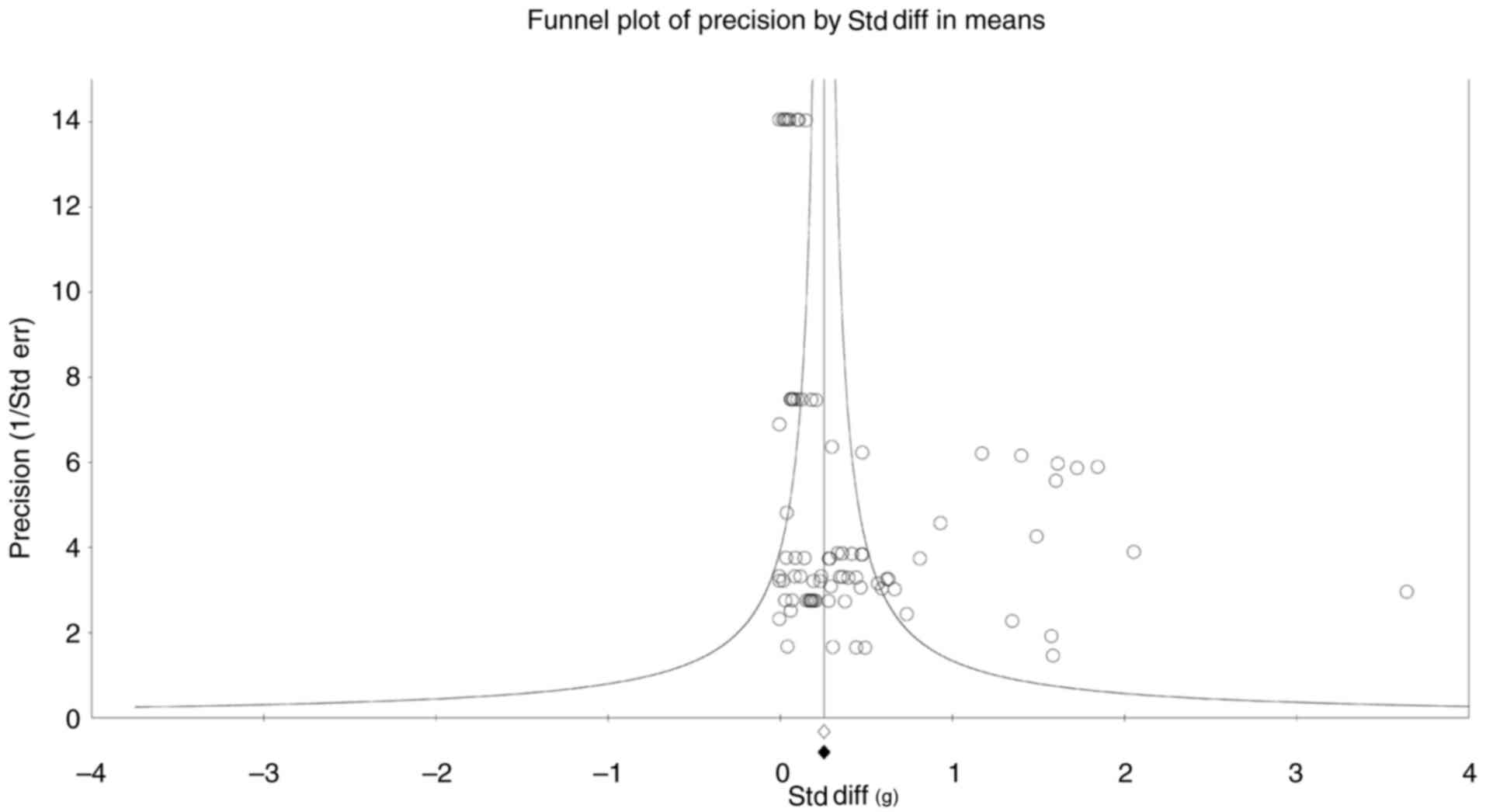
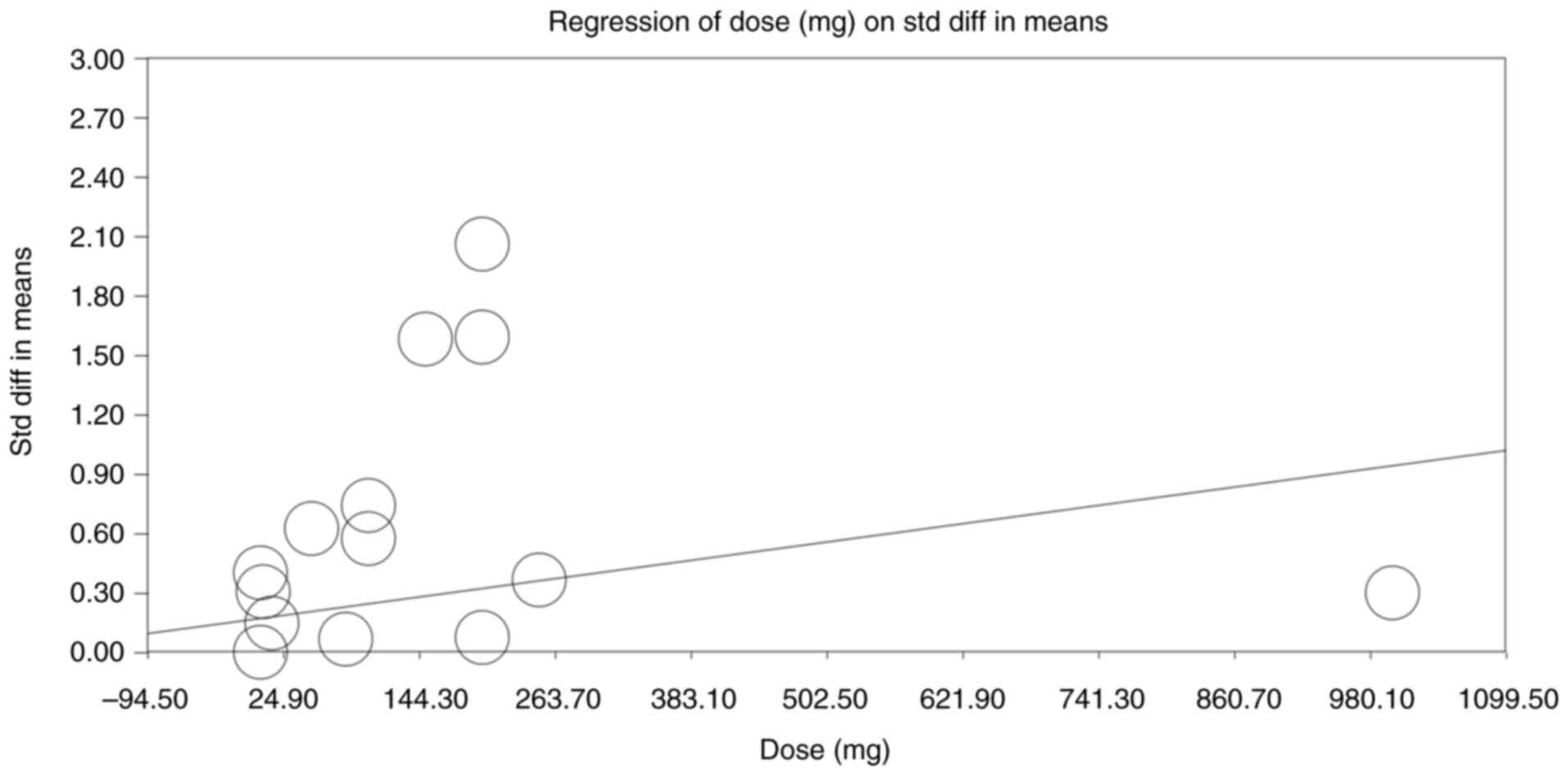
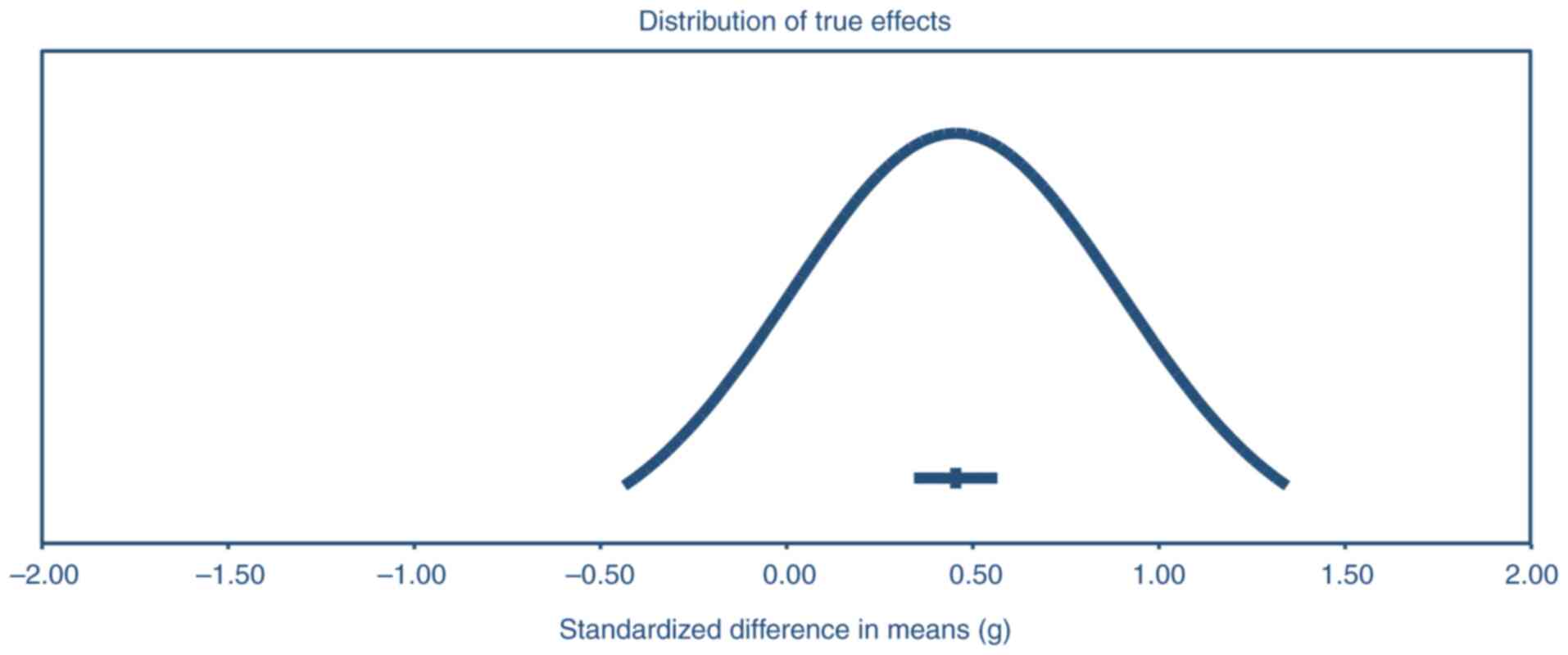
|
1
|
Shores MM, Sloan KL, Matsumoto AM, Moceri
VM, Felker B and Kivlahan DR: Increased incidence of diagnosed
depressive illness in hypogonadal older men. Arch Gen Psychiatry.
61:162–167. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Barrett-Connor E, Goodman-Gruen D and
Patay B: Endogenous sex hormones and cognitive function in older
men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 84:3681–3685. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Jayaraman A, Lent-Schochet D and Pike CJ:
Diet-induced obesity and low testosterone increase
neuroinflammation and impair neural function. J Neuroinflammation.
11(162)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Munari EV, Amer M, Amodeo A, Bollino R,
Federici S, Goggi G, Giovanelli L, Persani L, Cangiano B and Bonomi
M: The complications of male hypogonadism: Is it just a matter of
low testosterone? Front Endocrinol (Lausanne).
14(1201313)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Lašaitė L, Čeponis J, Preikša RT and
Žilaitienė B: Effects of two-year testosterone replacement therapy
on cognition, emotions and quality of life in young and middle-aged
hypogonadal men. Andrologia. 49:2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Nieschlag E, Behre HM, Kliesch S and
Nieschlag S (eds): Andrology: Male Reproductive Health and
Dysfunction. 4th edition. Springer Nature, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-31574-9. Accessed
October 27, 2023.
|
|
7
|
Janowsky JS, Chavez B and Orwoll E: Sex
steroids modify working memory. J Cogn Neurosci. 12:407–414.
2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Cherrier MM, Asthana S, Plymate S, Baker
L, Matsumoto AM, Peskind E, Raskind MA, Brodkin K, Bremner W,
Petrova A, et al: Testosterone supplementation improves spatial and
verbal memory in healthy older men. Neurology. 57:80–88.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Emmelot-Vonk MH, Verhaar HJ, Nakhai Pour
HR, Aleman A, Lock TM, Bosch JL, Grobbee DE and van der Schouw YT:
Effect of testosterone supplementation on functional mobility,
cognition, and other parameters in older men: A randomized
controlled trial. JAMA. 299:39–52. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Zhang Z, Kang D and Li H: Testosterone and
cognitive impairment or dementia in middle-aged or aging males:
Causation and intervention, a systematic review and meta-analysis.
J Geriatr Psychiatry Neurol. 34:405–417. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Hong SW, Cho YJ, Lee JH, Suh YS and Kim
DH: Effect of testosterone supplementation on cognition in elderly
men: A systematic meta-analysis. Korean J Geriatr Gerontol.
24:24–33. 2023.
|
|
12
|
Farajdokht F, Farhoudi M, Majdi A, Zamanlu
M, Sadigh-Eteghad S, Vahedi S and Mahmoudi J: Testosterone may hold
therapeutic promise for the treatment of ischemic stroke in aging:
A closer look at laboratory findings. Adv Pharm Bull. 9:48–55.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Roselli CE, Abdelgadir SE, Rønnekleiv OK
and Klosterman SA: Anatomic distribution and regulation of
aromatase gene expression in the rat brain. Biol Reprod. 58:79–87.
1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Luine VN: Sex steroids and cognitive
function. J Neuroendocrinol. 20:866–872. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Holland J, Bandelow S and Hogervorst E:
Testosterone levels and cognition in elderly men: A review.
Maturitas. 69:322–337. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Huo S, Scialli AR, McGarvey S, Hill E,
Tügertimur B, Hogenmiller A, Hirsch AI and Fugh-Berman A: Treatment
of men for ‘low testosterone’: A systematic review. PLoS One.
11(e0162480)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Zitzmann M, Faber S and Nieschlag E:
Association of specific symptoms and metabolic risks with serum
testosterone in older men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 91:4335–4343.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron
I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, Shamseer L, Tetzlaff JM, Akl EA, Brennan
SE, et al: The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for
reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 372(n71)2021.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Thorlund K, Imberger G, Johnston BC, Walsh
M, Awad T, Thabane L, Gluud C, Devereaux PJ and Wetterslev J:
Evolution of heterogeneity (I2) estimates and their 95% confidence
intervals in large meta-analyses. PLoS One.
7(e39471)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
IntHout J, Ioannidis JP, Rovers MM and
Goeman JJ: Plea for routinely presenting prediction intervals in
meta-analysis. BMJ Open. 6(e010247)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Asih PR, Wahjoepramono EJ, Aniwiyanti V,
Wijaya LK, de Ruyck K, Taddei K, Fuller SJ, Sohrabi H, Dhaliwal SS,
Verdile G, et al: Testosterone replacement therapy in older male
subjective memory complainers: Double-blind randomized crossover
placebo-controlled clinical trial of physiological assessment and
safety. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 14:576–586. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Cherrier MM, Plymate S, Mohan S, Asthana
S, Matsumoto AM, Bremner W, Peskind E, Raskind M, Latendresse S,
Haley AP and Craft S: Relationship between testosterone
supplementation and insulin-like growth factor-I levels and
cognition in healthy older men. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 29:65–82.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Cherrier MM, Matsumoto AM, Amory JK,
Johnson M, Craft S, Peskind ER and Raskind MA: Characterization of
verbal and spatial memory changes from moderate to
supraphysiological increases in serum testosterone in healthy older
men. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 32:72–79. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Cherrier MM, Anderson K, Shofer J, Millard
S and Matsumoto AM: Testosterone treatment of men with mild
cognitive impairment and low testosterone levels. Am J Alzheimers
Dis Other Demen. 30:421–430. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Gray PB, Singh AB, Woodhouse LJ, Storer
TW, Casaburi R, Dzekov J, Dzekov C, Sinha-Hikim I and Bhasin S:
Dose-dependent effects of testosterone on sexual function, mood,
and visuospatial cognition in older men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
90:3838–3846. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Gregori G, Celli A, Barnouin Y, Paudyal A,
Armamento-Villareal R, Napoli N, Qualls C and Villareal DT:
Cognitive response to testosterone replacement added to intensive
lifestyle intervention in older men with obesity and hypogonadism:
Prespecified secondary analyses of a randomized clinical trial. Am
J Clin Nutr. 114:1590–1599. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Haren MT, Wittert GA, Chapman IM, Coates P
and Morley JE: Effect of oral testosterone undecanoate on
visuospatial cognition, mood and quality of life in elderly men
with low-normal gonadal status. Maturitas. 50:124–133.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Konaka H, Sugimoto K, Orikasa H, Iwamoto
T, Takamura T, Takeda Y, Shigehara K, Iijima M, Koh E and Namiki M:
EARTH study group. Effects of long-term androgen replacement
therapy on the physical and mental statuses of aging males with
late-onset hypogonadism: A multicenter randomized controlled trial
in Japan (EARTH study). Asian J Androl. 18:25–34. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Ly LP, Jimenez M, Zhuang TN, Celermajer
DS, Conway AJ and Handelsman DJ: A double-blind,
placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial of transdermal
dihydrotestosterone gel on muscular strength, mobility, and quality
of life in older men with partial androgen deficiency. J Clin
Endocrinol Metab. 86:4078–4088. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Yamaguchi K, Ishikawa T, Chiba K and
Fujisawa M: Assessment of possible effects for testosterone
replacement therapy in men with symptomatic late-onset
hypogonadism. Andrologia. 43:52–56. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Cherrier MM, Matsumoto AM, Amory JK, Ahmed
S, Bremner W, Peskind ER, Raskind MA, Johnson M and Craft S: The
role of aromatization in testosterone supplementation: Effects on
cognition in older men. Neurology. 64:290–296. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Janowsky JS, Oviatt SK and Orwoll ES:
Testosterone influences spatial cognition in older men. Behav
Neurosci. 108:325–332. 1994.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Kenny AM, Bellantonio S, Gruman CA, Acosta
RD and Prestwood KM: Effects of transdermal testosterone on
cognitive function and health perception in older men with low
bioavailable testosterone levels. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci.
57:M321–M325. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Kenny AM, Fabregas G, Song C, Biskup B and
Bellantonio S: Effects of testosterone on behavior, depression, and
cognitive function in older men with mild cognitive loss. J
Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 59:75–78. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Huang G, Wharton W, Bhasin S, Harman SM,
Pencina KM, Tsitouras P, Li Z, Hally KA, Asthana S, Storer TW and
Basaria S: Effects of long-term testosterone administration on
cognition in older men with low or low-to-normal testosterone
concentrations: A prespecified secondary analysis of data from the
randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled TEAAM trial. Lancet
Diabetes Endocrinol. 4:657–665. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Maki PM, Ernst M, London ED, Mordecai KL,
Perschler P, Durso SC, Brandt J, Dobs A and Resnick SM:
Intramuscular testosterone treatment in elderly men: Evidence of
memory decline and altered brain function. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
92:4107–4114. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Vaughan C, Goldstein FC and Tenover JL:
Exogenous testosterone alone or with finasteride does not improve
measurements of cognition in healthy older men with low serum
testosterone. J Androl. 28:875–882. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Wahjoepramono EJ, Asih PR, Aniwiyanti V,
Taddei K, Dhaliwal SS, Fuller SJ, Foster J, Carruthers M, Verdile
G, Sohrabi HR and Martins RN: The effects of testosterone
supplementation on cognitive functioning in older men. CNS Neurol
Disord Drug Targets. 15:337–343. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Wolf OT, Preut R, Hellhammer DH, Kudielka
BM, Schürmeyer TH and Kirschbaum C: Testosterone and cognition in
elderly men: A single testosterone injection blocks the practice
effect in verbal fluency, but has no effect on spatial or verbal
memory. Biol Psychiatry. 47:650–654. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Resnick SM, Matsumoto AM, Stephens-Shields
AJ, Ellenberg SS, Gill TM, Shumaker SA, Pleasants DD,
Barrett-Connor E, Bhasin S, Cauley JA, et al: Testosterone
treatment and cognitive function in older men with low testosterone
and age-associated memory impairment. JAMA. 317:717–727.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Ponce OJ, Spencer-Bonilla G,
Alvarez-Villalobos N, Serrano V, Singh-Ospina N,
Rodriguez-Gutierrez R, Salcido-Montenegro A, Benkhadra R, Prokop
LJ, Bhasin S and Brito JP: The efficacy and adverse events of
testosterone replacement therapy in hypogonadal men: A systematic
review and meta-analysis of randomized, placebo-controlled trials.
J Clin Endocrinol Metab: Mar 17, 2018, (Epub ahead of print).
|
|
42
|
Cai Z and Li H: An updated review:
Androgens and cognitive impairment in older men. Front Endocrinol
(Lausanne). 11(586909)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Kuwahara N, Nicholson K, Isaacs L and
MacLusky NJ: Androgen effects on neural plasticity. Androg Clin Res
Ther. 2:216–230. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Bidzan L, Jurek P, Olech M, Bidzan-Wiącek
M, Bidzan-Bluma I and Bidzan M: Somatic comorbidity and the
progression of cognitive impairment. Front Aging Neurosci.
15(1219449)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Hua JT, Hildreth KL and Pelak VS: Effects
of testosterone therapy on cognitive function in aging: A
systematic review. Cogn Behav Neurol. 29:122–138. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
McEwen BS and Woolley CS: Estradiol and
progesterone regulate neuronal structure and synaptic connectivity
in adult as well as developing brain. Exp Gerontol. 29:431–436.
1994.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Amin Z, Canli T and Epperson CN: Effect of
estrogen-serotonin interactions on mood and cognition. Behav Cogn
Neurosci Rev. 4:43–58. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Frye CA: Effects and mechanisms of
progestogens and androgens in ictal activity. Epilepsia. 51 (Suppl
3):S135–S140. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Yeo S, Holl K, Peñaherrera N, Wissinger U,
Anstee K and Wyn R: Burden of male hypogonadism and major
comorbidities, and the clinical, economic, and humanistic benefits
of testosterone therapy: A narrative review. Clinicoecon Outcomes
Res. 13:31–38. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Hoffmann CM, Petrov ME and Lee RE: Aerobic
physical activity to improve memory and executive function in
sedentary adults without cognitive impairment: A systematic review
and meta-analysis. Prev Med Rep. 23(101496)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Kleinloog JPD, Mensink RP, Ivanov D, Adam
JJ, Uludağ K and Joris PJ: Aerobic exercise training improves
cerebral blood flow and executive function: A randomized,
controlled cross-over trial in sedentary older men. Front Aging
Neurosci. 11(333)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Lisco G, Giagulli VA, De Tullio A, De
Pergola G, Guastamacchia E and Triggiani V: Age-related male
hypogonadism and cognitive impairment in the elderly: Focus on the
effects of testosterone replacement therapy on cognition.
Geriatrics (Basel). 5(76)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Čeponis J, Swerdloff RS and Wang C:
Androgen replacement therapy in hypogonadal men. In: Male
Hypogonadism: Basic, Clinical and Therapeutic Principles. Winters S
and Huhtaniemi I (eds). Humana Press, Cham, pp367-397, 2017.
https://link.springer.com/book/10.1007/978-3-319-53298-1.
Accessed April 26, 2017.
|